Novel Approaches for the Solid-Phase Synthesis of Dihydroquinazoline-2(1H)-One Derivatives and Biological Evaluation as Potential Anticancer Agents
Abstract
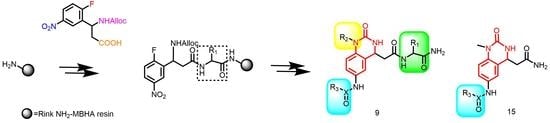
:1. Introduction
2. Results and Discussion
2.1. Chemistry
2.2. Biological Evaluation
2.2.1. In Vitro Anticancer Activity
2.2.2. Antioxidant Activity Measurement with the DPPH• Assay
2.3. Computational Evaluation
2.3.1. Bioinformatics Prediction
2.3.2. ADMET Studies
3. Experimental Section
3.1. Materials and Instruments
3.2. Chemistry
3.2.1. Synthesis of the Tetrafunctional Scaffold
3.2.2. Typical Procedure for the Synthesis of Resin-Bound Quinazolinones
- (a)
- Coupling of an Amino Acid to the Resin
- (b)
- N-Acylation with N-Alloc-3-amino-3-(2-fluoro-5-nitrophenyl)propionic acid
- (c)
- Nucleophilic Substitution of the Fluoro Group
- (d)
- Removal of the Alloc Protective Base
- (e)
- Cyclization using Carbonyldiimidazole
- (f)
- Reduction of the Aromatic Nitro Group
- (g)
- Coupling with Carboxylic Acid/Sulfonyl Chloride
- N-Fmoc-3-amino-3-(2-fluoro-5-nitrophenyl)propionic acid 3’: white solid; yield: 68.2%; mp 200.8–201.2 °C; 1H NMR (600 MHz, DMSO) δ 8.36 (dd, J = 6.1, 2.8 Hz, 1H), 8.22 (dd, J = 8.7, 3.9 Hz, 2H), 7.87 (t, J = 7.2 Hz, 2H), 7.65 (dd, J = 15.3, 7.5 Hz, 2H), 7.49 (t, J = 9.1 Hz, 1H), 7.39 (dt, J = 11.9, 7.5 Hz, 2H), 7.27 (dt, J = 7.2, 3.6 Hz, 2H), 5.27 (td, J = 8.6, 6.1 Hz, 1H), 4.34–4.28 (m, 2H), 4.20 (t, J = 6.8 Hz, 1H), 2.74 (ddd, J = 22.1, 16.2, 7.5 Hz, 2H); 13C NMR (151 MHz, DMSO) δ 171.60, 164.11, 162.41 (C-F, d, 1JC-F = 255.86 Hz), 155.75, 144.63, 144.30, 143.98, 141.19, 141.16, 132.24, 132.13 (C-F, d, 2JC-F = 16.5 Hz), 128.12, 128.06 (C-F, d, 3JC-F = 8.68 Hz), 127.48, 127.45, 125.71, 125.64 (C-F, d, 3JC-F = 10.61 Hz), 125.54, 125.52, 124.36, 124.32, 120.63, 120.57, 117.61, 117.44 (C-F, d, 2JC-F = 24.60 Hz), 65.94, 47.09, 45.6; MS (ESI) (m/z): 450.12, [M + H+]: 451.10.
- 3-{4-{2-[(1-amino-3-hydroxy-1-oxopropan-2-yl)amino]-2-oxoethyl}-6-nitro-2-oxo-3,4-dihydroquinazolin-1(2H)-yl}propan-1-aminium 2,2,2-trifluoroacetate (CA1-6)·TFA: yellow solid; yield 93%; 1H NMR (600 MHz, DMSO) δ 8.15–8.10 (m, 1H), 8.07 (dd, J = 25.3, 2.5 Hz, 1H), 7.96 (d, J = 8.0 Hz, 1H), 7.86 (s, 3H), 7.52 (dd, J = 53.4, 2.7 Hz, 1H), 7.34–7.19 (m, 2H), 7.08 (d, J = 9.3 Hz, 1H), 4.89 (dtd, J = 25.9, 6.5, 2.8 Hz, 1H), 4.19 (td, J = 10.0, 5.1 Hz, 1H), 3.97–3.90 (m, 2H), 3.56–3.39 (m, 2H), 2.90 (d, J = 5.8 Hz, 2H), 2.70–2.53 (m, 2H), 1.97–1.75 (m, 2H); 13C NMR (151 MHz, DMSO) δ 172.39 (d, J = 6.2 Hz), 169.27, 158.74 (C-F, q, 2JC-F = 31.6 Hz), 153.15, 143.77, 141.54, 124.69, 124.22, 122.70, 117.46 (C-F, q, 1JC-F = 299.3 Hz), 114.01, 62.08, 55.25, 50.07, 44.45, 37.07, 25.46; MS (ESI) (m/z): 394. 16, [M + H+]: 395.15.
- 4-{2-[(1-amino-3-hydroxy-1-oxopropan-2-yl)amino]-2-oxoethyl}-1-(3-ammoniopropyl)-2-oxo-1,2,3,4-tetrahydroquinazolin-6-aminium 2,2,2-trifluoroacetate (CA1-7)·TFA: brown solid; yield 76%; 1H NMR (600 MHz, DMSO) δ 7.99 (dd, J = 20.8, 7.9 Hz, 1H), 7.88 (s, 1H), 7.33 (d, J = 14.9 Hz, 1H), 7.13 (ddd, J = 30.6, 18.0, 5.7 Hz, 2H), 7.05 (d, J = 1.8 Hz, 1H), 4.76 (dtd, J = 19.5, 6.6, 2.7 Hz, 1H), 4.23 (dd, J = 12.3, 5.5 Hz, 1H), 3.93–3.74 (m, 1H), 3.56 (dddd, J = 31.8, 26.5, 10.2, 5.4 Hz, 1H), 2.94–2.83 (m, 1H), 2.55 (td, J = 14.8, 7.5 Hz, 1H), 1.93–1.75 (m, 1H); 13C NMR (151 MHz, DMSO) δ 172.52, 169.60, 159.08, 158.86 (C-F, q, 2JC-F = 32.4 Hz), 154.02, 135.78, 125.03, 121.84, 120.15, 119.92, 118.23, 116.25 (C-F, q, 1JC-F = 299.3 Hz), 114.55, 62.02, 55.46, 50.23, 44.42, 39.05, 37.13, 25.48; MS (ESI) (m/z): 364.19, [M + H+]: 365.20.
- 3-{4-{2-[(1-amino-3-hydroxy-1-oxopropan-2-yl)amino]-2-oxoethyl}-6-(isonicotinamido)-2-oxo-3,4-dihydroquinazolin-1(2H)-yl}propan-1-aminium 2,2,2-trifluoroacetate (CA1-a)·TFA: orange solid; yield 86%; 1H NMR (600 MHz, DMSO) δ 10.53 (d, J = 19.5 Hz, 1H), 8.85 (s, 2H), 8.06–7.93 (m, 3H), 7.79 (s, 3H), 7.68 (ddd, J = 18.6, 8.8, 2.3 Hz, 1H), 7.62 (s, 1H), 7.32 (d, J = 14.5 Hz, 1H), 7.18–7.11 (m, 1H), 7.11–7.00 (m, 2H), 4.80 (dd, J = 9.3, 3.8 Hz, 1H), 4.26 (dt, J = 7.8, 5.4 Hz, 1H), 3.94–3.84 (m, 2H), 3.54 (ddd, J = 15.9, 10.9, 5.5 Hz, 2H), 2.89 (dd, J = 12.5, 6.2 Hz, 2H), 2.73–2.52 (m, 2H), 1.88 (ddt, J = 19.1, 13.6, 6.7 Hz, 2H); 13C NMR (151 MHz, DMSO) δ 172.58, 169.80, 163.55, 158.94 (C-F, q, 2JC-F = 32.4 Hz), 154.15, 149.58, 143.49, 134.05, 133.18, 124.04, 122.58, 120.97, 119.13 (C-F, q, 1JC-F = 247.39 Hz), 113.79, 62.07, 55.54, 50.69, 44.73, 38.89, 37.19, 25.65; MS (ESI) (m/z): 469.21, [M + H+]: 470.15.
