Microbial-Transferred Metabolites of Black Tea Theaflavins by Human Gut Microbiota and Their Impact on Antioxidant Capacity
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Results
2.1. Mass Fragmentation Behavior Analyses of TFs
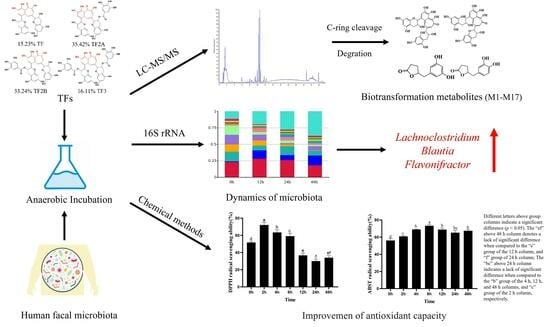
2.2. Metabolites of TFs by In Vitro Human Fecal Fermentation
2.3. Biotransformation Pathway of TFs by In Vitro Human Fecal Fermentation
2.4. Dynamics of Microbiota during Fermentation Process
2.5. Antioxidant Activity of TF Fermentation
3. Discussion
4. Materials and Methods
4.1. Chemicals
4.2. Sample Preparation
4.3. Preparation of the General Anaerobic Medium Broth
4.4. Fecal Sample Collection and In Vitro Fermentation of TFs with Human Gut Microbiota
4.5. Identification of the Microbial Metabolites of TFs by UPLC-Q-Orbitrap-MS/MS
4.6. Analysis of Gut Microbiota Composition after Fermentation with TFs
4.7. Metabolic Profiling Analysis Based on UPLC-Orbitrap MS/MS
4.8. Evaluation of Antioxidant Activity
4.9. Data Analysis
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
Sample Availability
References
- Zhang, S.; Ohland, C.; Jobin, C.; Sang, S. Black Tea Theaflavin Detoxifies Metabolic Toxins in the Intestinal Tract of Mice. Mol. Nutr. Food Res. 2021, 65, e2000887. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shan, Z.; Nisar, M.F.; Li, M.; Zhang, C.; Wan, C.C. Theaflavin Chemistry and Its Health Benefits. Oxid. Med. Cell. Longev. 2021, 2021, 6256618. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, B.; Mao, Q.; Xiong, R.; Zhou, D.; Huang, S.; Saimaiti, A.; Shang, A.; Luo, M.; Li, H.; Li, H.; et al. Preventive Effects of Different Black and Dark Teas on Obesity and Non-Alcoholic Fatty Liver Disease and Modulate Gut Microbiota in High-Fat Diet Fed Mice. Foods 2022, 11, 3457. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Drynan, J.W.; Clifford, M.N.; Obuchowicz, J.; Kuhnert, N. The Chemistry of Low Molecular Weight Black Tea Polyphenols. Nat. Prod. Rep. 2010, 27, 417–462. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, J.; Wang, J.; Yuan, H.; Ouyang, W.; Li, J.; Hua, J.; Jiang, Y. Effects of Fermentation Temperature and Time on the Color Attributes and Tea Pigments of Yunnan Congou Black Tea. Foods 2022, 11, 1845. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, Y.; Li, W.; Xu, Y.; Jin, E.; Tu, Y. Evaluation of the Antioxidant Effects of Four Main Theaflavin Derivatives through Chemiluminescence and DNA Damage Analyses. J. Zhejiang Univ. Sci. B 2011, 12, 744–751. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Liu, W.; Li, J. Theaflavin-3, 3’-Digallate Attenuates Rheumatoid Inflammation in Mice Through the Nuclear Factor-ΚB and MAPK Pathways. Arch. Immunol. Ther. Exp. 2019, 67, 153–160. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- O’Neill, E.J.; Termini, D.; Albano, A.; Tsiani, E. Anti-Cancer Properties of Theaflavins. Molecules 2021, 26, 987. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Henning, S.M.; Aronson, W.; Niu, Y.; Conde, F.; Lee, N.H.; Seeram, N.P.; Lee, R.P.; Lu, J.; Harris, D.M.; Moro, A.; et al. Tea Polyphenols and Theaflavins Are Present in Prostate Tissue of Humans and Mice after Green and Black Tea Consumption. J. Nutr. 2006, 136, 1839–1843. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Pereira-Caro, G.; Moreno-Rojas, J.M.; Brindani, N.; Del Rio, D.; Lean, M.E.J.; Hara, Y.; Crozier, A. Bioavailability of Black Tea Theaflavins: Absorption, Metabolism, and Colonic Catabolism. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2017, 65, 5365–5374. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Khan, N.; Mukhtar, H. Tea Polyphenols in Promotion of Human Health. Nutrients 2018, 11, 39. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Tao, W.; Cao, W.; Yu, B.; Chen, H.; Gong, R.; Luorong, Q.; Luo, J.; Yao, L.; Zhang, D. Hawk Tea Prevents High-Fat Diet-Induced Obesity in Mice by Activating the AMPK/ACC/SREBP1c Signaling Pathways and Regulating the Gut Microbiota. Food Funct. 2022, 13, 6056–6071. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wu, G.; Sun, X.; Cheng, H.; Xu, S.; Li, D.; Xie, Z. Large Yellow Tea Extract Ameliorates Metabolic Syndrome by Suppressing Lipogenesis through SIRT6/SREBP1 Pathway and Modulating Microbiota in Leptin Receptor Knockout Rats. Foods 2022, 11, 1638. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, Z.; Huang, S.; Li, T.; Li, N.; Han, D.; Zhang, B.; Xu, Z.Z.; Zhang, S.; Pang, J.; Wang, S.; et al. Gut Microbiota from Green Tea Polyphenol-Dosed Mice Improves Intestinal Epithelial Homeostasis and Ameliorates Experimental Colitis. Microbiome 2021, 9, 184. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, W.; Zhu, X.; Lu, Q.; Zhang, L.; Wang, X.; Liu, R. C-Ring Cleavage Metabolites of Catechin and Epicatechin Enhanced Antioxidant Activities through Intestinal Microbiota. Food Res. Int. 2020, 135, 109271. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, C.; Vervoort, J.; van den Elzen, J.; Beekmann, K.; Baccaro, M.; de Haan, L.; Rietjens, I.M.C.M. Interindividual Differences in Human In Vitro Intestinal Microbial Conversion of Green Tea (-)-Epigallocatechin-3-O-Gallate and Consequences for Activation of Nrf2 Mediated Gene Expression. Mol. Nutr. Food Res. 2021, 65, 2000934. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zeng, X.; Zheng, Y.; He, Y.; Zhang, J.; Peng, W.; Su, W. Microbial Metabolism of Naringin and the Impact on Antioxidant Capacity. Nutrients 2022, 14, 3765. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bao, T.; Zhang, M.; Zhou, Y.; Chen, W. Phenolic Profile of Jujube Fruit Subjected to Gut Microbiota Fermentation and Its Antioxidant Potential against Ethyl Carbamate-Induced Oxidative Damage. J. Zhejiang Univ. Sci. B 2021, 22, 397–409. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, W.; Zhang, L.; Zhao, L.; Yan, F.; Zhu, X.; Lu, Q.; Liu, R. Metabolomic Profiles of A-Type Procyanidin Dimer and Trimer with Gut Microbiota in Vitro. J. Func. Foods 2021, 85, 104637. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, H.; Parks, T.A.; Chen, X.; Gillitt, N.D.; Jobin, C.; Sang, S. Structural Identification of Mouse Fecal Metabolites of Theaflavin 3,3’-Digallate Using Liquid Chromatography Tandem Mass Spectrometry. J. Chromatogr. A 2011, 1218, 7297–7306. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Chen, H.; Hayek, S.; Rivera Guzman, J.; Gillitt, N.D.; Ibrahim, S.A.; Jobin, C.; Sang, S. The Microbiota Is Essential for the Generation of Black Tea Theaflavins-Derived Metabolites. PLoS ONE 2012, 7, e51001. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Liu, Z.; de Bruijn, W.J.C.; Bruins, M.E.; Vincken, J.P. Microbial Metabolism of Theaflavin-3,3’-Digallate and Its Gut Microbiota Composition Modulatory Effects. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2021, 69, 232–245. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yassin, G.H.; Koek, J.H.; Jayaraman, S.; Kuhnert, N. Identification of Novel Homologous Series of Polyhydroxylated Theasinensins and Theanaphthoquinones in the SII Fraction of Black Tea Thearubigins Using ESI/HPLC Tandem Mass Spectrometry. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2014, 62, 9848–9859. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, B.; Zhou, J.; Meng, Q.; Zhang, Y.; Zhang, S.; Zhang, L. Comparative Analysis of Fecal Phenolic Content between Normal and Obese Rats after Oral Administration of Tea Polyphenols. Food Funct. 2018, 9, 4858–4864. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Q.; Van Herreweghen, F.; Onyango, S.O.; De Mey, M.; Van de Wiele, T. In Vitro Microbial Metabolism of (+)-Catechin Reveals Fast and Slow Converters with Individual-Specific Microbial and Metabolite Markers. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2022, 70, 10405–10416. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, C.; Zhang, W.; Lin, H.; Zhang, L.; Wu, F.; Wang, Y.; Yu, S.; Peng, X.; Cheng, W.; Li, M.; et al. Effect of Theaflavin-3,3’-Digallate on Leptin-Deficient Induced Nonalcoholic Fatty Liver Disease Might Be Related to Lipid Metabolism Regulated by the Fads1/PPARδ/Fabp4 Axis and Gut Microbiota. Front. Pharmacol. 2022, 13, 925264. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Selma, M.V.; Espín, J.C.; Tomás-Barberán, F.A. Interaction between Phenolics and Gut Microbiota: Role in Human Health. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2009, 57, 6485–6501. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Riva, A.; Kolimár, D.; Spittler, A.; Wisgrill, L.; Herbold, C.W.; Abrankó, L.; Berry, D. Conversion of Rutin, a Prevalent Dietary Flavonol, by the Human Gut Microbiota. Front. Microbiol. 2020, 11, 585428. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oehmcke-Hecht, S.; Mandl, V.; Naatz, L.T.; Dühring, L.; Köhler, J.; Kreikemeyer, B.; Maletzki, C. Streptococcus Gallolyticus Abrogates Anti-Carcinogenic Properties of Tannic Acid on Low-Passage Colorectal Carcinomas. Sci. Rep. 2020, 10, 4714. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Yin, J.; Ma, Y.; Liang, C.; Gao, J.; Wang, H.; Zhang, L. A Systematic Study of the Metabolites of Dietary Acacetin in Vivo and in Vitro Based on UHPLC-Q-TOF-MS/MS Analysis. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2019, 67, 5530–5543. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cao, H.; Chen, X.; Jassbi, A.R.; Xiao, J. Microbial Biotransformation of Bioactive Flavonoids. Biotechnol. Adv. 2015, 33, 214–223. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Huang, A.; Jiang, Z.; Tao, M.; Wen, M.; Xiao, Z.; Zhang, L.; Zha, M.; Chen, J.; Liu, Z.; Zhang, L. Targeted and Nontargeted Metabolomics Analysis for Determining the Effect of Storage Time on the Metabolites and Taste Quality of Keemun Black Tea. Food Chem. 2021, 359, 129950. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, W.; Jiang, S.; Qian, D.; Shang, E.-X.; Duan, J.-A. Analysis of Interaction Property of Calycosin-7-O-β-D-Glucoside with Human Gut Microbiota. J. Chromatogr. B Anal. Technol. Biomed. Life Sci. 2014, 963, 16–23. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, Y.; Zhong, X.; Yan, J.; Sun, C.; Zhao, X.; Wang, X. Potential Roles of Gut Microbes in Biotransformation of Natural Products: An Overview. Front. Microbiol. 2022, 13, 956378. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liang, Y.; Zhao, W.; Wang, C.; Wang, Z.; Wang, Z.; Zhang, J. A Comprehensive Screening and Identification of Genistin Metabolites in Rats Based on Multiple Metabolite Templates Combined with UHPLC-HRMS Analysis. Molecules 2018, 23, 1862. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Dong, G.-M.; Yu, H.; Pan, L.-B.; Ma, S.-R.; Xu, H.; Zhang, Z.-W.; Han, P.; Fu, J.; Yang, X.-Y.; Keranmu, A.; et al. Biotransformation of Timosaponin BII into Seven Characteristic Metabolites by the Gut Microbiota. Molecules 2021, 26, 3861. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yan, Y.; Fu, C.; Cui, X.; Pei, X.; Li, A.; Qin, X.; Du, C.; Du, H. Metabolic Profile and Underlying Antioxidant Improvement of Ziziphi Spinosae Folium by Human Intestinal Bacteria. Food Chem. 2020, 320, 126651. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]






