The Motion Paradigm of Pre-Dock Zearalenone Hydrolase Predictions with Molecular Dynamics and the Docking Phase with Umbrella Sampling
Abstract
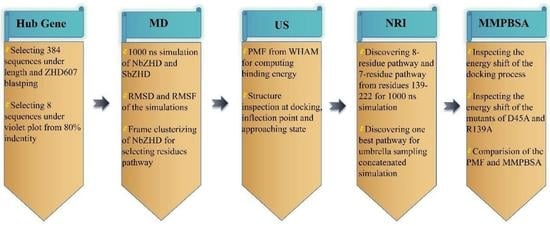
:1. Introduction
2. Results
2.1. An Evolutional Analysis of Hydrolase and the Hub-Gene Definition
2.2. Extensive Simulation of Molecular States
2.3. Motion Paradigm from Umbrella Sampling
2.4. Alanine Scanning Mutations for Inspecting Energy Shifting
3. Materials and Methods
3.1. Lactone Hydrolases Co-Evolutionary Relation Analysis
3.2. Molecular Dynamics Analysis of Lacton Hydrolase
3.3. Umbrella Sampling
3.4. Structural Pathway and Energy Analysis
4. Discussion
4.1. Hub Genes and MSA Survey the Extensive Character of Protein
4.2. Umbrella Sampling and Molecular Dynamics Inspect Conformation Veer
4.3. Sub-Protein and Energy Analysis Conveys Detailed Conformation Shifting
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Bennett, J.W.; Klich, M. Mycotoxins. Clin. Microbiol. Rev. 2003, 16, 497–516. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Lei, Y.; Zhao, L.; Ma, Q.; Zhang, J.; Zhou, T.; Gao, C.; Ji, C. Degradation of zearalenone in swine feed and feed ingredients by Bacillus subtilis ANSB01G. World Mycotoxin J. 2014, 7, 143–151. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gruber-Dorninger, C.; Jenkins, T.; Schatzmayr, G. Global Mycotoxin Occurrence in Feed: A Ten-Year Survey. Toxins 2019, 11, 375. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Bullerman, L.B.; Bianchini, A. Stability of mycotoxins during food processing. Int. J. Food Microbiol. 2007, 119, 140–146. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yang, K.; Li, K.; Pan, L.; Luo, X.; Xing, J.; Wang, J.; Wang, L.; Wang, R.; Zhai, Y.; Chen, Z. Effect of Ozone and Electron Beam Irradiation on Degradation of Zearalenone and Ochratoxin A. Toxins 2002, 12, 138. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Abd Alla, E.S.A.M. Zearalenone: Incidence, toxigenic fungi and chemical decontamination in Egyptian cereals. Food Nahr. 1997, 41, 362–365. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bai, X.; Sun, C.; Xu, J.; Liu, D.; Han, Y.; Wu, S.; Luo, X. Detoxification of zearalenone from corn oil by adsorption of functionalized GO systems. Appl. Surf. Sci. 2018, 430, 198–207. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kakeya, H.; Takahashi-Ando, N.; Kimura, M.; Onose, R.; Yamaguchi, I.; Osada, H. Biotransformation of the Mycotoxin, Zearalenone, to a Non-estrogenic Compound by a Fungal Strain of Clonostachys sp. Biosci. Biotechnol. Biochem. 2002, 66, 2723–2726. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Chen, S.; Pan, L.; Liu, S.; Pan, L.; Li, X.; Wang, B. Recombinant expression and surface display of a zearalenone lactonohydrolase from Trichoderma aggressivum in Escherichia coli. Protein Expr. Purif. 2021, 187, 105933. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zheng, Y.; Liu, W.; Chen, C.-C.; Hu, X.; Liu, W.; Ko, T.-P.; Tang, X.; Wei, H.; Huang, J.-W.; Guo, R.-T. Crystal Structure of a Mycoestrogen-Detoxifying Lactonase from Rhinocladiella mackenziei: Molecular Insight into ZHD Substrate Selectivity. ACS Catal. 2018, 8, 4294–4298. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Altalhi, A.D.; El-Deeb, B. Localization of zearalenone detoxification gene(s) in pZEA-1 plasmid of Pseudomonas putida sp. strain ZEA-1 and expressed in Escherichia coli. Malays. J. Microbiol. 