Quantitative HPLC–UV Study of Lignans in Anthriscus sylvestris
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Results and Discussion
2.1. Method Development
2.2. Method Validation
2.2.1. Chromatographic Performance
2.2.2. Identity
2.2.3. Linearity
2.2.4. Detection and Quantitation Limits
2.2.5. Trueness and Precision
2.2.6. Robustness
2.2.7. Stability
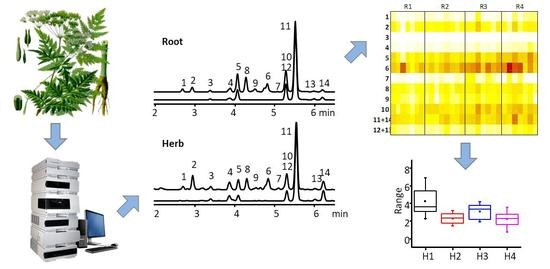
2.3. Samples Analysis
3. Materials and Methods
3.1. Samples and Reagents
3.2. Extraction
3.3. HPLC analysis
3.4. HPLC–MS/MS Analysis
4. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Dall’Acqua, S.; Giorgetti, M.; Cervellati, R.; Innocenti, G. Deoxypodophyllotoxin Content and Antioxidant Activity of Aerial Parts of Anthriscus sylvestris Hoffm. Z. Naturforschung 2006, 61c, 658–662. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kozawa, M.; Baba, K.; Matsuyama, Y.; Kido, T.; Sakai, M.; Takemoto, T. Components of the Root of Anthriscus sylvestris Hoffm. II. Insecticidal Activity. Chem. Pharm. Bull. 1982, 30, 2885–2888. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Milovanovic, M.; Picuric-Jovanovic, K.; Vucelic-Radovic, B.; Vrbaski, Z. Antioxidant Effects of Flavonoids of Anthriscus sylvestris in Lard. J. Am. Oil Chem. Soc. 1996, 73, 773–776. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Orčić, D.; Berežni, S.; Škorić, D.; Mimica Dukić, N. Comprehensive study of Anthriscus sylvestris lignans. Phytochemistry 2021, 192, 112958. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hendrawati, O.; Woerdenbag, H.J.; Michiels, P.J.A.; Aantjes, H.G.; Van Damd, A.; Kayser, O. Identification of lignans and related compounds in Anthriscus sylvestris by LC–ESI-MS/MS and LC-SPE–NMR. Phytochemistry 2011, 72, 2172–2179. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Koulman, A.; Kubbinga, M.E.; Batterman, S.; Woerdenbag, H.J.; Pras, N.; Woolley, J.G.; Quax, W.J. A Phytochemical Study of Lignans in Whole Plants and Cell Suspension Cultures of Anthriscus sylvestris. Planta Med. 2003, 69, 733–738. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Šibul, F.; Orčić, D.; Svirčev, E.; Mimica-Dukić, N. Optimization of extraction conditions for secondary biomolecules from various plant species. Hem. Ind. 2016, 70, 473–483. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- European Commission Decision (EC). No. 657/2002 of 12 August 2002 implementing Council Directive 96/23/EC concerning the performance of analytical methods and the interpretation of results. Off. J. 2002, L221, 8–36. [Google Scholar]
- AOAC International. Guidelines for Standard Method Performance Requirements. In AOAC Official Methods of Analysis, 20th ed.; AOAC International: Rockville MD, USA, 2016; Appendix F; pp. 1–18. [Google Scholar]
- European Commission. SANTE/12682/2019. In Guidance Document on Analytical Quality Control and Method Validation Procedures for Pesticides Residues Analysis in Food and Feed; European Commission, Directorate General for Health and Food Safety: Brussels, Belgium, 2019; pp. 1–48. [Google Scholar]
- ICH Q2 (R1) (1994) Validation of Analytical Procedures: Text and Methodology—Step 5. Available online: https://www.ema.europa.eu/en/documents/scientific-guideline/ich-q-2-r1-validation-analytical-procedures-text-methodology-step-5_en.pdf (accessed on 10 December 2021).
