Adsorptive Features of Magnetic Activated Carbons Prepared by a One-Step Process towards Brilliant Blue Dye
Abstract
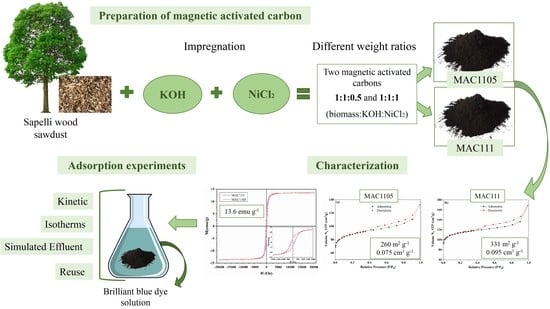
:1. Introduction
2. Results and Discussion
2.1. Features of the Magnetic Activated Carbons
2.1.1. Scanning Electron Microscopy Images
2.1.2. Functional Groups on the Magnetic Activated Carbons Surface
2.1.3. Textural Characteristics
2.1.4. Thermal Analysis
2.1.5. X-ray Diffraction
2.1.6. Magnetic Features
2.2. Adsorption Results
2.2.1. Kinetic Profiles of BB Adsorption
2.2.2. Adsorption Isotherms
2.2.3. Regeneration and Reuse Study
2.2.4. Application of MACs to Treat a Simulated Effluent
3. Material and Methods
3.1. Materials
3.2. Preparation of the Magnetic Activated Carbons
3.3. MACs Characterization
3.4. Kinetic and Equilibrium Adsorption Experiments
3.5. Kinetic and Equilibrium Models
3.6. Regeneration and Reuse Experiments
3.7. Application in a Simulated Effluent
4. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Patra, B.R.; Mukherjee, A.; Nanda, S.; Dalai, A.K. Biochar production, activation and adsorptive applications: A review. Environ. Chem. Lett. 2021, 19, 2237–2259. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Haleem, A.; Shafiq, A.; Chen, S.-Q.; Nazar, M. A Comprehensive Review on Adsorption, Photocatalytic and Chemical Degradation of Dyes and Nitro-Compounds over Different Kinds of Porous and Composite Materials. Molecules 2023, 28, 1081. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alias, S.S.; Harun, Z.; Azhar, F.H.; Ibrahim, S.A.; Johar, B. Comparison between commercial and synthesised nano flower-like rutile TiO2 immobilised on green super adsorbent towards dye wastewater treatment. J. Clean. Prod. 2019, 251, 119448. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shah, L.A.; Malik, T.; Siddiq, M.; Haleem, A.; Sayed, M.; Naeem, A. TiO2 nanotubes doped poly(vinylidene fluoride) polymer membranes (PVDF/TNT) for efficient photocatalytic degradation of brilliant green dye. J. Environ. Chem. Eng. 2019, 7, 103291. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bhatti, H.N.; Safa, Y.; Yakout, S.M.; Shair, O.H.; Iqbal, M.; Nazir, A. Efficient removal of dyes using carboxymethyl cellulose/alginate/polyvinyl alcohol/rice husk composite: Adsorption/desorption, kinetics and recycling studies. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2020, 150, 861–870. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wekoye, J.N.; Wanyonyi, W.C.; Wangila, P.T.; Tonui, M.K. Kinetic and equilibrium studies of Congo red dye adsorption on cabbage waste powder. Environ. Chem. Ecotoxicol. 2020, 2, 24–31. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ortiz-Martínez, A.; Godínez, L.A.; Martínez-Sánchez, C.; García-Espinoza, J.; Robles, I. Preparation of modified carbon paste electrodes from orange peel and used coffee ground. New materials for the treatment of dye-contaminated solutions using electro-Fenton processes. Electrochim. Acta 2021, 390, 138861. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dotto, J.; Fagundes-Klen, M.R.; Veit, M.T.; Palácio, S.M.; Bergamasco, R. Performance of different coagulants in the coagulation/flocculation process of textile wastewater. J. Clean. Prod. 2018, 208, 656–665. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arunprasath, T.; Sudalai, S.; Meenatchi, R.; Jeyavishnu, K.; Arumugam, A. Biodegradation of triphenylmethane dye malachite green by a newly isolated fungus strain. Biocatal. Agric. Biotechnol. 