| No. | RT. | Tentative Identification | Formula | Theoretical Mass m/z | Experimental Mass m/z | Error (ppm) | MS/MS Fragments |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| M0 | 11.78 | Theaflavine-3,3′-digallate (TF3) a | C43H32O20 | 868.14869 | 868.14860 | 2.18 | 125.02446, 169.01471, 241.05067, 137.02467, 401.06854 |
| M1 | 11.5 | Theaflavin-3-gallate (TF2A) a | C36H28O16 | 716.13828 | 716.13813 | −0.21 | 125.02444, 169.01422, 241.05037, 137.02438, 269.04541 |
| M2 | 11.71 | Theaflavin-3′-gallate (TF2B) a | C36H28O16 | 716.13828 | 716.13837 | 0.13 | 125.02448, 169.01419, 241.05066, 137.02434, 269.04565 |
| M3 | 11.28 | Theaflavin (TF1) a | C29H24O12 | 564.12732 | 564.12598 | −2.38 | 241.05074, 125.02456, 137.02448, 169.01471, 201.05573, 269.04507 |
| M4 | 11.24 | Theaflavin quinone (TQ) | C29H22O12 | 562.11057 | 562.11048 | −0.16 | 125.02420, 137.02396, 257.04355, 229.04915 |
| M5 | 11.05 | Theanaphthoquinone (TNQ) | C28H22O11 | 534.11675 | 534.11658 | −0.32 | 137.02464, 125.02448, 349.07263, 165.01912, 241.04950 |
| M6 | 9.1 | Dihydro-theaflavin (DH-TF1) | C29H26O12 | 566.14297 | 566.14234 | −1.11 | 92.59178, 125.02444, 137.02446, 229.05040, 201.05640, 241.05029 |
| M7 | 9.16 | Dihydro-theaflavin (DH-TF1) | C29H26O12 | 566.14297 | 566.14320 | 0.41 | 92.59232, 125.02444, 137.02441 165.01921, 201.05542, 229.05046 |
| M8 | 8.71 | Tetrahydro-theaflavin (TH-TF1) | C29H28O12 | 568.15862 | 568.15693 | −2.97 | nd |
| M9 | 3.48 | Gallic acid a | C7H6O5 | 170.02207 | 170.02209 | 0.53 | 169.01416, 125.02441, 97.02950 |
| M10 | 3.60 | Pyrogallol a | C6H6O3 | 126.03224 | 126.03237 | 1.03 | 125.02447, 97.02958, 81.03468 |
| M11 | 8.69 | 5-(3′,5′-Dihydroxyphenyl)-γ-valerolactone | C11H12O4 | 208.0741 | 208.07407 | −0.14 | 207.06631, 163.07660, 123.04533, 122.03704, 81.0346 |
| M12 | 9.34 | 5-(3′,4′-Dihydroxyphenyl)-γ-valerolactone | C11H12O4 | 208.0741 | 208.07398 | −0.57 | 163.07663, 207.06635, 122.03751, 81.0347 |
| M13 | 9.81 | 5-(Dihydroxyphenyl)-γ-valeric acid (DiHPVA) | C11H14O4 | 210.08975 | 210.08910 | −3.09 | 123.08167, 165.09203, 81.03470, 147.08159, 191.07146 |
| M14 | 8.81 | 3-(3′,4′-Dihydroxyphenyl) propanoic acid a | C9H10O4 | 182.05845 | 182.05843 | −0.11 | 112.98575, 92.99384, 136.98364, 181.09854 |
| M15 | 11.10 | Phenylacetic acid a | C8H8O2 | 136.05297 | 136.05312 | 1.11 | 91.05544 |
| M16 | 9.40 | 3-Hydroxyphenylacetic acid a | C8H8O3 | 152.04789 | 152.04777 | −0.73 | 107.05035, 151.04008 |
| M17 | 7.84 | 4-Hydroxybenzoic acid a | C7H6O3 | 138.03224 | 138.03210 | −1.01 | 93.03462, 95.05029, 137.06078 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Sun, L.; Su, Y.; Hu, K.; Li, D.; Guo, H.; Xie, Z. Microbial-Transferred Metabolites of Black Tea Theaflavins by Human Gut Microbiota and Their Impact on Antioxidant Capacity. Molecules 2023, 28, 5871. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules28155871
Sun L, Su Y, Hu K, Li D, Guo H, Xie Z. Microbial-Transferred Metabolites of Black Tea Theaflavins by Human Gut Microbiota and Their Impact on Antioxidant Capacity. Molecules. 2023; 28(15):5871. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules28155871
Chicago/Turabian StyleSun, Li, You Su, Kaiyin Hu, Daxiang Li, Huimin Guo, and Zhongwen Xie. 2023. "Microbial-Transferred Metabolites of Black Tea Theaflavins by Human Gut Microbiota and Their Impact on Antioxidant Capacity" Molecules 28, no. 15: 5871. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules28155871
APA StyleSun, L., Su, Y., Hu, K., Li, D., Guo, H., & Xie, Z. (2023). Microbial-Transferred Metabolites of Black Tea Theaflavins by Human Gut Microbiota and Their Impact on Antioxidant Capacity. Molecules, 28(15), 5871. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules28155871