- 3-{4-{2-[(1-amino-3-hydroxy-1-oxopropan-2-yl)amino]-2-oxoethyl}-6-benzamido-2-oxo-3,4-dihydroquinazolin-1(2H)-yl}propan-1-aminium 2,2,2-trifluoroacetate (CA1-b)·TFA: yellow solid; yield 85%; 1H NMR (600 MHz, DMSO) δ 10.19 (d, J = 12.5 Hz, 1H), 8.04–7.97 (m, 1H), 7.97–7.92 (m, 2H), 7.74 (s, 3H), 7.70–7.65 (m, 1H), 7.65–7.62 (m, 1H), 7.60 (t, J = 7.3 Hz, 1H), 7.54 (td, J = 7.6, 1.7 Hz, 2H), 7.32 (d, J = 21.9 Hz, 1H), 7.10 (d, J = 10.7 Hz, 1H), 7.08–6.96 (m, 2H), 4.81–4.73 (m, 1H), 4.26 (dq, J = 7.7, 5.4 Hz, 1H), 3.88 (dtt, J = 21.2, 14.3, 7.0 Hz, 2H), 2.89 (dd, J = 12.6, 6.5 Hz, 2H), 2.65–2.52 (m, 2H), 1.94–1.82 (m, 2H); 13C NMR (151 MHz, DMSO) δ 172.52, 169.79, 165.64, 158.62, 158.39 (C-F, q, 2JC-F = 34.82 Hz), 154.18, 135.25, 133.90, 133.51, 132.00, 128.88, 128.02, 123.94, 120.83, 119.01, 113.69 (C-F, q, 1JC-F = 275.78 Hz), 62.11, 55.48, 50.67, 44.71, 38.87, 37.22, 25.67; MS (ESI) (m/z): 468.21, [M + H+]: 469.20.
- 3-{4-{2-[(1-amino-3-hydroxy-1-oxopropan-2-yl)amino]-2-oxoethyl}-6-(4-methylbenzamido)-2-oxo-3,4-dihydroquinazolin-1(2H)-yl}propan-1-aminium 2,2,2-trifluoroacetate (CA1-c)·TFA: white solid; yield 82%; 1H NMR (600 MHz, DMSO) δ 10.10 (d, J = 11.8 Hz, 1H), 7.99 (dd, J = 40.7, 7.9 Hz, 1H), 7.88 (dd, J = 10.2, 8.2 Hz, 2H), 7.73 (s, 3H), 7.67 (ddd, J = 14.4, 8.8, 2.1 Hz, 1H), 7.62 (s, 1H), 7.37–7.28 (m, 3H), 7.10 (d, J = 9.6 Hz, 1H), 7.07–6.95 (m, 2H), 4.81–4.72 (m, 1H), 4.26 (dq, J = 7.7, 5.4 Hz, 1H), 3.88 (pd, J = 14.2, 6.7 Hz, 2H), 3.59 (dd, J = 10.6, 5.5 Hz, 2H), 2.88 (dd, J = 12.6, 6.3 Hz, 2H), 2.63–2.52 (m, 2H), 2.39 (s, 3H), 1.93–1.83 (m, 2H); 13C NMR (151 MHz, DMSO) δ 172.56, 169.88, 169.73 (C-F, q, 2JC-F = 22.39 Hz), 165.43, 154.17, 142.01, 133.98, 133.41, 132.40, 132.34, 129.40, 128.05, 120.81, 119.00 (C-F, q, 1JC-F = 279.55 Hz), 118.32, 113.66, 62.09, 55.49, 50.67, 44.70, 38.82, 37.22, 25.67, 21.47; MS (ESI) (m/z): 482.23, [M + H+]: 483.20.
- 3-{4-{2-[(1-amino-3-hydroxy-1-oxopropan-2-yl)amino]-2-oxoethyl}-6-(4-fluorobenzamido)-2-oxo-3,4-dihydroquinazolin-1(2H)-yl}propan-1-aminium 2,2,2-trifluoroacetate (CA1-d)·TFA: yellow solid; yield 79%; 1H NMR (600 MHz, DMSO) δ 10.20 (d, J = 16.2 Hz, 1H), 8.11–7.89 (m, 3H), 7.73 (s, 3H), 7.66 (ddd, J = 17.0, 8.9, 2.2 Hz, 1H), 7.61 (s, 1H), 7.43–7.35 (m, 2H), 7.32 (d, J = 25.3 Hz, 1H), 7.10 (d, J = 13.3 Hz, 1H), 7.08–6.96 (m, 2H), 4.83–4.71 (m, 1H), 4.29–4.22 (m, 1H), 3.95–3.83 (m, 2H), 2.89 (dd, J = 12.5, 6.3 Hz, 2H), 2.64–2.52 (m, 2H), 1.88 (ddd, J = 21.5, 10.8, 5.5 Hz, 2H); 13C NMR (151 MHz, DMSO) δ 172.57, 169.77, 164.55, 163.69 (C-F, q, 1JC-F = 249.32 Hz), 158.38 (C-F, q, 2JC-F = 31.83 Hz), 154.15, 133.78, 133.56, 131.69, 130.75, 123.95, 120.83, 119.02 (C-F, q, 1JC-F = 274.60 Hz), 115.88, 115.74, 113.70, 62.10, 55.49, 50.66, 44.65, 38.84, 37.19, 25.66; MS (ESI) (m/z): 486.20, [M + H+]: 487.20.
- 3-{4-{2-[(1-amino-3-hydroxy-1-oxopropan-2-yl)amino]-2-oxoethyl}-6-(nicotinamido)-2-oxo-3,4-dihydroquinazolin-1(2H)-yl}propan-1-aminium 2,2,2-trifluoroacetate (CA1-e)·TFA: yellow solid; yield 84%; 1H NMR (600 MHz, DMSO) δ 10.45 (d, J = 15.6 Hz, 1H), 9.15 (d, J = 8.4 Hz, 1H), 8.80 (d, J = 4.6 Hz, 1H), 8.38 (ddd, J = 9.7, 8.0, 4.0 Hz, 1H), 7.99 (dd, J = 39.8, 7.9 Hz, 1H), 7.79 (s, 3H), 7.67 (dd, J = 11.7, 3.1 Hz, 1H), 7.65–7.63 (m, 1H), 7.62 (dd, J = 6.4, 2.2 Hz, 1H), 7.31 (s, 1H), 7.10 (dd, J = 12.0, 9.7 Hz, 2H), 7.07–6.99 (m, 1H), 4.80–4.74 (m, 1H), 4.27–4.25 (m, 1H), 3.93–3.82 (m, 2H), 3.62–3.48 (m, 2H), 2.89 (dd, J = 12.6, 6.3 Hz, 2H), 2.64–2.52 (m, 2H), 1.94–1.83 (m, 2H); 13C NMR (151 MHz, DMSO) δ 172.58, 169.75, 163.82, 158.67 (C-F, q, 2JC-F = 35.9 Hz), 154.17, 151.69, 148.35, 136.83, 133.83, 133.47, 131.23, 124.40, 124.02, 120.84, 119.02, 117.32, 115.38 (C-F, q, 1JC-F = 283.7 Hz), 113.77, 62.06, 55.47, 50.65, 44.65, 38.88, 37.20, 25.66; MS (ESI) (m/z): 469.21, [M + H+]: 470.20.
