The Fate and Intermediary Metabolism of Soyasapogenol in the Rat
Abstract
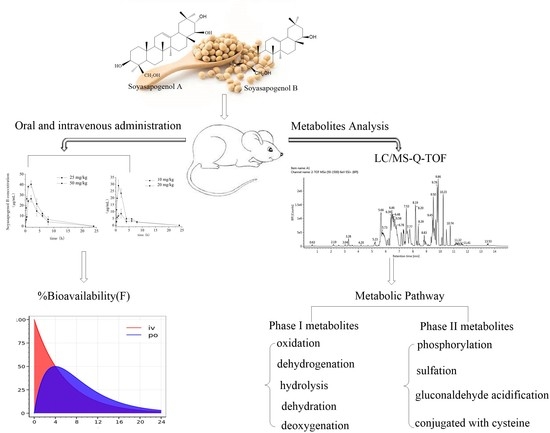
:1. Introduction
2. Results and Discussion
2.1. Optimization of the UPLC–Q-TOF–MS/MS Method
2.2. Comparison of Plasma Soyasapogenol Concentrations in Rats after Soyasapogenol Intake
2.2.1. Pharmacokinetics of Oral Administration
2.2.2. Pharmacokinetics of Intravenous Injection
2.3. Bioavailability of Soyasapogenols
2.4. Identification of Liver Metabolites of Soyasapogenols
2.4.1. Metabolite Identification and Metabolic Characteristic Elucidation of Soyasapogenol A
2.4.2. Metabolite Identification and Metabolic Characteristic Elucidation of Soyasapogenol B
2.5. Metabolic Pathway of Soyasapogenols In Vivo
3. Materials and Methods
3.1. Chemicals and Reagents
3.2. Preparation of Soyasapogenol Standard Solution
3.3. Preparation and Application of Dosing Solutions
3.4. Animals
3.5. Metabolic Kinetics and Bile Metabolism Experiment of Soyasapogenols
3.5.1. Oral Administration
3.5.2. Intravenous Injection Experiment
3.5.3. Perfusion of the Small Intestine
3.6. Processing and Analysis of Plasma Samples
3.7. Processing and Analysis of Bile Samples
3.8. Instrumentation and LC–MS/MS Analytical Conditions
3.9. Mass Spectrometry Analysis Using Xevo G2-XS QTOF Instrument
3.10. Data Processing
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
Sample Availability
References
- Zhang, W.; Popovich, D.G. Chemical and Biological Characterization of Oleanane Triterpenoids from Soy. Molecules 2009, 14, 2959–2975. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Zhao, D.Y. Challenges associated with elucidating the mechanisms of the hypocholesterolaemic activity of saponins. J. Funct. Foods 2016, 23, 52–65. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guang, C.; Chen, J.; Sang, S.; Cheng, S. Biological Functionality of Soyasaponins and Soyasapogenols. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2014, 62, 8247–8255. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhou, Y.F.; Farooqi, A.A.; Xu, B.J. Comprehensive review on signaling pathways of dietary saponins in cancer cells suppression. Crit. Rev. Food Sci. Nutr. 2021, 1–26. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kamo, S.; Suzuki, S.; Sato, T. Comparison of bioavailability (I) between soyasaponins and soyasapogenols, and (II) between group A and B soyasaponins. Nutrition 2014, 30, 596–601. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Navarro del Hierro, J.; Herrera, T.; Fornari, T.; Reglero, G.; Martin, D. The gastrointestinal behavior of saponins and its significance for their bioavailability and bioactivities. J. Funct. Foods 2018, 40, 484–497. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Neacsu, M.; Raikos, V.; Benavides-Paz, Y.; Duncan, S.H.; Duncan, G.J.; Christie, J.S.; Johnstone, A.M.; Russell, W.R. Sapogenol is a Major Microbial Metabolite in Human Plasma Associated with High Protein Soy-Based Diets: The Relevance for Functional Food Formulations. Foods 2020, 9, 422. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Gao, S.; Basu, S.; Yang, Z.; Deb, A.; Hu, M. Bioavailability Challenges Associated with Development of Saponins As Therapeutic and Chemopreventive Agents. Curr. Drug Targets 2012, 13, 1885–1899. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kang, J.; Badger, T.M.; Ronis, M.J.J.; Wu, X.L. Non-isoflavone Phytochemicals in Soy and Their Health Effects. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2010, 58, 8119–8133. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, W.; Popovich, D.G. Effect of Soyasapogenol A and Soyasapogenol B Concentrated Extracts on Hep-G2 Cell Proliferation and Apoptosis. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2008, 56, 2603–2608. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oleszek, M.; Oleszek, W. Saponins in Food; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2020. [Google Scholar]
- Furtado, N.A.J.C.; Pirson, L.; Edelberg, H.; Miranda, L.M.; Loira-Pastoriza, C.; Preat, V.; Larondelle, Y.; André, C.M. Pentacyclic Triterpene Bioavailability: An Overview of In Vitro and In Vivo Studies. Molecules 2017, 22, 400. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Chen, Y.H.; Bi, J.H.; Xie, M.; Zhang, H.; Shi, Z.Q.; Guo, H.; Yin, H.B.; Zhang, J.N.; Xin, G.Z.; Song, H.P. Classification-based strategies to simplify complex traditional Chinese medicine (TCM) researches through liquid chromatography-mass spectrometry in the last decade (2011–2020): Theory, technical route and difficulty. J. Chromatogr. A 2021, 1651, 462307. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mao, Q.; Xu, J.D.; Kong, M.; Shen, H.; Zhu, H.; Zhou, S.S.; Li, S.L. LC-MS-based Metabolomics in Traditional Chinese Medicines Research: Personal Experiences. Chin. Herb. Med. 2017, 9, 14–21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gao, X.; Li, Y.; Meng, M.; Wang, P.; Feng, Y.; Jia, J.; Qin, X. Exploration of chemical composition and absorption characteristics of Chaigui granules based on UHPLC-Q-orbitrap-MS/MS. J. Pharm. Biomed. Anal. 2020, 187, 113293. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dong, G.M.; Yu, H.; Pan, L.B.; Ma, S.R.; Xu, H.; Zhang, Z.W.; Han, P.; Fu, J.; Yang, X.Y.; Keranmu, A.; et al. Biotransformation of Timosaponin BII into Seven Characteristic Metabolites by the Gut Microbiota. Molecules 2021, 26, 3861. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Farag, M.A.; Porzel, A.; Wessjohann, L.A. Comparative metabolite profiling and fingerprinting of medicinal licorice roots using a multiplex approach of GC-MS, LC-MS and 1D NMR techniques. Phytochemistry 2012, 76, 60–72. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pan, C.H.; Qi, D.Y.; Zhao, D.Y. Determination of Soyasapogenols Absorption Characteristics in Rat Gut Using in Situ Single-pass Intestinal Perfusion Model. Sci. Technol. Food Ind. (Chin.) 2021, 42, 336–342. [Google Scholar]
- Guo, X.; Cheng, M.; Hu, P.; Shi, Z.; Chen, S.; Liu, H.; Shi, H.; Xu, Z.; Tian, X.; Huang, C. Absorption, Metabolism, and Pharmacokinetics Profiles of Norathyriol, an Aglycone of Mangiferin, in Rats by HPLC-MS/MS. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2018, 66, 12227–12235. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Singh, D.; Chaudhuri, P.K. Structural characteristics, bioavailability and cardioprotective potential of saponins. Integr. Med. Res. 2018, 7, 33–43. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, K.; Chen, F.; Li, C. Absorption, Disposition, and Pharmacokinetics of Saponins from Chinese Medicinal Herbs: What Do We Know and What Do We Need to Know More? Curr. Drug Metab. 2012, 13, 577–598. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, T.; Li, S.; Sun, Y.; Pi, Z.; Liu, S.; Song, F.; Liu, Z. Systematically characterize the absorbed effective substances of Wutou Decoction and their metabolic pathways in rat plasma using UHPLC-Q-TOF-MS combined with a target network pharmacological analysis. J. Pharm. Biomed. Anal. 2017, 141, 95–107. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ghosh, J.; Das, J.; Manna, P.; Sil, P.C. Arjunolic acid, a triterpenoid saponin, prevents acetaminophen (APAP)-induced liver and hepatocyte injury via the inhibition of APAP bioactivation and JNK-mediated mitochondrial protection. Free. Radic. Biol. Med. 2010, 48, 535–553. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- He, C.; Zhou, D.; Li, J.; Han, H.; Ji, G.; Yang, L.; Wang, Z. Identification of 20(S)-protopanaxatriol metabolites in rats by ultra-performance liquid chromatography coupled with electrospray ionization quadrupole time-of-flight tandem mass spectrometry and nuclear magnetic resonance spectroscopy. J. Pharm. Biomed. Anal. 2014, 88, 497–508. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pan, C.H.; Qi, D.Y.; Zhao, D.Y. Isolation and purification of soyasapogenol A and B starting from soy hypocotyls: High-speed counter-current chromatography versus preparative high-performance liquid chromatography. J. Liq. Chromatogr. Relat. Technol. 2021, 44, 103–113. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]





| Parameter | Unit | Soyasapogenol A | Soyasapogenol B | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 10 mg/kg | 20 mg/kg | 25 mg/kg | 50 mg/kg | ||
| AUC(0-t) | mg/L*h | 35.198 | 88.619 | 96.029 | 157.218 |
| AUC(0-∞) | mg/L*h | 50.700 | 95.507 | 110.513 | 178.341 |
| T1/2z | h | 2.552 | 1.966 | 2.288 | 2.266 |
| Tmax | h | 2 | 1 | 2 | 2 |
| CLz/F | L/h/kg | 0.394 | 0.209 | 0.181 | 0.112 |
| Cmax | mg/L | 8.59 | 28.99 | 26.37 | 40.29 |
| Ratio of B/A in test sample | - | 2.5 | 2.5 | ||
| Ratio of B/A in plasma level (AUC) | - | 2.17 | 1.87 | ||
| Bioavailability (F,%) | 73.10 | 67.34 | 60.94 | 69.01 | |
| Parameter | Unit | Soyasapogenol A | Soyasapogenol B | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 10 mg/kg | 20 mg/kg | 25 mg/kg | 50 mg/kg | ||
| AUC(0-t) | mg/L*h | 56.029 | 114.473 | 76.214 | 154.392 |
| AUC(0-∞) | mg/L*h | 69.355 | 141.82 | 181.347 | 258.42 |
| T1/2z | h | 3.535 | 3.475 | 5.138 | 5.528 |
| Tmax | h | 0.03 | 0.03 | 0.03 | 0.03 |
| CLz/F | L/h/kg | 0.288 | 0.141 | 0.246 | 0.077 |
| Cmax | mg/L | 31.7 | 101.65 | 43.26 | 66.85 |
| The Serial Number | Metabolites | Molecular Formula | [M + H]+ m/z | Retention Time (min) | Fragment Ion Information | Metabolic Pathways |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| M0 | Soyasapogenol A | C30H50O4 | 475.3803 | 10.28 | 185.1321, 283.2627, 333.2782, 337.2521 | Prototype |
| M2 | Soyasapogenol A–H2O | C30H48O3 | 457.3678 | 9.92 | 166.2149, 187.1435, 403.2801 | Dehydration |
| M3 | Soyasapogenol A–O | C30H50O3 | 459.3831 | 10.36 | 190.2349, 320.2433, 408.2959 | Deoxidation |
