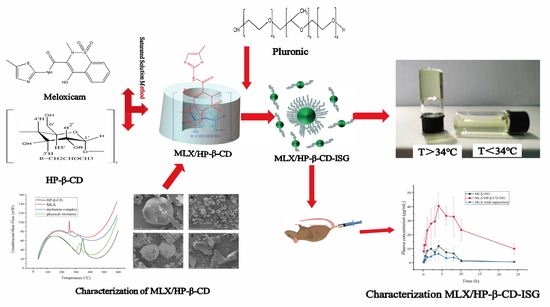
Preparation and In Vitro and In Vivo Evaluation of Rectal In Situ Gel of Meloxicam Hydroxypropyl-β-cyclodextrin Inclusion Complex
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Results and Discussion
2.1. Preparation of the Inclusion Complex of the MLX/HP-β-CD
2.2. Optimization of the Preparation Method of the MLX/HP-β-CD Complexes
2.3. Characterization of the MLX/HP-β-CD Inclusion Compounds
2.3.1. Solubility
2.3.2. Phase Solubility
2.3.3. Differential Scanning Calorimetry (DSC)
2.3.4. Scanning Electron Microscope (SEM)
2.3.5. Powder X-ray Diffraction (PXRD)
2.3.6. Fourier Transform Infrared Spectroscopy (FTIR)
2.4. Investigation of the Ratio of P407 and P188
2.5. Characterization of MLX/HP-β-CD-ISG
2.5.1. Measurement of the Gelation Temperature and Gelation Time
2.5.2. Measurement of the Gel Strength
2.5.3. Measurement of the Viscosity
2.5.4. Measurement of pH
2.5.5. Measurement of the Rheological Properties
2.5.6. Measurement of the Stability
2.6. In Vitro Drug Release Study
2.7. Pharmacokinetic Studies
2.8. Rectal Retention Test
2.9. Rat rectal Mucosal Irritation
3. Materials and Methods
3.1. Materials
3.2. Animals
3.3. Screening of the Preparation Methods of Inclusion Compounds
3.4. Optimization of the Preparation Method of the MLX/HP-β-CD Complexes
3.5. Characterization of the MLX/HP-β-CD Complexes
3.5.1. Solubility
3.5.2. Phase Solubility
3.5.3. Differential Scanning Calorimetry (DSC)
3.5.4. Scanning Electron Microscope (SEM)
3.5.5. Powder X-ray Diffraction (PXRD)
3.5.6. Fourier Transform Infrared Spectroscopy (FTIR)
3.6. Preparation of the Rectal In Situ Gel of MLX/HP-β-CD Inclusion Complex
3.6.1. Preparation of the In Situ Gel and Determination of the Gelation Temperature
3.6.2. Investigation of the Ratio of P407 and P188
3.6.3. Measurement of the Gelation Temperature and Gelation Time
3.6.4. Measurement of Gel Strength
3.6.5. Measurement of the Viscosity
3.6.6. Measurement of pH
3.6.7. Measurement of the Rheological Properties
3.6.8. Measurement of Stability
3.7. In Vitro Drug Release Study
3.8. Pharmacokinetic Study
3.8.1. HPLC Method
3.8.2. Grouping and Dosing
3.8.3. Collection and Treatment of the Plasma Samples
3.9. Rectal Retention Test
3.10. Rat Rectal Mucosal Irritation
3.11. Statistical Analysis
4. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
Sample Availability
References
- Rarokar, N.; Gurav, S.; Khedekar, P. Meloxicam encapsulated nanostructured colloidal self-assembly for evaluating antitumor and anti-inflammatory efficacy in 3D printed scaffolds. J. Biomed. Mater. Res. A 2021, 109, 1441–1456. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhou, Y.; Dong, X.; Xiu, P.; Wang, X.; Yang, J.; Li, L.; Li, Z.; Sun, P.; Shi, X.; Zhong, J. Meloxicam, a selective COX-2 inhibitor, mediates hypoxia-inducible factor-(HIF-)1α signaling in hepatocellular carcinoma. Oxidative Med. Cell. Longev. 2020, 7079308. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cheney, M.L.; Weyna, D.R.; Shan, N.; Hanna, M.; Wojtas, L.; Zaworotko, M.J. Coformer selection in pharmaceutical cocrystal development: A case study of a meloxicam aspirin cocrystal that exhibits enhanced solubility and pharmacokinetics. J. Pharm. Sci. 2011, 100, 2172–2181. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nagai, N.; Ogata, F.; Otake, H.; Kawasaki, N. Oral administration system based on meloxicam nanocrystals: Decreased dose due to high bioavailability attenuates risk of gastrointestinal side effects. Pharmaceutics 2020, 12, 313. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ambrus, R.; Kocbek, P.; Kristl, J.; Sibanc, R.; Rajkó, R.; Szabó-Révész, P. Investigation of preparation parameters to improve the dissolution of poorly water-soluble meloxicam. Int. J. Pharm. 2009, 381, 153–159. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jafar, M.; Khalid, M.S.; Alghamdi, H.; Amir, M.; Al-Makki, S.A.; Alotaibi, O.S.; Al-Rmais, A.A.; Imam, S.S.; Alshehri, S.; Gilani, S.J. Formulation of Apigenin-Cyclodextrin-Chitosan Ternary Complex: Physicochemical Characterization, In Vitro and In Vivo Studies. AAPS PharmSciTech 2022, 23, 71. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Isadiartuti, D.; Rosita, N.; Ekowati, J.; Syahrani, A.; Ariyani, T.; Rifqi, M.A. The thermodynamic study of p-methoxycinnamic acid inclusion complex formation, using β-cyclodextrin and hydroxypropyl-β-cyclodextrin. J. Basic Clin. Physiol. Pharmacol. 