Structure and Vibrational Spectroscopy of C82 Fullerenol Valent Isomers: An Experimental and Theoretical Joint Study
Abstract
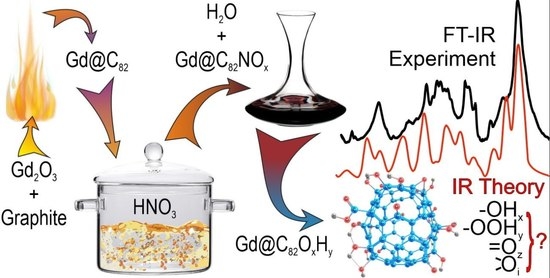
:1. Introduction
2. Results and Discussion
2.1. FTIR Spectrum of Hydroxylated Gd Endohedral Complexes
2.2. Atomic Structure of C82O28H20 Valent Isomers
2.3. Theoretical IR Spectra of C82O28H20 Valent Isomers
3. Methods
3.1. Experimental Methods
3.2. Computational Details
4. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Dostalova, S.; Moulick, A.; Milosavljevic, V.; Guran, R.; Kominkova, M.; Cihalova, K.; Heger, Z.; Blazkova, L.; Kopel, P.; Hynek, D.; et al. Antiviral Activity of Fullerene C60 Nanocrystals Modified with Derivatives of Anionic Antimicrobial Peptide Maximin H5. Mon. Chem. Chem. Mon. 2016, 147, 905–918. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shoji, M.; Takahashi, E.; Hatakeyama, D.; Iwai, Y.; Morita, Y.; Shirayama, R.; Echigo, N.; Kido, H.; Nakamura, S.; Mashino, T.; et al. Anti-Influenza Activity of C60 Fullerene Derivatives. PLoS ONE 2013, 8, e66337. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marchesan, S.; Da Ros, T.; Spalluto, G.; Balzarini, J.; Prato, M. Anti-HIV Properties of Cationic Fullerene Derivatives. Bioorg. Med. Chem. Lett. 2005, 15, 3615–3618. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Galvan, Y.; Alperovich, I.; Zolotukhin, P.; Prazdnova, E.; Mazanko, M.; Belanova, A.; Chistyakov, V. Fullerenes as Anti-Aging Antioxidants. Curr. Aging Sci. 2017, 10, 56–67. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sergeeva, V.; Kraevaya, O.; Ershova, E.; Kameneva, L.; Malinovskaya, E.; Dolgikh, O.; Konkova, M.; Voronov, I.; Zhilenkov, A.; Veiko, N.; et al. Antioxidant Properties of Fullerene Derivatives Depend on Their Chemical Structure: A Study of Two Fullerene Derivatives on HELFs. Oxidative Med. Cell. Longev. 2019, 2019, 4398695. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Roy, P.; Bag, S.; Chakraborty, D.; Dasgupta, S. Exploring the Inhibitory and Antioxidant Effects of Fullerene and Fullerenol on Ribonuclease A. ACS Omega 2018, 3, 12270–12283. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sargazi, S.; ER, S.; Mobashar, A.; Gelen, S.S.; Rahdar, A.; Ebrahimi, N.; Hosseinikhah, S.M.; Bilal, M.; Kyzas, G.Z. Aptamer-Conjugated Carbon-Based Nanomaterials for Cancer and Bacteria Theranostics: A Review. Chem. Biol. Interact. 2022, 361, 109964. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bolskar, R.D. Fullerenes for Drug Delivery BT—Encyclopedia of Nanotechnology; Bhushan, B., Ed.; Springer: Dordrecht, The Netherlands, 2016; pp. 1267–1281. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Al-Tamimi, B.H.; Farid, S.B.H. Fullerenes and Nanodiamonds for Medical Drug Delivery; Mallik, A.K., Ed.; IntechOpen: Rijeka, Croatia, 2021; Chapter 5. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wharton, T.; Wilson, L.J. Highly-Iodinated Fullerene as a Contrast Agent For X-Ray Imaging. Bioorg. Med. Chem. 2002, 10, 3545–3554. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Grushko, Y.S.; Kozlov, V.S.; Sedov, V.P.; Kolesnik, S.G.; Lebedev, V.T.; Shilin, V.A.; Khodorkovsky, M.A.; Artamonova, T.O.; Shakhmin, A.L.; Shamanin, V.V.; et al. MRI-Contrasting System Based on Water-Soluble Fullerene/Gd-Metallofullerene Mixture. Fuller. Nanotub. Carbon Nanostruct. 2010, 18, 417–421. