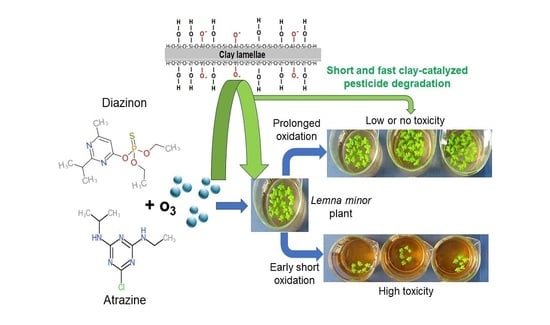
Ecotoxicity of Diazinon and Atrazine Mixtures after Ozonation Catalyzed by Na+ and Fe2+ Exchanged Montmorillonites on Lemna minor
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Results and Discussion
2.1. Intrinsic Effect of Pesticide on Plant Growth
2.2. Change in Photosynthetic Pigments
2.3. ROS Level under Pesticide Stress
2.4. Effect of Adsorption and Catalytic Ozonation
2.5. Toxicity Changes upon Pesticide Adsorption
2.6. Toxicity Induced by Pesticide Degradation
2.7. Effect of Pesticide Removal on ROS Level
3. Materials and Methods
3.1. Clay Materials Preparation and Characterization
3.2. Pesticide Stock Solutions
3.3. Adsorption and Ozonation Experiments
3.4. Lemna minor Cultivation
3.5. Lemna Plants Exposure to Pesticide
3.6. Growth Inhibition
3.7. Pigment Content and ROS Level
3.8. Statistical Analysis
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
Sample Availability
References
- Malhotra, N.; Chen, K.H.; Huang, J.C.; Lai, H.T.; Uapipatanakul, B.; Roldan, M.J.M.; Macabeo, A.P.G.; Ger, T.R.; Hsiao, C.D. Physiological effects of neonicotinoid insecticides on non-target aquatic animals—An updated review. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2021, 22, 9591. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Matozzo, V.; Fabrello, J.; Masiero, L.; Ferraccioli, F.; Finos, L.; Pastore, P.; Di Gangi, I.M.; Bogialli, S. Ecotoxicological risk assessment for the herbicide glyphosate to non-target aquatic species: A case study with the mussel Mytilus galloprovincialis. Environ. Poll. 2018, 233, 623–632. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pisa, L.W.; Amaral-Rogers, V.; Belzunces, L.P.; Bonmatin, J.M.; Downs, C.A.; Goulson, D.; Kreutzweiser, D.P.; Krupke, C.; Liess, M.; McField, M. Effects of neonicotinoids and fipronil on non-target invertebrates. Environ. Sci. Poll. Res. 2015, 22, 68–102. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pan, G.; Dutta, H.M. The inhibition of brain acetylcholinesterase activity of juvenile largemouth bass Micropterus salmoides by sublethal concentrations of Diazinon. Environ. Res. 1998, 79, 133–137. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Richard, E.P.; Goss, J.R.; Arntzen, C.J.; Slife, F.W. Determination of herbicide inhibition of photosynthetic electron transport by fluorescence. Weed Sci. 1983, 31, 361–367. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Üner, N.; Oruç, E.Ö.; Sevgiler, Y.; Şahin, N.; Durmaz, H.; Usta, D. Effects of diazinon on acetylcholinesterase activity and lipid peroxidation in the brain of Oreochromis niloticus. Environ. Toxicol. Pharm. 2006, 21, 241–245. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Čolović, M.; Krstić, D.; Petrović, S.; Leskovac, A.; Joksić, G.; Savić, J.; Franko, M.; Trebše, P.; Vasić, V. Toxic effects of diazinon and its photodegradation products. Toxicol. Lett. 2010, 193, 9–18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, N.; Xu, Y.; Sun, C.; Zhu, L.; Sun, S.; Zhao, Y.; Hu, C. Removal of atrazine in catalytic degradation solutions by microalgae Chlorella sp. and evaluation of toxicity of degradation products via algal growth and photosynthetic activity. Ecotoxicol. Environ. Saf. 2021, 207, 111546. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Felsot, A.S. Options for cleanup and disposal of pesticide wastes generated on a small-scale. J. Environ. Sci. Health B 1996, 31, 365–381. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ware, G.W.; Albert, L.A.; Bro-Rasmussen, F.; Crosby, D.; de Voogt, P.; Frehse, H.; Hutzinger, O.; Mayer, F.L.; Morgan, D.; Park, D.L. Disposal and degradation of pesticide waste. Rev. Environ. Contam. Toxicol. Contin. Residue Rev. 2003, 177, 123–200. [Google Scholar]
- Masten, S.J.; Davies, S.H. The use of ozonation to degrade organic contaminants in wastewaters. Environ. Sci. Technol. 1994, 28, 180A–185A. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jović, M.; Manojlović, D.; Stanković, D.; Dojčinović, B.; Obradović, B.; Gašić, U.; Roglić, G. Degradation of triketone herbicides, mesotrione and sulcotrione, using advanced oxidation processes. J. Hazard. Mat. 2013, 260, 1092–1099. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Azzouz, A. Advances in oxidative decomposition of oxalic acid in aqueous media. Adv. Chem. Res. 2012, 14, 1–31. [Google Scholar]
