Use of Biochar Prepared from the Açaí Seed as Adsorbent for the Uptake of Catechol from Synthetic Effluents
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Results and Discussion
2.1. Textural Characteristics
2.2. TGA Analysis
2.3. Infrared Spectroscopy (FTIR)
2.4. Elemental Analysis
2.5. Hydrophobicity Test (HI)
2.6. Zero-Charge Point (pHpcz)
2.7. Adsorption Kinetics
2.8. Adsorption Isotherm
2.9. Adsorption Thermodynamics
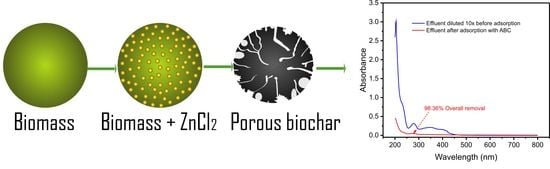
2.10. Simulated Effluent Removal
3. Materials and Methods
3.1. Biochar Carbon Preparation
3.2. Characterization of Açaí-Activated Biochar
3.3. Adsorption Studies on ABC
3.4. Synthetic Wastewater
4. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
Sample Availability
References
- Parida, V.K.; Saidulu, D.; Majumder, A.; Srivastava, A.; Gupta, B.; Gupta, A.K. Emerging contaminants in wastewater: A critical review on occurrence, existing legislation, risk assessment, and sustainable treatment alternatives. J. Environ. Chem. Eng. 2021, 9, 105966. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rodriguez-Narvaez, O.M.; Peralta-Hernandez, J.M.; Goonetilleke, A.; Bandala, E.R. Treatment technologies for emerging contaminants in water: A review. Chem. Eng. J. 2017, 323, 361–380. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Rizzo, L.; Malato, S.; Antakyali, D.; Beretsou, V.G.; Đolić, M.B.; Gernjak, W.; Heath, E.; Ivancev-Tumbas, I.; Karaolia, P.; Ribeiro, A.R.L.; et al. Consolidated vs. new advanced treatment methods for the removal of contaminants of emerging concern from urban wastewater (Review). Sci. Total Environ. 2019, 655, 986–1008. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fatta-Kassinos, D.; Michael, C. Wastewater reuse applications and contaminants of emerging concern. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2013, 20, 3493–3495. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Geissena, V.; Mol, H.; Klumpp, E.; Umlauf, G.; Nadal, M.; van der Ploeg, M.; van de Zee, S.E.A.T.M.; Ritsema, C.J. Emerging pollutants in the environment: A challenge for water resource management. Inter. Soil Water Conser. Res. 2015, 3, 57–65. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kottuparambil, S.; Kim, Y.J.; Choi, H.; Kim, M.S.; Park, A.; Park, J.; Shin, W.; Han, T. A rapid phenol toxicity test based on photosynthesis and movement of the freshwater flagellate, Euglena agilis Carter. Aquat. Toxicol. 2014, 155, 9–14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cimirro, N.F.G.M.; Lima, E.C.; Cunha, M.R.; Thue, P.S.; Grimm, A.; dos Reis, G.S.; Rabiee, N.; Saeb, M.R.; Keivanimehr, F.; Habibzadeh, S. Removal of diphenols using pine biochar. Kinetics, equilibrium, thermodynamics, and mechanism of uptake. J. Mol. Liq. 2022, 364, 119979. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- NORMAN. The Network of Reference Laboratories, Research Centres, and Related Organizations for Monitoring of Emerging Environmental Substances. 2022. Available online: www.norman-network.net (accessed on 7 September 2022).