2019, 17, 672–679. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hassan, M.M.; Carr, C.M. A critical review on recent advancements of the removal of reactive dyes from dyehouse effluent by ion-exchange adsorbents. Chemosphere 2018, 209, 201–219. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- de Salomón, Y.L.O.; Georgin, J.; Franco, D.S.P.; Netto, M.S.; Foletto, E.L.; Allasia, D.; Dotto, G.L. Application of seed residues from Anadenanthera macrocarpa and Cedrela fissilis as alternative adsorbents for remarkable removal of methylene blue dye in aqueous solutions. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2020, 28, 2342–2354. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dotto, G.L.; McKay, G. Current scenario and challenges in adsorption for water treatment. J. Environ. Chem. Eng. 2020, 8, 103988. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tahir, M.A.; Bhatti, H.N.; Iqbal, M. Solar Red and Brittle Blue direct dyes adsorption onto Eucalyptus angophoroides bark: Equilibrium, kinetics and thermodynamic studies. J. Environ. Chem. Eng. 2016, 4, 2431–2439. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jawad, A.H.; Abdulhameed, A.S.; Reghioua, A.; Yaseen, Z.M. Zwitterion composite chitosan-epichlorohydrin/zeolite for adsorption of methylene blue and reactive red 120 dyes. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2020, 163, 756–765. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Puchana-Rosero, M.; Adebayo, M.A.; Lima, E.C.; Machado, F.M.; Thue, P.S.; Vaghetti, J.C.; Umpierres, C.S.; Gutterres, M. Microwave-assisted activated carbon obtained from the sludge of tannery-treatment effluent plant for removal of leather dyes. Colloids Surf. A Physicochem. Eng. Asp. 2016, 504, 105–115. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yunus, Z.M.; Al-Gheethi, A.; Othman, N.; Hamdan, R.; Ruslan, N.N. Removal of heavy metals from mining effluents in tile and electroplating industries using honeydew peel activated carbon: A microstructure and techno-economic analysis. J. Clean. Prod. 2019, 251, 119738. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rashid, J.; Tehreem, F.; Rehman, A.; Kumar, R. Synthesis using natural functionalization of activated carbon from pumpkin peels for decolourization of aqueous methylene blue. Sci. Total. Environ. 2019, 671, 369–376. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kang, K.; Nanda, S.; Lam, S.S.; Zhang, T.; Huo, L.; Zhao, L. Enhanced fuel characteristics and physical chemistry of microwave hydrochar for sustainable fuel pellet production via co-densification. Environ. Res. 2020, 186, 109480. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sarker, T.R.; Pattnaik, F.; Nanda, S.; Dalai, A.K.; Meda, V.; Naik, S. Hydrothermal pretreatment technologies for lignocellulosic biomass: A review of steam explosion and subcritical water hydrolysis. Chemosphere 2021, 284, 131372. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Supong, A.; Bhomick, P.C.; Baruah, M.; Pongener, C.; Sinha, U.B.; Sinha, D. Adsorptive removal of Bisphenol A by biomass activated carbon and insights into the adsorption mechanism through density functional theory calculations. Sustain. Chem. Pharm. 2019, 13, 100159. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zazycki, M.A.; Godinho, M.; Perondi, D.; Foletto, E.L.; Collazzo, G.C.; Dotto, G.L. New biochar from pecan nutshells as an alternative adsorbent for removing reactive red 141 from aqueous solutions. J. Clean. Prod. 2018, 171, 57–65. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.; Wang, S.-L.; Xie, T.; Cao, J. Activated carbon derived from waste tangerine seed for the high-performance adsorption of carbamate pesticides from water and plant. Bioresour. Technol. 2020, 316, 123929. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Van Thuan, T.; Quynh, B.T.P.; Nguyen, T.D.; Ho, V.T.T.; Bach, L.G. Response surface methodology approach for optimization of Cu2+, Ni2+ and Pb2+ adsorption using KOH-activated carbon from banana peel. Surf. Interfaces 2017, 6, 209–217. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Enniya, I.; Rghioui, L.; Jourani, A. Adsorption of hexavalent chromium in aqueous solution on activated carbon prepared from apple peels. Sustain. Chem. Pharm. 2018, 7, 9–16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sajjadi, S.-A.; Meknati, A.; Lima, E.C.; Dotto, G.L.; Mendoza-Castillo, D.I.; Anastopoulos, I.; Alakhras, F.; Unuabonah, E.I.; Singh, P.; Hosseini-Bandegharaei, A. A novel route for preparation of chemically activated carbon from pistachio wood for highly efficient Pb(II) sorption. J. Environ. Manag. 2019, 236, 34–44. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kumar, A.; Gupta, H. Activated carbon from sawdust for naphthalene removal from contaminated water. Environ. Technol. Innov. 2020, 20, 101080. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chikri, R.; Elhadiri, N.; Benchanaa, M.; El Maguana, Y. Efficiency of Sawdust as Low-Cost Adsorbent for Dyes Removal. J. Chem. 2020, 2020, 8813420. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mallakpour, S.; Sirous, F.; Hussain, C.M. Sawdust, a versatile, inexpensive, readily available bio-waste: From mother earth to valuable materials for sustainable remediation technologies. Adv. Colloid Interface Sci. 2021, 295, 102492. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vieira, L.H.S.; Sabino, C.M.S.; Júnior, F.H.S.; Rocha, J.S.; Castro, M.O.; Alencar, R.S.; da Costa, L.S.; Viana, B.C.; de Paula, A.J.; Soares, J.M.; et al. Strategic design of magnetic carbonaceous nanocomposites and its application as multifunctional adsorbent. Carbon 2020, 161, 758–771. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, X.; Wang, Y.; Zhang, T.C.; Xiang, G.; Wang, X.; Yuan, S. One-Pot Synthesis of a Magnetic TiO2/PTh/γ-Fe2O3 Heterojunction Nanocomposite for Removing Trace Arsenite via Simultaneous Photocatalytic Oxidation and Adsorption. Ind. Eng. Chem. Res. 2020, 60, 528–540. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moosavi, S.; Lai, C.W.; Gan, S.; Zamiri, G.; Pivehzhani, O.A.; Johan, M.R. Application of Efficient Magnetic Particles and Activated Carbon for Dye Removal from Wastewater. ACS Omega 2020, 5, 20684–20697. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.; Zhang, Y.; Zhang, T.C.; Xiang, G.; Wang, X.; Yuan, S. Removal of Trace Arsenite through Simultaneous Photocatalytic Oxidation and Adsorption by Magnetic Fe3O4@PpPDA@TiO2 Core–Shell Nanoparticles. ACS Appl. Nano Mater. 2020, 3, 8495–8504. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Du, Q.; Zhang, S.; Song, J.; Zhao, Y.; Yang, F. Activation of porous magnetized biochar by artificial humic acid for effective removal of lead ions. J. Hazard. Mater. 