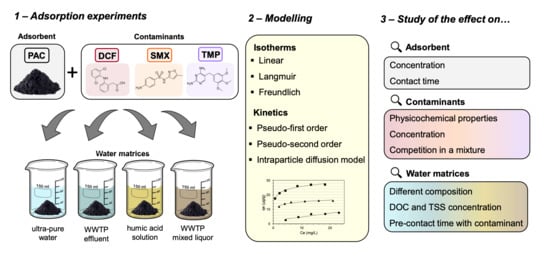
Study of the Influence of the Wastewater Matrix in the Adsorption of Three Pharmaceuticals by Powdered Activated Carbon
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Results and Discussion
2.1. Effect of the Contact Time and Initial Concentration of Pharmaceuticals
2.2. Kinetics
2.3. Sorption Isotherms in Ultra-Pure Water and Competition Effect
2.4. Influence of the Water Matrix
2.5. Influence of the Pre-Equilibrium Time between Pharmaceuticals and DOM on Adsorption
3. Materials and Methods
3.1. Adsorbent and Adsorbates
3.2. Water Matrices
3.3. Batch Adsorption Experiments
3.4. HPLC Analysis
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
Sample Availability
References
- Luo, Y.; Guo, W.; Ngo, H.H.; Nghiem, L.D.; Hai, F.I.; Zhang, J.; Liang, S.; Wang, X.C. A Review on the Occurrence of Micropollutants in the Aquatic Environment and Their Fate and Removal during Wastewater Treatment. Sci. Total Environ. 2014, 473–474, 619–641. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Verlicchi, P.; Galletti, A.; Petrovic, M.; BarcelÓ, D. Hospital Effluents as a Source of Emerging Pollutants: An Overview of Micropollutants and Sustainable Treatment Options. J. Hydrol. 2010, 389, 416–428. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rizzo, L.; Malato, S.; Antakyali, D.; Beretsou, V.G.; Đolić, M.B.; Gernjak, W.; Heath, E.; Ivancev-Tumbas, I.; Karaolia, P.; Lado Ribeiro, A.R.; et al. Consolidated vs New Advanced Treatment Methods for the Removal of Contaminants of Emerging Concern from Urban Wastewater. Sci. Total Environ. 2019, 655, 986–1008. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Khan, N.A.; Khan, S.U.; Ahmed, S.; Farooqi, I.H.; Yousefi, M.; Mohammadi, A.A.; Changani, F. Recent Trends in Disposal and Treatment Technologies of Emerging-Pollutants- A Critical Review. TrAC Trends Anal. Chem. 2020, 122, 115744. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mailler, R.; Gasperi, J.; Coquet, Y.; Derome, C.; Buleté, A.; Vulliet, E.; Bressy, A.; Varrault, G.; Chebbo, G.; Rocher, V. Removal of Emerging Micropollutants from Wastewater by Activated Carbon Adsorption: Experimental Study of Different Activated Carbons and Factors Influencing the Adsorption of Micropollutants in Wastewater. J. Environ. Chem. Eng. 2016, 4, 1102–1109. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Margot, J.; Kienle, C.; Magnet, A.; Weil, M.; Rossi, L.; de Alencastro, L.F.; Abegglen, C.; Thonney, D.; Chèvre, N.; Schärer, M.; et al. Treatment of Micropollutants in Municipal Wastewater: Ozone or Powdered Activated Carbon? Sci. Total Environ. 2013, 461–462, 480–498. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Verlicchi, P.; Al Aukidy, M.; Galletti, A.; Petrovic, M.; Barceló, D. Hospital Effluent: Investigation of the Concentrations and Distribution of Pharmaceuticals and Environmental Risk Assessment. Sci. Total Environ. 2012, 430, 109–118. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, X.; Hai, F.I.; Nghiem, L.D. Simultaneous Activated Carbon Adsorption within a Membrane Bioreactor for an Enhanced Micropollutant Removal. Bioresour. Technol. 2011, 102, 5319–5324. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Alvarino, T.; Torregrosa, N.; Omil, F.; Lema, J.M.; Suarez, S. Assessing the Feasibility of Two Hybrid MBR Systems Using PAC for Removing Macro and Micropollutants. J. Environ. Manag. 2017, 203, 831–837. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Löwenberg, J.; Zenker, A.; Baggenstos, M.; Koch, G.; Kazner, C.; Wintgens, T. Comparison of Two PAC/UF Processes for the Removal of Micropollutants from Wastewater Treatment Plant Effluent: Process Performance and Removal Efficiency. Water Res. 2014, 56, 26–36. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guillossou, R.; Le Roux, J.; Mailler, R.; Pereira-Derome, C.; Varrault, G.; Bressy, A.; Vulliet, E.; Morlay, C.; Nauleau, F.; Rocher, V.; et al. Influence of Dissolved Organic Matter on the Removal of 12 Organic Micropollutants from Wastewater Effluent by Powdered Activated Carbon Adsorption. Water Res. 2020, 172, 115487. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gutiérrez, M.; Ghirardini, A.; Borghesi, M.; Bonnini, S.; Mutavdžić Pavlović, D.; Verlicchi, P. Removal of Micropollutants Using a Membrane Bioreactor Coupled with Powdered Activated Carbon — A Statistical Analysis Approach. Sci. Total Environ. 2022, 840, 156557. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alves, T.C.; Cabrera-Codony, A.; Barceló, D.; Rodriguez-mozaz, S.; Pinheiro, A.; Gonzalez-olmos, R. Influencing Factors on the Removal of Pharmaceuticals from Water with Micro-Grain Activated Carbon. Water Res. 2018, 144, 402–412. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zietzschmann, F.; Stützer, C.; Jekel, M. Granular Activated Carbon Adsorption of Organic Micro-Pollutants in Drinking Water and Treated Wastewater - Aligning Breakthrough Curves and Capacities. Water Res. 2016, 92, 180–187. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zietzschmann, F.; Worch, E.; Altmann, J.; Ruhl, A.S.; Sperlich, A.; Meinel, F.; Jekel, M. Impact of EfOM Size on Competition in Activated Carbon Adsorption of Organic Micro-Pollutants from Treated Wastewater. Water Res. 2014, 65, 297–306. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hernandez-Ruiz, S.; Abrell, L.; Wickramasekara, S.; Chefetz, B.; Chorover, J. Quantifying PPCP Interaction with Dissolved Organic Matter in Aqueous Solution: Combined Use of Fluorescence Quenching and Tandem Mass Spectrometry. Water Res. 2012, 46, 943–954. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jin, J.; Feng, T.; Gao, R.; Ma, Y.; Wang, W.; Zhou, Q.; Li, A. Ultrahigh Selective Adsorption of Zwitterionic PPCPs Both in the Absence and Presence of Humic Acid: Performance and Mechanism. J. Hazard. Mater. 2018, 348, 117–124. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gutiérrez, M.; Grillini, V.; Mutavdžić Pavlović, D.; Verlicchi, P. Activated Carbon Coupled with Advanced Biological Wastewater Treatment: A Review of the Enhancement in Micropollutant Removal. Sci. Total Environ. 2021, 790, 148050. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Boehler, M.; Zwickenpflug, B.; Hollender, J.; Ternes, T.; Joss, A.; Siegrist, H. Removal of Micropollutants in Municipal Wastewater Treatment Plants by Powder-Activated Carbon. Water Sci. Technol. 2012, 66, 2115–2121. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Streicher, J.; Ruhl, A.S.; Gnirß, R.; Jekel, M. Where to Dose Powdered Activated Carbon in a Wastewater Treatment Plant for Organic Micro-Pollutant Removal. Chemosphere 2016, 156, 88–94. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Verlicchi, P.; Al Aukidy, M.; Zambello, E. Occurrence of Pharmaceutical Compounds in Urban Wastewater: Removal, Mass Load and Environmental Risk after a Secondary Treatment—A Review. Sci. Total Environ. 2012, 429, 123–155. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fatta-Kassinos, D.; Meric, S.; Nikolaou, A. Pharmaceutical Residues in Environmental Waters and Wastewater: Current State of Knowledge and Future Research. Anal. Bioanal. Chem. 2011, 399, 251–275. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- McArdell, C.S.; Kovalova, L.; Siegrist, H. Input and Elimination of Pharmaceuticals and Disinfectants from Hospital Wastewater. Final Project Report; Eawag: Das Wasserforschungs-Institut des ETH-Bereichs: Dübendorf, Switzerland, 2011. [Google Scholar]
- Oaks, J.L.; Gilbert, M.; Virani, M.Z.; Watson, R.T.; Meteyer, C.U.; Rideout, B.A.; Shivaprasad, H.L.; Ahmed, S.; Chaudhry, M.J.I.; Arshad, M.; et al. Diclofenac Residues as the Cause of Vulture Population Decline in Pakistan. Nature 2004, 427, 630–633. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- European Commission European Commission. Commission Implementing Decision (EU) 2015/495 of 20 March 2015 Establishing a Watch List of Substances for Union-Wide Monitoring in the Field of Water Policy Pursuant to Directive 2008/105/EC of the European Parliament and of T. Off. J. Eur. Union L 78 2015, 2015, 40–42. [Google Scholar]