- Michałowicz, J.; Duda, W. Phenols—Sources and Toxicity. Polish J. Environ. Stud. 2007, 16, 347–362. [Google Scholar]
- Qu, Y.; Qin, L.; Guo, M.; Liu, X.; Yang, Y. Multilayered molecularly imprinted composite membrane based on porous carbon nanospheres/pDA cooperative structure for selective adsorption and separation of phenol. Sep. Purif. Technol. 2022, 280, 119915. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Z.; Yi, G.; Li, P.; Wang, X.; Wang, X.; Zhang, C.; Zhang, Y.; Sun, Q. Eu/GO/PbO2 composite-based anode for highly efficient electrochemical oxidation of hydroquinone. Colloids Surf. A 2022, 642, 128632. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ke, P.; Zeng, D.; Wang, R.; Cui, J.; Li, X.; Fu, Y. Magnetic carbon microspheres as a reusable catalyst in heterogeneous Fenton system for the efficient degradation of phenol in wastewater. Colloids Surf. A 2022, 638, 128265. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shahabivand, S.; Mortazavi, S.S.; Mahdavinia, G.R.; Darvishi, F. Phenol biodegradation by immobilized Rhodococcus qingshengii isolated from coking effluent on Na-alginate and magnetic chitosan-alginate nanocomposite. J. Environ. Manag. 2022, 307, 114586. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Leite, A.J.B.; Sophia, A.C.; Thue, P.S.; dos Reis, G.S.; Dias, S.L.P.; Lima, E.C.; Vaghetti, J.C.P.; Pavan, F.A.; de Alencar, W.S. Activated carbon from avocado seeds for the removal of phenolic compounds from aqueous solutions. Desalin. Water Treat. 2017, 71, 168–181. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Cunha, M.R.; Lima, E.C.; Lima, D.R.; da Silva, R.S.; Thue, P.S.; Seliem, M.K.; Sher, F.; dos Reis, G.S.; Larsson, S.H. Removal of captopril pharmaceutical from synthetic pharmaceutical-industry wastewaters: Use of activated carbon derived from Butia catarinensis. J. Environ. Chem. Eng. 2020, 8, 1–9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thue, P.S.; dos Reis, G.S.; Lima, E.C.; Sieliechi, J.M.; Dotto, G.L.; Wamba, A.G.N.; Dias, S.L.P.; Pavan, F.A. Activated carbon obtained from Sapelli wood sawdust by microwave heating for o-cresol adsorption. Res. Chem. Intermed. 2017, 43, 1063–1087. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Yao, X.; Ji, L.; Guo, J.; Ge, S.; Lu, W.; Chen, Y.; Cai, L.; Wang, Y.; Song, W. An abundant porous biochar material derived from wakame (Undaria pinnatifida) with high adsorption performance for three organic dyes. Bioresour. Technol. 2020, 318, 124082. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Amole, A.R.; Araromi, D.O.; Alade, A.O.; Afolabi, T.J.; Adeyi, V.A. Biosorptive removal of nitrophenol from aqueous solution using ZnCl2-modified groundnut shell: Optimization, equilibrium, kinetic, and thermodynamic studies. Int. J. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2021, 18, 1859–1876. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Carvalho, C.O.; Rodrigues, D.L.C.; Lima, E.C.; Umpierres, C.S.; Chaguezac, D.F.C.; Machado, F.M. Kinetic, equilibrium, and thermodynamic studies on the adsorption of ciprofloxacin by activated carbon produced from Jerivá (Syagrus romanzoffiana). Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2019, 26, 4690–4702. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Leite, A.J.B.; Saucier, C.; Lima, E.C.; dos Reis, G.S.; Umpierres, C.S.; Mello, B.L.; Shirmardi, M.; Dias, S.L.P.; Sampaio, C.H. Activated carbons from avocado seed: Optimization and application for removal of several emerging organic compounds. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2018, 25, 7647–7661. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Nascimento, B.F.; de Araujo, C.M.B.; do Nascimento, A.C.; da Silva, F.L.H.; de Melo, D.J.N.; Jaguaribe, E.F.; Cavalcanti, J.V.F.L.; da Motta Sobrinho, M.A. Detoxification of sisal bagasse hydrolysate using activated carbon produced from the gasification of açaí waste. J. Hazard. Mater. 2021, 409, 124494. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brito, M.J.P.; Borges, J.F.; de Oliveira, T.P.; Santos, M.P.F.; de Souza, E.C., Jr.; Santos, L.S.; Bonomo, R.C.F.; Veloso, C.M. Royal blue dianix CC dye adsorption onto biochars: Kinetics, diffusion modeling, equilibrium, and thermodynamic adsorption data. Desalin. Water Treat. 2020, 197, 424–437. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thue, P.S.; Umpierres, C.S.; Lima, E.C.; Lima, D.R.; Machado, F.M.; dos Reis, G.S.; da Silva, R.S.; Pavan, F.A.; Tran, H.N. Single-step pyrolysis for producing magnetic activated carbon from tucumã (Astrocaryum aculeatum) seed and nickel(II) chloride and zinc(II) chloride. Application for removal of Nicotinamide and Propanolol. J. Hazard. Mater. 2020, 398, 122903. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Thue, P.S.; Lima, D.R.; Naushad, M.; Lima, E.C.; Albuquerque, Y.R.T.; Dias, S.L.P.; Cunha, M.R.C.; Dotto, G.L.; Brum, I.A.S. High removal of emerging contaminants from wastewater by activated carbons derived from the shell of cashew of Para. Carbon Lett. 2021, 31, 13–28. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Domingues, A.F.N.; Mattietto, R.A.; Oliveira, M. Lipid content in Euterpe olerácea Mart. Embrapa Amazônia Oriental-Research and Development Bulletin. 2017. Available online: https://www.infoteca.cnptia.embrapa.br/infoteca/bitstream/doc/1062268/1/BOLETIMPD115Ainfo.pdf (accessed on 22 September 2022).