2020, 389, 122115. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Feng, Z.; Chen, H.; Li, H.; Yuan, R.; Wang, F.; Chen, Z.; Zhou, B. Preparation, characterization, and application of magnetic activated carbon for treatment of biologically treated papermaking wastewater. Sci. Total. Environ. 2020, 713, 136423. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pereira, D.; Rocha, L.S.; Gil, M.V.; Otero, M.; Silva, N.J.O.; Esteves, V.I.; Calisto, V. In situ functionalization of a cellulosic-based activated carbon with magnetic iron oxides for the removal of carbamazepine from wastewater. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2020, 28, 18314–18327. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Salem, S.; Teimouri, Z.; Salem, A. Fabrication of magnetic activated carbon by carbothermal functionalization of agriculture waste via microwave-assisted technique for cationic dye adsorption. Adv. Powder Technol. 2020, 31, 4301–4309. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thue, P.S.; Umpierres, C.S.; Lima, E.C.; Lima, D.R.; Machado, F.M.; dos Reis, G.S.; da Silva, R.S.; Pavan, F.A.; Tran, H.N. Single-step pyrolysis for producing magnetic activated carbon from tucumã (Astrocaryum aculeatum) seed and nickel(II) chloride and zinc(II) chloride. Application for removal of nicotinamide and propanolol. J. Hazard. Mater. 2020, 398, 122903. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bai, X.; Yu, L.; Hua, Z.; Tang, Z.; Zhang, J. Synthesis and characterization of superparamagnetic activated carbon adsorbents based on cyanobacteria. Mater. Chem. Phys. 2015, 163, 407–415. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lütke, S.F.; Igansi, A.V.; Pegoraro, L.; Dotto, G.L.; Pinto, L.A.; Cadaval, T.R. Preparation of activated carbon from black wattle bark waste and its application for phenol adsorption. J. Environ. Chem. Eng. 2019, 7, 103396. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thue, P.S.; Lima, E.C.; Sieliechi, J.M.; Saucier, C.; Dias, S.L.; Vaghetti, J.C.; Rodembusch, F.S.; Pavan, F.A. Effects of first-row transition metals and impregnation ratios on the physicochemical properties of microwave-assisted activated carbons from wood biomass. J. Colloid Interface Sci. 2017, 486, 163–175. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Muniandy, L.; Adam, F.; Mohamed, A.R.; Ng, E.-P. The synthesis and characterization of high purity mixed microporous/mesoporous activated carbon from rice husk using chemical activation with NaOH and KOH. Microporous Mesoporous Mater. 2014, 197, 316–323. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ogungbenro, A.E.; Quang, D.V.; Al-Ali, K.A.; Vega, L.F.; Abu-Zahra, M.R. Synthesis and characterization of activated carbon from biomass date seeds for carbon dioxide adsorption. J. Environ. Chem. Eng. 2020, 8, 104257. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ferreira, S.D.; Altafini, C.R.; Perondi, D.; Godinho, M. Pyrolysis of Medium Density Fiberboard (MDF) wastes in a screw reactor. Energy Convers. Manag. 2015, 92, 223–233. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Duan, S.; Ma, W.; Pan, Y.; Meng, F.; Yu, S.; Wu, L. Synthesis of magnetic biochar from iron sludge for the enhancement of Cr (VI) removal from solution. J. Taiwan Inst. Chem. Eng. 2017, 80, 835–841. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fontana, K.B.; Chaves, E.S.; Sanchez, J.D.; Watanabe, E.R.; Pietrobelli, J.M.; Lenzi, G.G. Textile dye removal from aqueous solutions by malt bagasse: Isotherm, kinetic and thermodynamic studies. Ecotoxicol. Environ. Saf. 2016, 124, 329–336. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Thommes, M.; Kaneko, K.; Neimark, A.V.; Olivier, J.P.; Rodriguez-Reinoso, F.; Rouquerol, J.; Sing, K.S.W. Physisorption of gases, with special reference to the evaluation of surface area and pore size distribution (IUPAC Technical Report). Pure Appl. Chem. 2015, 87, 1051–1069. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- da Silva, M.C.; Schnorr, C.; Lütke, S.F.; Knani, S.; Nascimento, V.X.; Lima, C.; Thue, P.S.; Vieillard, J.; Silva, L.F.; Dotto, G.L. KOH activated carbons from Brazil nut shell: Preparation, characterization, and their application in phenol adsorption. Chem. Eng. Res. Des. 2022, 187, 387–396. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Y.; Li, Y.; Li, L.; Shi, X.; Wang, Z. Preparation and analysis of activated carbon from sewage sludge and corn stalk. Adv. Powder Technol. 2016, 27, 684–691. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, F.; Zhu, X.; Jin, W.; Fan, J.; Clark, J.H.; Zhang, S. Optimized synthesis of granular fuel and granular activated carbon from sawdust hydrochar without binder. J. Clean. Prod. 2020, 276, 122711. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yuan, Y.; Huang, L.; Zhang, T.C.; Ouyang, L.; Yuan, S. One-step synthesis of ZnFe2O4-loaded biochar derived from leftover rice for high-performance H2S removal. Sep. Purif. Technol. 2021, 279, 119686. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cunha, M.R.; Lima, E.C.; Lima, D.R.; da Silva, R.S.; Thue, P.S.; Seliem, M.K.; Sher, F.; dos Reis, G.S.; Larsson, S.H. Removal of captopril pharmaceutical from synthetic pharmaceutical-industry wastewaters: Use of activated carbon derived from Butia catarinensis. J. Environ. Chem. Eng. 2020, 8, 104506. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cazetta, A.L.; Pezoti, O.; Bedin, K.C.; Silva, T.L.; Junior, A.P.; Asefa, T.; Almeida, V.C. Magnetic Activated Carbon Derived from Biomass Waste by Concurrent Synthesis: Efficient Adsorbent for Toxic Dyes. ACS Sustain. Chem. Eng. 2015, 4, 1058–1068. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, L.; Shao, Y.; Liu, J.; Ye, Z.; Zhang, H.; Ma, J.; Jia, Y.; Gao, W.; Li, Y. Preparation and Characterization of Magnetic Porous Carbon Microspheres for Removal of Methylene Blue by a Heterogeneous Fenton Reaction. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2014, 6, 7275–7285. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lawtae, P.; Tangsathitkulchai, C. The Use of High Surface Area Mesoporous-Activated Carbon from Longan Seed Biomass for Increasing Capacity and Kinetics of Methylene Blue Adsorption from Aqueous Solution. Molecules 2021, 26, 6521. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lyu, W.; Yu, M.; Li, J.; Feng, J.; Yan, W. Adsorption of anionic acid red G dye on polyaniline nanofibers synthesized by FeCl3 oxidant: Unravelling the role of synthetic conditions. Colloids Surfaces A Physicochem. Eng. Asp. 2022, 647, 129203. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Patra, C.; Gupta, R.; Bedadeep, D.; Narayanasamy, S. Surface treated acid-activated carbon for adsorption of anionic azo dyes from single and binary adsorptive systems: A detail insight. Environ. Pollut. 