- Azzouz, A.; Kotbi, A.; Niquette, P.; Sajin, T.; Ursu, A.; Rami, A.; Monette, F.; Hausler, R. Ozonation of oxalic acid catalyzed by ion-exchanged montmorillonite in moderately acidic media. React. Kinet. Mech. Catal. 2010, 99, 289–302. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Azzouz, A.; Mirila, D.-C.; Nistor, D.-I.; Boudissa, F.; Roy, R. Advances in the oxidative degradation of organic pollutants: Prospects for catalyzed oxidation processes targeting total mineralization. In Advances in Chemestry Research; Taylor, J.C., Ed.; Nova Science Publishers: Hauppauge, NY, USA, 2019; Volume 49, p. 55467. [Google Scholar]
- Benghaffour, A.; Foka-Wembe, E.-N.; Dami, M.; Dewez, D.; Azzouz, A. Insight into natural medium remediation through ecotoxicity correlation with clay catalyst selectivity in organic molecule ozonation. Dalton Trans. 2022, 11, 4366–4376. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Boudissa, F.; Mirilà, D.; Arus, V.-A.; Terkmani, T.; Semaan, S.; Proulx, M.; Nistor, I.D.; Roy, R.; Azzouz, A. Acid-treated clay catalysts for organic dye ozonation—Thorough mineralization through optimum catalyst basicity and hydrophilic character. J. Hazard. Mat. 2019, 364, 356–366. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Boudissa, F.; Zekkari, M.; Arus, V.-A.; Ouargli-Saker, R.; Nabil, B.; Roy, R.; Azzouz, A. Clay-catalyzed ozonation of endocrinedisrupting compounds in solvent-free media–to better understand soil catalytic capacity. Dalton Trans. 2020, 49, 16693–16706. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Larouk, S.; Ouargli, R.; Shahidi, D.; Olhund, L.; Shiao, T.C.; Chergui, N.; Sehili, T.; Roy, R.; Azzouz, A. Catalytic ozonation of Orange-G through highly interactive contributions of hematite and SBA-16 to better understand azo-dye oxidation in nature. Chemosphere 2017, 168, 1648–1657. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shahidi, D.; Moheb, A.; Abbas, R.; Larouk, S.; Roy, R.; Azzouz, A. Total mineralization of sulfamethoxazole and aromatic pollutants through Fe2+-montmorillonite catalyzed ozonation. J. Hazard. Mater. 2015, 298, 338–350. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shahidi, D.; Roy, R.; Azzouz, A. Total removal of oxalic acid via synergistic parameter interaction in montmorillonite catalyzed ozonation. J. Environ. Chem. Engin. 2014, 2, 20–30. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shahidi, D.; Roy, R.; Azzouz, A. Advances in catalytic oxidation of organic pollutants—Prospects for thorough mineralization by natural clay catalysts. Appl. Catal. B Environ. 2015, 174–175, 277–292. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aydın, R.; Köprücü, K. Acute toxicity of diazinon on the common carp (Cyprinus carpio L.) embryos and larvae. Pest. Biochem. Physiol. 2005, 82, 220–225. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hamm, J.; Hinton, D. The role of development and duration of exposure to the embryotoxicity of diazinon. Aquat. Toxicol. 2000, 48, 403–418. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Klementová, Š.; Hornychová, L.; Šorf, M.; Zemanová, J.; Kahoun, D. Toxicity of atrazine and the products of its homogeneous photocatalytic degradation on the aquatic organisms Lemna minor and Daphnia magna. Environ. Sci. Poll. Res. 2019, 26, 27259–27267. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sánchez-Bayo, F. Insecticides mode of action in relation to their toxicity to non-target organisms. J. Environ. Anal. Toxicol. S 2012, 4, S4-002. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, W. Literature review on duckweed toxicity testing. Environ. Res. 1990, 52, 7–22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cáceres, T.; Megharaj, M.; Naidu, R. Toxicity and transformation of fenamiphos and its metabolites by two micro algae Pseudokirchneriella subcapitata and Chlorococcum sp. Sci. Tot. Environ. 