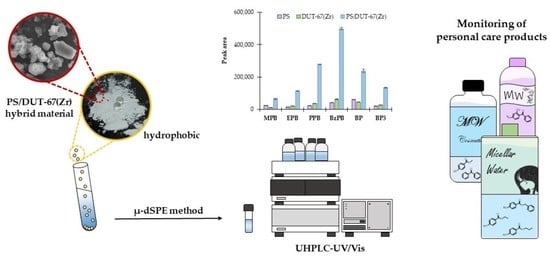
Hybrid Materials Formed with Green Metal-Organic Frameworks and Polystyrene as Sorbents in Dispersive Micro-Solid-Phase Extraction for Determining Personal Care Products in Micellar Cosmetics
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Experimental Section
2.1. Standards, Reagents, Materials, and Samples
2.2. Instrumentation
2.3. Procedures
2.3.1. Synthesis of MOFs
2.3.2. Synthesis of Hybrid Materials Based on PS and MOFs
2.3.3. Dispersive Micro-Solid-Phase Extraction (μ-dSPE) Method
3. Results and Discussion
3.1. Characterization of the PS/MOF Materials
3.2. Chromatographic Method: Analytical Quality Parameters
3.3. Preliminary Study: Material Selection
3.4. Optimization of the μ-dSPE Method
3.5. Analytical Performance of the μ-dSPE-UHPLC-UV/Vis Method
3.6. Comparison with Other Methods
3.7. Analysis of Micellar Cosmetic Samples
4. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
Sample Availability
Abbreviations
| ACN | Acetonitrile |
| AIBN | Azobisisobutyronitrile |
| BET | Brunauer, Emmett and Teller |
| BP | Benzophenone |
| BP3 | Benzophenone-3 |
| BzPB | Benzylparaben |
| CIM | Canary Islands Materials (code for MOFs) |
| COFs | Covalent-organic frameworks |
| DESs | Deep eutectic solvents |
| DMF | Dimethylformamide |
| DUT | Dresden University of Technology (code for MOFs) |
| EF | Enrichment factor |
| EPB | Ethylparaben |
| ER | Extraction efficiency |
| ESM | Electronic supporting material |
| FT-IR | Fourier transform infrared spectroscopy |
| H2TDC | 2,5-thiophenedicarboxylic acid |
| ILs | Ionic liquids |
| LC-MS | Liquid chromatography tandem mass spectrometry |
| LLE | Liquid-liquid extraction |
| LODs | Limits of detection |
| LOQs | Limits of quantification |
| MIL | Material Institute Lavoisier (code for MOFs) |
| MIPs | Molecular imprinted polymers |
| MOFs | Metal-organic frameworks |
| MPB | Methylparaben |
| NPs | Nanoparticles |
| PCPs | Personal care products |
| PPB | Propylparaben |
| PS | Polystyrene |
| PS/CIM-80(Al) | Polystyrene/CIM-80(Al) MOF-based hybrid material |
| PS/DUT-67(Zr) | Polystyrene/DUT-67(Zr) MOF-based hybrid material |
| PS/MOF | Hybrid material based on polystyrene and metal-organic framework |
| PVDF | Polyvinylidene fluoride |
| PVP | Polyvinylpyrrolidone |
| PXRD | Powder X-ray diffraction |
| R2 | Coefficient of determination |
| RR | Relative recoveries |
| RSDs | Relative standard deviations |
| S/N | Signal-to-noise ratio |
| SBUs | Secondary building units |
| SEMs | Scanning electron microscopes |
| SPE | Solid-phase extraction |
| SPME | Solid-phase microextraction |
| TG/DTA | Thermogravimetric/differential thermal analysis |
| UHPLC | Ultra-high performance liquid chromatography |
| UHPLC-UV/Vis | Ultra-high performance liquid chromatography coupled to ultraviolet/visible detection |
| UV/Vis | Ultraviolet/visible detection |
| ZIF | Zeolitic imidazolate framework (code for MOFs) |
| μ-dSPE | Dispersive micro-solid-phase extraction |
| μ-SPE | Micro-solid-phase extraction |
References
- Pawliszyn, J. Theory of Extraction. In Comprehensive Sampling and Sample Preparation: Analytical Techniques for Scientists, 1st ed.; Pawliszyn, J., Ed.; Elsevier: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2012; Volume 2, pp. 1–25. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Armenta, S.; Garrigues, S.; de la Guardia, M.; Esteve-Turrillas, F.A. Green Analytical Chemistry. In Encyclopedia of Analytical Science, 3rd ed.; Worsfold, P., Poole, C., Townshend, A., Miró, M., Eds.; Elsevier: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2019; pp. 356–361. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maciel, E.V.S.; de Toffoli, A.L.; Neto, E.S.; Nazario, C.E.D.; Lanças, F.M. New materials in sample preparation: Recent advances and future trends. TrAC Trends Anal. Chem. 2019, 119, 115633. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Feng, J.; Loussala, H.M.; Han, S.; Ji, X.; Li, C.; Sun, M. Recent advances of ionic liquids in sample preparation. TrAC Trends Anal. Chem. 2020, 125, 115833. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Trujillo-Rodríguez, M.J.; Pino, V.; Miró, M. High-throughput microscale extraction using ionic liquids and derivatives: A review. J. Sep. Sci. 2020, 43, 1890–1907. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sajid, M.; Płotka-Wasylka, J. Nanoparticles: Synthesis, characteristic, and applications in analytical and other sciences. Microchem. J. 2020, 154, 104623. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Santana-Mayor, Á.; Rodríguez-Ramos, R.; Herrera-Herrera, A.V.; Socas-Rodríguez, B.; Rodríguez-Delgado, M.Á. Deep eutectic solvents. The new generation of green solvents in analytical chemistry. TrAC Trends Anal. Chem. 2021, 134, 116108. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- González-Sálamo, J.; Jiménez-Skrzypek, G.; Ortega-Zamora, C.; González-Curbelo, M.Á.; Hernández-Borges, J. Covalent Organic Frameworks in Sample Preparation. Molecules 2020, 25, 3288. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Turiel, E.; Martín-Esteban, A. Molecularly imprinted polymers-based microextraction techniques. TrAC Trends Anal. Chem. 2019, 118, 574–586. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bazargan, M.; Ghaemi, F.; Amiri, A.; Mirzaei, M. Metal-organic framework-based sorbents in analytical sample preparation. Coord. Chem. Rev. 2021, 445, 214107. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rocío-Bautista, P.; González-Hernández, P.; Pino, V.; Pasán, J.; Afonso, A.M. Metal-organic frameworks as novel sorbents in dispersive-based microextraction approaches. TrAc Trends Anal. Chem. 2017, 90, 114–134. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pacheco-Fernández, I.; González-Hernández, P.; Pasán, J.; Ayala, J.H.; Pino, V. The Rise of Metal-Organic Frameworks in Analytical Chemistry. In Handbook of Smart Materials in Analytical Chemistry, 1st ed.; de la Guardia, M., Esteve-Turrillas, F.A., Eds.; Wiley: Weinheim, Germany, 2019; Volume 1, pp. 463–502. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Carrasco-Correa, E.J.; Pacheco-Fernández, I.; Herrero-Martínez, J.M.; Pino, V. Reticular materials in sorbent-based extraction methods. In Analytical Sample Preparation with Nano- and Other High-Perfirmance Materials, 1st ed.; Lucena, R., Cárdenas, S., Eds.; Elsevier: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2021; Volume 1, pp. 323–376. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Taima-Mancera, I.; Pino, V. Reticular materials as chiral stationary phases in chromatography. J. Chromatogr. Open 2021, 1, 100002. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maya, F.; Palomino Cabello, C.; Figuerola, A.; Turnes Palomino, G.; Cerdà, V. Immobilization of Metal-Organic Frameworks on Supports for Sample Preparation and Chromatographic Separation. Chromatographia 2019, 82, 361–375. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kumar, P.; Vellingiri, K.; Kim, K.-H.; Brown, R.J.C.; Manos, M.J. Modern progress in metal-organic frameworks and their composites for diverse applications. Microporous Mesoporous Mat. 2017, 253, 251–265. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mukherjee, S.; Datta, K.K.R.; Fischer, R.A. Hydrophobicity: A key factor en route to applications of metal-organic frameworks. Trends Chem. 2021, 3, 911–925. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, X.; Wang, B.; Alsalme, A.; Xiang, S.; Zhang, Z.; Chen, B. Design and applications of water-stable metal-organic frameworks: Status and challenges. Coord. Chem. Rev. 2020, 423, 213507. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dhaka, S.; Kumar, R.; Deep, A.; Kurade, M.B.; Ji, S.-W.; Jeon, B.-H. Metal-organic frameworks (MOFs) for the removal of emerging contaminants from aquatic environments. Coord. Chem. Rev. 2019, 380, 330–352. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, Q.-L.; Xu, Q. Metal-organic framework composites. Chem. Soc. Rev. 2014, 43, 5468–5512. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gutiérrez-Serpa, A.; Jiménez-Abizanda, A.I.; Jiménez-Moreno, F.; Pasán, J.; Pino, V. Core-shell microparticles formed by the metal-organic framework CIM-80(Al) (Silica@CIM-80(Al)) as sorbent material in miniaturized dispersive solid-phase extraction. Talanta 2020, 211, 120723. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sohrabi, M.R. Preconcentration of mercury(II) using a thiol-functionalized metal-organic framework nanocomposite as a sorbent. Microchim. Acta 2014, 181, 435–444. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, S.; Peng, L.; Syzgantseva, O.A.; Trukhina, O.; Kochetygov, I.; Justin, A.; Sun, D.T.; Abedini, H.; Syzgantseva, M.A.; Oveisi, E.; et al. Preparation of High Porous Metal-Organic Frameworks Beads for Metal Extraction from Liquid Streams. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2020, 142, 13415–13425. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, S.; Si, H.; Li, J.; Jia, M.; Hou, X. Metal organic framework/chitosan foams functionalized with polyethylene oxide as a sorbent for enrichment and analysis of bisphenols in beverages and water. New J. Chem. 2020, 44, 1485–1492. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jalilian, N.; Ebrahimzadeh, H.; Asgharinezhad, A.A. Preparation of magnetite/multiwalled carbon nanotubes/metal-organic framework composite for dispersive magnetic micro solid phase extraction of parabens and phthalate esters from water samples and various types of cream for their determination with liquid chromatography. J. Chromatogr. A 2019, 1608, 460426. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jia, Y.; Wang, Y.; Yan, M.; Wang, Q.; Xu, H.; Wang, X.; Zhou, H.; Hao, Y.; Wang, M. Fabrication of iron oxide@MOF-808 as a sorbent for magnetic solid phase extraction of benzoylurea insecticides in tea beverages and juice samples. J. Chromatogr. A 2020, 1615, 460766. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hu, Z.; Wang, X.; Wang, J.; Chen, X. PEGylation of metal-organic framework for selective isolation of glycoprotein immunoglobulin G. Talanta 2020, 208, 120433. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shih, Y.-H.; Wang, K.-Y.; Singco, B.; Lin, C.-H.; Huang, H.-Y. Metal-Organic Framework-Polymer Composite as a Highly Efficient Sorbent for Sulfonamide Adsorption and Desorption: Effect of Coordinatively Unsaturated Metal Site and Topology. Langmuir 2016, 32, 11465–11473. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tan, Y.; Sun, Z.; Meng, H.; Han, Y.; Wu, J.; Xu, J.; Xu, Y.; Zhang, X. A new MOFs/polymer hybrid membrane: MIL-68(Al)/PVDF, fabrication and application in high-efficient removal of p-nitrophenol and methylene blue. Sep. Purif. Technol. 2019, 215, 217–226. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kuo, Y.-C.; Pal, S.; Li, F.-Y.; Lin, C.-H. Polystyrene-Supported Core-Shell Beads with Aluminium MOF Coating for Extraction of Organic Pollutants. Chem. Asian, J. 2019, 14, 3675–3681. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- del Rio, M.; Palomino Cabello, C.; Gonzalez, V.; Maya, F.; Barra, J.B.; Cerdà, V.; Turnes Palomino, G. Metal Oxide Assisted Preparation of Core-Shell Beads with Dense Metal-Organic Framework Coatings for the Enhanced Extraction of Organic Pollutants. Chem. Eur. J. 2016, 22, 11770–11777. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, H.; Zhang, Q.; Zhu, S. Preparation of raspberry-like ZIF-8/PS composite spheres via dispersion polymerization. Dalton Trans. 2015, 44, 16752–16757. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, H.J.; Cho, W.; Oh, M. Advanced fabrication of metal-organic frameworks: Template-directed formation of polystyrene@ZIF-8 core-shell and hollow ZIF-8 microspheres. Chem. Commun. 2012, 48, 221–223. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rocío-Bautista, P.; Pino, V.; Ayala, J.H.; Ruiz-Pérez, C.; Vallcorba, O.; Afonso, A.M.; Pasán, J. A green metal-organic framework to monitor water contaminants. RSC Adv. 2018, 8, 31304–31310. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Reinsch, H.; Waitschat, S.; Chavan, S.M.; Lillerud, K.P.; Stock, N. A Facile “Green” Route for Scalable Batch Production and Continuous Synthesis of Zirconium MOFs. Eur. J. Inorg. Chem. 2016, 2016, 4490–4498. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, M.; Wang, Q.; Zhang, M.; Deng, Q.; Chen, D. Facile fabrication of raspberry-like composite microspheres for the construction of superhydrophobic films and applications in highly efficient oil-water separation. RSC Adv. 2017, 7, 39471–39479. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Bon, V.; Senkovska, I.; Baburin, I.A.; Kaskel, S. Zr- and Hf-Based Metal-Organic Frameworks: Tracking Down the Polymorphism. Cryst. Crowth Des. 2013, 13, 1231–1237. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Reinsch, H.; Homburg, T.; Heidenreich, N.; Fröhlich, D.; Hennninger, S.; Wark, M.; Stock, N. Green Synthesis of a New Al-MOF Based on the Aliphatic Linker Mesaconic Acid: Structure, Properties and In Situ Crystallisation Studies of Al-MIL-68-Mes. Chem. Eur. J. 2018, 24, 2173–2181. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gamage, N.-D.H.; McDonald, K.A.; Matzger, A.J. MOF-5-Polystyrene: Direct Production from Monomer, Improved Hydrolytic Stability, and Unique Guest Adsorption. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 2016, 55, 12099–12103. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, S.; Karve, V.V.; Justin, A.; Kochetygov, I.; Espín, J.; Asgari, M.; Trukhina, O.; Sun, D.T.; Peng, L.; Queen, W.L. Enhancing MOF performance through the introduction of polymer guests. Coord. Chem. Rev. 2021, 427, 213525. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Grover, A.; Mohiuddin, I.; Malik, A.K.; Aulakh, J.S.; Kukkar, D.; Kim, K.-H. Chitosan-Ni/Fe layered double hydroxide composites as an efficient solid phase extraction sorbent for HPLC-PDA monitoring of parabens in personal care products. Chemosphere 2021, 264, 128429. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mpupa, A.; Mashile, G.P.; Nomngongo, P.N. Ultrasound-assisted dispersive solid phase nanoextraction of selected personal care products in wastewater followed by their determination using high performance liquid chromatography-diode array detector. J. Hazard. Mater. 2019, 370, 33–41. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Morés, L.; da Silva, A.C.; Merib, J.; Dias, A.N.; Carasek, E. A natural and renewable biosorbent phase as a low-cost approach in disposable pipette extraction technique for the determination of emerging contaminants in lake water samples. J. Sep. Sci. 2019, 42, 1404–1411. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Li, J.; Jiang, Y.; Sun, Y.; Wang, X.; Ma, P.; Song, D.; Fei, Q. Extraction of parabens by melamine sponge with determination by high performance liquid chromatography. J. Sep. Sci. 2021, 1–9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- González-Hernández, P.; Lago, A.B.; Pasán, J.; Ruiz-Pérez, C.; Ayala, J.H.; Afonso, A.M.; Pino, V. Application of a Pillared-Layer Zn-Triazolate Metal-Organic Framework in the Dispersive Miniaturized Solid-Phase Extraction of Personal Care Products from Wastewater Samples. Molecules 2019, 24, 690. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Muckoya, V.A.; Idris, A.O.; Nomngongo, P.N.; Ngila, J.C. Synthesized carbon nanodots for simultaneous extraction of personal care products and organophosphorus pesticides in wastewater samples prior to LC-MS/MS determination. Anal. Bioanal. Chem. 2019, 411, 6173–6187. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rocío-Bautista, P.; Martínez-Benito, C.; Pino, V.; Pasán, J.; Ayala, J.H.; Ruiz-Pérez, C.; Afonso, A.M. The metal-organic framework HKUST-1 as efficient sorbent in a vortex-assisted dispersive micro solid-phase extraction of parabens from environmental waters, cosmetic creams, and human urine. Talanta 2015, 139, 13–20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rashvand, M.; Vosough, M.; Kargosha, K. Preparation of magnetic nanographene sorbent for extraction and quantification of targeted PPCPs in environmental water samples. RSC Adv. 2016, 6, 75609–75617. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mashile, G.P.; Mpupa, A.; Nomngongo, P.N. In-Syringe Micro Solid-Phase Extraction Method for the Separation and Preconcentration of Parabens in Environmental Water Samples. Molecules 2018, 23, 1450. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Gutiérrez-Serpa, A.; Kundu, T.; Pasán, J.; Jiménez-Abizanda, A.I.; Kaskel, S.; Senkovska, I.; Pino, V. Zirconium-Based Metal-Organic Frameworks Mixed-Matrix Membranes as Analytical Devices for the Trace Analysis of Complex Cosmetic Samples in the Assessment of Their Personal Care Product Content. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2022, in press. [CrossRef]





| Analyte (Abbreviation) | Structure | Molecular Weight (g·mol−1) | Molecular Dimensions a (Å3) | Vapor Pressure b (N·m−2) | pKa | Log Kow c |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Methylparaben (MPB) |  | 152.15 | 5 × 3 × 9 | 3.16×10−2 | 8.50 | 1.96 |
| Ethylparaben (EPB) |  | 166.17 | 5 × 4 × 11 | 1.24×10−2 | 8.34 | 2.47 |
| Propylparaben (PPB) |  | 180.20 | 5 × 4 × 12 | 4.09×10−2 | 8.50 | 3.04 |
| Benzylparaben (BzPB) |  | 228.24 | 9 × 8 × 12 | - | - | 3.56 |
| Benzophenone (BP) |  | 182.22 | 6 × 6 × 9 | 0.257 | - | 3.18 |
| Benzophenone-3 (BP3) |  | 228.24 | 6 × 6 × 12 | 8.83×10−4 | 7.10 | 3.79 |
| PCPs | Slope ± Sb a | R2 b | Sx/y c | LOD d (μg·L−1) | Working Range (μg·L−1) | Intra-Day RSD e (%) | Inter-Day RSD e (%) | EF f | ER g (%) | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 75 (μg·L−1) | 650 (μg·L−1) | 75 (μg·L−1) | 650 (μg·L−1) | ||||||||
| MPB | 972 ± 23 | 0.9978 | 18,182 | 3.00 | 10.0–800 | 8.29 | 13.6 | 21.8 | 20.4 | 0.577 | 10.4 |
| EPB | 1425 ± 28 | 0.9985 | 21,875 | 1.30 | 4.30–800 | 7.50 | 12.5 | 21.5 | 21.2 | 1.19 | 21.4 |
| PPB | 3001 ± 41 | 0.9993 | 32,088 | 0.50 | 1.70–800 | 5.72 | 10.5 | 20.4 | 21.1 | 2.28 | 41.1 |
| BzPB | 4868 ± 176 | 0.9935 | 139,562 | 0.75 | 2.50–800 | 3.21 | 8.77 | 10.3 | 14.8 | 4.94 | 89.0 |
| BP | 3626 ± 62 | 0.9988 | 48,736 | 1.00 | 3.35–800 | 18.4 | 10.8 | 23.5 | 13.3 | 2.52 | 45.4 |
| BP3 | 969 ± 11 | 0.9995 | 8575 | 1.00 | 3.35–800 | 12.2 | 19.6 | 12.5 | 12.9 | 1.96 | 35.3 |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Napolitano-Tabares, P.I.; Gutiérrez-Serpa, A.; Jiménez-Abizanda, A.I.; Jiménez-Moreno, F.; Pasán, J.; Pino, V. Hybrid Materials Formed with Green Metal-Organic Frameworks and Polystyrene as Sorbents in Dispersive Micro-Solid-Phase Extraction for Determining Personal Care Products in Micellar Cosmetics. Molecules 2022, 27, 813. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules27030813
Napolitano-Tabares PI, Gutiérrez-Serpa A, Jiménez-Abizanda AI, Jiménez-Moreno F, Pasán J, Pino V. Hybrid Materials Formed with Green Metal-Organic Frameworks and Polystyrene as Sorbents in Dispersive Micro-Solid-Phase Extraction for Determining Personal Care Products in Micellar Cosmetics. Molecules. 2022; 27(3):813. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules27030813
Chicago/Turabian StyleNapolitano-Tabares, Patricia I., Adrián Gutiérrez-Serpa, Ana I. Jiménez-Abizanda, Francisco Jiménez-Moreno, Jorge Pasán, and Verónica Pino. 2022. "Hybrid Materials Formed with Green Metal-Organic Frameworks and Polystyrene as Sorbents in Dispersive Micro-Solid-Phase Extraction for Determining Personal Care Products in Micellar Cosmetics" Molecules 27, no. 3: 813. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules27030813
APA StyleNapolitano-Tabares, P. I., Gutiérrez-Serpa, A., Jiménez-Abizanda, A. I., Jiménez-Moreno, F., Pasán, J., & Pino, V. (2022). Hybrid Materials Formed with Green Metal-Organic Frameworks and Polystyrene as Sorbents in Dispersive Micro-Solid-Phase Extraction for Determining Personal Care Products in Micellar Cosmetics. Molecules, 27(3), 813. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules27030813