Ionic Liquids as Organocatalysts for Nucleophilic Fluorination: Concepts and Perspectives
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Promotion of SN2 Fluorination by ILs Using Alkali Metal Fluorides
3. SN2 Fluorination Facilitated by Polymer-Supported ILs
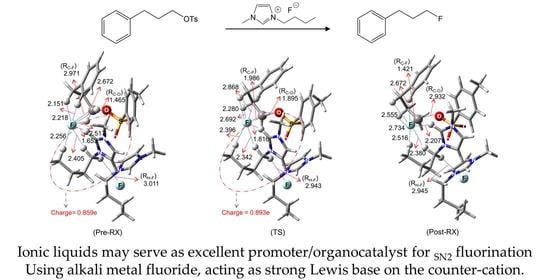
4. Mechanistic Features of IL-Facilitated SN2 Fluorination Using Metal Fluorides
5. Salt Effects
6. Organocatalysis of Nucleophilic Fluorination by IL Derivatives
7. Aromatic (SNAr) Fluorination of Diaryliodonium Salts Using MFs
8. Theoretical Approaches: Supramolecule–Continuum vs. QM/MM Theory
9. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Yu, L.H. (Ed.) Ionic Liquids in Green Organic Synthesis and Catalysis; CRC press: New York, NY, USA, 2021. [Google Scholar]
- Wasserscheid, P.; Keim, W. Ionic Liquids—New “Solutions” for Transition Metal Catalysis. Angew. Chem. 2000, 39, 3772–3789. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hallett, J.P.; Welton, T. Room-Temperature Ionic Liquids: Solvents for Synthesis and Catalysis. 2. Chem. Rev. 2011, 111, 3508–3576. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chakraborti, A.K.; Roy, S.R. On Catalysis by Ionic Liquids. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2009, 131, 6902–6903. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sarkar, A.; Roy, S.R.; Parikh, N.; Chakraborti, A.K. Nonsolvent Application of Ionic Liquids: Organo-Catalysis by 1-Alkyl-3-Methylimidazolium Cation Based Room-Temperature Ionic Liquids for Chemoselective N-Tert-Butyloxycarbonylation of Amines and the Influence of the C-2 Hydrogen on Catalytic Efficiency. J. Org. Chem. 2011, 76, 7132–7140. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xiao, Y.; Malhotra, S.V. Friedel-Crafts Acylation Reactions in Pyridinium Based Ionic Liquids. J. Organomet. Chem. 2005, 690, 3609–3613. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Carmichael, A.J.; Earle, M.J.; Holbrey, J.D.; McCormac, P.B.; Seddon, K.R. The Heck Reaction in Ionic Liquids: A Multiphasic Catalyst System. Org. Lett. 1999, 1, 997–1000. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peng, J.; Deng, Y. Cycloaddition of Carbon Dioxide to Propylene Oxide Catalyzed by Ionic Liquids. New J. Chem. 2001, 25, 639–641. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, X.; Ngwa, C.; Zheng, Q. A Simple and Efficient Procedure for Knoevenagel Reaction Promoted by Imidazolium-Based Ionic Liquids. Curr. Org. Synth. 2016, 13, 101–110. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zare, A.; Hasaninejad, A.; Parhami, A.; Moosavi-Zare, A.R.; Khedri, F.; Parsaee, Z.; Abdolalipoor-Saretoli, M.; Khedri, M.; Roshankar, M.; Deisi, H. Ionic Liquid 1-Butyl-3-Methylimidazolium Bromide ([Bmim]Br): A Green and Neutral Reaction Media for the Efficient, Catalyst-Free Synthesis of Quinoxaline Derivatives. J. Serbian Chem. Soc. 2010, 75, 1315–1324. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jakhar, K. Facile and Environment-Friendly Fluorinations Using Ionic Liquids. Curr. Org. Synth. 2022, 19, 1–25. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marrucho, I.M.; Branco, L.C.; Rebelo, L.P.N. Ionic Liquids in Pharmaceutical Applications. Annu. Rev. Chem. Biomol. Eng. 2014, 5, 527–546. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, J.W.; Shin, J.Y.; Chun, Y.S.; Jang, H.B.; Song, C.E.; Lee, S. Toward Understanding the Origin of Positive Effects of Ionic Liquids on Catalysis: Formation of More Reactive Catalysts and Stabilization of Reactive Intermediates and Transition States in Ionic Liquids. Acc. Chem. Res. 2010, 43, 985–994. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, D.W.; Song, C.E.; Chi, D.Y. New Method of Fluorination Using Potassium Fluoride in Ionic Liquid: Significantly Enhanced Reactivity of Fluoride and Improved Selectivity. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2002, 124, 10278–10279. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kim, D.W.; Song, C.E.; Chi, D.Y. Significantly Enhanced Reactivities of the Nucleophilic Substitution Reactions in Ionic Liquid. J. Org. Chem. 2003, 68, 4281–4285. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kim, D.W.; Chi, D.Y. Polymer-Supported Ionic Liquids: Imidazolium Salts as Catalysts for Nucleophilic Substitution Reactions Including Fluorinations. Angew. Chemie Int. Ed. 2004, 43, 483–485. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pârvulescu, V.I.; Hardacre, C. Catalysis in Ionic Liquids. Chem. Rev. 2007, 107, 2615–2665. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Van Rantwijk, F.; Sheldon, R.A. Biocatalysis in Ionic Liquids. Chem. Rev. 2007, 107, 2757–2785. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Earle, M.; Forestier, A.; Olivier-Bourbigou, H.; Wasserscheid, P. Organic Synthesis. In Ionic Liquids in Synthesis, 1st ed.; Wasserscheid, P., Welton, T., Eds.; Wiley-VCH Verlag: Weinheim, Germany, 2002; pp. 174–287. [Google Scholar]
- Welton, T. Ionic Liquids: A Brief History. Biophys. Rev. 2018, 10, 691–706. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, D.W.; Hong, D.J.; Seo, J.W.; Kim, H.S.; Kim, H.K.; Song, C.E.; Chi, D.Y. Hydroxylation of Alkyl Halides with Water in Ionic Liquid: Significantly Enhanced Nucleophilicity of Water. J. Org. Chem. 2004, 69, 3186–3189. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Earle, M.J.; McCormac, P.B.; Seddon, K.R. Regioselective Alkylation in Ionic Liquids. Chem. Commun. 1998, 2245–2246. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chauvin, Y.; Hirschauer, A.; Olivier, H. Alkylation of Isobutane with 2-Butene Using 1-Butyl-3-Methylimidazolium Chloride—Aluminium Chloride Molten Salts as Catalysts. J. Mol. Catal. 1994, 92, 155–165. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fischer, T.; Sethi, A.; Welton, T.; Woolf, J. Diels-Alder Reactions in Room-Temperature Ionic Liquids. Tetrahedron Lett. 1999, 40, 793–796. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bortolami, M.; Mattiello, L.; Scarano, V.; Vetica, F.; Feroci, M. In Situ Anodically Oxidized BMIm-BF4: A Safe and Recyclable BF3 Source. J. Org. Chem. 2021, 86, 16151–16157. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Beil, S.; Markiewicz, M.; Pereira, C.S.; Stepnowski, P.; Thöming, J.; Stolte, S. Toward the Proactive Design of Sustainable Chemicals: Ionic Liquids as a Prime Example. Chem. Rev. 2021, 121, 13132–13173. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, X.; Lu, G.; Xu, Z.; Cai, C. Facile Synthesis of Indolizines via 1, 3-Dipolar Cycloadditions in [Omim] Br: The Promotion of the Reaction through Noncovalent Interactions. ACS Sustain. Chem. Eng. 2017, 5, 9279–9285. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sysoeva, A.A.; Novikov, A.S.; Il’in, M.V.; Suslonov, V.V.; Bolotin, D.S. Predicting the Catalytic Activity of Azolium-Based Halogen Bond Donors: An Experimentally-Verified Theoretical Study. Org. Biomol. Chem. 2021, 19, 7611–7620. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oh, Y.H.; Choi, H.; Park, C.; Kim, D.W.; Lee, S. Harnessing Ionic Interactions and Hydrogen Bonding for Nucleophilic Fluorination. Molecules 2020, 25, 721. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, D.W.; Choe, Y.S.; Chi, D.Y. A New Nucleophilic Fluorine-18 Labeling Method for Aliphatic Mesylates: Reaction in Ionic Liquids Shows Tolerance for Water. Nucl. Med. Biol. 2003, 30, 345–350. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bolton, R. Radiohalogen Incorporation into Organic Systems. J. Label. Compd. Radiopharm. Off. J. Int. Isot. Soc. 2002, 45, 485–528. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, J.W.; Oliveira, M.T.; Jang, H.B.; Lee, S.; Chi, D.Y.; Kim, D.W.; Song, C.E. Hydrogen-Bond Promoted Nucleophilic Fluorination: Concept, Mechanism and Applications in Positron Emission Tomography. Chem. Soc. Rev. 2016, 45, 4638–4650. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, J.W.; Yan, H.; Jang, H.B.; Kim, H.K.; Park, S.; Lee, S.; Chi, D.Y.; Song, C.E. Bis-Terminal Hydroxy Polyethers as All-Purpose, Multifunctional Organic Promoters: A Mechanistic Investigation and Applications. Angew. Chemie 2009, 121, 7819–7822. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shinde, S.S.; Lee, B.S.; Chi, D.Y. Synergistic Effect of Two Solvents, Tert-Alcohol and Lonic Liquid, in One Molecule in Nucleophilic Fluorination. Org. Lett. 2008, 10, 733–735. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bouvet, S.; Pegot, B.; Marrot, J.; Magnier, E. Solvent Free Nucleophilic Introduction of Fluorine with [Bmim][F]. Tetrahedron Lett. 2014, 55, 826–829. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oh, Y.-H.; Ahn, D.-S.; Chung, S.-Y.; Jeon, G.-H.; Park, S.-W.; Oh, S.J.; Kim, D.W.; Kil, H.S.; Chi, D.Y.; Lee, S. Facile SN2 Reaction in Protic Solvent: Quantum Chemical Analysis. J. Phys. Chem. A 2007, 111, 10152–10161. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oh, Y.H.; Jang, H.B.; Im, S.; Song, M.J.; Kim, S.Y.; Park, S.W.; Chi, D.Y.; Song, C.E.; Lee, S. SN2 Fluorination Reactions in Ionic Liquids: A Mechanistic Study towards Solvent Engineering. Org. Biomol. Chem. 2011, 9, 418–422. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kim, D.W.; Ahn, D.-S.; Oh, Y.-H.; Lee, S.; Kil, H.S.; Oh, S.J.; Lee, S.J.; Kim, J.S.; Ryu, J.S.; Moon, D.H.; et al. A New Class of SN2 Reactions Catalyzed by Protic Solvents: Facile Fluorination for Isotopic Labeling of Diagnostic Molecules. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2006, 128, 16394–16397. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pliego Jr, J.R. Molecular Dynamics and Cluster-Continuum Insights on Bulk Alcohols Effects on SN2 Reactions of Potassium and Cesium Fluorides with Alkyl Halides. J. Mol. Liq. 2017, 237, 157–163. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Silva, S.L.; Valle, M.S.; Pliego, J.R., Jr. Nucleophilic Fluorination with KF Catalyzed by 18-Crown-6 and Bulky Diols: A Theoretical and Experimental Study. J. Org. Chem. 2020, 85, 15457–15465. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, D.W.; Jeong, H.-J.; Lim, S.T.; Sohn, M.-H.; Chi, D.Y. Facile Nucleophilic Fluorination by Synergistic Effect between Polymer-Supported Ionic Liquid Catalyst and Tert-Alcohol Reaction Media System. Tetrahedron 2008, 64, 4209–4214. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shinde, S.S.; Lee, B.S.; Chi, D.Y. Polymer-Supported Protic Functionalized Ionic Liquids for Nucleophilic Substitution Reactions: Superior Catalytic Activity Compared to Other Ionic Resins. Tetrahedron Lett. 2008, 49, 4245–4248. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sawamura, T.; Kuribayashi, S.; Inagi, S.; Fuchigami, T. Recyclable Polymer-Supported Iodobenzene-Mediated Electrocatalytic Fluorination in Ionic Liquid. Adv. Synth. Catal. 2010, 352, 2757–2760. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Choi, H.; Oh, Y.