2007, 3, 29–36. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, T.; Wang, M.; Li, X.; Wang, H.; Zhao, G.; Wu, P.; Lu, Z.; Zhang, G. The replacement of main cap domain to improve the activity of a ZEN lactone hydrolase with broad substrate spectrum. Biochem. Eng. J. 2022, 182, 108418. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, X.; Tu, T.; Luo, H.; Huang, H.; Su, X.; Wang, Y.; Wang, Y.; Zhang, J.; Bai, Y.; Yao, B. Biochemical Characterization and Mutational Analysis of a Lactone Hydrolase from Phialophora americana. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2019, 68, 2570–2577. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Robert, X.; Gouet, P. Deciphering key features in protein structures with the new ENDscript server. Nucleic Acids Res. 2014, 42, W320–W324. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Vanommeslaeghe, K., Jr.; MacKerell, A. Automation of the CHARMM General Force Field (CGenFF) I: Bond Perception and Atom Typing. J. Chem. Inf. Model. 2012, 52, 3144–3154. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Van Der Spoel, D.; Lindahl, E.; Hess, B.; Groenhof, G.; Mark, A.E.; Berendsen, H.J.C. GROMACS: Fast, flexible, and free. J. Comput. Chem. 2005, 26, 1701–1718. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ferrenberg, A.M.; Swendsen, R.H. Optimized Monte Carlo data analysis. Phys. Rev. Lett. 1989, 63, 1195–1198. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, J.; Wang, J.; Han, W.; Xu, D. Neural relational inference to learn long-range allosteric interactions in proteins from molecular dynamics simulations. Nat. Commun. 2002, 13, 1661. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Miller, B.R., III; McGee, T.D., Jr.; Swails, J.M.; Homeyer, N.; Gohlke, H.; Roitberg, A.E. MMPBSA.py: An Efficient Program for End-State Free Energy Calculations. J. Chem. Theory Comput. 2012, 8, 3314–3321. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Valdés-Tresanco, M.S.; Valdés-Tresanco, M.E.; Valiente, P.A.; Moreno, E. gmx_MMPBSA: A New Tool to Perform End-State Free Energy Calculations with GROMACS. J. Chem. Theory Comput. 2021, 17, 6281–6291. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, J.; Zhu, L.; Chen, J.; Wang, W.; Zhang, R.; Li, Y.; Zhang, Q.; Wang, W. Degradation mechanism for Zearalenone ring-cleavage by Zearalenone hydrolase RmZHD: A QM/MM study. Sci. Total Environ. 2019, 709, 135897. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bauer, T.L.; Buchholz, P.C.F.; Pleiss, J. The modular structure of α/β-hydrolases. FEBS J. 2020, 287, 1035–1053. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Scarselli, F.; Tsoi, A.C.; Gori, M.; Hagenbuchner, M. Graphical-Based Learning Environments for Pattern Recognition. In Structural, Syntactic, and Statistical Pattern Recognition—SSPR/SPR 2004; Fred, A., Caelli, T.M., Duin, R.P.W., Campilho, A.C., de Ridder, D., Eds.; Lecture Notes in Computer Science; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2004; Volume 3138. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Peng, W.; Ko, T.-P.; Yang, Y.; Zheng, Y.; Chen, C.-C.; Zhu, Z.; Huang, C.-H.; Zeng, Y.-F.; Huang, J.-W.; Wang, A.H.-J.; et al. Crystal structure and substrate-binding mode of the mycoestrogen-detoxifying lactonase ZHD from Clonostachys rosea. RSC Adv. 2014, 4, 62321–62325. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, M.; Tan, J.; Xu, Z.; Huang, J.; Tian, Y.; Chen, B.; Wu, Y.; Tong, Y.; Zhu, Y. Computational design of enhanced detoxification activity of a zearalenone lactonase from Clonostachys rosea in acidic medium. RSC Adv. 2019, 9, 31284–31295. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Liu, Y.; Wan, Y.; Zhu, J.; Yu, Z.; Tian, X.; Han, J.; Zhang, Z.; Han, W. Theoretical Study on Zearalenol Compounds Binding with Wild Type Zearalenone Hydrolase and V153H Mutant. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2018, 19, 2808. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]









| Item | Number of AA | Pathway | Probability |
|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | 8 | 209 → 139 → 145 → 155 → 174 → 176 → 178 → 183 | 85.778% |
| 2 | 8 | 209 → 139 → 145 → 155 → 174 → 176 → 178 → 186 | 81.800% |
| 3 | 7 | 183 → 177 → 174 → 154 → 149 → 146 → 202 | 99.999% |
| 4 | 7 | 184 → 177 → 174 → 154 → 149 → 146 → 202 | 99.974% |
| 5 | 7 | 181 → 177 → 174 → 154 → 149 → 146 → 202 | 99.971% |
| 6 | 7 | 184 → 176 → 175 → 154 → 150 → 146 → 202 | 99.935% |
| 7 | 7 | 182 → 176 → 175 → 154 → 150 → 146 → 202 | 99.935% |
| 8 | 7 | 184 → 176 → 174 → 154 → 149 → 146 → 202 | 99.922% |
| 9 | 7 | 182 → 176 → 174 → 154 → 149 → 146 → 202 | 99.922% |
| 10 | 7 | 184 → 176 → 175 → 154 → 149 → 146 → 202 | 99.914% |
| 11 | 7 | 182 → 176 → 175 → 154 → 149 → 146 → 202 | 99.913% |
| 12 | 7 | 181 → 176 → 175 → 154 → 150 → 146 → 202 | 99.907% |
| 13 | 7 | 186 → 176 → 175 → 154 → 149 → 146 → 202 | 99.901% |
| Enzyme | ΔVDW | ΔEEL | ΔEMM | ΔGSOLV | ΔGGAS | ΔGbind |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| NbZHD(1) | −31.84 ± 7.06 | −2.97 ± 1.03 | −34.81 ± 8.09 | 26.68 ± 5.42 | −34.82 ± 7.74 | −8.14 ± 3.74 |
| D45A | −31.84 ± 7.06 | −3.00 ± 1.04 | −34.84 ± 8.10 | 26.71 ± 5.43 | −34.84 ± 7.75 | −8.13 ± 3.74 |
| NbZHD(2) | −31.84 ± 7.06 | −2.97 ± 1.03 | −34.81 ± 8.09 | 26.07 ± 5.21 | −34.82 ± 7.74 | −8.75 ± 3.97 |
| R139A | −31.84 ± 7.06 | −2.96 ± 1.03 | −34.80 ± 8.09 | 26.04 ± 5.32 | −34.80 ± 7.74 | −8.76 ± 3.94 |
| NbZHD | −31.84 ± 7.06 | −2.97 ± 1.03 | −34.81 ± 8.09 | 26.38 ± 5.32 | −34.82 ± 7.74 | −8.45 ± 3.86 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Hong, X.-Z.; Han, Z.-G.; Yang, J.-K.; Liu, Y.-H. The Motion Paradigm of Pre-Dock Zearalenone Hydrolase Predictions with Molecular Dynamics and the Docking Phase with Umbrella Sampling. Molecules 2023, 28, 4545. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules28114545
Hong X-Z, Han Z-G, Yang J-K, Liu Y-H. The Motion Paradigm of Pre-Dock Zearalenone Hydrolase Predictions with Molecular Dynamics and the Docking Phase with Umbrella Sampling. Molecules. 2023; 28(11):4545. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules28114545
Chicago/Turabian StyleHong, Xi-Zhi, Zheng-Gang Han, Jiang-Ke Yang, and Yi-Han Liu. 2023. "The Motion Paradigm of Pre-Dock Zearalenone Hydrolase Predictions with Molecular Dynamics and the Docking Phase with Umbrella Sampling" Molecules 28, no. 11: 4545. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules28114545
APA StyleHong, X. -Z., Han, Z. -G., Yang, J. -K., & Liu, Y. -H. (2023). The Motion Paradigm of Pre-Dock Zearalenone Hydrolase Predictions with Molecular Dynamics and the Docking Phase with Umbrella Sampling. Molecules, 28(11), 4545. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules28114545