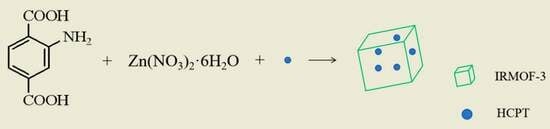
One-Pot Preparation of HCPT@IRMOF-3 Nanoparticles for pH-Responsive Anticancer Drug Delivery
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Results and Discussion
2.1. Characterization of the Materials
2.2. Drug Loading and Release of HCPT@IRMOF-3
2.3. Cell Cytotoxicity Assay
3. Materials and Methods
3.1. Materials
3.2. Preparation of HCPT@ IRMOF-3
3.3. Preparation of IRMOF-3 and HCPT Loading
3.4. Characterizations
3.5. HCPT Release Study
3.6. Cytotoxicity Study
4. Conclusions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Bray, F.; Ferlay, J.; Soerjomataram, I.; Siegel, R.L.; Torre, L.A.; Jemal, A. Global cancer statistics 2018: GLOBOCAN estimates of incidence and mortality worldwide for 36 cancers in 185 countries. CA Cancer J. Clin. 2018, 68, 394–424. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ansarinik, Z.; Kiyani, H.; Yoosefian, M. Investigation of self-assembled poly(ethyleneglycol)-poly(L-lactic acid) micelle as potential drug delivery system for poorly water soluble anticancer drug abemaciclib. J. Mol. Liq. 2022, 365, 120192. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Litauszki, K.; Igriczné, É.K.; Pamlényi, K.; Szarka, G.; Kmetty, Á.; Kovács, Z. Controlled Drug Release from Laser Treated Polymeric Carrier. J. Pharm. Sci. 2022, 111, 3297–3303. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aditi; Qanungo, K. Nano particles as drug delivery agents for antitubercular drugs. AIP Conf. Proc. 2023, 2535, 060006. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aramideh, A.; Ashjari, M.; Niazi, Z. Effects of natural polymers for enhanced silica-based mesoporous drug carrier. J. Drug Deliv. Sci. Technol. 2023, 81, 104189. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aslani, R.; Namazi, H. Synthesis of a new polymer from arginine for the preparation of antioxidant, pH-sensitive, and photoluminescence nanocomposite as a cancer drugs carrier. J. Ind. Eng. Chem. 2022, 112, 335–347. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wiśniewska, P.; Haponiuk, J.; Saeb, M.R.; Rabiee, N.; Bencherif, S. Mitigating metal-organic framework (MOF) toxicity for biomedical applications. Chem. Eng. J. 2023, 471, 144400. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, D.; Li, N.; Liu, W.; Xu, S.; Sun, Y.; Qiao, Z.; Zhong, C. Highly water-stable MOF-74 synthesized by in-situ trace polymer modification. Polymer 2023, 281, 126112. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, W.; Zhang, W.; Chen, G.; Chen, Y.; Ma, J.; Huang, D.; Zhao, Q.; Wu, B. Visible light-driven oxidation of non-native substrate by laccase attached on Ru-based metal-organic frameworks. J. Environ. Sci. 2024, 137, 741–753. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jia, C.; Wang, J.; Wang, H.; Zhu, S.; Zhang, X.; Wang, Y. Performance and mechanism of La-Fe metal-organic framework as a highly efficient adsorbent for fluoride removal from mine water. J. Environ. Sci. 2024, 139, 245–257. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Young, C.; Wang, J.; Kim, J.; Sugahara, Y.; Henzie, J.; Yamauchi, Y. Controlled chemical vapor deposition for synthesis of nanowire arrays of metal-organic frameworks and their thermal conversion to carbon/metal oxide hybrid materials. Chem. Mater. 2018, 30, 3379–3386. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Coluccia, M.; Parisse, V.; Guglielmi, P.; Giannini, G.; Secci, D. Metal-organic frameworks (MOFs) as biomolecules drug delivery systems for anticancer purposes. Eur. J. Med. Chem. 2022, 244, 114801. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nadizadeh, Z.; Naimi-Jamal, M.R.; Panahi, L. Mechanochemical solvent-free in situ synthesis of drug-loaded {Cu2(1,4-bdc)2(dabco)}n MOFs for controlled drug delivery. J. Solid State Chem. 2018, 259, 35–42. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mohan, B.; Dhiman, D.; Virender; Mehak; Priyanka; Sun, Q.; Jan, M.; Singh, G.; Raghav, N. Metal-organic frameworks (MOFs) structural properties and electrochemical detection capability for cancer biomarkers. Microchem. J. 2023, 193, 108956. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vakili, R.; Xu, S.J.; Janabi, N.A.; Gorgojo, P.; Holmes, S.M.; Fan, X.L. Microwave-assisted synthesis of zirconium-based metal organic frameworks (MOFs): Optimization and gas adsorption. Microporous Mesoporous Mater. 2018, 260, 45–53. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Z.; Liu, J.; Feng, L.; Liu, X.; Xu, Y.; Zhou, F.; Liu, W. Coupling tandem MOFs in metal-insulator-metal resonator advanced chemo-sieving sensing. Nano Today 2023, 48, 101726. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ebrahimi, A.K.; Barani, M.; Sheikhshoaie, I. Fabrication of a new superpara magnetic metal-organic framework with core-shell nanocomposite structures: Characterization, biocompatibility, and drug release study. Mater. Sci. Eng. C 2018, 92, 349–355. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wen, H.M.; Li, L.; Lin, R.B.; Li, B.; Hu, B.; Zhou, W.; Hu, J.; Chen, B. Fine-tuning of nano-traps in a stable metal-organic framework for highly efficient removal of propyne from propylene. J. Mater. Chem. A 2018, 6, 6931–6937. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sharma, A.; Bedi, S.; Verma, K.; Lal, B.; John, V.; Kumar, R.; Kaushal, S.; Badru, R. Ce-Zr UiO-66 MOF as recyclable heterogeneous catalyst for selective N-methylation. Polyhedron 2023, 242, 116517. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Samui, A.; Pal, K.; Karmakar, P.; Sahu, S. In situ synthesized lactobionic acid conjugated NMOFs, a smart material for imaging and targeted drug delivery in hepatocellular carcinoma. Mater. Sci. Eng. C 2019, 98, 772–781. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mohan, B.; Priyanka; Singh, G.; Chauhan, A.; Armando; Pombeiro, J.L.; Ren, P. Metal-organic frameworks (MOFs) based luminescent and electrochemical sensors for food contaminant detection. J. Hazard. Mater. 2023, 453, 131324. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sharma, D.; Sjunjemmenla; Kumar, D.; Takhar, D.; Birajdar, B.; Kumar, V.; Khare, N. Stable metal-organic framework (MOF) integrated BCZT for improved photo-electrochemical water splitting. J. Mater. Sci. Eng. B 2023, 297, 116769. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Torkashvand, Z.; Sepehrmansourie, H.; Zolfigol, M.A.; Habi, M.A.A. Application of Ti-MOF-UR as a new porous catalyst for the preparation of pyrazolo[3,4-b]quinoline and pyrazolo[4,3-e]pyridines. Mol. Catal. 2023, 541, 113107. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gao, C.; Mu, X.; Yuan, W.; Zhang, P.; Wang, Y.; Zhai, Q. Construction of new multi-cage-based MOFs using flexible triangular ligands for efficient gas adsorption and separation. J. Solid State Chem. 2023, 322, 123994. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, K.; Zhang, L.; Hu, Q.; Zhang, X.; Zhang, J.; Cui, Y.; Yang, Y.; Lia, B.; Qian, G. A zirconium-based metal-organic framework with encapsulated anionic drug for uncommonly controlled oral drug delivery. Microporous Mesoporous Mater. 2019, 275, 229–234. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gupta, V.; Mohiyuddin, S.; Sachdev, A.; Soni, P.K.; Gopinath, P.; Tyagi, S. PEG functionalized zirconium dicarboxylate MOFs for docetaxel drug delivery in vitro. J. Drug Deliv. Sci. Technol. 2019, 52, 846–855. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tran, N.L.N.; Hoang, D.V.; Pham, A.T.T.; Phuong, N.T.T.; Mai, N.X.D.; Chi, T.T.K.; Hien, B.T.T.; Phan, T.B.; Tran, N.H.T. Novel composites of nano-metal-organic frameworks (IRMOF-3) and silver nanoparticles for the ultra-sensitive performance of SERS sensing and optical fiber modes. J. Sci. Adv. Mater. Devices 2023, 8, 100584. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Koosha, S.; Alavinia, S.; Ghorbani-Vaghei, R. CuI nanoparticles-immobilized on a hybrid material composed of IRMOF-3 and a sulfonamide-based porous organic polymer as an efficient nanocatalyst for one-pot synthesis of 2,3-disubstituted benzo[b]furans. Arabian J. Chem. 2023, 16, 104975. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, C.; Yu, H.; Sun, J.; Zhou, C.; Li, X.; Su, Z.M.; Liu, F.; Khakhinov, V. Luminescent composites by in-suit encapsulating dye in IRMOF-3 for ratiometric temperature sensing and tunable white light emission. Dyes Pigm. 2022, 198, 110000. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abdelhameed, R.; EI-Naggar, M.; Taha, M.; Nabil, S.; Youssef, M.; Awwad, N.; Sayed, M. Designing a sensitive luminescent probe for organophosphorus insecticides detection based on post-synthetic modification of IRMOF-3. J. Mol. Struct. 2020, 1199, 127000. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ullah, S.; Bustam, M.A.; Assiri, M.A.; Al-Sehemi, A.G.; Kareem, F.A.; Mukhtar, A.; Ayoub, M.; Gonfa, G. Synthesis and characterization of iso-reticular metal-organic Framework-3 (IRMOF-3) for CO2/CH4 adsorption: Impact of post-synthetic aminomethyl propanol (AMP) functionalization. J. Nat. Gas Sci. Eng. 2019, 72, 103014. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Couvreur, P.; Vauthier, C. Nanotechnology: Intelligent Design to Treat Complex Disease. Pharm. Res. 2006, 23, 1417–1450. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lin, W.; Cui, Y.; Yang, Y.; Hu, Q.; Qian, G. A biocompatible metal-organic framework as a pH and temperature dual-responsive drug carrier. Dalton Trans. 2018, 47, 15882–15887. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pan, Y.; Wang, S.; He, X.; Tang, W.; Wang, J.; Shao, A.; Zhang, J. A combination of glioma in vivo imaging and in vivo drug delivery by metal–organic framework based composite nanoparticles. J. Mater. Chem. B 2019, 7, 7683–7689. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Prabhu, R.; Mohamed, A.; Anjali, R.; Archunan, G.; Prabhu, N.M.; Pugazhendhi, A.; Suganthy, N. Ecofriendly one pot fabrication of methyl gallate@ZIF-L nanoscale hybrid as pH responsive drug delivery system for lung cancer therapy. Process Biochem. 2019, 84, 39–52. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kalosakas, G. Interplay between Diffusion and Bond Cleavage Reaction for Determining Release in Polymer-Drug Conjugates. Materials 2023, 16, 4595. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]







| Cell Line | HCPT | HCPT@IRMOF-3 |
|---|---|---|
| Hela | 0.004 ± 0.001 | 0.061 ± 0.008 |
| Neuroblastoma (SH-SY5Y) | 8.94 × 10−4 ± 6.5 × 10−5 | 0.052 ± 4.3 × 10−3 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the author. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Cheng, H. One-Pot Preparation of HCPT@IRMOF-3 Nanoparticles for pH-Responsive Anticancer Drug Delivery. Molecules 2023, 28, 7703. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules28237703
Cheng H. One-Pot Preparation of HCPT@IRMOF-3 Nanoparticles for pH-Responsive Anticancer Drug Delivery. Molecules. 2023; 28(23):7703. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules28237703
Chicago/Turabian StyleCheng, Hongda. 2023. "One-Pot Preparation of HCPT@IRMOF-3 Nanoparticles for pH-Responsive Anticancer Drug Delivery" Molecules 28, no. 23: 7703. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules28237703
APA StyleCheng, H. (2023). One-Pot Preparation of HCPT@IRMOF-3 Nanoparticles for pH-Responsive Anticancer Drug Delivery. Molecules, 28(23), 7703. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules28237703