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, Z.; Zhen, M.; Zhou, C.; Li, L.; Jia, W.; Liu, S.; Li, X.; Liao, X.; Wang, C. A Gadofullerene Based Liver-Specific MRI Contrast Agent for an Early Diagnosis of Orthotopic Hepatocellular Carcinoma. J. Mater. Chem. B 2021, 9, 5722–5728. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moreno-Vicente, A.; Mulet-Gas, M.; Dunk, P.W.; Poblet, J.M.; Rodríguez-Fortea, A. Probing the Formation of Halogenated Endohedral Metallofullerenes: Predictions Confirmed by Experiments. Carbon N. Y. 2018, 129, 750–757. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zou, T.; Zhen, M.; Li, J.; Chen, D.; Feng, Y.; Li, R.; Guan, M.; Zhang, Y.; Shu, C.; Wang, C. The Effect of Hemiketals on the Relaxivity of Endohedral Gadofullerenols. RSC Adv. 2015, 5, 96253–96257. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tóth, É.; Bolskar, R.D.; Borel, A.; González, G.; Helm, L.; Merbach, A.E.; Sitharaman, B.; Wilson, L.J. Water-Soluble Gadofullerenes: Toward High-Relaxivity, PH-Responsive MRI Contrast Agents. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2005, 127, 799–805. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Q.; Xu, L.; Zhang, X.; Li, N.; Zheng, J.; Guan, M.; Fang, X.; Wang, C.; Shu, C. Enhanced Photodynamic Efficiency of an Aptamer-Guided Fullerene Photosensitizer toward Tumor Cells. Chem.—Asian J. 2013, 8, 2370–2376. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wakimoto, T.; Uchida, K.; Mimura, K.; Kanagawa, T.; Mehandjiev, T.R.; Aoshima, H.; Kokubo, K.; Mitsuda, N.; Yoshioka, Y.; Tsutsumi, Y.; et al. Hydroxylated Fullerene: A Potential Antiinflammatory and Antioxidant Agent for Preventing Mouse Preterm Birth. Am. J. Obstet. Gynecol. 2015, 213, 708.e1–708.e9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Grebowski, J.; Konopko, A.; Krokosz, A.; DiLabio, G.A.; Litwinienko, G. Antioxidant Activity of Highly Hydroxylated Fullerene C60 and Its Interactions with the Analogue of α-Tocopherol. Free Radic. Biol. Med. 2020, 160, 734–744. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Semenov, K.N.; Andrusenko, E.V.; Charykov, N.A.; Litasova, E.V.; Panova, G.G.; Penkova, A.V.; Murin, I.V.; Piotrovskiy, L.B. Carboxylated Fullerenes: Physico-Chemical Properties and Potential Applications. Prog. Solid State Chem. 2017, 47–48, 19–36. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yan, Q.-B.; Zheng, Q.-R.; Su, G. Theoretical Study on the Structures, Properties and Spectroscopies of Fullerene Derivatives C66X4 (X = H, F, Cl). Carbon N. Y. 2007, 45, 1821–1827. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tang, C.; Chen, S.; Zhu, W.; Zhang, A.; Zhang, K.; Liu, M. Stabilities, Aromaticity, Infrared Spectra, and Optical Properties of Exohedral Fullerene Derivatives C76X18(X = H, F, Cl, and Br). Eur. Phys. J. D 2014, 68, 19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shakirova, A.A.; Tomilin, F.N.; Pomogaev, V.A.; Vnukova, N.G.; Churilov, G.N.; Kudryasheva, N.S.; Tchaikovskaya, O.N.; Ovchinnikov, S.G.; Avramov, P.V. Synthesis, Mass Spectroscopy Detection, and Density Functional Theory Investigations of the Gd Endohedral Complexes of C82 Fullerenols. Computation 2021, 9, 58. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dawid, A.; Górny, K.; Gburski, Z. Water Solvent Effect on Infrared and Raman Spectra of C60(OH)24 Fullerenol Isomers: DFT Study. J. Phys. Chem. C 2017, 121, 2303–2315. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Z.; Gao, X.; Zhao, Y. Mechanisms of Antioxidant Activities of Fullerenols from First-Principles Calculation. J. Phys. Chem. A 2018, 122, 8183–8190. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, X.-J.; Yang, X.-H.; Song, L.-M.; Ren, H.-J.; Tao, T.-Z. A DFT Study on Structure, Stability, and Optical Property of Fullerenols. Struct. Chem. 2013, 24, 1185–1192. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dawid, A.; Górny, K.; Gburski, Z. The Influence of Distribution of Hydroxyl Groups on Vibrational Spectra of Fullerenol C60(OH)24 Isomers: DFT Study. Spectrochim. Acta Part A Mol. Biomol. Spectrosc. 2015, 136, 1993–1997. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bai, H.; Gao, H.; Feng, W.; Zhao, Y.; Wu, Y. Interaction in Li@Fullerenes and Li+@Fullerenes: First Principle Insights to Li-Based Endohedral Fullerenes. Nanomaterials 2019, 9, 630. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gao, H.; Sun, Y.; Zhang, J.; Wang, Q.; Wu, Y.; Bai, H. Understanding Endohedral Behaviors of Ten-Electron Atomic and Cluster System inside C60 from First-Principles. Phys. E Low-Dimens. Syst. Nanostruct. 2021, 127, 114532. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dai, X.; Gao, Y.; Xin, M.; Wang, Z.; Zhou, R. The Ground State and Electronic Structure of Gd@ C82: A Systematic Theoretical Investigation of First Principle Density Functionals. J. Chem. Phys. 2014, 141, 244306. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Martínez-Flores, C.; Basiuk, V.A. Ln@C60 Endohedral Fullerenes: A DFT Analysis for the Complete Series from Lanthanum to Lutetium. Comput. Theor. Chem. 2022, 1217, 113878. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- AlZahrani, A.Z. Cerium-Doped Endohedral Fullerene: A Density-Functional Theory Study. ISRN Condens. Matter Phys. 2012, 2012, 208234. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Senapati, L.; Schrier, J.; Whaley, K.B. Electronic Transport, Structure, and Energetics of Endohedral Gd@C82 Metallofullerenes. Nano Lett. 2004, 4, 2073–2078. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Velarde-Salcedo, M.V.; Gallo, M.; Guirado-López, R.A. Low Hydroxylated Fullerenes: Stability, Thermal Behavior, and Vibrational Properties. J. Phys. Chem. C 2018, 122, 13117–13129. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Palotás, J.; Martens, J.; Berden, G.; Oomens, J. Laboratory IR Spectra of the Ionic Oxidized Fullerenes C60O+ and C60OH+. J. Phys. Chem. A 2022, 126, 2928–2935. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cui, R.; Li, J.; Huang, H.; Zhang, M.; Guo, X.; Chang, Y.; Li, M.; Dong, J.; Sun, B.; Xing, G. Novel Carbon Nanohybrids as Highly Efficient Magnetic Resonance Imaging Contrast Agents. Nano Res. 2015, 8, 1259–1268. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shanbogh, P.P.; Sundaram, N.G. Fullerenes Revisited. Resonance 2015, 20, 123–135. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wei, T.; Wang, S.; Liu, F.; Tan, Y.; Zhu, X.; Xie, S.; Yang, S. Capturing the Long-Sought Small-Bandgap Endohedral Fullerene Sc3N@C82 with Low Kinetic Stability. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2015, 137, 3119–3123. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Roy, D.; Porwal, D.; Mukhopadhyay, K.; Ram, K. Theoretical Studies on C82 Fullerene with Encapsulated Germanium Metal. Synth. React. Inorg. Met. Nano-Metal Chem. 2006, 36, 43–46. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shimada, T.; Ohno, Y.; Okazaki, T.; Sugai, T.; Suenaga, K.; Kishimoto, S.; Mizutani, T.; Inoue, T.; Taniguchi, R.; Fukui, N.; et al. Transport Properties of C78, C90 and Dy@C82 Fullerenes-Nanopeapods by Field Effect Transistors. Phys. E Low-Dimens. Syst. Nanostruct. 2004, 21, 1089–1092. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mikawa, M.; Kato, H.; Okumura, M.; Narazaki, M.; Kanazawa, Y.; Miwa, N.; Shinohara, H. Paramagnetic Water-Soluble Metallofullerenes Having the Highest Relaxivity for MRI Contrast Agents. Bioconjug. Chem. 2001, 12, 510–514. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Meng, J.; Liang, X.; Chen, X.; Zhao, Y. Biological Characterizations of [Gd@C82(OH)22]n Nanoparticles as Fullerene Derivatives for Cancer Therapy. Integr. Biol. 2013, 5, 43–47. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Horiguchi, Y.; Kudo, S.; Nagasaki, Y. Gd@C82 Metallofullerenes for Neutron Capture Therapy—Fullerene Solubilization by Poly(Ethylene Glycol)-Block-Poly(2-(N, N-Diethylamino)Ethyl Methacrylate) and Resultant Efficacy in Vitro. Sci. Technol. Adv. Mater. 2011, 12, 44607. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, X.; Wang, C. The Potential Biomedical Platforms Based on the Functionalized Gd@C82 Nanomaterials. VIEW 2020, 1, e7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rodríguez-Zavala, J.G.; Tenorio, F.J.; Samaniego, C.; Méndez-Barrientos, C.I.; Peña-Lecona, F.G.; Muñoz-Maciel, J.; Flores-Moreno, R. Theoretical Study on the Sequential Hydroxylation of C82 Fullerene Based on Fukui Function. Mol. Phys. 2011, 109, 1771–1783. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, J.; Li, F.; Miao, X.; Zhao, J.; Jing, L.; Yang, G.; Jia, X. Most Stable Structures of Polyhydroxylated Endohedral Metallofullerene Gd@C82(OH)x (X = 1–24) from Density Function Theory. Chem. Phys. Lett. 2010, 492, 68–70. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dudnik, A.I.; Vnukova, N.G.; Drokin, N.A.; Bondarev, V.S.; Shestakov, N.P.; Tomashevich, Y.V.; Churilov, G.N. Electrophysical Properties of Hydroxylated Endohedral Metallofullerene with Gadolinium. J. Phys. Chem. Solids 2019, 135, 109094. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Husebo, L.O.; Sitharaman, B.; Furukawa, K.; Kato, T.; Wilson, L.J. Fullerenols Revisited as Stable Radical Anions. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2004, 126, 12055–12064. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, B.-C.; Wang, H.-W.; Tso, H.-C.; Chen, T.-L.; Chou, Y.-M. Theoretical Studies of C70(OH)n (N = 14, 16, 18 and 20) Fullerenols. J. Mol. Struct. THEOCHEM 2002, 581, 177–186. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, J.; Wang, T.; Feng, Y.; Zhang, Y.; Zhen, M.; Shu, C.; Jiang, L.; Wang, Y.; Wang, C. A Water-Soluble Gadolinium Metallofullerenol: Facile Preparation, Magnetic Properties and Magnetic Resonance Imaging Application. Dalt. Trans. 2016, 45, 8696–8699. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Churilov, G.N.; Krätschmer, W.; Osipova, I.V.; Glushenko, G.A.; Vnukova, N.G.; Kolonenko, A.L.; Dudnik, A.I. Synthesis of Fullerenes in a High-Frequency Arc Plasma under Elevated Helium Pressure. Carbon N. Y. 2013, 62, 389–392. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Akiyama, K.; Hamano, T.; Nakanishi, Y.; Takeuchi, E.; Noda, S.; Wang, Z.; Kubuki, S.; Shinohara, H. Non-HPLC Rapid Separation of Metallofullerenes and Empty Cages with TiCl4 Lewis Acid. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2012, 134, 9762–9767. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chiang, L.Y.; Swirczewski, J.W.; Hsu, C.S.; Chowdhury, S.K.; Cameron, S.; Creegan, K. Multi-Hydroxy Additions onto C60 Fullerene Molecules. J. Chem. Soc. Chem. Commun. 1992, 24, 1791–1793. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gaus, M.; Goez, A.; Elstner, M. Parametrization and Benchmark of DFTB3 for Organic Molecules. J. Chem. Theory Comput. 2013, 9, 338–354. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Avramov, P.V.; Kuklin, A.V. Topological and Quantum Stability of Low-Dimensional Crystalline Lattices with Multiple Nonequivalent Sublattices. New J. Phys. 2022, 24, 103015. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barca, G.M.J.; Bertoni, C.; Carrington, L.; Datta, D.; De Silva, N.; Deustua, J.E.; Fedorov, D.G.; Gour, J.R.; Gunina, A.O.; Guidez, E.; et al. Recent Developments in the General Atomic and Molecular Electronic Structure System. J. Chem. Phys. 2020, 152, 154102. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rüger, R.; Niehaus, T.; van Lenthe, E.; Heine, T.; Visscher, L. Vibrationally Resolved UV/Vis Spectroscopy with Time-Dependent Density Functional Based Tight Binding. J. Chem. Phys. 2016, 145, 184102. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Inakollu, V.S.S.; Yu, H. A Systematic Benchmarking of Computational Vibrational Spectroscopy with DFTB3: Normal Mode Analysis and Fast Fourier Transform Dipole Autocorrelation Function. J. Comput. Chem. 2018, 39, 2067–2078. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]


Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Tomilin, F.N.; Artyushenko, P.V.; Shchugoreva, I.A.; Rogova, A.V.; Vnukova, N.G.; Churilov, G.N.; Shestakov, N.P.; Tchaikovskaya, O.N.; Ovchinnikov, S.G.; Avramov, P.V. Structure and Vibrational Spectroscopy of C82 Fullerenol Valent Isomers: An Experimental and Theoretical Joint Study. Molecules 2023, 28, 1569. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules28041569
Tomilin FN, Artyushenko PV, Shchugoreva IA, Rogova AV, Vnukova NG, Churilov GN, Shestakov NP, Tchaikovskaya ON, Ovchinnikov SG, Avramov PV. Structure and Vibrational Spectroscopy of C82 Fullerenol Valent Isomers: An Experimental and Theoretical Joint Study. Molecules. 2023; 28(4):1569. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules28041569
Chicago/Turabian StyleTomilin, Felix N., Polina V. Artyushenko, Irina A. Shchugoreva, Anastasia V. Rogova, Natalia G. Vnukova, Grigory N. Churilov, Nikolay P. Shestakov, Olga N. Tchaikovskaya, Sergei G. Ovchinnikov, and Pavel V. Avramov. 2023. "Structure and Vibrational Spectroscopy of C82 Fullerenol Valent Isomers: An Experimental and Theoretical Joint Study" Molecules 28, no. 4: 1569. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules28041569
APA StyleTomilin, F. N., Artyushenko, P. V., Shchugoreva, I. A., Rogova, A. V., Vnukova, N. G., Churilov, G. N., Shestakov, N. P., Tchaikovskaya, O. N., Ovchinnikov, S. G., & Avramov, P. V. (2023). Structure and Vibrational Spectroscopy of C82 Fullerenol Valent Isomers: An Experimental and Theoretical Joint Study. Molecules, 28(4), 1569. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules28041569