Determination of Aniline in Soil by ASE/GC-MS
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Experimental Section
2.1. Materials and Instrumentation
2.2. GC-MS Conditions
2.3. Accelerated Solvent Extractor (ASE) Operating Conditions
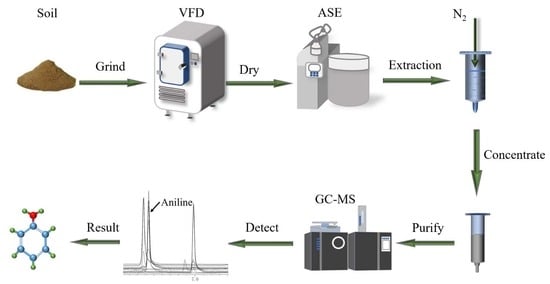
2.4. Samples Preparation and Pretreatment
2.5. Standard Solution and Standard Curve Line
3. Results and Discussion
3.1. The Influence of Vacuum Freezing Time on the Recovery Rate of the Aniline Matrix Spike
3.2. The Influence of ASE on the Recovery Rate of Aniline Matrix Spike
3.3. The Influence of Sample Transfer on the Recovery Rate of Aniline Matrix Spike
3.4. The Influence of Nitrogen-Blowing Concentration on the Recovery Rate of Aniline Matrix Spike
3.5. The Influence of Solvent Exchange on the Recovery Rate of Aniline Matrix Addition
3.6. The Influence of Other Factors on the Recovery Rate of Aniline Matrix Spike
3.7. Validation of the ASE/GC-MS Method
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
Sample Availability
References
- Feng, Y.; Chen, L.-L.; Zhang, T.; Wu, Y.-H.; Song, L.; Wang, Y. Research progress on health effects of aniline. Chin. J. Prev. Med. 2020, 54, 213–218. [Google Scholar]
- Boulahlib, S.; Boudina, A.; Si-Ahmed, K.; Bessekhouad, Y.; Trari, M. Development and validation of a fast and simple HPLC method for the simultaneous determination of aniline and its degradation products in wastewater. Anal. Methods 2016, 8, 5949–5956. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pereira, L.; Mondal, P.K.; Alves, M. Aromatic Amines Sources, Environmental Impact and Remediation. In Pollutants in Buildings, Water and Living Organisms; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2015; pp. 297–346. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Angioi, S.; Polati, S.; Roz, M.; Rinaudo, C.; Gianotti, V.; Gennaro, M. Sorption studies of chloroanilines on kaolinite and montmorillonite. Environ. Pollut. 2005, 134, 35–43. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, Y.; Wang, H.; Shang, Y.; Yang, K. Simultaneous removal of aniline, nitrogen and phosphorus in aniline-containing wastewater treatment by using sequencing batch reactor. Bioresour. Technol. 2016, 207, 422–429. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Herrero, M.; Rovira, J.; Esplugas, R.; Nadal, M.; Domingo, J.L. Human exposure to trace elements, aromatic amines and formaldehyde in swimsuits: Assessment of the health risks. Environ. Res. 2020, 181, 108951. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, H.; Wang, J.; Abdel-Rahman, S.Z.; Boor, P.J.; Khan, M.F. Induction of base excision repair enzymes NTH1 and APE1 in rat spleen following aniline exposure. Toxicol. Appl. Pharmacol. 2013, 267, 276–283. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Mohanta, V.L.; Mishra, B.K. Integration of cancer and non-cancer human health risk assessment for Aniline enriched groundwater: A fuzzy inference system-based approach. Environ. Geochem. Health 2020, 42, 3623–3639. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zimmermann, T.; Ensinger, W.J.; Schmidt, T.C. In Situ Derivatization/Solid-Phase Microextraction: Determination of Polar Aromatic Amines. Anal. Chem. 2004, 76, 1028–1038. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schowanek, D.; Carr, R.; David, H.; Douben, P.; Hall, J.; Kirchmann, H. A risk-based methodology for deriving quality standards for organic contaminants in sewage sludge for use in agriculture–conceptual framework. Regulat. Toxicol. Pharmacol. 2004, 40, 227–251. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kouimtzis, T.; Papadoyannis, I.; Sofoniou, M. Determination of aminophenol isomers in water samples by extraction and thin-layer chromatography densitometry. Microchem. J. 1981, 26, 51–54. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Meiping, Z.; Xinxiang, Z.; Yuanzong, L. A New Spectrophometric M ethod for the De termination of Aniline in Environment Water Samples. Anal. Lett. 2000, 33, 3067. [Google Scholar]