- 3-{4-{2-[(1-amino-3-hydroxy-1-oxopropan-2-yl)amino]-2-oxoethyl}-2-oxo-6-(picolinamido)-3,4-dihydroquinazolin-1(2H)-yl}propan-1-aminium 2,2,2-trifluoroacetate (CA1-f)·TFA: orange solid; yield 76%; 1H NMR (600 MHz, DMSO) δ 10.67–10.53 (m, 1H), 8.79–8.69 (m, 1H), 8.15 (d, J = 7.8 Hz, 1H), 8.07 (t, J = 7.7 Hz, 1H), 7.99 (dd, J = 17.4, 7.9 Hz, 1H), 7.78 (dd, J = 7.1, 4.4 Hz, 5H), 7.68 (dd, J = 6.6, 4.9 Hz, 1H), 7.29 (s, 1H), 7.08 (d, J = 7.3 Hz, 1H), 7.01 (dd, J = 52.7, 2.0 Hz, 2H), 4.84–4.74 (m, 1H), 4.33–4.20 (m, 1H), 3.97–3.80 (m, 2H), 3.65–3.49 (m, 2H), 2.89 (dt, J = 12.7, 6.3 Hz, 2H), 2.65–2.51 (m, 2H), 1.97–1.78 (m, 2H); 13C NMR (151 MHz, DMSO) δ 172.54, 169.82, 162.62, 158.88 (C-F, q, 2JC-F = 34.93 Hz), 154.11, 150.32, 148.88, 138.61, 133.77, 133.07, 127.33, 123.94, 122.71, 120.74, 118.90, 117.17 (C-F, q, 1JC-F = 71.71 Hz), 113.78, 62.08, 55.48, 50.68 (d, J = 12.5 Hz), 44.58, 38.88, 37.20, 25.66; MS (ESI) (m/z): 469.21, [M + H+]: 470.15.
- 3-{4-{2-[(1-amino-3-hydroxy-1-oxopropan-2-yl)amino]-2-oxoethyl}-2-oxo-6-(2-phenoxyacetamido)-3,4-dihydroquinazolin-1(2H)-yl}propan-1-aminium 2,2,2-trifluoroacetate (CA1-g)·TFA: white solid; yield 85%; 1H NMR (600 MHz, DMSO) δ 10.03 (d, J = 14.1 Hz, 1H), 7.98 (dd, J = 37.5, 7.9 Hz, 1H), 7.77 (s, 3H), 7.58–7.51 (m, 1H), 7.4 (dd, J = 14.2, 2.0 Hz, 1H), 7.32 (t, J = 7.8 Hz, 2H), 7.30 (d, J = 3.8 Hz, 1H), 7.10 (s,1H), 7.07–6.95 (m, 5H), 4.87 (d, J = 34.2 Hz, 1H), 4.78–4.69 (m, 1H), 4.60 (d, J = 4.2 Hz, 2H), 4.24 (dq, J = 10.4, 5.2 Hz, 1H), 3.93–3.79 (m, 2H), 3.55 (d, J = 42.7 Hz, 2H), 2.87 (d, J = 5.4 Hz, 2H), 2.62–2.51 (m, 2H), 1.86 (dq, J = 12.8, 6.9 Hz, 2H); 13C NMR (151 MHz, DMSO) δ 172.63, 172.54, 169.73, 163.55, 158.83 (C-F, q, 2JC-F = 30.59 Hz), 154.12, 149.83, 149.58, 143.49, 134.05, 133.18, 124.04, 122.58, 120.97, 119.13, 115.48 (C-F, q, 1JC-F = 255.65 Hz), 113.79, 62.07, 55.48, 51.80, 50.63, 44.73, 38.92, 37.19, 25.65; MS (ESI) (m/z): 498.22, [M + H+]: 499.20.
- 3-{4-{2-[(1-amino-3-hydroxy-1-oxopropan-2-yl)amino]-2-oxoethyl}-2-oxo-6-[3-(pyridin-3-yl)propanamido]-3,4-dihydroquinazolin-1(2H)-yl}propan-1-aminium 2,2,2-trifluoroacetate (CA1-h)·TFA: yellow solid; yield 92%; 1H NMR (600 MHz, DMSO) δ 9.96 (d, J = 15.4 Hz, 1H), 8.78 (s, 1H), 8.70 (s, 1H), 8.27 (d, J = 7.6 Hz, 1H), 7.98 (dd, J = 38.9, 7.9 Hz, 1H), 7.85 (s, 3H), 7.83–7.80 (m, 1H), 7.42 (s, 1H), 7.40 (dd, J = 5.0, 2.6 Hz, 1H), 7.30 (d, J = 6.5 Hz, 1H), 7.11 (d, J = 7.3 Hz, 1H), 7.06–6.92 (m, 2H), 4.83–4.65 (m, 1H), 4.24 (dtd, J = 7.8, 5.3, 2.4 Hz, 1H), 3.89–3.79 (m, 2H), 3.64–3.44 (m, 2H), 3.06 (t, J = 7.1 Hz, 2H), 2.87 (dd, J = 12.3, 6.2 Hz, 2H), 2.74 (d, J = 7.2 Hz, 2H), 2.65–2.51 (m, 2H), 1.93–1.78 (m, 2H); 13C NMR (151 MHz, DMSO) δ 172.55, 169.86, 169.68, 159.02, 158.80 (C-F, q, 2JC-F = 33.5 Hz), 154.18, 144.44, 143.33, 142.52, 140.36, 133.79, 133.09, 130.88, 126.24, 124.05, 119.56, 118.02, 117.71, 116.06 (C-F, q, 1JC-F = 294.9 Hz), 113.78, 62.06, 55.47, 50.58, 44.56, 38.84, 37.14, 36.86, 28.04, 25.63; MS (ESI) (m/z): 497.24, [M + H+]: 498.25.
- 3-{4-{2-[(1-amino-3-hydroxy-1-oxopropan-2-yl)amino]-2-oxoethyl}-2-oxo-6-[2-(thiophen-2-yl)acetamido]-3,4-dihydroquinazolin-1(2H)-yl}propan-1-aminium 2,2,2-trifluoroacetate (CA1-i)·TFA: pale brown solid; yield 90%; 1H NMR (600 MHz, DMSO) δ 10.18 (d, J = 15.2 Hz, 1H), 7.99 (dd, J = 38.4, 7.9 Hz, 1H), 7.8 (s, 3H), 7.45 (dd, J = 23.6, 5.1 Hz, 2H), 7.41–7.35 (m, 1H), 7.30 (d, J = 4.2 Hz, 1H), 7.10 (d, J = 9.6 Hz, 1H), 7.08–6.90 (m, 4H), 4.77–4.67 (m, 1H), 4.28–4.21 (m, 1H), 3.86 (t, J = 9.1 Hz, 4H), 3.61–3.48 (m, 2H), 2.93–2.82 (m, 2H), 2.62–2.51 (m, 2H), 1.86 (ddd, J = 22.5, 10.5, 4.8 Hz, 2H); 13C NMR (151 MHz, DMSO) δ 172.56, 169.79, 168.19, 158.70 (C-F, q, 2JC-F = 32.3 Hz), 154.15, 137.64, 133.80, 133.27, 129.82, 127.11, 126.77, 125.49, 124.12, 119.62, 117.82, 115.69 (C-F, q, 1JC-F = 321.4 Hz), 113.82, 62.06, 55.46, 50.57, 44.53, 38.83, 37.86, 37.16, 25.63; MS (ESI) (m/z): 488.18, [M + H+]: 489.20.