- FDA. Bioanalytical Method Validation. In Guidance for Industry; U.S. Department of Health and Human Services, Food and Drug Administration, Center for Drug Evaluation and Research (CDER), Center for Veterinary Medicine (CVM): Rockville, MD, USA, 2018; pp. 1–41. [Google Scholar]
- Mohagheghzadeh, A.; Schmidt, T.J.; Bayindir, Ü.; Fuss, E.; Mehregan, I.; Alfermann, A.W. Diarylbutyrolactone Lignans from Linum corymbulosum in vitro Cultures. Planta Med. 2006, 72, 1165–1167. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Schmidt, T.J.; Alfermann, A.W.; Fuss, E. High-performance liquid chromatography/mass spectrometric identification of dibenzylbutyrolactonetype lignans: Insights into electrospray ionization tandem mass spectrometric fragmentation of lign-7-eno-9,90-lactones and application to the lignans of Linum usitatissimum L. (Common Flax). Rapid Commun. Mass Spectrom. 2008, 22, 3642–3650. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Koulman, A.; Bos, R.; Medarde, M.; Pras, N.; Quax, W.J. A Fast and Simple GC MS Method for Lignan Profiling in Anthriscus sylvestris and Biosynthetically Related Plant Species. Planta Med. 2001, 67, 858–862. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Koulman, A. Podophyllotoxin. A Study of the Biosynthesis, Evolution, Function and Use of Podophyllotoxin and Related Lignans. Ph.D. Thesis, Rijksuniversiteit, Groningen, The Netherlands, 2003. [Google Scholar]


| Cpd | R(17.4.2021.) | R(27.4.2021.) | R(17.5.2021.) | R(4.6.2021.) | H(17.4.2021.) | H(27.4.2021.) | H(17.5.2021.) | H(4.6.2021.) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | 0.32 ± 0.21 | 0.35 ± 0.18 | 0.49 ± 0.70 | 0.72 ± 0.45 | 0.078 ± 0.060 | 0.069 ± 0.048 | 0.042 ± 0.025 | 0.037 ± 0.026 |
| 2 | 1.9 ± 1.2 | 2.22 ± 0.69 | 3.5 ± 3.3 | 3.6 ± 2.5 | 0.79 ± 0.27 | 0.95 ± 0.28 | 0.82 ± 0.16 | 0.45 ± 0.20 |
| 3 | 0.038 ± 0.018 | 0.047 ± 0.033 | 0.058 ± 0.022 | 0.089 ± 0.046 | 0.020 ± 0.011 | 0.026 ± 0.023 | 0.0127 ± 0.0032 | 0.0095 ± 0.0054 |
| 4 | 0.19 ± 0.11 | 0.31 ± 0.12 | 0.43 ± 0.21 | 0.71 ± 0.39 | 0.105 ± 0.089 | 0.125 ± 0.081 | 0.069 ± 0.034 | 0.085 ± 0.073 |
| 5 | 3.8 ± 2.1 | 5.1 ± 2.1 | 7.3 ± 4.3 | 11.6 ± 4.8 | 0.52 ± 0.48 | 0.40 ± 0.13 | 0.307 ± 0.090 | 0.23 ± 0.14 |
| 6 | 11.0 ± 8.4 | 11.0 ± 4.2 | 18.6 ± 5.5 | 22 ± 13 | 4.3 ± 1.9 | 2.28 ± 0.63 | 3.05 ± 0.90 | 2.23 ± 0.90 |
| 7 | 0.15 ± 0.12 | 0.42 ± 0.21 | 1.18 ± 0.85 | 0.58 ± 0.68 | 0.22 ± 0.26 | 0.155 ± 0.088 | 0.190 ± 0.062 | 0.091 ± 0.033 |
| 8 | 2.14 ± 0.62 | 2.8 ± 1.5 | 3.9 ± 2.1 | 3.6 ± 1.8 | 0.37 ± 0.24 | 0.32 ± 0.20 | 0.215 ± 0.068 | 0.090 ± 0.080 |
| 9 | 1.43 ± 0.53 | 1.42 ± 0.76 | 2.3 ± 1.0 | 2.3 ± 1.6 | 0.22 ± 0.14 | 0.151 ± 0.091 | 0.113 ± 0.078 | 0.067 ± 0.067 |
| 10 | 3.7 ± 2.1 | 6.0 ± 1.7 | 9.6 ± 4.9 | 9.0 ± 3.3 | 0.80 ± 0.64 | 0.76 ± 0.80 | 0.63 ± 0.23 | 0.34 ± 0.16 |
| 11+14 | 5.8 ± 1.6 | 5.9 ± 3.7 | 8.4 ± 3.3 | 10.1 ± 7.1 | 1.00 ± 0.35 | 0.94 ± 0.36 | 0.77 ± 0.23 | 0.58 ± 0.39 |
| 12+13 | 0.96 ± 0.38 | 1.04 ± 0.46 | 1.11 ± 0.64 | 2.0 ± 1.1 | 0.24 ± 0.22 | 0.17 ± 0.10 | 0.085 ± 0.025 | 0.086 ± 0.059 |
| Σ | 31 ± 12 | 37 ± 13 | 57 ± 23 | 66 ± 26 | 8.6 ± 3.9 | 6.3 ± 2.5 | 6.3 ± 1.3 | 4.3 ± 1.9 |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Orčić, D.; Berežni, S.; Mimica-Dukić, N. Quantitative HPLC–UV Study of Lignans in Anthriscus sylvestris. Molecules 2022, 27, 6072. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules27186072
Orčić D, Berežni S, Mimica-Dukić N. Quantitative HPLC–UV Study of Lignans in Anthriscus sylvestris. Molecules. 2022; 27(18):6072. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules27186072
Chicago/Turabian StyleOrčić, Dejan, Sanja Berežni, and Neda Mimica-Dukić. 2022. "Quantitative HPLC–UV Study of Lignans in Anthriscus sylvestris" Molecules 27, no. 18: 6072. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules27186072
APA StyleOrčić, D., Berežni, S., & Mimica-Dukić, N. (2022). Quantitative HPLC–UV Study of Lignans in Anthriscus sylvestris. Molecules, 27(18), 6072. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules27186072