High-Temperature Spin Crossover in Iron(II) Complexes with 2,6-Bis(1H-imidazol-2-yl)pyridine
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Materials
2.2. Synthesis of [FeL2]SO4 0.5H2O (1·0.5H2O)
2.3. Synthesis of [FeL2]Br2·H2O (2·H2O) and [FeL2](ReO4)2 (3)
2.4. Synthesis of [FeL2]B10H10∙H2O (4∙H2O) and [FeL2]B12H12∙1.5H2O (5·1.5H2O)
2.5. Measurement and Characterization
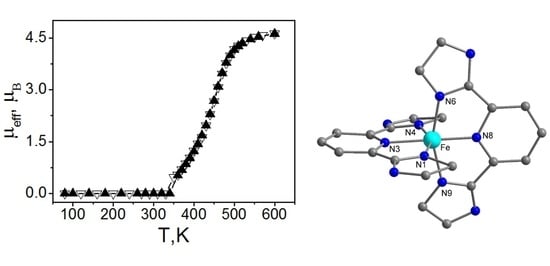
3. Results and Discussion
4. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
Sample Availability
References
- Gutlich, P.; Goodwin, H. Spin Crossover in Transition Metal Compounds I–III; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2004; pp. 233–235. [Google Scholar]
- Halcrow, M.A. Spin-Crossover Materials Properties and Applications; John Wiley & Sons Ltd.: Chichester, UK, 2013; p. 562. [Google Scholar]
- Shatruk, M.; Phan, H.; Chrisostomo, B.A.; Suleimenova, A. Symmetry-breaking structural phase transitions in spin crossover complexes. Coord. Chem. Rev. 2015, 289–290, 62–73. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Feltham, H.L.C.; Barltrop, A.S.; Brooker, S. Spin crossover in iron(II) complexes of 3,4,5-tri-substituted-1,2,4-triazole (Rdpt), 3,5-di-substituted-1,2,4-triazolate (dpt−), and related ligands. Coord. Chem. Rev. 2017, 344, 26–53. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Scott, H.S.; Staniland, R.W.; Kruger, P.E. Spin crossover in homoleptic Fe(II) imidazolylimine complexes. Coord. Chem. Rev. 2018, 362, 24–43. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kumar, K.S.; Ruben, M. Emerging trends in spin crossover (SCO) based functional materials and devices. Coord. Chem. Rev. 2017, 346, 176–205. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lavrenova, L.G. Spin crossover in homo- and heteroligand iron(II) complexes with tris(pyrazol-1-yl)methane derivatives. Rus. Chem. Bull. 2018, 67, 1142–1152. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shakirova, O.G.; Lavrenova, L.G. Spin crossover in new iron(II) coordination compounds with tris(pyrazol-1-yl)methane. Crystals 2020, 10, 843. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kahn, O.; Krober, J.; Jay, C. Spin transition molecular materials for displays and data recording. Adv. Mater. 1992, 4, 718–728. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gamez, P.; Costa, J.S.; Quesada, M.; Aromí, G. Iron Spin-Crossover compounds: From fundamental studies to practical applications. Dalton Trans. 2009, 7845–7853. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hayami, S.; Holmes, S.M.; Halcrow, M.A. Spin-state switches in molecular materials chemistry. J. Mater. Chem. C 2015, 3, 7775–7778. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kumar, K.S.; Bayeh, Y.; Gebretsadik, T.; Elemo, F.; Gebrezgiabher, M.; Thomas, M.; Ruben, M. Spin-crossover in iron(II)-Schiff base complexes. Dalton Trans. 2019, 48, 15321–15377. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Halcrow, M.A. Manipulating metal spin states for biomimetic, catalytic and molecular materials chemistry. Dalton Trans. 2020, 49, 15560–15567. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Letard, J.-F.; Daro, N.; Aymonier, C.; Cansell, F.; Saint-Martin, S. Nouveau Materiau a Transition de spin, son Procede de Preparation. European Patent 2391631, 7 December 2011. [Google Scholar]
- Bousseksou, A.; Vieu, C.; Letard, J.-F.; Demont, P.; Tuchagues, J.-P.; Malaquin, L.; Menegotto, J.; Salmon, L. Molecular Memory and Method for Making Same. European Patent 1430552, 2004. Available online: https://data.epo.org/gpi/EP1430552A1-MOLECULAR-MEMORY-AND-METHOD-FOR-MAKING-SAME (accessed on 28 June 2022).