- 3-{4-{2-[(1-amino-3-hydroxy-1-oxopropan-2-yl)amino]-2-oxoethyl}-6-[(2-methoxyphenyl)sulfonamido]-2-oxo-3,4-dihydroquinazolin-1(2H)-yl}propan-1-aminium 2,2,2-trifluoroacetate (CA1-j)·TFA: yellow solid; yield 71%; 1H NMR (600 MHz, DMSO) δ 9.73 (d, J = 35.7 Hz, 1H), 7.96 (dd, J = 10.1, 8.1 Hz, 1H), 7.75 (s, 3H), 7.72–7.68 (m, 1H), 7.59–7.54 (m, 1H), 7.33 (d, J = 24.0 Hz, 1H), 7.18 (d, J = 8.4 Hz, 1H), 7.12 (d, J = 22.3 Hz, 1H), 7.02 (td, J = 7.5, 2.7 Hz, 1H), 6.99–6.90 (m, 3H), 6.87 (d, J = 8.1 Hz, 1H), 4.67–4.59 (m, 1H), 4.24 (dt, J = 7.7, 5.3 Hz, 1H), 3.90 (s, 3H), 3.81–3.71 (m, 2H), 3.63–3.53 (m, 2H), 2.82 (d, J = 6.0 Hz, 2H), 2.41 (tt, J = 14.6, 7.2 Hz, 2H), 1.78 (ddd, J = 19.9, 11.7, 4.8 Hz, 2H); 13C NMR (151 MHz, DMSO) δ 172.53, 169.57, 158.81 (C-F, q, 2JC-F = 33.8 Hz), 154.15, 153.99, 135.47, 134.17, 132.17, 130.62, 126.85, 124.46, 120.98, 120.55, 119.43, 119.62, 116.85 (C-F, q, 1JC-F = 294.6 Hz), 113.24, 62.11, 56.56, 55.45, 50.29, 44.42, 38.88, 37.14, 25.53; MS (ESI) (m/z): 534.19, [M + H+]: 535.20.
- 5-amino-4-{2-{1-isopentyl-2-oxo-6-[3-(pyridin-3-yl)propanamido]-1,2,3,4-tetrahydroquinazolin-4-yl}acetamido}-5-oxopentan-1-aminium 2,2,2-trifluoroacetate (CA3)·TFA: light brown solid; yield 74%; 1H NMR (600 MHz, DMSO) δ 9.95 (d, J = 18.9 Hz, 1H), 8.73 (d, J = 45.9 Hz, 1H), 8.25 (dd, J = 12.5, 8.1 Hz, 1H), 8.13 (dd, J = 34.3, 8.2 Hz, 1H), 7.80 (dd, J = 13.1, 6.9 Hz, 1H), 7.47–7.36 (m, 1H), 7.12 (d, J = 4.7 Hz, 1H), 6.92–6.85 (m, 1H), 4.70–4.59 (m, 1H), 4.30–4.18 (m, 1H), 3.91–3.67 (m, 1H), 3.10–3.02 (m, 1H), 2.82–2.69 (m, 2H), 2.45 (ddd, J = 14.5, 7.7, 4.1 Hz, 1H), 1.75–1.41 (m, 4H), 0.93 (d, J = 6.6 Hz, 3H); 13C NMR (151 MHz, DMSO) δ 173.69, 169.78, 158.86 (C-F, q, 2JC-F = 31.9 Hz), 153.95, 144.62, 143.24, 142.62, 133.65, 133.47, 133.29, 126.19, 124.50, 124.30, 119.64, 117.59, 116.05, (C-F, q, 1JC-F = 292.8 Hz), 115.69, 113.79, 52.16, 51.82, 50.60, 44.28, 38.96, 36.87, 36.04, 29.27, 28.04, 26.16, 23.89, 23.04, 22.88; MS (ESI) (m/z): 537.31, [M + H+]: 538.30.
- 2-{2-[1-benzyl-2-oxo-6-(2-phenoxyacetamido)-1,2,3,4-tetrahydroquinazolin-4-yl]acetamido}-2-methylpropanamide (CA4): white solid; yield 75%; 1H NMR (600 MHz, DMSO) δ 10.07 (d, J = 112.5 Hz, 1H), 7.95 (d, J = 13.3 Hz, 1H), 7.48 (d, J = 2.0 Hz, 1H), 7.39–7.26 (m, 5H), 7.23 (dd, J = 15.1, 7.5 Hz, 2H), 7.18–7.04 (m, 2H), 7.02–6.68 (m, 6H), 5.05 (d, J = 11.9 Hz, 1H), 4.80–4.62 (m, 3H), 4.52–4.45 (m, 1H), 2.53 (d, J = 6.6 Hz, 2H), 1.34–1.24 (m, 6H); 13C NMR (151 MHz, DMSO) δ 176.74, 169.17, 166.70, 158.24, 154.24, 138.43, 133.85, 132.90, 129.96, 128.94, 127.15, 126.81, 124.02, 121.63, 120.05, 118.36, 115.08, 114.41, 67.45, 56.41, 50.70, 45.09, 25.92, 25.40; MS (ESI) (m/z): 529.23, [M + H+]: 530.25.
- 4-{2-{1-(3-ammoniopropyl)-2-oxo-6-[2-(thiophen-2-yl)acetamido]-1,2,3,4-tetrahydroquinazolin-4-yl}acetamido}-4-carbamoylpiperidin-1-aminium 2,2,2-trifluoroacetate (CA5)·TFA: yellowish white solid; yield 84%; 1H NMR (600 MHz, DMSO) δ 10.18 (s, 1H), 8.57 (d, J = 8.9 Hz, 1H), 8.35 (d, J = 9.0 Hz, 1H), 8.14 (s, 1H), 7.79 (s, 3H), 7.49–7.42 (m, 2H), 7.39 (dd, J = 4.4, 2.0 Hz, 1H), 7.23 (s, 1H), 7.06 (d, J = 2.6 Hz, 1H), 7.02–6.97 (m, 4H), 4.69 (td, J = 6.6, 2.7 Hz, 1H), 3.94–3.88 (m, 2H), 3.85 (s, 2H), 3.13–2.84 (m, 6H), 2.64–2.54 (m, 2H), 2.13–2.06 (m, 2H), 1.97 (d, J = 10.6 Hz, 2H), 1.87 (ddd, J = 23.3, 14.5, 7.2 Hz, 2H); 13C NMR (151 MHz, DMSO) δ 174.92, 169.92, 168.24, 158.58 (C-F, q, 2JC-F = 32.3Hz), 154.21, 137.63, 136.59, 133.79, 133.33, 127.15, 126.78, 125.54, 124.00, 119.58, 117.55 (C-F, q, 1JC-F = 305.48 Hz), 113.91, 55.89, 50.19, 44.39, 39.11, 37.87, 37.17, 29.17, 28.02, 25.61; MS (ESI) (m/z): 527.23, [M + H+]: 528.20.
- N-[4-(2-amino-2-oxoethyl)-1-methyl-2-oxo-1,2,3,4-tetrahydroquinazolin-6-yl]nicotinamide (CA6-a): yellow solid; yield 74%; 1H NMR (600 MHz, DMSO) δ 10.48 (s, 1H), 9.17 (s, 1H), 8.82 (s, 1H), 8.42 (d, J = 7.9 Hz, 1H), 7.68 (dd, J = 8.5, 1.8 Hz, 2H), 7.59 (s, 1H), 7.35 (s, 1H), 7.03 (s, 1H), 7.00–6.90 (m, 2H), 4.68 (t, J = 5.4 Hz, 1H), 3.19 (s, 3H), 2.44 (dd, J = 6.8, 2.1 Hz, 2H); 13C NMR (151 MHz, DMSO) δ 171.53, 163.58, 154.49, 151.18, 148.20, 147.99, 137.31, 135.56, 133.25, 124.59, 124.42, 120.77, 118.68, 113.56, 50.20, 43.85, 29.64; MS (ESI) (m/z): 339.13, [M + H+]: 340.15.