2021, 32, 663–667. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Celebioglu, A.; Yildiz, Z.I.; Uyar, T. Thymol/cyclodextrin inclusion complex nanofibrous webs: Enhanced water solubility, high thermal stability and antioxidant property of thymol. Food Res. Int. 2018, 106, 280–290. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bandarkar, F.S.; Vavia, P.R. An optimized commercially feasible milling technique for molecular encapsulation of meloxicam in β-cyclodextrin. Drug Dev. Ind. Pharm. 2011, 37, 1318–1328. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Samprasit, W.; Akkaramongkolporn, P.; Kaomongkolgit, R.; Opanasopit, P. Cyclodextrin-based oral dissolving films formulation of taste-masked meloxicam. Pharm. Dev. Technol. 2018, 23, 530–539. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Samprasit, W.; Akkaramongkolporn, P.; Ngawhirunpat, T.; Rojanarata, T.; Opanasopit, P. Formulation and evaluation of meloxicam oral disintegrating tablet with dissolution enhanced by combination of cyclodextrin and ion exchange resins. Drug Dev. Ind. Pharm. 2015, 41, 1006–1016. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rein, S.M.T.; Lwin, W.W.; Tuntarawongsa, S.; Phaechamud, T. Meloxicam-loaded solvent exchange-induced in situ forming beta-cyclodextrin gel and microparticle for periodontal pocket delivery. Mater. Sci. Eng. C 2020, 117, 111275. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jafar, M.; Salahuddin, M.; Kayed, T.S.; Ahmad, N.; Al-Eid, H.A.; Al-Qarros, A.H. Buoyant in situ gels of meloxicam-β-cyclodextrintriethanolamine ternary complex for oral delivery; from a box-behnken experimental design to in vivo activity detail. Asian J. Chem. 2017, 29, 1275–1284. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ainurofiq, A.; Choiri, S. Development and optimization of a meloxicam/β-cyclodextrin complex for orally disintegrating tablet using statistical analysis. Pharm. Dev. Technol. 2018, 23, 464–475. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shende, P.K.; Gaud, R.S.; Bakal, R.; Patil, D. Effect of inclusion complexation of meloxicam with β-cyclodextrin-and β-cyclodextrin-based nanosponges on solubility, in vitro release and stability studies. Colloids Surf. B Biointerfaces 2015, 136, 105–110. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Muankaew, C.; Jansook, P.; Loftsson, T. Evaluation of γ-cyclodextrin effect on permeation of lipophilic drugs: Application of cellophane/fused octanol membrane. Pharm. Dev. Technol. 2017, 22, 562–570. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mizera, M.; Muratov, E.N.; Alves, V.M.; Tropsha, A.; Cielecka-Piontek, J. Computer-aided discovery of new solubility-enhancing drug delivery system. Biomolecules 2020, 10, 913. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bialik, M.; Kuras, M.; Sobczak, M.; Oledzka, E. Achievements in Thermosensitive Gelling Systems for Rectal Administrationt. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2021, 22, 5500. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Balakrishnan, P.; Song, C.K.; Cho, H.J.; Yang, S.G.; Kim, D.D.; Yong, C.S.; Choi, H.G. Inclusion complex effect on the bioavailability of clotrimazole from poloxamer-based solid suppository. Arch. Pharmacal Res. 2012, 35, 1169–1175. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, H.R.; Tseng, C.C.; Lin, Y.J.; Ling, M.H. A novel in-situ-gelling liquid suppository for site-targeting delivery of anti-colorectal cancer drugs. J. Biomater. Sci. Polym. Ed. 2012, 23, 807–822. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pandey, M.; Choudhury, H.; Binti-Abd-Aziz, A.; Bhattamisra, S.K.; Gorain, B.; Su, J.S.T.; Tan, C.L.; Chin, W.Y.; Yip, K.Y. Potential of stimuli-responsive in situ gel system for sustained ocular drug delivery: Recent progress and contemporary research. Polymers 2021, 13, 1340. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xue, P.; Wang, L.; Xu, J.; Liu, J.; Pan, X.; Zhao, Y.; Xu, H. Temperature-sensitive hydrogel for rectal perfusion improved the therapeutic effect of Kangfuxin liquid on DSS-induced ulcerative colitis mice: The inflammation alleviation and the colonic mucosal barriers repair. Int. J. Pharm. 2020, 589, 119846–119856. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, L.L.; Zheng, W.S.; Chen, S.H.; Han, Y.X.; Jiang, J.D. Development of rectal delivered thermoreversible gelling film encapsulating a 5-fluorouracil hydroxypropyl-β-cyclodextrin complex. Carbo-Hydr. Polym. 2016, 137, 9–18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hadžiabdić, J.; Elezović, A.; Rahić, O.; Mujezin, I. Effect of cyclodextrin complexation on the aqueous solubility of diazepam and nitrazepam: Phase-solubility analysis, thermodynamic properties. Am. J. Anal. Chem. 2012, 3, 811–819. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khalil, R.M.; Abd El-Bary, A.; Kassem, M.A.; Ghorab, M.M.; Ahmed, M.B. Solid lipid nanoparticles for topical delivery of meloxicam: Development and in vitro characterization. Eur. Sci. J. 2013, 9, 779–798. [Google Scholar]
- Liu, H.; Luo, J.; Yang, P.; Yang, X.; Yan, J.; Yao, Q. Stability, Antioxidant Activity and Intestinal Permeation of Oleuropein Inclusion Complexes with Beta-Cyclodextrin and Hydroxypropyl-Beta-Cyclodextrin. Molecules 2022, 27, 5077. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kulkarni, A.D.; Belgamwar, V.S. Inclusion complex of chrysin with sulfobutyl ether-β-cyclodextrin (Captisol®): Preparation, characterization, molecular modelling and in vitro anticancer activity. J. Mol. Struct. 2017, 1128, 563–571. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baboota, S.; Agarwal, S.P. Preparation and characterisation of meloxicam hydroxy propyl β-cyclodextrin inclusion complex. J. Incl. Phenom. Macrocycl. Chem. 2005, 51, 219–224. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jannin, V.; Lemagnen, G.; Gueroult, P.; Larrouture, D.; Tuleu, C. Rectal route in the 21st Century to treat children. Adv. Drug Deliv. Rev. 2014, 73, 34–49. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fernández-Ferreiro, A.; Fernández-Bargiela, N.; Varela, M.S.; Martínez, M.G.; Pardo, M.; Piñeiro-Ces, A.; Méndez, J.B.; Barcia, M.G.; Lamas, M.J.; Otero-Espinar, F. Cyclodextrin-polysaccharide-based, in situ-gelled system for ocular antifungal delivery. Beilstein J. Org. Chem. 2014, 10, 2903–2911. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bibby, D.C.; Davies, N.M.; Tucker, I.G. Mechanisms by which cyclodextrins modify drug release from polymeric drug delivery systems. Int. J. Pharm. 2000, 197, 1–11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Otero-Espinar, F.J.; Torres-Labandeira, J.J.; Alvarez-Lorenzo, C.; Blanco-Méndez, J. Cyclodextrins in drug delivery systems. J. Drug Deliv. Sci. Technol. 2010, 20, 289–301. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Z.M.; Lv, Y.N.; Wang, L.L.; Yuan, M.; Xi, X.R.; Wang, A.P. Preparation and Quality Evaluation of Meloxicam Nanosuspension. J. Yantai Univ. (Nat. Sci. Eng. Ed.) 2021, 34, 429–435. [Google Scholar]
- Mourtzinos, I.; Salta, F.; Yannakopoulou, K.; Chiou, A.; Karathanos, V.T. Encapsulation of olive leaf extract in beta-cyclodextrin. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2007, 55, 8088–8094. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lobatto, V.L.; Argüello, G.A.; Caira, M.R.; Bujan, E.I. Trifluralin and two of its photodegradation products: Crystal structures and phase solubility/UV studies with cyclodextrins. J Phys Org Chem. 2019, 32, e4006. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, L.; Han, X.; Xu, X.; Zhang, Q.; Zeng, Y.; Su, Q.; Liu, Y.; Sheng, Y.; Xie, X. Optimization and evaluation of the thermosensitive in situ and adhesive gel for rectal delivery of budesonide. AAPS PharmSciTech 2020, 21, 97. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chul Soon, Y.; Young-Kwon, C.; Yong-II, K.; Byung-Joo, P.; Qi-Zhe, Q.; Jong-Dai, R.; Chong-Kook, K.; Han-Gon, C. Physicochemical characterization and in vivo evaluation of thermosensitive diclofenac liquid suppository. Arch. Pharm. Res. 2003, 26, 162–167. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Özgüney, I.; Kardhiqi, A. Properties of bioadhesive ketoprofen liquid suppositories: Preparation, determination of gelation temperature, viscosity studies and evaluation of mechanical properties using texture analyzer by 4 × 4 factorial design. Pharm. Dev. Technol. 2014, 19, 968–975. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Q1A(R2); Stability Testing of New Drug Substances and Products. Guideline, ICH Harmonised Tripartite: London, UK, 2003.