- Piedrahita-Bello, M.; Angulo-Cervera, J.E.; Courson, R.; Molnár, G.; Malaquin, L.; Thibault, C.; Tondu, B.; Salmon, L.; Bousseksou, A. 4D printing with spin-crossover polymer composites. J. Mater. Chem. C 2020, 8, 6001–6005. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nguyen, T.D.; Veauthier, J.M.; Angles-Tamayo, G.F.; Chavez, D.E.; Lapsheva, E.L.; Myers, T.W.; Nelson, T.R.; Schelter, E.J. Correlating mechanical sensitivity with spin transition in the explosive spin crossover complex [Fe(Htrz)3]n[ClO4]2n. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2020, 142, 4842–4851. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yuan, J.; Wu, S.Q.; Liu, M.J.; Sato, O.; Kou, H.Z. Rhodamine 6G-labeled pyridyl aroylhydrazone Fe(II) complex exhibiting synergetic spin crossover and fluorescence. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2018, 140, 9426–9433. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Benaicha, B.; Van Do, K.; Yangui, A.; Pittala, N.; Lusson, A.; Sy, M.; Bouchez, G.; Fourati, H.; Gomez-Garcia, C.J.; Triki, S.; et al. Interplay between spin-crossover and luminescence in a multifunctional single crystal iron(II) complex: Towards a new generation of molecular sensors. Chem. Sci. 2019, 10, 6791–6798. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Boča, M.; Jameson, R.F.; Linert, W. Fascinating variability in the chemistry and properties of 2,6-bis-(benzimidazol-2-yl)-pyridine and 2,6-bis-(benzthiazol-2-yl)-pyridine and their complexes. Coord. Chem. Rev. 2011, 255, 290–317. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lavrenova, L.G.; Dyukova, I.I.; Korotaev, E.V.; Sheludyakova, L.A.; Varnek, V.A. Spin crossover in new iron(II) complexes with 2,6-bis(benzimidazole-2-yl)pyridine. Rus. J. Inorg. Chem. 2020, 65, 30–35. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ivanova, A.D.; Korotaev, E.V.; Komarov, V.Y.; Sheludyakova, L.A.; Varnek, V.A.; Lavrenova, L.G. Spin-crossover in iron(ii) coordination compounds with 2,6-bis(benzimidazol-2-yl)pyridine. New J. Chem. 2020, 44, 5834–5840. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ivanova, A.D.; Lavrenova, L.G.; Korotaev, E.V.; Trubina, S.V.; Sheludyakova, L.A.; Petrov, S.A.; Zhizhin, K.Y.; Kuznetsov, N.T. High-temperature spin crossover in complexes of iron(II) closo-borates with 2,6-bis(benzimidazol-2-yl)pyridine. Russ. J. Inorg. Chem. 2020, 65, 1687–1694. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ivanova, A.D.; Korotaev, E.V.; Komarov, V.Y.; Sukhikh, T.S.; Trubina, S.V.; Sheludyakova, L.A.; Petrov, S.A.; Tikhonov, A.Y.; Lavrenova, L.G. Spin crossover in iron(II) complexes with new ligand 2,6-bis(4,5-dimethyl-1H-imidazole-2-yl)pyridine. Inorg. Chim. Acta 2022, 532, 120746. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stupka, G.; Gremaud, L.; Bernardinelli, G.; Williams, A.F. Redox state switching of transition metals by deprotonation of the tridentate ligand 2,6-bis(imidazol-2-yl)pyridine. Dalton Trans. 2004, 407–412. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hammes, B.S.; Damiano, B.J.; Tobash, P.H.; Hidalgo, M.J.; Yap, G.P.A. Tuning the redox properties of a 1-D supramolecular array via selective deprotonation of coordinated imidazoles around a Mn(II) center. Inorg. Chem. Commun. 2005, 8, 513–516. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arruda, E.G.R.; Farias, M.A.; Jannuzzi, S.A.V.; Almeida Gonsales, S.; Timm, R.A.; Sharma, S.; Zoppellaro, G.; Kubota, L.T.; Knobel, M.; Formiga, A.L.B. Synthesis, structural and magnetic characterization of a copper(II) complex of 2,6-di(1H-imidazol-2-yl)pyridine and its application in copper-mediated polymerization catalysis. Inorg. Chim. Acta 2017, 466, 456–463. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ren, C.-X.; Li, S.-Y.; Yin, Z.-Z.; Lu, X.; Ding, Y.-Q. [2,6-Bis(4,5-dihydro-1H-imidazol-2-yl)pyridine]dichloridomanganese(II). Acta Cryst. E 2009, 65, m572–m573. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Shang, S.-M.; Ren, C.-X.; Wang, X.; Lu, L.-D.; Yang, X.-J. Bis[2,6-bis (4,5-dihydro-1H-imidazol-2-yl)pyridine]manganese(II) bis-(per-chlorate) acetonitrile solvate. Acta Cryst. E 2009, 65, m1023–m1024. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Voss, M.E.; Beer, C.M.; Mitchell, S.A.; Blomgren, P.A.; Zhichkin, P.E. A simple and convenient one-pot method for the preparation of heteroaryl-2-imidazoles from nitriles. Tetrahedron 2008, 64, 645–651. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Miller, H.C.; Muetterties, E.L.; Boone, J.L.; Garrett, P.; Hawthorne, M.F. Borane anions. Inorg. Synth. 1967, 10, 81–91. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Piminov, P.A.; Baranov, G.N.; Bogomyagkov, A.V.; Berkaev, D.E.; Borin, V.M.; Dorokhov, V.L.; Karnaev, S.E.; Kiselev, V.A.; Levichev, E.B.; Meshkov, O.I.; et al. Synchrotron radiation research and application at VEPP-4. Phys. Procedia 2016, 84, 19–26. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Klementev, K.V. Extraction of the fine structure from x-ray absorption spectra. J. Phys. D Appl. Phys. 2001, 34, 209. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gurman, S.J.; Binsted, N.; Ross, I. A rapid, exact curved-wave theory for EXAFS calculations. J. Phys. C Solid State Phys. 1984, 17, 143–151. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nakamoto, K. Infrared and Raman Spectra of Inorganic and Coordination Compounds; John Wiley & Sons Inc.: New York, NY, USA, 1986. [Google Scholar]
- Lever, A.B.P. Inorganic Electronic Spectroscopy, 2nd ed.; Elsevier: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 1985; ISBN 978-0-444-42389-4. [Google Scholar]
- Hauser, A. Ligand Field Theoretical Considerations. Spin Crossover in Transition Metal Compounds I; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2004; Volume 233, pp. 49–58. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sugano, S.; Tanabe, Y.; Kamimura, H. Multiplets of Transition—Metal ions in Crystals; Academic Press: New York, NY, USA; Pure and Applied Physics: London, UK, 1970. [Google Scholar]
- Selwood, P.W. Magnetochemistry; Interscience Publishers: New York, NY, USA, 1956. [Google Scholar]
- Rakitin, Y.V.; Kalinnikov, V.T. Modern Magnetochemistry; Nauka: St. Petersburg, Russia, 1994. [Google Scholar]








| Bonds | Ri, Å | Angles | Ω, Deg. | ||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1·0.5H2O | 2·H2O | 4∙H2O | 5·1.5H2O | 1·0.5H2O | 2·H2O | 4∙H2O | 5·1.5H2O | ||
| Fe(1)-N(1) | 1.96 | 1.97 | 1.98 | 1.94 | N(1)Fe(1)N(8) | 107.9 | 102.6 | 105.9 | 102.6 |
| Fe(1)-N(3) | 1.96 | 1.91 | 1.93 | 1.95 | N(1)Fe(1)N(6) | 95.3 | 92.5 | 95.1 | 100.1 |
| Fe(1)-N(4) | 1.95 | 1.97 | 1.98 | 1.93 | N(1)Fe(1)N(9) | 97.1 | 92.1 | 96.6 | 102.2 |
| Fe(1)-N(6) | 1.95 | 1.96 | 1.98 | 1.96 | N(1)Fe(1)N(3) | 75.2 | 79.8 | 75.6 | 85.3 |
| Fe(1)-N(8) | 1.86 | 1.88 | 1.90 | 1.86 | N(3)Fe(1)N(9) | 97.8 | 102.1 | 100.3 | 102.9 |