- N-[4-(2-amino-2-oxoethyl)-1-methyl-2-oxo-1,2,3,4-tetrahydroquinazolin-6-yl]-2-phenoxyacetamide (CA6-b): white solid; yield 78%; 1H NMR (600 MHz, DMSO) δ 10.04 (s, 1H), 7.57 (dd, J = 8.8, 2.2 Hz, 1H), 7.43 (d, J = 2.1 Hz, 1H), 7.34–7.30 (m, 3H), 7.02–6.97 (m, 4H), 6.95–6.90 (m, 2H), 4.68–4.63 (m, 3H), 3.16 (s, 3H), 2.41 (dd, J = 6.8, 3.8 Hz, 2H); 13C NMR (151 MHz, DMSO) δ 171.50, 166.66, 158.30, 154.47, 135.24, 132.93, 129.98, 124.43, 121.63, 120.10, 118.04, 115.14, 113.55, 67.54, 50.15, 43.77, 29.61; MS (ESI) (m/z): 368.15, [M + H+]: 369.15.
- 2-{6-[(2-methoxyphenyl)sulfonamido]-1-methyl-2-oxo-1,2,3,4-tetrahydroquinazolin-4-yl}acetamide (CA7-a): white solid; yield 84%; 1H NMR (600 MHz, DMSO) δ 9.71 (s, 1H), 7.68 (dd, J = 7.8, 1.6 Hz, 1H), 7.56–7.52 (m, 1H), 7.27 (s, 1H), 7.17 (d, J = 8.3 Hz, 1H), 6.99 (t, J = 7.6 Hz, 1H), 6.95 (dd, J = 8.7, 2.4 Hz, 2H), 6.92 (d, J = 2.3 Hz, 1H), 6.84 (s, 1H), 6.78 (d, J = 8.8 Hz, 1H), 4.54 (td, J = 6.8, 2.9 Hz, 1H), 3.92 (s, 3H), 3.07 (s, 3H), 2.28 (ddd, J = 50.0, 14.7, 6.9 Hz, 2H); 13C NMR (151 MHz, DMSO) δ 171.24, 156.76, 154.36, 135.83, 135.38, 131.95, 130.74, 126.64, 124.74, 121.05, 120.49, 119.14, 113.80, 113.17, 56.52, 49.87, 43.61, 29.55; MS (ESI) (m/z): 404.12, [M + H+]: 405.10.
- 2-{6-[(2-fluorophenyl)sulfonamido]-3-[(2-fluorophenyl)sulfonyl]-1-methyl-2-oxo-1,2,3,4-tetrahydroquinazolin-4-yl}acetamide (CA7-b’): white solid; yield 76%; 1H NMR (600 MHz, DMSO) δ 7.93–7.78 (m, 4H), 7.54 (t, J = 8.2 Hz, 2H), 7.47 (dt, J = 12.2, 7.7 Hz, 2H), 7.35 (s, 1H), 7.20 (d, J = 3.0 Hz, 1H), 7.10 (dd, J = 8.7, 2.1 Hz, 1H), 7.01 (dd, J = 7.6, 5.5 Hz, 2H), 6.94 (s, 1H), 4.65 (td, J = 6.8, 3.2 Hz, 1H), 3.18 (s, 3H), 2.32 (ddd, J = 21.4, 15.0, 6.9 Hz, 2H); 13C NMR (151 MHz, DMSO) δ 171.11, 159.59, 157.89 (C-F, q, 1JC-F = 254.62 Hz), 153.93, 141.03, 138.46, 132.04, 131.89, 129.12, 125.74, 125.64, 124.99, 118.18, 114.20, 49.48, 43.65, 29.86; MS (ESI) (m/z): 550.08, [M + H+]: 551.10.
3.3. Biological Evaluation
3.3.1. In Vitro Anticancer Activity
3.3.2. DPPH• Assay for Measurement of Antiradical Activity
3.4. Computational Evaluation
3.4.1. Bioinformatics Prediction
- (a)
- Prediction of disease targets
- (b)
- Protein interaction (PPI) network analysis
- (c)
- GO annotation and KEGG pathway enrichment analysis
- (d)
- Molecular docking
3.4.2. ADMET Studies
4. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
Sample Availability
References
- Bray, F.; Ferlay, J.; Soerjomataram, I.; Siegel, R.L.; Torre, L.A.; Jemal, A. Global cancer statistics 2018: GLOBOCAN estimates of incidence and mortality worldwide for 36 cancers in 185 countries. CA-Cancer J. Clin. 2018, 68, 394–424. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Firuzi, O.; Javidnia, K.; Mansourabadi, E.; Saso, L.; Mehdipour, A.R.; Miri, R. Reversal of multidrug resistance in cancer cells by novel asymmetrical 1,4-dihydropyridines. Arch. Pharm. Res. 2013, 36, 1392–1402. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bonnet, M.; Hong, C.R.; Wong, W.W.; Liew, L.P.; Shome, A.; Wang, J.L.; Gu, Y.C.; Stevenson, R.J.; Qi, W.; Anderson, R.F.; et al. Next-Generation Hypoxic Cell Radiosensitizers: Nitroimidazole Alkylsulfonamides. J. Med. Chem. 2018, 61, 1241–1254. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Teoh, D.; Ayeni, T.A.; Rubatt, J.M.; Adams, D.J.; Grace, L.; Starr, M.D.; Barry, W.T.; Berchuck, A.; Murphy, S.K.; Secord, A.A. Dasatinib (BMS-35482) has synergistic activity with paclitaxel and carboplatin in ovarian cancer cells. Gynecol. Oncol. 2011, 121, 187–192. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Farghaly, A.R. Synthesis of some new indole derivatives containing pyrazoles with potential antitumor activity. Arkivoc 2010, 2010, 177–187. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Dohle, W.; Jourdan, F.L.; Menchon, G.; Prota, A.E.; Foster, P.A.; Mannion, P.; Hamel, E.; Thomas, M.P.; Kasprzyk, P.G.; Ferrandis, E.; et al. Quinazolinone-Based Anticancer Agents: Synthesis, Antiproliferative SAR, Antitubulin Activity, and Tubulin Co-crystal Structure. J. Med. Chem. 2018, 61, 1031–1044. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Farooq, S.; Mazhar, A.; Ihsan Ul, H.; Ullah, N. One-pot multicomponent synthesis of novel 3, 4-dihydro-3-methyl-2(1H)-quinazolinone derivatives and their biological evaluation as potential antioxidants, enzyme inhibitors, antimicrobials, cytotoxic and anti-inflammatory agents. Arab. J. Chem. 2020, 13, 9145–9165. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Morales, G.A.; Corbett, J.W.; DeGrado, W.F. Solid-phase synthesis of benzopiperazinones. J. Org. Chem. 1998, 63, 1172–1177. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Camacho, M.E.; Chayah, M.; García, M.E.; Fernández-Sáez, N.; Arias, F.; Gallo, M.A.; Carrión, M.D. Quinazolinones, Quinazolinthiones, and Quinazolinimines as Nitric Oxide Synthase Inhibitors: Synthetic Study and Biological Evaluation. Arch. Pharm. 2016, 349, 638–650. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Le, Y.; Gan, Y.; Fu, Y.; Liu, J.; Li, W.; Zou, X.; Zhou, Z.; Wang, Z.; Ouyang, G.; Yan, L. Design, synthesis and in vitro biological evaluation of quinazolinone derivatives as EGFR inhibitors for antitumor treatment. J. Enzym. Inhib. Med. Chem. 2020, 35, 555–564. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Da Silva, G.M.S.; Sant’Anna, C.M.R.; Barreiro, E.J. A novel 3D-QSAR comparative molecular field analysis (CoMFA) model of imidazole and quinazolinone functionalized p38 MAP kinase inhibitors. Bioorgan. Med. Chem. 2004, 12, 3159–3166. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stelmach, J.E.; Liu, L.P.; Patela, S.B.; Pivnichny, J.V.; Scapin, G.; Singh, S.; Hop, C.; Wang, Z.; Strauss, J.R.; Cameron, P.M.; et al. Design and synthesis of potent, orally bioavailable dihydroquinazolinone inhibitors of p38 MAP kinase. Bioorg. Med. Chem. Lett. 2003, 13, 277–280. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fish, P.V.; Filippakopoulos, P.; Bish, G.; Brennan, P.E.; Bunnage, M.E.; Cook, A.S.; Federov, O.; Gerstenberger, B.S.; Jones, H.; Knapp, S.; et al. Identification of a Chemical Probe for Bromo and Extra C-Terminal Bromodomain Inhibition through Optimization of a Fragment-Derived Hit. J. Med. Chem. 2012, 55, 9831–9837. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rangachari, D.; To, C.; Shpilsky, J.E.; VanderLaan, P.A.; Kobayashi, S.S.; Mushajiang, M.; Lau, C.J.; Paweletz, C.P.; Oxnard, G.R.; Jänne, P.A.; et al. EGFR-Mutated Lung Cancers Resistant to Osimertinib through EGFR C797S Respond to First-Generation Reversible EGFR Inhibitors but Eventually Acquire EGFR T790M/C797S in Preclinical Models and Clinical Samples. J. Thorac. Oncol. 2019, 14, 1995–2002. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tomás-Loba, A.; Manieri, E.; González-Terán, B.; Mora, A.; Leiva-Vega, L.; Santamans, A.M.; Romero-Becerra, R.; Rodríguez, E.; Pintor-Chocano, A.; Feixas, F.; et al. p38γ is essential for cell cycle progression and liver tumorigenesis. Nature 2019, 568, 557–560. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Vitos-Faleato, J.; Real, S.M.; Gutierrez-Prat, N.; Villanueva, A.; Llonch, E.; Drosten, M.; Barbacid, M.; Nebreda, A.R. Requirement for epithelial p38α in KRAS-driven lung tumor progression. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2020, 117, 2588–2596. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Picaud, S.; Da Costa, D.; Thanasopoulou, A.; Filippakopoulos, P.; Fish, P.V.; Philpott, M.; Fedorov, O.; Brennan, P.; Bunnage, M.E.; Owen, D.R.; et al. PFI-1, a Highly Selective Protein Interaction Inhibitor, Targeting BET Bromodomains. Cancer Res. 2013, 73, 3336–3346. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Wang, X.-Q.; Wang, W.; Peng, M.; Zhang, X.-Z. Free radicals for cancer theranostics. Biomaterials 2021, 266, 120474. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dadiboyena, S.; Arfaoui, A.; Amri, H.; Piedrafita, F.J.; Nefzi, A. Diversity oriented synthesis and IKK inhibition of aminobenzimidazole tethered quinazoline-2,4-diones, thioxoquinazolin-4-ones, benzodiazepine-2,3,5-triones, isoxazoles and isoxazolines. Bioorg. Med. Chem. Lett. 2015, 25, 685–689. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Hioki, H.; Matsushita, K.; Nakamura, S.; Horiuchi, H.; Kubo, M.; Harada, K.; Fukuyama, Y. Solid-phase combinatorial synthesis of 2-arylquinazolines and 2-arylquinazolinones by an 4-alkoxyaniline linker. J. Comb. Chem. 2008, 10, 620–623. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kundu, B.; Partani, P.; Duggineni, S.; Sawant, D. Solid-phase synthesis of 2-aminoquinazolinone derivatives with two- and three-point diversity. J. Comb. Chem. 2005, 7, 909–915. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, Y.; Ostresh, J.M.; Houghten, R.A. A traceless approach for the parallel solid-phase synthesis of 2-(arylamino)quinazolinones. J. Org. Chem. 2002, 67, 5831–5834. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abdildinova, A.; Gong, Y.-D. Current Parallel Solid-Phase Synthesis of Drug-like Oxadiazole and Thiadiazole Derivatives for Combinatorial Chemistry. Acs. Comb. Sci. 2018, 20, 309–329. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abdildinova, A.; Kurth, M.J.; Gong, Y.-D. Heterocycles as a Peptidomimetic Scaffold: Solid-Phase Synthesis Strategies. Pharmaceuticals 2021, 14, 449. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cherkupally, S.; Gurrala, P.; Nagaraj, A.; Srinivas, A. Synthesis and biological study of novel methylene-bis-benzofuranyl. Org. Commun. 2008, 1, 84–94. [Google Scholar]
- Samel, A.B.; Pai, N.R. Synthesis of Novel Aryloxy Propanoyl Thiadiazoles as Potential Antihypertensive Agents. J. Chin. Chem. Soc-Taip. 2010, 57, 1327–1330. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, X.; Dixon, S.; Kurth, M.J.; Lam, K.S. Traceless solid-phase synthesis of 1,4-disubstituted-6-nitro- 3,4-dihydro-1H-quinoline-2-ones. Tetrahedron Lett. 2005, 46, 5361–5364. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, X.B.; Song, A.M.; Dixon, S.; Kurth, M.J.; Lam, K.S. Facile solid phase synthesis of 1,2-disubstituted-6-nitro-1,4dihydroquinazolines using a tetrafunctional scaffold. Tetrahedron Lett. 2005, 46, 427–430. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pennington, L.D.; Aquila, B.M.; Choi, Y.; Valiulin, R.A.; Muegge, I. Positional Analogue Scanning: An Effective Strategy for Multiparameter Optimization in Drug Design. J. Med. Chem. 2020, 63, 8956–8976. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Carpenter, R.D.; DeBerdt, P.B.; Lam, K.S.; Kurth, M.J. Carbodiimide-based benzimidazole library method. J. Comb. Chem. 2006, 8, 907–914. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ke, Y.; Hu, T.-X.; Huo, J.-F.; Yan, J.-K.; Wang, J.-Y.; Yang, R.-H.; Xie, H.; Liu, Y.; Wang, N.; Zheng, Z.-J.; et al. Synthesis and in vitro biological evaluation of novel derivatives of Flexicaulin A condensation with amino acid trifluoroacetate. Eur. J. Med. Chem. 2019, 182, 111645. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Montebugnoli, D.; Bravo, P.; Brenna, E.; Mioskowski, C.; Panzeri, W.; Viani, F.; Volonterioa, A.; Wagner, A.; Zanda, M. Traceless solid-phase synthesis of 2,4,6-chlorodiamino and triaminopyrimidines. Tetrahedron 2003, 59, 7147–7156. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hussan, K.P.S.; Babu, T.D.; Pareeth, C.M.; Joshy, G.; Mathew, D.; Thayyil, M.S. Antioxidant activity of erlotinib and gefitinib: Theoretical and experimental insights. Free. Radic. Res. 2022, 56, 196–208. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Moon, D.O.; Kim, M.O.; Heo, M.S.; Lee, J.D.; Choi, Y.H.; Kim, G.Y. Gefitinib induces apoptosis and decreases telomerase activity in MDA-MB-231 human breast cancer cells. Arch. Pharmacal Res. 2009, 32, 1351–1360. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Thibault, B.; Jean-Claude, B. Dasatinib + Gefitinib, a non platinum-based combination with enhanced growth inhibitory, anti-migratory and anti-invasive potency against human ovarian cancer cells. J. Ovarian Res. 2017, 10, 31. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Kaji, K.; Nishimura, N.; Seki, K.; Sato, S.; Saikawa, S.; Nakanishi, K.; Furukawa, M.; Kawaratani, H.; Kitade, M.; Moriya, K.; et al. Sodium glucose cotransporter 2 inhibitor canagliflozin attenuates liver cancer cell growth and angiogenic activity by inhibiting glucose uptake. Int. J. Cancer 2018, 142, 1712–1722. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Mohammadi, V.; Behbahani, A.B.; Rafiee, G.R.; Hosseini, S.Y.; Zarei, M.A.; Okhovat, M.A.; Takhshid, M.A. The effects of specific expression of apoptin under the control of PSES and PSA promoter on cell death and apoptosis of LNCaP cells. Iran. J. Basic Med. Sci. 2017, 20, 1354–1359. [Google Scholar]