2008, 398, 53–59. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cai, X.; Ye, J.; Sheng, G.; Liu, W. Time-dependent degradation and toxicity of diclofop-methyl in algal suspensions: Emerging contaminants. Environ. Sci. Poll. Res. 2009, 16, 459–465. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kurade, M.B.; Kim, J.R.; Govindwar, S.P.; Jeon, B.H. Insights into microalgae mediated biodegradation of diazinon by Chlorella vulgaris: Microalgal tolerance to xenobiotic pollutants and metabolism. Algal Res. 2016, 20, 126–134. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mishra, I.; Sabat, G. Phytotoxicity of Profenofos 50% EC (curacron 50 EC) to Vigna radiata, L. seedlings: II. Studies on Biochemical Parameters. Int. J. Appl. Sci. Biotechnol. 2015, 3, 101–105. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brain, R.A.; Hosmer, A.J.; Desjardins, D.; Kendall, T.Z.; Krueger, H.O.; Wall, S.B. Recovery of duckweed from time-varying exposure to atrazine. Environ. Toxicol. Chem. 2012, 31, 1121–1128. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fairchild, J.; Ruessler, D.; Haverland, P.; Carlson, A. Comparative sensitivity of Selenastrum capricornutum and Lemna minor to sixteen herbicides. Arch. Environ. Contam. Toxicol. 1997, 32, 353–357. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kumar, K.S.; Han, T. Physiological response of Lemna species to herbicides and its probable use in toxicity testing. Toxicol. Environ. Health Sci. 2010, 2, 39–49. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mohammad, M.; Itoh, K.; Suyama, K. Effects of herbicides on Lemna gibba and recovery from damage after prolonged exposure. Arch. Environ. Contam. Toxicol. 2010, 58, 605–612. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Casida, J.E. Pest toxicology: The primary mechanisms of pesticide action. Chem. Res. Toxicol. 2009, 22, 609–619. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Foyer, C.H.; Lopez-Delgado, H.; Dat, J.F.; Scott, I.M. Hydrogen peroxide-and glutathione-associated mechanisms of acclimatory stress tolerance and signalling. Physiol. Planta. 1997, 100, 241–254. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alla, M.N.; Hassan, N. Changes of antioxidants levels in two maize lines following atrazine treatments. Plant Physiol. Biochem. 2006, 44, 202–210. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chaves, M.M.; Pereira, J.S.; Maroco, J.; Rodrigues, M.L.; Ricardo, C.P.P.; Osório, M.L.; Carvalho, I.; Faria, T.; Pinheiro, C. How plants cope with water stress in the field? Photosynthesis and growth. Ann. Bot. 2002, 89, 907–916. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gille, G.; Sigler, K. Oxidative stress and living cells. Folia Microbiol. 1995, 40, 131–152. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, Y.Y.; Häder, D.P. Reactive oxygen species and UV-B: Effect on cyanobacteria. Photochem. Photobiol. Sci. 2002, 1, 729–736. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Knörzer, O.C.; Böger, P. Antagonizing peroxidizing herbicides. In Peroxidizing Herbicides; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2019; pp. 303–327. [Google Scholar]
- Li, X.; Wu, T.; Huang, H.; Zhang, S. Atrazine accumulation and toxic responses in maize Zea mays. J. Environ. Sci. 2012, 24, 203–208. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mittler, R. Oxidative stress, antioxidants and stress tolerance. Trends Plant Sci. 2002, 7, 405–410. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Assaad, E.; Azzouz, A.; Nistor, D.; Ursu, A.V.; Sajin, T.; Miron, D.N.; Monette, F.; Niquette, P.; Hausler, R. Metal removal through synergic coagulation–flocculation using an optimized chitosan–montmorillonite system. Appl. Clay Sci. 2007, 37, 258–274. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kabwadza-Corner, P.; Matsue, N.; Johan, E.; Henmi, T. Mechanism of Diazinon adsorption on iron modified montmorillonite. Am. J. Anal. Chem. 2014, 5, 70–76. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Foka-Wembe, E.N.; Benghafour, A.; Dewez, D.; Azzouz, A. Clay-Catalyzed ozonation of organic pollutants in water and toxicity on Lemna minor: Effects of molecular structure and interactions. Molecules 2023, 28, 222. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Scribner, E.A.; Thurman, E.; Goolsby, D.A.; Meyer, M.T.; Battaglin, W.A.; Kolpin, D.W. Summary of significant results from studies of triazine herbicides and their degradation products in surface water, ground water, and precipitation in the midwestern United States during the 1990s. In Scientific Investigations Report; 2005-5094; USGS Publications Warehouse: Reston, VA, USA, 2005. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tixier, C.; Sancelme, M.; Aїt-Aїssa, S.; Widehem, P.; Bonnemoy, F.; Cuer, A.; Truffaut, N.; Veschambre, H. Biotransformation of phenylurea herbicides by a soil bacterial strain, Arthrobacter sp. N2: Structure, ecotoxicity and fate of diuron metabolite with soil fungi. Chemosphere 2002, 46, 519–526. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tchounwoul, P.; Wilson, B.; Ishaque, A.; Ransome, R.; Huang, M.J.; Leszczynski, J. Toxicity assessment of atrazine and related triazine compounds in the microtox assay, and computational modeling for their structure-activity relationship. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2000, 1, 63–74. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ku, Y.; Chang, J.L.; Cheng, S.C. Effect of solution pH on the hydrolysis and photolysis of diazinon in aqueous solution. Wat. Air Soil Poll. 1998, 108, 445–456. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kouloumbos, V.N.; Tsipi, D.F.; Hiskia, A.E.; Nikolic, D.; van Breemen, R.B. Identification of photocatalytic degradation products of diazinon in TiO2 aqueous suspensions using GC/MS/MS and LC/MS with quadrupole time-of-flight mass spectrometry. J. Am. Soc. Mass Spec. 2003, 14, 803–817. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Q.; Pehkonen, S.O. Oxidation of diazinon by aqueous chlorine: Kinetics, mechanisms, and product studies. J. Agri. Food Chem. 1999, 47, 1760–1766. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Debski, B.; Kania, B.F.; Kuryl, T. Transformations of diazinon, an organophosphate compound in the environment and poisoning by this compound. Ecol. Brat. 2007, 26, 68. [Google Scholar]
- Benghaffour, A.; Dewez, D.; Azzouz, A. Correlation of pesticide ecotoxicity with clay mineral dispersion effect on adsorption and ozonation—An approach through impact assessment on Lemna minor. Appl. Clay Sci. 2023, 241, 107001. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- OECD. 221: Lemna sp. growth inhibition test. In OECD Guidelines for the Testing of Chemicals, Section 2; Organization for Economic Cooperation and Development: Paris, France, 2006; pp. 1–22. [Google Scholar]
- Lichtenthaler, H.K. Chlorophylls and carotenoids: Pigments of photosynthetic biomembranes. In Methods in Enzymology; Elsevier: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 1987; Volume 148, pp. 350–382. [Google Scholar]









Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Benghaffour, A.; Azzouz, A.; Dewez, D. Ecotoxicity of Diazinon and Atrazine Mixtures after Ozonation Catalyzed by Na+ and Fe2+ Exchanged Montmorillonites on Lemna minor. Molecules 2023, 28, 6108. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules28166108
Benghaffour A, Azzouz A, Dewez D. Ecotoxicity of Diazinon and Atrazine Mixtures after Ozonation Catalyzed by Na+ and Fe2+ Exchanged Montmorillonites on Lemna minor. Molecules. 2023; 28(16):6108. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules28166108
Chicago/Turabian StyleBenghaffour, Amina, Abdelkrim Azzouz, and David Dewez. 2023. "Ecotoxicity of Diazinon and Atrazine Mixtures after Ozonation Catalyzed by Na+ and Fe2+ Exchanged Montmorillonites on Lemna minor" Molecules 28, no. 16: 6108. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules28166108
APA StyleBenghaffour, A., Azzouz, A., & Dewez, D. (2023). Ecotoxicity of Diazinon and Atrazine Mixtures after Ozonation Catalyzed by Na+ and Fe2+ Exchanged Montmorillonites on Lemna minor. Molecules, 28(16), 6108. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules28166108