2020, 266, 115102. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Q.; Luo, C.; Lai, Z.; Chen, S.; He, D.; Mu, J. Honeycomb-like cork activated carbon with ultra-high adsorption capacity for anionic, cationic and mixed dye: Preparation, performance and mechanism. Bioresour. Technol. 2022, 357, 127363. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Giles, C.H.; Smith, D.; Huitson, A. A general treatment and classification of the solute adsorption isotherm. I. Theoretical. J. Colloid Interface Sci. 1974, 47, 755–765. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Şenol, Z.M.; Gürsoy, N.; Şimşek, S.; Özer, A.; Karakuş, N. Removal of food dyes from aqueous solution by chitosan-vermiculite beads. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2020, 148, 635–646. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mittal, A. Use of hen feathers as potential adsorbent for the removal of a hazardous dye, Brilliant Blue FCF, from wastewater. J. Hazard. Mater. 2006, 128, 233–239. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arabkhani, P.; Javadian, H.; Asfaram, A.; Sadeghfar, F.; Sadegh, F. Synthesis of magnetic tungsten disulfide/carbon nanotubes nanocomposite (WS2/Fe3O4/CNTs-NC) for highly efficient ultrasound-assisted rapid removal of amaranth and brilliant blue FCF hazardous dyes. J. Hazard. Mater. 2021, 420, 126644. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gupta, V.; Mittal, A.; Krishnan, L.; Mittal, J. Adsorption treatment and recovery of the hazardous dye, Brilliant Blue FCF, over bottom ash and de-oiled soya. J. Colloid Interface Sci. 2006, 293, 16–26. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hernández-Hernández, K.A.; Solache-Ríos, M.; Díaz-Nava, M.C. Removal of Brilliant Blue FCF from Aqueous Solutions Using an Unmodified and Iron-Modified Bentonite and the Thermodynamic Parameters of the Process. Water Air Soil Pollut. 2013, 224, 1562. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ho, Y.S.; McKay, G. A Comparison of Chemisorption Kinetic Models Applied to Pollutant Removal on Various Sorbents. Process Saf. Environ. Prot. 1998, 76, 332–340. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Langmuir, I. The adsorption of gases on plane surfaces of glass, mica and platinum. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 1918, 40, 1361–1403. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Freundlich, H.M.F. Über die Adsorption in Lösungen. Z. Phys. Chem. 1907, 57U, 385–470. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sips, R. On the Structure of a Catalyst Surface. J. Chem. Phys. 1948, 16, 490–495. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]










| Activated Carbon | BET Surface Area (m2 g−1) | Total Pore Volume (cm3 g−1) | Average Pore Size (nm) |
|---|---|---|---|
| MAC1105 | 260.0 | 0.075 | 3.69 |
| MAC111 | 331.5 | 0.095 | 3.60 |
| Sample | Coercivity (HC, Oe) | Saturation Magnetization (MS, emu g−1) | Remanence (MR, emu g−1) |
|---|---|---|---|
| MAC1105 | 150.2 | 13.6 | 3.2 |
| MAC111 | 200.2 | 13.6 | 4.1 |
| Model | Activated Carbon | |
|---|---|---|
| MAC1105 | MAC111 | |
| PFO | ||
| q1 (mg g−1) | 25.79 | 47.93 |
| k1 (min−1) | 0.396 | 0.612 |
| R2 | 0.9785 | 0.9983 |
| R2adj | 0.9480 | 0.9959 |
| ARE (%) | 3.83 | 1.00 |
| PSO | ||
| q2 (mg g−1) | 26.62 | 48.36 |
| k2 (g mg−1 min−1) | 0.035 | 0.072 |
| R2 | 0.9931 | 0.9991 |
| R2adj | 0.9832 | 0.9977 |
| ARE (%) | 2.12 | 0.70 |