- Cheng, Y.; Luo, R.; Zheng, H.; Wang, B.; Liu, Y.; Liu, D.; Chen, J.; Xu, W.; Li, A.; Zhu, Y. Synergistic anti-tumor efficacy of sorafenib and fluvastatin in hepatocellular carcinoma. Oncotarget 2017, 8, 23265–23276. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Nwachukwu, I.D.; Sarteshnizi, R.A.; Udenigwe, C.C.; Aluko, R.E. A Concise Review of Current In Vitro Chemical and Cell-Based Antioxidant Assay Methods. Molecules 2021, 26, 4865–4881. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ali, H.M.; Abo-Shady, A.; Sharaf Eldeen, H.A.; Soror, H.A.; Shousha, W.G.; Abdel-Barry, O.A.; Saleh, A.M. Structural features, kinetics and SAR study of radical scavenging and antioxidant activities of phenolic and anilinic compounds. Chem. Cent. J. 2013, 7, 53–62. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Akiyama, T.; Sudo, C.; Ogawara, H.; Toyoshima, K.; Yamamoto, T. The product of the human c-erbB-2 gene: A 185-kilodalton glycoprotein with tyrosine kinase activity. Science 1986, 232, 1644–1646. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Slamon, D.J.; Godolphin, W.; Jones, L.A.; Holt, J.A.; Wong, S.G.; Keith, D.E.; Levin, W.J.; Stuart, S.G.; Udove, J.; Ullrich, A.; et al. Studies of the HER-2/neu proto-oncogene in human breast and ovarian cancer. Science 1989, 244, 707–712. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Smolinska, M.J.; Page, T.H.; Urbaniak, A.M.; Mutch, B.E.; Horwood, N.J. Hck tyrosine kinase regulates TLR4-induced TNF and IL-6 production via AP-1. J. Immunol. 2011, 187, 6043–6051. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Waters, J.P.; Pober, J.S.; Bradley, J.R. Tumour necrosis factor in infectious disease. J. Psychopathol. 2013, 230, 132–147. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fruman, D.A.; Meyers, R.E.; Cantley, L.C. Phosphoinositide kinases. Annu. Rev. Biochem. 1998, 67, 481–507. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Staal, S.P. Molecular cloning of the akt oncogene and its human homologues AKT1 and AKT2: Amplification of AKT1 in a primary human gastric adenocarcinoma. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 1987, 84, 5034–5037. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Weng, L.P.; Smith, W.M.; Dahia, P.L.; Ziebold, U.; Gil, E.; Lees, J.A.; Eng, C. PTEN suppresses breast cancer cell growth by phosphatase activity-dependent G1 arrest followed by cell death. Cancer Res. 1999, 59, 5808–5814. [Google Scholar]
- Ishikawa, T.; Seto, M.; Banno, H. Design and synthesis of novel human epidermal growth factor receptor 2 (HER2)/epidermal growth factor receptor (EGFR) dual inhibitors bearing a pyrrolo[3,2-d]pyrimidine scaffold. J. Med. Chem. 2011, 54, 8030–8050. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Takabatake, D.; Fujita, T.; Shien, T.; Kawasaki, K.; Taira, N.; Yoshitomi, S.; Takahashi, H.; Ishibe, Y.; Ogasawara, Y.; Doihara, H. Tumor inhibitory effect of gefitinib (ZD1839, Iressa) and taxane combination therapy in EGFR-overexpressing breast cancer cell lines (MCF7/ADR, MDA-MB-231). Int. J. Cancer 2007, 120, 181–188. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Ohta, T.; Ohmichi, M.; Shibuya, T.; Takahashi, T.; Tsutsumi, S.; Takahashi, K.; Kurachi, H. Gefitinib (ZD1839) increases the efficacy of cisplatin in ovarian cancer cells. Cancer Biol. Ther. 2012, 13, 408–416. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Wang, W.; Gao, Y.; Hai, J.; Yang, J.; Duan, S. HER2 decreases drug sensitivity of ovarian cancer cells via inducing stem cell-like property in an NFκB-dependent way. Biosci. Rep. 2019, 39, 1–12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Lipinski, C.A.; Lombardo, F.; Dominy, B.W.; Feeney, P.J. Experimental and computational approaches to estimate solubility and permeability in drug discovery and development settings. Adv. Drug. Deliver. Rev. 2001, 46, 3–26. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Noh, H.Y.; Lu, J.; Hanif Siddiqi, M.; Natatajan, S.; Kang, S.; Ahn, S.; Kim, Y.J.; Yang, D.C. Computational Investigation of Ginsenoside F1 from Panax ginseng Meyer as p38 MAP Kinase Inhibitor: Molecular Docking and Dynamics Simulations, ADMET Analysis, and Drug Likeness Prediction. Iran. J. Pharm. Res. 2018, 17, 1318–1327. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Suzuki, R.; Konno, H. Stain Protocol for the Detection of N-Terminal Amino Groups during Solid-Phase Peptide Synthesis. Org. Lett. 2020, 22, 3309–3312. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Morales, F.J.; Jiménez-Pérez, S. Free radical scavenging capacity of Maillard reaction products as related to colour and fluorescence. Food Chem. 2001, 72, 119–125. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]










 | |||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| No. | Entry | R1′ | R2 | R3′ | Purity b (%) | Crude Yield a (%) | MS c (Found, M + H+) |
| 1 | CA1-6 |  |  | -NO2 | 63 | 93 | 395.15 |
| 2 | CA1-7 |  |  | -NH2 | 85 | 76 | 365.20 |
| 3 | CA1-a |  |  |  | 87 | 86 | 470.15 |
| 4 | CA1-b |  |  |  | 73 | 85 | 469.20 |
| 5 | CA1-c |  |  |  | 82 | 82 | 483.20 |
| 6 | CA1-d |  |  |  | 78 | 79 | 487.20 |
| 7 | CA1-e |  |  |  | 87 | 84 | 470.20 |
| 8 | CA1-f |  |  |  | 90 | 76 | 470.15 |
| 9 | CA1-g |  |  |  | 72 | 85 | 499.20 |