| Fe(1)-N(9) | 1.96 | 1.95 | 1.96 | 1.96 | N(3)Fe(1)N(4) | 75.8 | 81.2 | 80.6 | 73.7 |
| 2σ2 (Fe-N), Å2 | 0.014 | 0.013 | 0.013 | 0.012 | Fi (*) | 2.7 | 2.5 | 1.8 | 1.6 |
| Compound | Central Ion–Scattering Atom | Ni | Ri, Å | 2σi2, Å2 | Fi |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| [FeL2](ReO4)2 | Fe–N | 6 | 1.96 | 0.010 | 2.7 |
| Fe–C | 8 | 2.78 | 0.014 | ||
| Fe–C | 4 | 3.20 |
| L | 1·0.5H2O | 2·H2O | 3 | 4·H2O | 5·1.5H2O | Assignment |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 3485 | 3433 | 3225 | 3269 | ν(OH) | ||
| 3100w | 3020w | 3147 3116 | 3050w | 3151 3130 | 3148 3129 | ν(NH) |
| 3079 3035 | 3060 3021 | 3067 | 3067 | 2954 2924 2854 | 2988 2040 2849 | ν(CH) |
| 1598 1573 1552 | 1595 1570 1550 | 1569 1551 1479 | 1593 1566 1552 | 1622 1558 1490 1469 | 1622 1558 1490 1471 | Rring |
| 1118 1085 1070 | ν(SO4) | |||||
| 903 | ν(ReO4) | |||||
| 2473 | 2493 | ν(B-H) | ||||
| 1086 1036 | 1105 1054 | δ(BBH) | ||||
| 496 | 491 | 485 | 485 | 484 | Fe(3d6)–ligand (π) charge-transfer transition | |
| 385 356 330 | 376 334 | 381 321 | 334 | 333 | ν(M-N) |
| Complex | λ(1A1 → 1T2) | λ(1A1 → 1B2) | λ(1A1 → 1T1) | λ(1A1 → 1A2) | λ(1A1 → 1E) | Calculated Parameter | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| B | C | ∆LS | ||||||
| 1·0.5H2O | 454 | 613 | 536 | |||||
| 2·H2O | 454 | 624 | 539 | |||||
| 3 | 432 | 603 | 503 | |||||
| 4·H2O | 475 | 518 | 620 | 109.3 | 482.0 | 1.97 × 104 | ||
| 5·1.5H2O | 465 | 518 | 620 | 137.5 | 606.5 | 1.98 × 104 | ||
| Complex | δ, mm/s | ε, mm/s | Γ, mm/s |
|---|---|---|---|
| 1·0.5H2O | 0.269 | 0.364 | 0.33 |
| 2·H2O | 0.266 | 0.342 | 0.25 |
| 3 | 0.288 | 0.464 | 0.28 |
| 4∙H2O | 0.278 (64%) 0.925 (36%) | 0.420 2.224 | 0.26 0.80 |
| 5·1.5H2O | 0.282 | 0.465 | 0.25 |
| Complex | Tc↑, K | Tc↓, K |
|---|---|---|
| [FeL2]SO4·0.5H2O | >420 | 409 |
| [FeL2]Br2·H2O | >420 | >420 |
| [FeL2](ReO4)2 | 340 | 340 |
| [FeL2]B10H10·H2O | 436 | 436 |
| [FeL2]B12H12·1.5H2O | 455 | 455 |
| [FeL2]B10H10 | 447 | 440 |
| [FeL2]B12H12 | 458 | 458 |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Lavrenova, L.G.; Shakirova, O.G.; Korotaev, E.V.; Trubina, S.V.; Tikhonov, A.Y.; Os’kina, I.A.; Petrov, S.A.; Zhizhin, K.Y.; Kuznetsov, N.T. High-Temperature Spin Crossover in Iron(II) Complexes with 2,6-Bis(1H-imidazol-2-yl)pyridine. Molecules 2022, 27, 5093. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules27165093
Lavrenova LG, Shakirova OG, Korotaev EV, Trubina SV, Tikhonov AY, Os’kina IA, Petrov SA, Zhizhin KY, Kuznetsov NT. High-Temperature Spin Crossover in Iron(II) Complexes with 2,6-Bis(1H-imidazol-2-yl)pyridine. Molecules. 2022; 27(16):5093. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules27165093
Chicago/Turabian StyleLavrenova, Ludmila G., Olga G. Shakirova, Evgeniy V. Korotaev, Svetlana V. Trubina, Alexsei Ya. Tikhonov, Irina A. Os’kina, Sergey A. Petrov, Konstantin Yu. Zhizhin, and Nikolay T. Kuznetsov. 2022. "High-Temperature Spin Crossover in Iron(II) Complexes with 2,6-Bis(1H-imidazol-2-yl)pyridine" Molecules 27, no. 16: 5093. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules27165093
APA StyleLavrenova, L. G., Shakirova, O. G., Korotaev, E. V., Trubina, S. V., Tikhonov, A. Y., Os’kina, I. A., Petrov, S. A., Zhizhin, K. Y., & Kuznetsov, N. T. (2022). High-Temperature Spin Crossover in Iron(II) Complexes with 2,6-Bis(1H-imidazol-2-yl)pyridine. Molecules, 27(16), 5093. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules27165093