- Zawadzka, A.; Gromadzinska, E. Analysis of Supercritical Thermohydrolysis of Aniline-Water Solution using Capillary Electrophoresis and HPLC: A Comparison. J. Liq. Chromatogr. Relat. Technol. 2005, 28, 847–855. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cardellicchio, N.; Cavalli, S.; Piangerelli, V.; Giandomenico, S.; Ragone, P. Determination of phenols in environmental samples by liquid chromatography—Electrochemistry. Anal. Bioanal. Chem. 1997, 358, 749–754. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abbasi, V.; Sarafraz-Yazdi, A.; Amiri, A.; Vatani, H. Determination of Aromatic Amines Using Solid-Phase Microextraction Based on an Ionic Liquid-Mediated Sol–Gel Technique. J. Chromatogr. Sci. 2016, 54, 677–681. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Young, A.; Lai, G.; Hung, B.; Yuen, A.; He, Y. Determination of Trace Chloroanilines in Environmental Water Samples Using Hollow Fiber-Based Liquid Phase Microextraction. Chromatographia 2011, 74, 83–88. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chiang, J.-S.; Huang, S.-D. Simultaneous derivatization and extraction of anilines in waste water with dispersive liquid-liquid microextraction followed by gas chromatography-mass spectrometric detection. Talanta 2008, 75, 70–75. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y.; Wu, W.J.; Zhou, W.E.; Ren, Z.Q.; Feng, X.S.; Zhang, F. Determination of 14 heterocyclic aromatic amines in meat products using solid-phase extraction and supercritical fluid chromatography coupled to triple quadrupole mass spectrometry. J. Sep. Sci. 2020, 43, 1372–1381. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, S.-P.; Huang, T.-H. Separation and determination of aminophenols and phenylenediamines by liquid chromatog-raphy and micellar electrokinetic capillary chromatography. Anal. Chim. Acta 2005, 534, 207–214. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cui, D.; Shen, D.; Wu, C.; Li, C.; Leng, D.; Zhao, M. Biodegradation of aniline by a novel bacterial mixed culture AC. Int. Biodeter. Biodegr. 2017, 125, 86–96. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Asthana, A.; Bose, D.; Durgbanshi, A.; Sanghi, S.; Kok, W. Determination of aromatic amines in water samples by capillary electrophoresis with electrochemical and fluorescence detection. J. Chromatogr. A 2000, 895, 197–203. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pace, C.M.; Donnelly, J.R.; Jeter, J.L.; Brumley, W.C.; Sovocool, G.W. Determination of aromatic amines in soils. J. AOAC Int. 1996, 79, 777–783. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Huang, X.; Qiu, N.; Yuan, D.; Lin, Q. Sensitive determination of strongly polar aromatic amines in water samples by stir bar sorptive extraction based on poly(vinylimidazole-divinylbenzene) monolithic material and liquid chromatographic analysis. J. Chromatogr. A 2009, 1216, 4354–4360. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Akyüz, M.; Ata, Ş. Simultaneous determination of aliphatic and aromatic amines in water and sediment samples by ion-pair extraction and gas chromatography-mass spectrometry. J. Chromatogr. A 2006, 1129, 88–94. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jurado-Sánchez, B.; Ballesteros, E.; Gallego, M. Comparison of microwave assisted, ultrasonic assisted and Soxhlet extrac-tions of N-nitrosamines and aromatic amines in sewage sludge, soils and sediments. Sci. Total Environ. 2013, 463, 293–301. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Luthria, D.; Vinjamoori, D.; Noel, K.; Ezzell, J. Accelerated Solvent Extraction, Oil Extraction and Analysis; AOCS Publishing: Urbana, IL, USA, 2019; pp. 25–38. [Google Scholar]
- Li, K.; Landriault, M.; Fingas, M.; Llompart, M. Accelerated solvent extraction (ASE) of environmental organic compounds in soils using a modified supercritical fluid extractor. J. Hazard. Mater. 2003, 102, 93–104. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Acter, T.; Cho, Y.; Kim, S.; Ahmed, A.; Kim, B.; Kim, S. Optimization and Application of APCI Hydrogen-Deuterium Exchange Mass Spectrometry (HDX MS) for the Speciation of Nitrogen Compounds. J. Am. Soc. Mass Spectrom. 2015, 26, 1522–1531. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Sun, H.; Ge, X.; Lv, Y.; Wang, A. Application of accelerated solvent extraction in the analysis of organic contaminants, bioactive and nutritional compounds in food and feed. J. Chromatogr. A 2012, 1237, 1–23. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Poole, C.F. Supercritical-fluid chromatography and supercritical-fluid extraction. J. Biochem. Biophys. Methods 2000, 43, 1–2. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Di Corcia, A.; Marchetti, M. Rapid and sensitive determination of phenylurea herbicides in water in the presence of their anilines by extraction with a Carbopack cartridge followed by liquid chromatography. J. Chromatogr. A 1991, 541, 365–373. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, Y.; Yang, K.; Shang, Y.; Zhang, H.; Wei, L.; Wang, H. Response and recovery of aerobic granular sludge to pH shock for simultaneous removal of aniline and nitrogen. Chemosphere 2019, 221, 366–374. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fasano, V.; Radcliffe, J.E.; Ingleson, M.J. Mechanistic Insights into the B(C6F5)3-Initiated Aldehyde-Aniline-Alkyne Reaction To Form Substituted Quinolines. Organometallics 2017, 36, 1623–1629. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Johnson, T.C.; Elbert, B.L.; Farley, A.J.M.; Gorman, T.W.; Genicot, C.; Lallemand, B.; Pasau, P.; Flasz, J.; Castro, J.L.; MacCoss, M.; et al. Direct sulfonylation of anilines mediated by visible light. Chem. Sci. 2017, 9, 629–633. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Shiraishi, Y.; Sakamoto, H.; Fujiwara, K.; Ichikawa, S.; Hirai, T. Selective photocatalytic oxidation of aniline to nitrosoben-zene by Pt nanoparticles supported on TiO2 under visible light irradiation. ACS Catal. 2014, 4, 2418–2425. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ni, K.; Meng, L.-G.; Wang, K.; Wang, L. Visible-Light-Promoted Oxidative Amidation of Bromoalkynes with Anilines: An Approach to α-Ketoamides. Org. Lett. 2018, 20, 2245–2248. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Riedel, T.; Dittmar, T. A Method Detection Limit for the Analysis of Natural Organic Matter via Fourier Transform Ion Cyclotron Resonance Mass Spectrometry. Anal. Chem. 2014, 86, 8376–8382. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Z.; Li, R. Method validation for the determination of aniline and 3,3′-dichlorobenzidine by gas chromatog-raphy-mass spectrometry. IOP Conf. Ser. Earth Environ. Sci. 2021, 769, 022026. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Teng, J.; Yang, J.; Lin, S.; Cheng, Y.X.; He, X.U. Determination of aniline and nitrobenzene compounds in fertilizers by gas chromatography-mass spectrometry. Chin. J. Anal. Lab. 2019, 38, 939–944. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]








