Thermodynamic and Kinetic Investigation of the Adsorption and Desorption of Trimethoprim and Its Main Metabolites in Mediterranean Crop Soils
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Results and Discussion
2.1. Preliminary Experiments
2.2. Adsorption Kinetics
2.3. ATR FT-IR Characterization
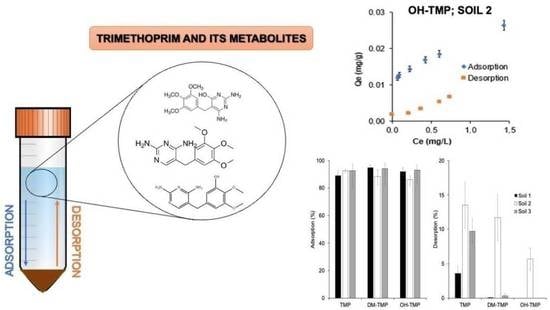
2.4. Adsorption Isotherms
2.5. Desorption Isotherms
2.6. Influence of Compounds Properties and Physicochemical Characteristics of the Soils on Compound Adsorption–Desorption Behavior
3. Materials and Methods
3.1. Chemicals and Reagents, Sampling, and Soil Preparation
3.2. Soil Characterization
3.3. Batch Experiments
3.3.1. Soil/Solution Ratio Optimization
3.3.2. Adsorption Kinetic
3.3.3. Adsorption Isotherms
3.3.4. Desorption Isotherms
3.4. Soil FT-IR Analysis
3.5. LC-MS/MS Analysis
3.6. Data and Statistical Analyses
4. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
Sample Availability
References
- Franklin, A.M.; Clinton, W.; Andrews, D.M.; Watson, J.E. Sorption and Desorption Behavior of Four Antibiotics at Concentrations Simulating Wastewater Reuse in Agricultural and Forested Soils. Chemosphere 2022, 289, 133038. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gbadegesin, L.A.; Tang, X.; Liu, C.; Cheng, J. Transport of Veterinary Antibiotics in Farmland Soil: Effects of Dissolved Organic Matter. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2022, 19, 1702. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Haenni, M.; Dagot, C.; Chesneau, O.; Bibbal, D.; Labanowski, J.; Vialette, M.; Bouchard, D.; Martin-Laurent, F.; Calsat, L.; Nazaret, S.; et al. Environmental contamination in a high-income country (France) by antibiotics, antibiotic-resistant bacteria, and antibiotic resistance genes: Status and possible causes. Environ. Int. 2022, 159, 107047. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y.; Cheng, D.; Xie, J.; Zhang, Y.; Wan, Y.; Zhang, Y.; Shi, X. Impacts of farmland application of antibiotic-contaminated manures on the occurrence of antibiotic residues and antibiotic resistance genes in soil: A meta-analysis study. Chemosphere 2022, 300, 134529. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Harrower, J.; McNaughtan, M.; Hunter, C.; Hough, R.; Zhang, Z.; Helwig, K. Chemical Fate and Partitioning Behavior of Antibiotics in the Aquatic Environment—A Review. Environ. Toxicol. Chem. 2021, 40, 3275–3298. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kuppusamy, S.; Kakarla, D.; Venkateswarlu, K.; Megharaj, M.; Yoon, Y.E.; Lee, Y.B. Veterinary antibiotics (VAs) contamination as a global agro-ecological issue: A critical view. Agric. Ecosyst. Environ. 2018, 257, 47–59. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mejías, C.; Martín, J.; Santos, J.L.; Aparicio, I.; Alonso, E. Occurrence of pharmaceuticals and their metabolites in sewage sludge and soil: A review on their distribution and environmental risk assessment. Trends Environ. Anal. Chem. 2021, 30, e00125. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Santos, J.L.; Martín, J.; Mejías, C.; Aparicio, I.; Alonso, E. Pharmaceuticals and Their Metabolites in Sewage Sludge and Soils: Distribution and Environmental Risk Assessment. In Emerging Pollutants in Sewage Sludge and Soils, 2nd ed.; Núñez-Delgado, A., Arias-Estévez, M., Eds.; The Handbook of Environmental Chemistry; Springer: Cham, Switzerland, 2022; Volume 114, pp. 19–34. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Goldman, J.L.; Leeder, J.S.; van Haandel, L.; Pearce, R.E. In vitro hepatic oxidative biotransformation of trimethoprim. Drug Metab. Dispos. 2015, 43, 1372–1380. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Zhang, C.; Barron, L.; Sturzenbaum, S. The transportation, transformation and (bio)accumulation of pharmaceuticals in the terrestrial ecosystem. Sci. Total Environ. 2021, 781, 146684. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, W.L.; Wu, Q.Y.; Huang, N.; Xu, Z.; Lee, M.Y.; Hu, H.Y. Potential risks from UV/H2O2 oxidation and UV photocatalysis: A review of toxic, assimilable, and sensory-unpleasant transformation products. Water Res. 2018, 141, 109–125. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Carter, L.J.; Harris, E.; Williams, M.; Ryan, J.J.; Kookana, R.S.; Boxall, A.B.A. Fate and uptake of pharmaceuticals in soil-plant systems. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2014, 62, 816–825. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shang, H.T.; Wang, J.L.; Wu, T.; Lin, J.; Mao, B.C. Adsorption of Naphthalene onto Loess Soil of Northwestern China. Energy Environ. 2020, 31, 1335–1349. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, J.; Zeng, J.; Mengchang, H.E. Effects of Temperature and Surfactants on Naphthalene and Phenanthrene Sorption by Soil. J. Environ. Sci. 2009, 21, 667–674. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- López-Piñeiro, A.; Peña, D.; Albarrán, A.; Becerra, D.; Sánchez-Llerena, J. Sorption, Leaching and Persistence of Metribuzin in Mediterranean Soils Amended with Olive Mill Waste of Different Degrees of Organic Matter Maturity. J. Environ. Manag. 2013, 122, 76–84. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sopeña, F.; Kirk, S.; Saran, S.; Gary, B. Assessing the Chemical and Biological Accessibility of the Herbicide Isoproturon in Soil Amended with Biochar. Chemosphere 2012, 88, 77–83. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Malvar, J.L.; Santos, J.L.; Martín, J.; Aparicio, I.; Alonso, E. Approach to the Dynamic of Carbamazepine and Its Main Metabolites in Soil Contamination through the Reuse of Wastewater and Sewage Sludge. Molecules 2020, 25, 5306. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Martín, J.; Mejías, C.; Santos, J.L.; Aparicio, I.; Alonso, E. Pharmaceuticals and Their Main Metabolites in Treated Sewage Sludge and Sludge-Amended Soil: Availability and Sorption Behavior. Molecules 2021, 26, 5910. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Paz, A.; Tadmor, G.; Malchi, T.; Blotevogel, J.; Borch, T.; Polubesova, T.; Chefetz, B. Fate of Carbamazepine, Its Metabolites, and Lamotrigine in Soils Irrigated with Reclaimed Wastewater: Sorption, Leaching and Plant Uptake. Chemosphere 2016, 160, 22–29. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wojsławski, J.; Białk-Bielińska, A.; Stepnowski, P.; Dołżonek, J. Leaching Behavior of Pharmaceuticals and Their Metabolites in the Soil Environment. Chemosphere 2019, 231, 269–275. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y.L.; Lin, S.S.; Dai, C.M.; Shi, L.; Zhou, X.F. Sorption-Desorption and Transport of Trimethoprim and Sulfonamide Antibiotics in Agricultural Soil: Effect of Soil Type, Dissolved Organic Matter, and PH. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2014, 21, 5827–5835. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, X.; Wang, J. A General Kinetic Model for Adsorption: Theoretical Analysis and Modeling. J. Mol. Liq. 2019, 288, 111100. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xiang, L.; Wang, X.D.; Chen, X.H.; Mo, C.H.; Li, Y.W.; Li, H.; Cai, Q.Y.; Zhou, D.M.; Wong, M.H.; Li, Q.X. Sorption Mechanism, Kinetics, and Isotherms of Di- n-Butyl Phthalate to Different Soil Particle-Size Fractions. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2019, 67, 4734–4745. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kočárek, M.; Kodesova, R.; Vondrackova, L.; Golovko, O.; Fér, M.; Klement, A.; Nikodem, A.; Jaksik, O.; Grabic, R. Simultaneous Sorption of Four Ionizable Pharmaceuticals in Different Horizons of Three Soil Types. Environ. Pollut. 2016, 218, 563–573. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lin, K.; Gan, J. Sorption and Degradation of Wastewater-Associated Non-Steroidal Anti-Inflammatory Drugs and Antibiotics in Soils. Chemosphere 2011, 83, 240–246. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- OECD. Adsorption-Desorption Using a Batch Equilibrium Method. In OECD Guideline for the Testing of Chemicals; Organization for Economic Cooperation and Development: Paris, France, 2000; Volume 106. [Google Scholar]