- Souza, L.K.C.; Gonçalves, A.A.S.; Queiroz, L.S.; Chaar, J.S.; Rocha Filho, G.N.; da Costa, C.E.F. Utilization of acai stone biomass for the sustainable production of nanoporous carbon for CO2 capture. Sustain. Mater. Technol. 2020, 25, 1–8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thue, P.S.; Lima, E.C.; Sieliechi, J.M.; Saucier, C.; Dias, S.L.P.; Vaghetti, J.C.P.; Rodembusch, F.S.; Pavan, F.A. Effects of first–row transition metals and impregnation ratios on the physicochemical properties of microwave-assisted activated carbons from wood biomass. J. Colloid Interface Sci. 2017, 486, 163–175. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- dos Reis, G.S.; Guy, M.; Mathieu, M.; Jebrane, M.; Lima, E.C.; Thyrel, M.; Dotto, G.L.; Larsson, S.H. A comparative study of chemical treatment by MgCl2, ZnSO4, ZnCl2, and KOH on physicochemical properties and acetaminophen adsorption performance of biobased porous materials from tree bark residues. Colloids Surf. A 2022, 642, 128626. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dos Reis, G.S.; Sampaio, C.H.; Lima, E.C.; Wilhelm, M. Preparation of novel adsorbents based on combinations of polysiloxanes and sewage sludge to remove pharmaceuticals from aqueous solutions. Colloids Surf. A 2016, 497, 304–315. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thommes, M.; Kaneko, K.; Neimark, A.V.; Olivier, J.P.; Rodriguez-Reinoso, F.J.; Rouquerol, K.S.; Sing, W. Physisorption of gases, with special reference to the evaluation of the surface area and pore size distribution (IUPAC Technical Report). Pure Appl. Chem. 2015, 87, 1051–1069. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Tran, H.N.; Tomul, F.; Nguyen, H.T.H.; Nguyen, D.T.; Lima, E.C.; Le, G.T.; Chang, C.T.; Masindi, V.; Woo, S.H. Innovative spherical biochar for pharmaceutical removal from water: Insight into adsorption mechanism. J. Hazard. Mater. 2020, 394, 122255. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, J.; Zhao, L.; Luo, J.; Gong, H.; Zhu, N. A sustainable reuse strategy of converting waste activated sludge into biochar for contaminants removal from water: Modifications, applications, and perspectives. J. Hazard. Mater. 2022, 438, 129437. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qin, Y.; Chai, B.; Wang, C.; Yan, J.; Fan, G.; Song, G. Removal of tetracycline onto KOH-activated biochar derived from rape straw: Affecting factors, mechanisms, and reusability inspection. Colloids Surf. A 2022, 640, 128466. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Smith, B. Infrared Spectral Interpretation: A Systematic Approach; CRC Press: Boca Raton, FL, USA, 1999; 264p, ISBN 0-8493-2463-7. [Google Scholar]
- Guy, M.; Mathieu, M.; Anastopoulos, I.P.; Martínez, M.G.; Rousseau, F.; Dotto, G.L.; de Oliveira, H.P.; Lima, E.C.; Thyrel, M.; Larsson, S.H.; et al. Process Parameters Optimization, Characterization, and Application of KOH-Activated Norway Spruce Bark Graphitic Biochars for Efficient Azo Dye Adsorption. Molecules 2022, 27, 456. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- dos Reis, G.S.; Larsson, S.H.; Thyrel, M.; Pham, T.N.; Lima, E.C.; de Oliveira, H.P.; Dotto, G.L. Preparation and Application of Efficient Biobased Carbon Adsorbents Prepared from Spruce Bark Residues for Efficient Removal of Reactive Dyes and Colors from Synthetic Effluents. Coatings 2021, 11, 772. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lima, E.C.; Dehghani, M.H.; Guleria, A.; Sher, F.; Karri, R.R.; Dotto, G.L.; Tran, H.N. Adsorption: Fundamental aspects and applications of adsorption for effluent treatment. In Green Technologies for the Defluoridation of Water; Dehghani, M.H., Karri, R., Lima, E.C., Eds.; Elsevier: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2021; pp. 41–88. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lima, E.C.; Sher, F.; Guleria, A.; Saeb, M.R.; Anastopoulos, I.; Tran, H.N.; Hosseini-Bandegharaei, A. Is one performing the treatment data of adsorption kinetics correctly? J. Environ. Chem. Eng. 2021, 9, 104813. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lima, E.C.; Hosseini-Bandegharaei, A.; Moreno-Piraján, J.C.; Anastopoulos, I. A critical review of the estimation of the thermodynamic parameters on adsorption equilibria. Wrong use of equilibrium constant in the Van’t Hoof equation for calculation of thermodynamic parameters of adsorption. J. Mol. Liq. 2019, 273, 425–434. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lima, E.C.; Hosseini-Bandegharaei, A.; Anastopoulos, I. Response to “Some remarks on a critical review of the estimation of the thermodynamic parameters on adsorption equilibria. Wrong use of equilibrium constant in the van’t Hoff equation for calculation of thermodynamic parameters of adsorption”. J. Mol. Liq. 2019, 280, 298–300. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lima, D.R.; Gomes, A.A.; Lima, E.C.; Umpierres, C.S.; Thue, P.S.; Panzenhagen, J.C.P.; Dotto, G.L.; El-Chaghaby, G.A.; de Alencar, W.S. Evaluation of efficiency and selectivity in the sorption process assisted by chemometric approaches: Removal of emerging contaminants from water. Spectrochim. Acta Part A Mol. Biomol. Spectrosc. 2019, 218, 366–373. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]







| Parameters | Value |
|---|---|
| Total surface area (m2·g−1) | 1315 |
| Micropore surface area (m2·g−1) | 170 |
| External surface area (m2·g−1) | 1145 |
| Total pore volume (cm3·g−1) | 0.7038 |
| volume of micropores (cm3·g−1) | 0.0720 |
| volume of mesopores (cm3·g−1) | 0.6318 |
| Sample | %C | %H | %N | % Ashes a | %O b |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Raw açaí seed | 43.29 | 5.98 | 1.25 | 1.89 | 47.59 |
| ABC | 72.20 | 3.33 | 1.63 | 0.11 | 22.73 |
| Co (mg L−1) | 350 | 700 |
|---|---|---|
| Avrami fractional-order | ||
| qe (mg·g−1) | 168.7 | 216.8 |
| kAV (min−1) | 0.2450 | 0.1894 |
| nAV | 1.097 | 1.105 |
| t1/2 (min) | 2.922 | 3.790 |
| t0.95 (min) | 11.09 | 14.26 |
| R2adj | 0.9993 | 0.9999 |
| SD (mg·g−1) | 1.402 | 0.8897 |
| BIC | 21.35 | 4.070 |
| Pseudo-first-order | ||
| qe (mg·g−1) | 169.1 | 217.4 |
| k1 (min−1) | 0.2404 | 0.1842 |
| t1/2 (min) | 2.884 | 3.764 |
| t0.95 (min) | 12.46 | 16.27 |
| R2adj | 0.9986 | 0.9988 |
| SD (mg·g−1) | 2.028 | 2.498 |
| BIC | 33.60 | 41.51 |
| Pseudo-second-order | ||
| qe (mg·g−1) | 176.6 | 228.8 |
| k2 (g mg−1 min−1) | 2.038 × 10−3 | 1.148 × 10−3 |