| Extraction Conditions | Measurement Result (mg kg−1) | Average (mg kg−1) | Standard Recovery Rate (%) | Standard Deviation (mg kg−1) | Relative Standard Deviation (%) | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | 2 | 3 | 4 | 5 | 6 | |||||
| 105 °C, 60% of cell volume | 0.338 | 0.354 | 0.352 | 0.347 | 0.342 | 0.349 | 0.347 | 69.4 | 0.008 | 2.4 |
| 100 °C, 40% of cell volume | 0.365 | 0.351 | 0.356 | 0.347 | 0.367 | 0.364 | 0.358 | 71.6 | 0.008 | 2.3 |
| Aniline Concentration (mg kg−1) | Measurement Result (mg kg−1) | Average (mg kg−1) | Standard Deviation (mg kg−1) | The Limit of Detection (mg kg−1) | The Limit of Quantitation (mg kg−1) | ||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | 2 | 3 | 4 | 5 | 6 | 7 | |||||
| 0.05 | 0.048 | 0.046 | 0.045 | 0.044 | 0.046 | 0.042 | 0.044 | 0.045 | 0.002 | 0.01 | 0.04 |
| Aniline Concentration (mg kg−1) | Measurement Result (mg kg−1) | Average (mg kg−1) | Standard Recovery Rate (%) | Standard Deviation (mg kg−1) | Relative Standard Deviation (%) | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | 2 | 3 | 4 | 5 | 6 | |||||
| 0.05 | 0.048 | 0.045 | 0.046 | 0.044 | 0.047 | 0.042 | 0.0453 | 90.6 | 0.002 | 4.8 |
| 0.10 | 0.087 | 0.079 | 0.085 | 0.083 | 0.094 | 0.094 | 0.0870 | 87.0 | 0.006 | 6.9 |
| 0.20 | 0.196 | 0.191 | 0.189 | 0.187 | 0.185 | 0.189 | 0.1895 | 94.8 | 0.004 | 2.0 |
| Aniline Concentration (mg kg−1) | Measurement Result (mg kg−1) | Average (mg kg−1) | Standard Recovery Rate (%) | Standard Deviation (mg kg−1) | Relative Standard Deviation (%) | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | 2 | 3 | 4 | 5 | 6 | |||||
| 0.05 | 0.047 | 0.043 | 0.049 | 0.045 | 0.043 | 0.044 | 0.0452 | 90.4 | 0.002 | 5.3 |
| 0.10 | 0.085 | 0.089 | 0.095 | 0.087 | 0.076 | 0.082 | 0.0857 | 85.7 | 0.006 | 7.5 |
| 0.20 | 0.184 | 0.177 | 0.183 | 0.169 | 0.177 | 0.182 | 0.1787 | 89.3 | 0.006 | 3.1 |
| Method | Standard Recovery Rate (%) | Relative Standard Deviation (%) | Limit of Quantitation (mg kg−1) | Ref. |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Microwave assisted extraction/GC-MS | 94–96 | 5.8–6.5 | 0.04 | [25] |
| Soxhlet extractions/GC-MS | 64.5–83.9 | 2.5~16.9 | 0.2 | [38] |
| Ultrasonic Extraction/GC-MS | 67.7~96.9 | 3.24~10.2 | 0.006 | [39] |
| Accelerated solvent extraction/GC-MS | 76–98 | 2.0–7.5 | 0.04 | this study |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Shi, Y.; Zhang, K. Determination of Aniline in Soil by ASE/GC-MS. Molecules 2022, 27, 2092. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules27072092
Shi Y, Zhang K. Determination of Aniline in Soil by ASE/GC-MS. Molecules. 2022; 27(7):2092. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules27072092
Chicago/Turabian StyleShi, Yongli, and Kai Zhang. 2022. "Determination of Aniline in Soil by ASE/GC-MS" Molecules 27, no. 7: 2092. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules27072092
APA StyleShi, Y., & Zhang, K. (2022). Determination of Aniline in Soil by ASE/GC-MS. Molecules, 27(7), 2092. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules27072092