| 10 | CA1-h |  |  |  | 76 | 92 | 498.25 |
| 11 | CA1-i |  |  |  | 67 | 90 | 489.20 |
| 12 | CA1-j |  |  |  | 82 | 71 | 535.20 |
| 13 | CA2 |  |  |  | - | - | - |
| 14 | CA3 |  |  |  | 64 | 74 | 538.30 |
| 15 | CA4 |  |  |  | 35 | 75 | 530.25 |
| 16 | CA5 |  |  |  | 78 | 84 | 528.20 |
| 17 | CA6-a | H | H3C- |  | 65 | 74 | 340.15 |
| 18 | CA6-b | H | H3C- |  | 59 | 78 | 369.15 |
| 19 | CA7-a | H | H3C- |  | 62 | 84 | 405.10 |
| 20 | CA7-b | H | H3C- |  | - | - | 393 |
| No. | IC50 (µM) a | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| HepG-2 | MDA-MB-231 | A2780 | LX-2 | |
| CA1-6 | 52.31 ± 3.45 | 81.20 ± 1.54 | 83.23 ± 2.69 | 97.90 ± 15.59 |
| CA1-7 | 59.29 ± 1.85 | 90.07 ± 10.89 | 79.84 ± 1.01 | >100 |
| CA1-a | 54.36 ± 3.45 | 86.04 ± 2.06 | 79.96 ± 2.15 | >100 |
| CA1-b | 60.12 ± 3.88 | 76.58 ± 2.42 | >100 | 85.80 ± 4.28 |
| CA1-c | 48.14 ± 2.34 | 92.36 ± 4.91 | >100 | 85.36 ± 1.78 |
| CA1-d | 49.59 ± 1.91 | 85.68 ± 4.87 | 88.34 ± 8.56 | >100 |
| CA1-e | 37.59 ± 5.53 | 85.69 ± 5.30 | 22.76 ± 0.22 | >100 |
| CA1-f | 44.43 ± 2.20 | 81.28 ± 1.21 | >100 | 96.98 ± 4.24 |
| CA1-g | 45.41 ± 0.59 | 82.21 ± 0.59 | 24.94 ± 7.22 | >100 |
| CA1-h | 56.93 ± 0.47 | 82.25 ± 11.41 | 86.06 ± 3.73 | 97.49 ± 3.52 |
| CA1-i | 49.77 ± 0.12 | 89.70 ± 3.79 | 34.44 ± 5.61 | >100 |
| CA1-j | 73.76 ± 1.03 | 76.28 ± 2.05 | 83.57 ± 1.24 | >100 |
| CA3 | 64.19 ± 4.69 | 86.05 ± 11.07 | 82.88 ± 2.13 | >100 |
| CA4 | 72.73 ± 2.76 | 87.13 ± 4.47 | 66.19 ± 4.10 | 72.85 ± 0.91 |
| CA5 | 65.46 ± 3.16 | 74.81 ± 0.27 | 32.29 ± 6.21 | >100 |
| CA6-a | >100 | >100 | >100 | >100 |
| CA6-b | 88.05 ± 1.39 | >100 | >100 | >100 |
| CA7-a | 86.43 ± 3.42 | 87.66 ± 2.58 | 82.85 ± 2.68 | >100 |
| CA7-b′ | 95.31 ± 5.47 | >100 | >100 | >100 |
| Gefitinib | 3.15 ± 0.91 | 10.20 ± 1.00 | 7.77 ± 0.70 | 20.16 ± 3.25 |
| Compounds | IC50 (µM) a | Compounds | IC50 (µM) a |
|---|---|---|---|
| CA1-6 | >1000 | CA1-i | 556.88 ± 24.52 |
| CA1-7 | 57.99 ± 0.38 | CA1-j | >1000 |
| CA1-a | >1000 | CA3 | >1000 |
| CA1-b | >1000 | CA4 | 950.82 ± 30.61 |
| CA1-c | 387.11 ± 58.79 | CA5 | 464.97 ± 8.61 |
| CA1-d | >1000 | CA6-a | >1000 |
| CA1-e | >1000 | CA6-b | >1000 |
| CA1-f | >1000 | CA7-a | >1000 |
| CA1-g | >1000 | CA7-b′ | >1000 |
| CA1-h | >1000 | Vc | 22.50 ± 0.57 |
| Gefitinib | 721 ± 16.25 |
| Protein | Comp. | PDB ID | Interaction Energy (kJ/mol) | Residue Involved in H Bonding | H-Bond Length (Å) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| HER2 | TAK-285 | 3RCD | THR798; MET801; THR862 | 4.60; 2.77; 2.69 | |
| CA1-e | 3PP0 | −61.4 | SER728; MET801; ARG849 | 2.22; 2.20/2.48; 2.58 | |
| CA1-g | 3PP0 | −71.2 | SER728; MET801; CYS805; ASP808; THR862; ASP863 | 2.86/2.17; 2.90; 2.93; 2.40; 2;49; 2.79 |
| Comp. | MW | ALogP | nHBD | nHBA | nRotB | nviolation | Absorption | Solubility | CYP2D6 | Hepatotoxicity | PPB | BBB |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Rule | ≤500 | ≤5 | ≤5 | ≤10 | ≤10 | ≤1 | ||||||
| CA1-6 | 412.40 | −2.39 | 6 | 8 | 9 | 1 | 3 | 4 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 4 |
| CA1-7 | 364.40 | −2.82 | 6 | 6 | 8 | 1 | 3 | 5 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 4 |
| CA1-a | 469.49 | −2.44 | 6 | 7 | 10 | 1 | 3 | 4 | 0 | 1 | 0 | 4 |
| CA1-b | 468.51 | −1.29 | 6 | 6 | 10 | 1 | 3 | 4 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 4 |
| CA1-c | 482.53 | −0.80 | 6 | 6 | 10 | 1 | 3 | 4 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 4 |
| CA1-d | 486.50 | −1.09 | 6 | 6 | 10 | 1 | 3 | 3 | 0 | 1 | 0 | 4 |
| CA1-e | 453.49 | −1.55 | 5 | 6 | 9 | 0 | 3 | 4 | 0 | 1 | 0 | 4 |
| CA1-f | 469.49 | −2.01 | 6 | 7 | 10 | 1 | 3 | 4 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 4 |
| CA1-g | 498.53 | −1.46 | 6 | 7 | 12 | 2 | 3 | 4 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 4 |
| CA1-h | 497.55 | −1.95 | 6 | 7 | 12 | 2 | 3 | 4 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 4 |
| CA1-i | 488.56 | −1.30 | 6 | 6 | 11 | 2 | 3 | 4 | 0 | 1 | 0 | 4 |
| CA1-j | 534.59 | −1.60 | 6 | 8 | 12 | 2 | 3 | 3 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 4 |
| CA3 | 537.65 | 0.75 | 5 | 6 | 14 | 1 | 3 | 3 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 4 |
| CA4 | 529.59 | 2.10 | 4 | 5 | 10 | 1 | 2 | 3 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 4 |
| CA5 | 527.64 | −1.25 | 6 | 6 | 10 | 2 | 3 | 3 | 0 | 1 | 0 | 4 |
| CA6-a | 339.35 | −0.33 | 3 | 4 | 4 | 0 | 0 | 4 | 0 | 1 | 0 | 4 |
| CA6-b | 368.39 | 0.66 | 3 | 4 | 6 | 0 | 0 | 3 | 0 | 1 | 0 | 4 |
| CA7-a | 404.44 | 0.51 | 3 | 5 | 6 | 0 | 1 | 3 | 0 | 1 | 1 | 4 |
| CA7-b | 550.56 | 2.30 | 2 | 6 | 7 | 1 | 2 | 2 | 0 | 1 | 1 | 4 |
| Gefitinib | 446.91 | 4.20 | 1 | 7 | 8 | 0 | 0 | 2 | 1 | 0 | 1 | 1 |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Wang, Q.; Pan, Y.; Luo, H.; Zhang, Y.; Gao, F.; Wang, J.; Zheng, J. Novel Approaches for the Solid-Phase Synthesis of Dihydroquinazoline-2(1H)-One Derivatives and Biological Evaluation as Potential Anticancer Agents. Molecules 2022, 27, 8577. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules27238577
Wang Q, Pan Y, Luo H, Zhang Y, Gao F, Wang J, Zheng J. Novel Approaches for the Solid-Phase Synthesis of Dihydroquinazoline-2(1H)-One Derivatives and Biological Evaluation as Potential Anticancer Agents. Molecules. 2022; 27(23):8577. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules27238577
Chicago/Turabian StyleWang, Qiong, Ying Pan, Hongjun Luo, Yanmei Zhang, Fenfei Gao, Jinzhi Wang, and Jinhong Zheng. 2022. "Novel Approaches for the Solid-Phase Synthesis of Dihydroquinazoline-2(1H)-One Derivatives and Biological Evaluation as Potential Anticancer Agents" Molecules 27, no. 23: 8577. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules27238577
APA StyleWang, Q., Pan, Y., Luo, H., Zhang, Y., Gao, F., Wang, J., & Zheng, J. (2022). Novel Approaches for the Solid-Phase Synthesis of Dihydroquinazoline-2(1H)-One Derivatives and Biological Evaluation as Potential Anticancer Agents. Molecules, 27(23), 8577. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules27238577