-H. Mechanism of Promotion of SN2 Fluorination by [Bmim] F in Solvent-Free Environment: Quantum Chemical Analysis. Chem. Phys. Lett. 2020, 756, 137857. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Anguille, S.; Garayt, M.; Schanen, V.; Grée, R. Activation of Nucleophilic Fluorination by Salts in Ionic Liquids and in Sulfolane. Adv. Synth. Catal. 2006, 348, 1149–1153. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oh, Y.-H.; Lee, S. Origin of Salt Effects in SN2 Fluorination Using KF Promoted by Ionic Liquids: Quantum Chemical Analysis. Molecules 2021, 26, 5738. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jadhav, V.H.; Jeong, H.-J.; Lim, S.T.; Sohn, M.-H.; Kim, D.W. Tailor-Made Hexaethylene Glycolic Ionic Liquids as Organic Catalysts for Specific Chemical Reactions. Org. Lett. 2011, 13, 2502–2505. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jadhav, V.H.; Kim, J.Y.; Chi, D.Y.; Lee, S.; Kim, D.W. Organocatalysis of Nucleophilic Substitution Reactions by the Combined Effects of Two Promoters Fused in a Molecule: Oligoethylene Glycol Substituted Imidazolium Salts. Tetrahedron 2014, 70, 533–542. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, S.; Kim, D.W. Organocatalysis of SN2 Reactions by Multifunctional Promotors: Ionic Liquids and Derivatives. In Sustainable Catalysis in Ionic Liquids, 1st ed.; Lozano, P., Ed.; CRC Press: Boca Raton, FL, USA, 2018; pp. 95–110. [Google Scholar]
- Oh, Y.; Lee, S. Hydrogen Bonding in SN2 Reactions Promoted or Inhibited by Ionic Liquids: Effects of Side Chain. Bull. Korean Chem. Soc. 2021, 42, 446–451. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Neumann, C.N.; Hooker, J.M.; Ritter, T. Concerted nucleophilic aromatic substitution with 19F− and 18F−. Nature 2016, 534, 369–373. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shah, A.; Pike, V.W.; Widdowson, D.A. The Synthesis of [18F]Fluoroarenes from the Reaction of Cyclotron-Produced [18F]Fluoride Ion with Diaryliodonium Salts. J. Chem. Soc. Perkin Trans. 1 1998, 2043–2046. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yoshimura, A.; Zhdankin, V. V Advances in Synthetic Applications of Hypervalent Iodine Compounds. Chem. Rev. 2016, 116, 3328–3435. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yagyu, T.; Takemoto, Y.; Yoshimura, A.; Zhdankin, V.V.; Saito, A. Iodine (III)-Catalyzed Formal [2+ 2+ 1] Cycloaddition Reaction for Metal-Free Construction of Oxazoles. Org. Lett. 2017, 19, 2506–2509. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Antonkin, N.S.; Vlasenko, Y.A.; Yoshimura, A.; Smirnov, V.I.; Borodina, T.N.; Zhdankin, V.V.; Yusubov, M.S.; Shafir, A.; Postnikov, P.S. Preparation and Synthetic Applicability of Imidazole-Containing Cyclic Iodonium Salts. J. Org. Chem. 2021, 86, 7163–7178. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xu, B.; Gao, Y.; Han, J.; Xing, Z.; Zhao, S.; Zhang, Z.; Ren, R.; Wang, L. Hypervalent Iodine (III)-Mediated Tosyloxylation of 4-Hydroxycoumarins. J. Org. Chem. 2019, 84, 10136–10144. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, H.; Wang, L.; Han, J. Deacetylative Aryl Migration of Diaryliodonium Salts with C (Sp2)–N Bond Formation toward Ortho-Iodo N-Aryl Sulfonamides. Org. Lett. 2020, 22, 3581–3585. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Edwards, R.; Wirth, T. [18F] 6-fluoro-3, 4-dihydroxy-l-phenylalanine–Recent Modern Syntheses for an Elusive Radiotracer. J. Label. Compd. Radiopharm. 2015, 58, 183–187. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Edwards, R.; Westwell, A.D.; Daniels, S.; Wirth, T. Convenient Synthesis of Diaryliodonium Salts for the Production of [18F]F-DOPA. European J. Org. Chem. 2015, 2015, 625–630. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tian, T.; Zhong, W.-H.; Meng, S.; Meng, X.-B.; Li, Z.-J. Hypervalent Iodine Mediated Para-Selective Fluorination of Anilides. J. Org. Chem. 2013, 78, 728–732. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maisonial-Besset, A.; Serre, A.; Ouadi, A.; Schmitt, S.; Canitrot, D.; Léal, F.; Miot-Noirault, E.; Brasse, D.; Marchand, P.; Chezal, J.M. Base/Cryptand/Metal-Free Automated Nucleophilic Radiofluorination of [18F]FDOPA from Iodonium Salts: Importance of Hydrogen Carbonate Counterion. Eur. J. Org. Chem. 2018, 2018, 7058–7065. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vāvere, A.L.; Neumann, K.D.; Butch, E.R.; Hu, B.; DiMagno, S.G.; Snyder, S.E. Improved, One-pot Synthesis of 6-[18F] Fluorodopamine and Quality Control Testing for Use in Patients with Neuroblastoma. J. Label. Compd. Radiopharm. 2018, 61, 1069–1080. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jang, K.S.; Jung, Y.-W.; Gu, G.; Koeppe, R.A.; Sherman, P.S.; Quesada, C.A.; Raffel, D.M. 4-[18F] Fluoro-m-Hydroxyphenethylguanidine: A Radiopharmaceutical for Quantifying Regional Cardiac Sympathetic Nerve Density with Positron Emission Tomography. J. Med. Chem. 2013, 56, 7312–7323. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Han, J.; Chen, H.; An, G.; Sun, X.; Li, X.; Liu, Y.; Zhao, S.; Wang, L. Hypervalent Iodonium Zwitterions and Nucleophilic Aromatic Substitution: A Multiple-Step Experiment in Organic Chemistry. J. Chem. Educ. 2021, 98, 3992–3998. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Il’in, M.V.; Sysoeva, A.A.; Novikov, A.S.; Bolotin, D.S. Diaryliodoniums as Hybrid Hydrogen-and Halogen-Bond-Donating Organocatalysts for the Groebke–Blackburn–Bienaymé Reaction. J. Org. Chem. 2022, 87, 4569–4579. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yunusova, S.N.; Novikov, A.S.; Soldatova, N.S.; Vovk, M.A.; Bolotin, D.S. Iodonium Salts as Efficient Iodine (III)-Based Noncovalent Organocatalysts for Knorr-Type Reactions. RSC Adv. 2021, 11, 4574–4583. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pliego, J.R.; Riveros, J.M. The Cluster-Continuum Model for the Calculation of the Solvation Free Energy of Ionic Species. J. Phys. Chem. A 2001, 105, 7241–7247. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, Y.; Truhlar, D.G. The M06 Suite of Density Functionals for Main Group Thermochemistry, Thermochemical Kinetics, Noncovalent Interactions, Excited States, and Transition Elements: Two New Functionals and Systematic Testing of Four M06-Class Functionals and 12 Other Function. Theor. Chem. Acc. 2008, 120, 215–241. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marenich, A.V.; Cramer, C.J.; Truhlar, D.G. Universal Solvation Model Based on Solute Electron Density and on a Continuum Model of the Solvent Defined by the Bulk Dielectric Constant and Atomic Surface Tensions. J. Phys. Chem. B 2009, 113, 6378–6396. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sánchez-Badillo, J.; Gallo, M.; Guirado-López, R.A.; González-García, R. Potential of Mean Force Calculations for an SN2 Fluorination Reaction in Five Different Imidazolium Ionic Liquid Solvents Using Quantum Mechanics/Molecular Mechanics Molecular Dynamics Simulations. J. Phys. Chem. B 2020, 124, 4338–4357. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Acevedo, O. Simulating Chemical Reactions in Ionic Liquids Using QM/MM Methodology. J. Phys. Chem. A 2014, 118, 11653–11666. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Allen, C.; McCann, B.W.; Acevedo, O. Ionic Liquid Effects on Nucleophilic Aromatic Substitution Reactions from QM/MM Simulations. J. Phys. Chem. B 2015, 119, 743–752. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Doherty, B.; Zhong, X.; Acevedo, O. Virtual Site OPLS Force Field for Imidazolium-Based Ionic Liquids. J. Phys. Chem. B 2018, 122, 2962–2974. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Acevedo, O.; Jorgensen, W.L.; Evanseck, J.D. Elucidation of Rate Variations for a Diels—Alder Reaction in Ionic Liquids from QM/MM Simulations. J. Chem. Theory Comput. 2007, 3, 132–138. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Doherty, B.; Zhong, X.; Gathiaka, S.; Li, B.; Acevedo, O. Revisiting OPLS Force Field Parameters for Ionic Liquid Simulations. J. Chem. Theory Comput. 2017, 13, 6131–6145. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yue, K.; Doherty, B.; Acevedo, O. Comparison between Ab Initio Molecular Dynamics and OPLS-Based Force Fields for Ionic Liquid Solvent Organization. J. Phys. Chem. B 2022, 126, 3908–3919. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- D’Anna, F.; Frenna, V.; Noto, R.; Pace, V.; Spinelli, D. Study of Aromatic Nucleophilic Substitution with Amines on Nitrothiophenes in Room-Temperature Ionic Liquids: Are the Different Effects on the Behavior of Para-like and Ortho-like Isomers on Going from Conventional Solvents to Room-Temperature Ionic Liquid. J. Org. Chem. 2006, 71, 5144–5150. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bhargava, B.L.; Yasaka, Y.; Klein, M.L. Hydrogen Evolution from Formic Acid in an Ionic Liquid Solvent: A Mechanistic Study by Ab Initio Molecular Dynamics. J. Phys. Chem. B 2011, 115, 14136–14140. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, X.; Lu, G.; Cai, C. Facile Aromatic Nucleophilic Substitution (SNAr) Reactions in Ionic Liquids: An Electrophile–Nucleophile Dual Activation by [Omim] Br for the Reaction. Green Chem. 2016, 18, 5580–5585. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oh, Y.; Lee, S. Enhancement of SNAr Reactions by CH3SO3− Ionic Liquid and Organic Solvent Dimethylformamide as Bifunctional Organocatalysts: A Mechanistic Study. Bull. Korean Chem. Soc. 2022, 43, 98–102. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, W.C.; Kang, S.M.; Lee, B.C.; Kim, S.E.; Kim, D.W. Multifunctional Crown-5-calix[4]arene-based Phase-Transfer Catalysts for Aromatic 18F-Fluorination. Org. Lett. 2020, 22, 9551–9555. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- D’Anna, F.; Marullo, S.; Noto, R. Ionic Liquids/[bmim][N3] Mixtures: Promising Media for the Synthesis of Aryl Azides by SNAr. J. Org. Chem. 2008, 73, 6224–6228. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shinde, S.S.; Bolik, K.-V.; Maschauer, S.; Prante, O. 18F-Fluorination Using Tri-Tert-Butanol Ammonium Iodide as Phase-Transfer Catalyst: An Alternative Minimalist Approach. Pharmaceuticals 2021, 14, 833. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oh, Y.-H.; Shinde, S.S.; Lee, S. Nucleophilic Radiofluorination Using Tri-Tert-Butanol Ammonium as a Bifunctional Organocatalyst: Mechanism and Energetics. Molecules 2022, 27, 1044. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
















| Entry | [bmim][BF4] mL (Equiv) | CH3CN (mL) | H2O (µL) | Reaction Time (h) | Yield of Product (%) | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | 2 | |||||
| 1 | 5 | – | 0 | 2 | – | 85 |
| 2 | 5 | – | 90 (5 equiv) | 1.5 | – | 92 |
| 3 | 3.2 | 1.6 | 90 | 1.5 | – | 93 |
| 4 | 1.6 | 3.2 | 90 | 1.5 | – | 94 |
| 5 | 3 | 1.5 | 500 | 1.5 | – | 88 |
| 6 | 1 | 4 | 90 | 1.5 | – | 92 |
| 7 | 0.57 (3) | 4.4 | 90 | 3 | – | 91 |
| 8 | 0.19 (1) | 4.8 | 90 | 6 | – | 89 |
| 9 | 0.1 (0.5) | 5 | 90 | 12 | trace | 84 |
| 10 | – | 5 | 0 | 24 | 86 | Trace |