| Model | Activated Carbon | |
|---|---|---|
| MAC1105 | MAC111 | |
| Langmuir | ||
| qm (mg g−1) | 37.32 | 91.80 |
| KL (L mg−1) | 0.314 | 1.655 |
| R2 | 0.9542 | 0.9946 |
| R2adj | 0.9359 | 0.9910 |
| ARE (%) | 7.58 | 2.28 |
| Freundlich | ||
| KF ((mg g−1)(mg L−1)−1/nF) | 21.46 | 67.52 |
| 1/nF | 0.114 | 0.077 |
| R2 | 0.9785 | 0.9927 |
| R2adj | 0.9699 | 0.9878 |
| ARE (%) | 5.79 | 2.44 |
| Sips | ||
| qS (mg g−1) | 60.73 | 98.12 |
| KS (L mg−1) | 0.346 | 1.938 |
| mS | 0.335 | 0.483 |
| R2 | 0.9937 | 0.9957 |
| R2adj | 0.9890 | 0.9894 |
| ARE (%) | 2.94 | 2.24 |
| Adsorbent | Dosage (g L−1) | pH | T (°C) | Adsorption capacity (mg g−1) | Reference |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| MAC1105 | 1.0 | 4.0 | 25 | 60.7 | This study |
| MAC111 | 1.0 | 4.0 | 25 | 98.1 | This study |
| Chitosan vermiculite beads | 5.0 a | 10.2 | 25 | 181.6 | [59] |
| Hen feather | 0.4 a | 2.0 | 30 | 317.0 b | [60] |
| Magnetic tungsten disulfide/carbon nanotubes nanocomposite | 0.3 a | 3.0 | 25 | 166.7 | [61] |
| Bottom ash | 4.0 a | 3.0 | 50 | 6.9 b | [62] |
| De-oiled soya | 2.0 a | 3.0 | 50 | 18.2 b | [62] |
| Unmodified clay | 10.0 a | 5.4 | 30 | 6.2 | [63] |
| Iron-modified clay | 10.0 a | 5.4 | 30 | 14.2 | [63] |
| Activated Carbon | Regenerating Agent | Concentration of the Regenerating Agent (mol L−1) | qe in the Second Cycle (mg g−1) a |
|---|---|---|---|
| MAC1105 | NaCl | 0.5 | 6.05 ± 0.65 |
| 1.0 | 5.80 ± 0.58 | ||
| NaOH | 10.5 | 7.09 ± 0.74 | |
| 1.0 | 5.89 ± 0.63 | ||
| NH4OH | 0.5 | 10.78 ± 1.01 | |
| 1.0 | 5.72 ± 0.69 | ||
| C3H6O | 0.5 | 8.58 ± 0.95 | |
| 1.0 | 7.35 ± 0.71 | ||
| MAC111 | NaCl | 0.5 | 34.96 ± 0.87 |
| 1.0 | 30.59 ± 1.23 | ||
| NaOH | 10.5 | 29.21 ± 0.91 | |
| 1.0 | 22.52 ± 1.13 | ||
| NH4OH | 0.5 | 36.64 ± 0.87 | |
| 1.0 | 31.04 ± 0.92 | ||
| C3H6O | 0.5 | 36.31 ± 1.04 | |
| 1.0 | 30.91 ± 0.98 | ||
| NaCl | 0.5 | 34.96 ± 0.87 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Nascimento, V.X.; Schnorr, C.; Lütke, S.F.; Da Silva, M.C.F.; Machado Machado, F.; Thue, P.S.; Lima, É.C.; Vieillard, J.; Silva, L.F.O.; Dotto, G.L. Adsorptive Features of Magnetic Activated Carbons Prepared by a One-Step Process towards Brilliant Blue Dye. Molecules 2023, 28, 1821. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules28041821
Nascimento VX, Schnorr C, Lütke SF, Da Silva MCF, Machado Machado F, Thue PS, Lima ÉC, Vieillard J, Silva LFO, Dotto GL. Adsorptive Features of Magnetic Activated Carbons Prepared by a One-Step Process towards Brilliant Blue Dye. Molecules. 2023; 28(4):1821. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules28041821
Chicago/Turabian StyleNascimento, Victoria X., Carlos Schnorr, Sabrina F. Lütke, Maria C. F. Da Silva, Fernando Machado Machado, Pascal S. Thue, Éder C. Lima, Julien Vieillard, Luis F. O. Silva, and Guilherme L. Dotto. 2023. "Adsorptive Features of Magnetic Activated Carbons Prepared by a One-Step Process towards Brilliant Blue Dye" Molecules 28, no. 4: 1821. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules28041821
APA StyleNascimento, V. X., Schnorr, C., Lütke, S. F., Da Silva, M. C. F., Machado Machado, F., Thue, P. S., Lima, É. C., Vieillard, J., Silva, L. F. O., & Dotto, G. L. (2023). Adsorptive Features of Magnetic Activated Carbons Prepared by a One-Step Process towards Brilliant Blue Dye. Molecules, 28(4), 1821. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules28041821