- Baldermann, A.; Stamm, F.M. Effect of kinetics, pH, aqueous speciation and presence of ferrihydrite on vanadium (V) uptake by allophanic and smectitic clays. Chem. Geol. 2022, 607, 121022. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, X.; Wang, J. Comparison of Linearization Methods for Modeling the Langmuir Adsorption Isotherm. J. Mol. Liq. 2019, 296, 111850. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marco-Brown, J.L.; Guz, L.; Olivelli, M.S.; Schampera, B.; Torres-Sánchez, R.M.; Curutchet, G.; Candal, R. New Insights on Crystal Violet Dye Adsorption on Montmorillonite: Kinetics and Surface Complexes Studies. Chem. Eng. J. 2018, 333, 495–504. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, Q.; Yang, L. The Adsorption of Basic Dyes from Aqueous Solution on Modified Peat-Resin Particle. Water Res. 2003, 37, 1535–1544. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, F.C.; Tseng, R.L.; Juang, R.S. Initial Behavior of Intraparticle Diffusion Model Used in the Description of Adsorption Kinetics. Chem. Eng. J. 2009, 153, 1–8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mutavdžić Pavlović, D.; Tolić Čop, K.; Barbir, V.; Gotovuša, M.; Lukač, I.; Lozančić, A.; Runje, M. Sorption of cefdinir, memantine, praziquantel and trimethoprim in sediment and soil samples. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2022, 29, 66841–66857. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mutavdžić Pavlović, D.; Tolić Čop, K.; Prskalo, H.; Runje, M. Influence of Organic Matter on the Sorption of Cefdinir, Memantine and Praziquantel on Different Soil and Sediment Samples. Molecules 2022, 27, 8008. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, X.-T.; Yu, P.-F.; Xiang, L.; Zhao, H.-M.; Li, Y.-W.; Li, H.; Zhang, X.-Y.; Cai, Q.-Y.; Mo, C.-H.; Wong, M.-H. Dynamics, thermodynamics, and mechanism of perfluorooctane sulfonate (PFOS) sorption to various soil particle-size fractions of paddy soil. Ecotox. Environ. Saf. 2020, 206, 111105. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, Y.; van Zwieten, L.; Wang, H.; Wang, L.; Li, R.; Qu, J.; Zhang, Y. Sorption of Pb(II) onto Biochar Is Enhanced through Co-Sorption of Dissolved Organic Matter. Sci. Total Environ. 2022, 825, 153686. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rodríguez-López, L.; Santás-Miguel, V.; Cela-Dablanca, R.; Núñez-Delgado, A.; Álvarez-Rodríguez, E.; Pérez-Rodríguez, P.; Arias-Estévez, M. Ciprofloxacin and trimethoprim adsorption/desorption in agricultural soils. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2022, 19, 8426. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mejías, C.; Martín, J.; Santos, J.L.; Aparicio, I.; Sánchez, M.I.; Alonso, E. Development and Validation of a Highly Effective Analytical Method for the Evaluation of the Exposure of Migratory Birds to Antibiotics and Their Metabolites by Faeces Analysis. Anal. Bioanal. Chem. 2022, 414, 3373–3386. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chemical BooK. Sourcing and Integrating Center of Chemicals Materials in China. Available online: https://www.chemicalbook.com/ (accessed on 21 September 2022).
- DrugBank Online. Database for Drug and Drug Target Info. Available online: https://go.drugbank.com/ (accessed on 21 September 2022).
- Lee, H.J.; Kim, D.W.; Chung, E.G. Strong links between load and manure and a comprehensive risk assessment of veterinary antibiotics with low KOW in intensive livestock farming watersheds. Chemosphere 2021, 279, 130902. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]




| Compound | C0 (mg/g) | PFO Model | PSO Model | IPD Model | |||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| R2 | qe, cal (mg/g) | k1 | R2 | k2 | qe, cal (mg/g) | R2,1 | kip,1 | C1 (mg/g) | R2,2 | kip,2 | C2 (mg/g) | ||