| t1/2 (min) | 2.716 | 3.692 |
| t0.95 (min) | 42.87 | 54.93 |
| R2adj | 0.9750 | 0.9752 |
| SD (mg·g−1) | 8.486 | 11.54 |
| BIC | 87.98 | 99.65 |
| Langmuir | 10 °C | 20 °C | 25 °C | 30 °C | 40 °C | 45 °C |
| Qmax (mg·g−1) | 288.5 | 280.7 | 246.5 | 275.8 | 253.4 | 212.4 |
| KL (L mg−1) | 0.01203 | 0.01471 | 0.02421 | 0.02070 | 0.05768 | 0.1705 |
| R2adj | 0.9739 | 0.9637 | 0.9935 | 0.9999 | 0.9578 | 0.9064 |
| SD (mg·g−1) | 12.04 | 14.80 | 5.973 | 0.9009 | 15.75 | 19.74 |
| BIC | 80.62 | 86.83 | 59.59 | 2.848 | 88.69 | 95.46 |
| Freundlich | 10 °C | 20 °C | 25 °C | 30 °C | 40 °C | 45 °C |
| KF (mg·g−1 (mg L−1)−1/nF) | 42.63 | 45.47 | 47.07 | 49.36 | 82.23 | 102.1 |
| nF | 3.528 | 3.653 | 3.864 | 3.723 | 5.419 | 8.023 |
| R2adj | 0.8947 | 0.8696 | 0.9654 | 0.9442 | 0.9836 | 0.9923 |
| SD (mg·g−1) | 24.17 | 28.05 | 13.82 | 18.58 | 9.831 | 5.658 |
| BIC | 101.5 | 106.0 | 84.77 | 0.9442 | 74.54 | 57.97 |
| Liu | 10 °C | 20 °C | 25 °C | 30 °C | 40 °C | 45 °C |
| Qmax (mg·g−1) | 249.3 | 243.6 | 274.3 | 279.0 | 339.5 | 334.2 |
| Kg (L mg−1) | 0.01403 | 0.01715 | 0.01832 | 0.02024 | 0.02385 | 0.02548 |
| nL | 1.812 | 1.993 | 0.7533 | 0.9658 | 0.4385 | 0.2510 |
| R2adj | 0.9999 | 0.9999 | 0.9999 | 0.9999 | 0.9999 | 0.9999 |
| SD (mg·g−1) | 0.1331 | 0.1661 | 0.2429 | 0.4831 | 0.2712 | 0.5374 |
| BIC | −53.01 | −46.37 | −34.97 | −14.34 | −31.66 | −11.15 |
| Temperature (K) | 283 | 293 | 298 | 303 | 313 | 318 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1.545 × 103 | 1.888 × 103 | 2.018 × 103 | 2.229 × 103 | 2.626 × 103 | 2.806 × 103 | |
| ∆G° (kJ·mol−1) | −17.28 | −18.38 | −18.85 | −19.42 | −20.49 | −20.99 |
| ∆H° (kJ·mol−1) | - | - | 12.74 | - | - | - |
| ∆S° (J·K−1 mol−1) | - | - | 106.1 | - | - | - |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Feitoza, U.d.S.; Thue, P.S.; Lima, E.C.; dos Reis, G.S.; Rabiee, N.; de Alencar, W.S.; Mello, B.L.; Dehmani, Y.; Rinklebe, J.; Dias, S.L.P. Use of Biochar Prepared from the Açaí Seed as Adsorbent for the Uptake of Catechol from Synthetic Effluents. Molecules 2022, 27, 7570. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules27217570
Feitoza UdS, Thue PS, Lima EC, dos Reis GS, Rabiee N, de Alencar WS, Mello BL, Dehmani Y, Rinklebe J, Dias SLP. Use of Biochar Prepared from the Açaí Seed as Adsorbent for the Uptake of Catechol from Synthetic Effluents. Molecules. 2022; 27(21):7570. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules27217570
Chicago/Turabian StyleFeitoza, Uendel dos Santos, Pascal S. Thue, Eder C. Lima, Glaydson S. dos Reis, Navid Rabiee, Wagner S. de Alencar, Beatris L. Mello, Younes Dehmani, Jörg Rinklebe, and Silvio L. P. Dias. 2022. "Use of Biochar Prepared from the Açaí Seed as Adsorbent for the Uptake of Catechol from Synthetic Effluents" Molecules 27, no. 21: 7570. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules27217570
APA StyleFeitoza, U. d. S., Thue, P. S., Lima, E. C., dos Reis, G. S., Rabiee, N., de Alencar, W. S., Mello, B. L., Dehmani, Y., Rinklebe, J., & Dias, S. L. P. (2022). Use of Biochar Prepared from the Açaí Seed as Adsorbent for the Uptake of Catechol from Synthetic Effluents. Molecules, 27(21), 7570. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules27217570