| M4 | Soyasapogenol A + H2O + C5H7NO3S | C35H59NO8S | 654.4005 | 9.24 | 117.0907, 292.1592, 462.2684, 534.3287 | Hydrolysis + with acetylcysteine |
| M5 | Soyasapogenol A + O | C30H50O5 | 491.3742 | 9.73 | 129.1607, 255.3044, 273.2602, 347.3641 | Oxidation |
| M6 | Soyasapogenol A + H2 | C30H52O4 | 477.3931 | 11.04 | 273.1810, 315.2651, 359.2912 | Reduction |
| M7 | Soyasapogenol A + C5H7NO3S | C35H57NO7S | 636.3946 | 7.29 | 193.1584, 253.1942, 460.2505, 478.2607 | Binding to acetylcysteine |
| Soyasapogenol A–H2O + C3H5NOS | C33H53NO4S | 560.3784 | 9.34 | 375.3043, 393.3139, 439.2520 | Dehydration + binding to cysteine | |
| M8 | Soyasapogenol A–H2O + C3H5NO2S | C33H53NO5S | 576.3732 | 7.63 | 119.0851, 285.2203, 306.1489, 522.2855 | Dehydration + with cysteine sulfhydryl group |
| M9 | Soyasapogenol A–H2O + C5H7NO3S | C35H55NO6S | 618.3851 | 7.24 | 255.2099, 357.2779, 423.3239, 462.2661 | Dehydration + binding with acetylcysteine |
| M10 | Soyasapogenol A–O–H2O + C3H5NOS | C33H53NO3S | 544.3844 | 9.73 | 273.2208, 485.2630 | Deoxidation + dehydration + binding to cysteine |
| M11 | Soyasapogenol A–O + C5H7NO3S | C35H57NO6S | 620.4007 | 8.42 | 141.1271, 340.1576, 365.2829 | Deoxidation + binding to acetylcysteine |
| M12 | Soyasapogenol A + O + C5H8N2O3S | C35H58N2O8S | 667.3980 | 9.92 | 337.2521, 459.2476, 565.3347, 609.3608 | Oxidation + binding to cysteinylglycine mercapto |
| M13 | Soyasapogenol A + O + C3H5NO2S | C33H55NO7S | 610.3754 | 9.26 | 89.0595, 133.0857, 247.2050, 333.2428 | Oxidation + binding to cysteine sulfhydryl groups |
| M14 | Soyasapogenol A + O + SO3 | C30H50O8S | 571.3298 | 8.73 | 209.1163, 277.2159, 335.2600, 427.3197 | Oxidation + sulfation |
| M15 | Soyasapogenol A + H2 + C6H8O6 | C36H60O10 | 653.4253 | 9.68 | 449.2132, 491.2973, 535.3234, 579.3498 | Reduction + gluconaldehyde acidification |
| M16 | Soyasapogenol A + H2 + HPO3 | C30H53O7P | 557.3606 | 9.20 | 124.9994, 291.2311, 339.1717 | Reduction + phosphorylation |
| The Serial Number | Metabolites | Molecular Formula | [M + H]+ m/z | Retention Time (min) | Fragment Ion Information | Metabolic Pathways |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| M0 | Soyasapogenol B | C30H50O3 | 459.3838 | 10.94 | 163.1106, 283.2627, 401.2284, 429.3716 | Prototype |
| M1 | Soyasapogenol B + H2O | C30H52O4 | 477.3926 | 11.04 | 185.1252, 342.2854, 370.3192 | Hydrolysis |
| M2 | Soyasapogenol B–H2O + C3H5NOS | C33H53NO3S | 544.3848 | 9.81 | 199.1472, 239.2363, 515.3103 | Dehydration + binding to cysteine |
| M3 | Soyasapogenol B + H2O + HPO3 | C30H53O7P | 557.3601 | 9.19 | 139.1112, 253.1939, 413.3035, 507.2914 | Hydrolysis + phosphorylation |
| M4-1 | Soyasapogenol B–H2 + C3H5NOS | C33H53NO4S | 560.3759 | 9.06 | 89.0596, 149.0956, 411.2872, 465.3320 | Dehydrogenation + binding to cysteine |
| M4-2 | Soyasapogenol B–H2O + C3H5NO2S | C33H53NO4S | 560.3778 | 9.34 | 145.1008, 199.1474, 427.3192, 490.2986 | Dehydration + with cysteine sulfhydryl group |
| M5-1 | Soyasapogenol B + O-H2 + C3H5NOS | C33H53NO5S | 576.3734 | 7.84 | 133.0857, 273.2206, 481.2611, 525.2875 | Oxidation + dehydrogenation + binding to cysteine |
| M5-2 | Soyasapogenol B–H2 + C3H5NO2S | C33H53NO5S | 576.3734 | 8.41 | 215.1785, 339.2672, 409.3090, 488.2865 | Dehydrogenation + binding to the thiol group of cysteine |