| 11 | 18-crown-6 (2) | 5 | 0 | 24 | 53 | 40 |

| Entry | Ionic Liquid | Cosolvent | Reaction Time (h) | Yield of Product (%) | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | 2a | 2b | 2c | ||||
| 1 | [bmim][PF6] | CH3CN | 2 | – | 90 | Trace | – |
| 2 | [bmim][SbF6] | CH3CN | 2 | – | 93 | – | – |
| 3 | [bmim][OTf] | CH3CN | 4 | – | 79 | 15 | – |
| 4 | [bmim][NTf2] | CH3CN | 5 | 61 | 35 | Trace | – |
| 5 | [bmim][BF4] | 1,4-dioxane | 1.5 | – | 91 | – | – |

| Entry | MF | Reaction Time (h) | Yield b (%) |
|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | LiF | 48 | – |
| 2 | NaF | 48 | – |
| 3 | KF | 1.5 | 93 |
| 4 | RbF | 30 min | 93 |
| 5 | CsF | 20 min | 95 |

| Entry | PS[hmim][BF4] [mg] (Equiv) | MF | CH3CN (mL) | t (h) | Yield of Product (%) | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 2 | 3a | 3b | 3c | |||||
| 1 | 1000 (2.2) | CsF | 12 | 1.5 | – | 97 | – | trace |
| 2 | – | CsF | 3 | 2 | 91 | trace | – | – |
| 3 | [bmim][BF4] (0.55) | CsF | 3 | 3 | 27 | 68 | – | – |
| 4 | 18-crown-6 (2) | CsF | 6 | 5 | trace | 88 | – | 7 |
| 5 | PS[hmim][OTf] (0.55) | CsF | 3 | 5 | trace | 91 | 6 | – |
| 6 | 250 (0.55) | RbF | 3 | 9 | – | 94 | 5 | – |
| 7 | 250 (0.55) | KF | 3 | 24 | – | 66 | 31 | – |

| Entry | PS[hmim][BF4] mg (Equiv) | MF | Temp. (°C) | Time (h) | Yield of Product (%) | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | 2a | 2b | |||||
| 1 | 227 (0.5) in CH3CN | CsF | 80 | 12 | 9 | 89 | – |
| 2 | – | CsF | 80 | 6 | – | 93 | 5 |
| 3 | PS[hmim][OTf] (0.5) | CsF | 80 | 2.5 | – | 95 | 3 |
| 4 | 227 (0.5) | RbF | 90 | 1.5 | – | 97 | 2 |
| 5 | – | RbF | 90 | 24 | 13 | 76 | 9 |
| 6 | 227 (0.5) | KF | 100 | 7 | – | 91 | 4 |
| 7 | – | KF | 100 | 24 | 90 | trace | 7 |
| 8 | 454 (1.0) | CsF | 80 | 1 | – | 96 | 2 |
| 9 | – in CH3CN | CsF | 100 | 2 | 91 | trace | – |
| 10 | 18-crown-6 (2.0) in CH3CN | KF | 100 | 24 | 53 | 40 | – |

| Entry | Time (min) | Temperature (°C) | BMIMF (Equiv) | Yield a (%) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | 10 | 80 | 2 | 66 |
| 2 | 10 | 100 | 2 | 66 |
| 3 | 10 | 80 | 3 | 77 |
| 3 | 30 | 80 | 1 | 49 |
| 4 | 30 | 80 | 2 | 84 |
| 5 | 30 | 80 | 3 | 95 (85) b |
| 6 | 360 | 80 | 5 | 83 |
| Ionic Liquids | E‡ | G‡100°C | SN2 Yield (%) |
|---|---|---|---|
| [bmim][BF4] | 19.8 | 21.9 | 24 |
| [bmim][OMs] | 20.3 | 20.8 | 32 |
| [mim-tOH][OMs] | 16.0 | 19.1 | 100 |
| Leaving Group (L) | ΔG‡ a CH3OH | ΔG‡ b CH3OH | ΔG‡ a [bmim] [BF4] | ΔG‡ a [bmim] [PF6] |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Br | 25.7 (26.0) | 30.8 | 25.8 (23.0) | 25.1 |
| OCH3 | 26.5 (23.6) | 30.7 | 27.6 (21.8) | 26.2 |
| OC6H5 | 25.1 | 30.5 | 23.8 (22.1) | 26.0 |
| OC6H4-4-NO2 | 24.5 (24.1) | 29.4 | 24.1 (21.5) | 29.1 |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Oh, Y.-H.; Kim, D.W.; Lee, S. Ionic Liquids as Organocatalysts for Nucleophilic Fluorination: Concepts and Perspectives. Molecules 2022, 27, 5702. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules27175702
Oh Y-H, Kim DW, Lee S. Ionic Liquids as Organocatalysts for Nucleophilic Fluorination: Concepts and Perspectives. Molecules. 2022; 27(17):5702. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules27175702
Chicago/Turabian StyleOh, Young-Ho, Dong Wook Kim, and Sungyul Lee. 2022. "Ionic Liquids as Organocatalysts for Nucleophilic Fluorination: Concepts and Perspectives" Molecules 27, no. 17: 5702. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules27175702
APA StyleOh, Y.-H., Kim, D. W., & Lee, S. (2022). Ionic Liquids as Organocatalysts for Nucleophilic Fluorination: Concepts and Perspectives. Molecules, 27(17), 5702. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules27175702