| TMP | 0.0881 | 0.9496 | 7.96 × 10−5 | 0.0041 | 0.9999 | 308 | 0.00197 | 0.9768 | 3.0 × 10−5 | 0.0017 | 0.9821 | 1.0 × 10−6 | 0.0019 |
| OH-TMP | 0.1125 | 0.4738 | 9.71 × 10−5 | 0.0039 | 0.9999 | 264 | 0.00206 | 0.9733 | 4.0 × 10−5 | 0.0017 | 0.9288 | 1.0 × 10−6 | 0.0020 |
| DM-TMP | 0.1230 | 0.8159 | 2.09 × 10−4 | 0.0027 | 0.9999 | 97 | 0.00203 | 0.9957 | 4.0 × 10−5 | 0.0016 | 0.9853 | 5.0 × 10−6 | 0.0018 |
| Adsorption | Desorption | |||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Soil | Model | Parameter | TMP | DM-TMP | OH-TMP | TMP | DM-TMP | OH-TMP |
| Soil 1 | Linear | Kd (L/g) | 0.014 | 0.024 | 0.024 | 0.024 | 0.880 | - |
| R2 | 0.996 | 0.970 | 0.970 | 0.929 | 0.968 | - | ||
| Langmuir | qmax (mg/g) | 0.051 | 0.076 | 0.076 | 0.187 | 0.044 | - | |
| KL (L/g) | 0.461 | 0.560 | 0.560 | 0.224 | 33.51 | - | ||
| R2 | 0.993 | 0.920 | 0.876 | 0.908 | 0.980 | - | ||
| Freundlich | KF (L/g) | 0.016 | 0.024 | 0.024 | 0.056 | 0.268 | - | |
| n | 0.778 | 0.634 | 0.634 | 1.320 | 0.702 | - | ||
| R2 | 0.997 | 0.995 | 0.979 | 0.954 | 0.993 | - | ||
| Soil 2 | Linear | Kd (L/g) | 0.024 | 0.010 | 0.010 | 0.010 | 0.012 | 0.007 |
| R2 | 0.975 | 0.991 | 0.991 | 0.971 | 0.989 | 0.955 | ||
| Langmuir | qmax (mg/g) | 0.068 | 0.035 | 0.024 | 0.036 | 0.032 | 0.031 | |
| KL (L/g) | 0.537 | 0.618 | 9.635 | 0.404 | 0.604 | 0.364 | ||
| R2 | 0.992 | 0.984 | 0.740 | 0.974 | 0.971 | 0.895 | ||
| Freundlich | KF (L/g) | 0.024 | 0.023 | 0.028 | 0.011 | 0.023 | 0.009 | |
| n | 0.790 | 0.277 | 0.489 | 0.807 | 0.277 | 0.904 | ||
| R2 | 0.990 | 0.954 | 0.721 | 0.979 | 0.954 | 0.896 | ||
| Soil 3 | Linear | Kd (L/g) | 0.007 | 0.008 | 0.008 | 0.019 | 0.204 | - |
| R2 | 0.717 | 0.734 | 0.734 | 0.996 | 0.800 | - | ||
| Langmuir | qmax (mg/g) | 0.018 | 0.018 | 0.028 | 0.090 | 0.018 | - | |
| KL (L/g) | 5.346 | 6.782 | 17.07 | 0.258 | 158.4 | - | ||
| R2 | 0.857 | 0.882 | 0.928 | 0.987 | 0.982 | - | ||
| Freundlich | KF (L/g) | 0.013 | 0.015 | 0.025 | 0.019 | 0.046 | - | |
| n | 0.368 | 0.364 | 0.190 | 0.909 | 0.361 | - | ||
| R2 | 0.791 | 0.810 | 0.833 | 0.991 | 0.954 | - | ||
| Soil 1 | Soil 2 | Soil 3 | |
|---|---|---|---|
| Silt, wt. % | 44.5 | 5.80 | 18.4 |
| Clay, wt. % | 30.8 | 19.9 | 16.0 |
| Fine sand, wt. % | 16.4 | 4.70 | 14.0 |
| Coarse sand, wt. % | 8.20 | 69.5 | 51.6 |
| Electrical conductivity, mS·cm−1 | 129 | 75 | 126 |
| Organic matter, wt. % | 0.91 | 0.58 | 2.01 |
| CEC, meq kg−1 | 234 | 200 | 144 |
| Ca Exchangeable, meq kg−1 | 140 | 154 | 106 |
| Mg Exchangeable, meq kg−1 | 26.3 | 9.5 | 19.5 |
| K Exchangeable, meq kg−1 | 7.8 | 2.1 | 4.6 |
| Na Exchangeable, meq kg−1 | <0.5 | <0.5 | <0.5 |
| pH | 8.27 | 8.21 | 8.06 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Mejías, C.; Santos, J.L.; Martín, J.; Aparicio, I.; Alonso, E. Thermodynamic and Kinetic Investigation of the Adsorption and Desorption of Trimethoprim and Its Main Metabolites in Mediterranean Crop Soils. Molecules 2023, 28, 437. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules28010437
Mejías C, Santos JL, Martín J, Aparicio I, Alonso E. Thermodynamic and Kinetic Investigation of the Adsorption and Desorption of Trimethoprim and Its Main Metabolites in Mediterranean Crop Soils. Molecules. 2023; 28(1):437. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules28010437
Chicago/Turabian StyleMejías, Carmen, Juan Luis Santos, Julia Martín, Irene Aparicio, and Esteban Alonso. 2023. "Thermodynamic and Kinetic Investigation of the Adsorption and Desorption of Trimethoprim and Its Main Metabolites in Mediterranean Crop Soils" Molecules 28, no. 1: 437. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules28010437
APA StyleMejías, C., Santos, J. L., Martín, J., Aparicio, I., & Alonso, E. (2023). Thermodynamic and Kinetic Investigation of the Adsorption and Desorption of Trimethoprim and Its Main Metabolites in Mediterranean Crop Soils. Molecules, 28(1), 437. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules28010437