| M6-1 | Soyasapogenol B–H2 + O2 + C3H5NOS | C33H53NO6S | 592.3690 | 6.21 | 121.0644, 179.1064, 351.2526, 427.2812 | Dehydrogenation + deoxidation + binding to cysteine |
| M6-2 | Soyasapogenol B + O–H2 + C3H5NO2S | C33H53NO6S | 592.3692 | 8.29 | 152.0374, 337.2518, 462.2663, 480.2770 | Oxidation + dehydrogenation + binding to cysteine sulfhydryl groups |
| M7 | Soyasapogenol B–O + C5H7NO3S | C35H57NO5S | 604.4046 | 9.33 | 149.0956, 231.1738, 275.1996, 526.2961 | Deoxidation + binding to acetylcysteine |
| M8 | Soyasapogenol B–H2 + C5H7NO3S | C35H59NO5S | 606.4217 | 7.76 | 103.0749, 276.1252, 339.2673, 464.2819 | Deoxidation + reduction + binding to acetylcysteine |
| M9 | Soyasapogenol B–O + H2 + C5H7NO3S | C35H55NO6S | 618.3843 | 7.23 | 163.1113, 243.2094, 393.2793, 502.2581 | Dehydrogenation + combining with cysteinylglycine mercapto |
| M10 | Soyasapogenol B + C5H7NO3S | C35H57NO6S | 620.3997 | 7.66 | 261.1839, 357.2776 | Binding to acetylcysteine |
| M11 | Soyasapogenol B–H2 + C5H8N2O3S | C35H56N2O6S | 633.3940 | 9.04 | 89.0594, 287.1460, 407.2023, 520.3314 | Dehydrogenation + binding to acetylcysteine |
| M12 | Soyasapogenol B + O–H2 + C5H7NO3S | C35H55NO7S | 634.3794 | 6.43 | 215.1424, 355.2622, 480.2767, 503.3029 | Oxidation + dehydrogenation + gluconaldehyde acidification |
| M13 | Soyasapogenol B + O + C5H7NO3S | C35H57NO7S | 636.3899 | 7.29 | 133.0853, 210.0425, 289.2152, 462.2657 | Oxidation + gluconaldehyde acidification |
| M14 | Soyasapogenol B–H2 + O2 + C5H7NO3S | C35H55NO8S | 650.3738 | 6.86 | 97.0643, 205.1216, 353.2458, 522.2850 | Dehydrogenation + deoxidation + gluconaldehyde acidification |
| M15 | Soyasapogenol B + H2O + C6H8O6 | C36H60O10 | 653.4280 | 9.68 | 221.2259, 361.1606, 518.3208, 546.3546 | Hydrolysis + gluconaldehyde acidification |
| Treatments | Bulk Solution | Soyasapogenol Composition | Low Dosage | High Dosage | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Dose (μ mol/kg BW) | Dose (mg/kg BW) | Dose (μ mol/kg BW) | Dose (mg/kg BW) | |||
| Oral administration (P.O.) | 0.5% (w/v) sodium carboxymethyl cellulose solution used as a vehicle | A | 21 | 10 | 42 | 20 |
| B | 55 | 25 | 109 | 50 | ||
| Intravenous injection (I.V.) | 0.5% (w/v) sodium carboxymethyl cellulose solution used as a vehicle | A | 21 | 10 | 42 | 20 |
| B | 55 | 25 | 109 | 50 | ||
| Perfusion of the small intestine | Krebs–Ringer bicarbonate buffer | A(B) | 10 mg/L(50 mg/L) | |||
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Pan, C.; Yan, Y.; Zhao, D. The Fate and Intermediary Metabolism of Soyasapogenol in the Rat. Molecules 2023, 28, 284. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules28010284
Pan C, Yan Y, Zhao D. The Fate and Intermediary Metabolism of Soyasapogenol in the Rat. Molecules. 2023; 28(1):284. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules28010284
Chicago/Turabian StylePan, Chenghui, Yonggang Yan, and Dayun Zhao. 2023. "The Fate and Intermediary Metabolism of Soyasapogenol in the Rat" Molecules 28, no. 1: 284. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules28010284
APA StylePan, C., Yan, Y., & Zhao, D. (2023). The Fate and Intermediary Metabolism of Soyasapogenol in the Rat. Molecules, 28(1), 284. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules28010284