- Q1B; Photostability Testing of New Drug Substance and Products. Guideline, ICH Harmonised Tripartite: London, UK, 1996.
- Huang, C.; Wang, C.; Zhang, W.; Yang, T.; Xia, M.; Lei, X.; Peng, Y.; Wu, Y.; Feng, J.; Li, D.; et al. Preparation, In Vitro and In Vivo Evaluation of Nanoemulsion In Situ Gel for Transnasal Delivery of Traditional Chinese Medicine Volatile Oil from Ligusticum sinense Oliv. cv. Chaxiong. Molecules 2022, 27, 7644. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Z.; Chen, L.; He, C.; Han, Y.; Han, M.; Zhang, Y.; Qi, L.; Xing, X.; Huang, W.; Gao, Z. Improving anti-tumor outcomes for colorectal cancer therapy through in situ thermosensitive gel loading harmine. Am. J. Transl. Res. 2020, 12, 1658–1671. [Google Scholar]










| Parameter | MLX-ISG | MLX/HP-β-CD-ISG | MLX Solid Suppository |
|---|---|---|---|
| t½ (h) | 4.12 ± 3.02 | 10.62 ± 4.76 | 4.64 ± 1.44 |
| Tmax (h) | 2.83 ± 1.33 | 4.50 ± 2.17 | 3.33 ± 0.52 |
| Cmax (µg/mL) | 13.57 ± 3.68 ** | 40.68 ± 4.89 **## | 7.70 ± 4.030 ## |
| AUC(0→t) (µg·h/mL) | 77.08 ± 19.04 ** | 491.44 ± 127.50 **## | 47.38 ± 23.48 ## |
| AUC(0→∞) (µg·h/mL) | 81.98 ± 15.90 ** | 387.77 ± 134.21 **## | 51.52 ± 21.97 ## |
| MRT(0→∞) (h) | 7.04 ± 4.62 | 16.79 ± 7.29 | 12.130 ± 12.02 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Lei, X.; Zhang, G.; Yang, T.; Wu, Y.; Peng, Y.; Wang, T.; Li, D.; Liu, Q.; Wang, C.; Zhang, G. Preparation and In Vitro and In Vivo Evaluation of Rectal In Situ Gel of Meloxicam Hydroxypropyl-β-cyclodextrin Inclusion Complex. Molecules 2023, 28, 4099. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules28104099
Lei X, Zhang G, Yang T, Wu Y, Peng Y, Wang T, Li D, Liu Q, Wang C, Zhang G. Preparation and In Vitro and In Vivo Evaluation of Rectal In Situ Gel of Meloxicam Hydroxypropyl-β-cyclodextrin Inclusion Complex. Molecules. 2023; 28(10):4099. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules28104099
Chicago/Turabian StyleLei, Xiaomeng, Guansheng Zhang, Tao Yang, Yuhuan Wu, Ying Peng, Tiantian Wang, Dongxun Li, Qian Liu, Canjian Wang, and Guosong Zhang. 2023. "Preparation and In Vitro and In Vivo Evaluation of Rectal In Situ Gel of Meloxicam Hydroxypropyl-β-cyclodextrin Inclusion Complex" Molecules 28, no. 10: 4099. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules28104099
APA StyleLei, X., Zhang, G., Yang, T., Wu, Y., Peng, Y., Wang, T., Li, D., Liu, Q., Wang, C., & Zhang, G. (2023). Preparation and In Vitro and In Vivo Evaluation of Rectal In Situ Gel of Meloxicam Hydroxypropyl-β-cyclodextrin Inclusion Complex. Molecules, 28(10), 4099. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules28104099