- Ternes, T.; Joss, A. Human Pharmaceuticals, Hormones and Fragrances—The Challenge of Micropollutants in Urban Water Management; IWA Publishing: Longon, UK, 2015; Volume 5, ISBN 9781780402468. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Salvestrini, S.; Fenti, A.; Chianese, S.; Iovino, P.; Musmarra, D. Diclofenac Sorption from Synthetic Water: Kinetic and Thermodynamic Analysis. J. Environ. Chem. Eng. 2020, 8, 104105. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Radjenović, J.; Petrović, M.; Barceló, D. Fate and Distribution of Pharmaceuticals in Wastewater and Sewage Sludge of the Conventional Activated Sludge (CAS) and Advanced Membrane Bioreactor (MBR) Treatment. Water Res. 2009, 43, 831–841. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alvarino, T.; Komesli, O.; Suarez, S.; Lema, J.M.M.; Omil, F. The Potential of the Innovative SeMPAC Process for Enhancing the Removal of Recalcitrant Organic Micropollutants. J. Hazard. Mater. 2016, 308, 29–36. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- European Commission. Commision Implementing Decision (EU) 2020/1161-4 August 2020-Establishing a Watch List of Substances for Union-Wide Monitoring in the Field of Water Policy Pursuant to Directive 2008/105/EC of the European Parliament and of the Council. Off. J. Eur. Union 2020, 257, 32–35. [Google Scholar]
- European Commission. Commission Implementing Decision (EU) 2022/1307 of 22 July 2022 Establishing a Watch List of Substances for Union-Wide Monitoring in the Field of Water Policy Pursuant to Directive 2008/105/EC of the European Parliament and of the Counci. Off. J. Eur. Union 2022, 197, 117–121. [Google Scholar]
- Paredes, L.; Alfonsin, C.; Allegue, T.; Omil, F.; Carballa, M. Integrating Granular Activated Carbon in the Post-Treatment of Membrane and Settler Effluents to Improve Organic Micropollutants Removal. Chem. Eng. J. 2018, 345, 79–86. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Behera, S.K.; Oh, S.Y.; Park, H.S. Sorption of Triclosan onto Activated Carbon, Kaolinite and Montmorillonite: Effects of PH, Ionic Strength, and Humic Acid. J. Hazard. Mater. 2010, 179, 684–691. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Delgado, N.; Capparelli, A.; Navarro, A.; Marino, D. Pharmaceutical Emerging Pollutants Removal from Water Using Powdered Activated Carbon: Study of Kinetics and Adsorption Equilibrium. J. Environ. Manag. 2019, 236, 301–308. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mutavdžić Pavlović, D.; Glavač, A.; Gluhak, M.; Runje, M. Sorption of Albendazole in Sediments and Soils: Isotherms and Kinetics. Chemosphere 2018, 193, 635–644. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Çalişkan, E.; Göktürk, S. Adsorption Characteristics of Sulfamethoxazole and Metronidazole on Activated Carbon. Sep. Sci. Technol. 2010, 45, 244–255. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Torrellas, S.A.; Rodriguez, A.R.; Escudero, G.O.; Martin, J.M.G.; Rodriguez, J.G. Comparative Evaluation of Adsorption Kinetics of Diclofenac and Isoproturon by Activated Carbon. J. Environ. Sci. Heal.—Part A Toxic/Hazardous Subst. Environ. Eng. 2015, 50, 1241–1248. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tran, H.N.; You, S.J.; Hosseini-Bandegharaei, A.; Chao, H.P. Mistakes and Inconsistencies Regarding Adsorption of Contaminants from Aqueous Solutions: A Critical Review. Water Res. 2017, 120, 88–116. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Walter, J.; Weber, J. Evolution of a Technology. J. Environ. Eng. 1984, 110, 899–917. [Google Scholar]
- Weber, W.J.; Morris, J.C. Kinetics of Adsorption on Carbon from Solution. J. Sanit. Eng. Div. 1963, 89, 31–60. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Suriyanon, N.; Punyapalakul, P.; Ngamcharussrivichai, C. Mechanistic Study of Diclofenac and Carbamazepine Adsorption on Functionalized Silica-Based Porous Materials. Chem. Eng. J. 2013, 214, 208–218. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xiang, L.; Xiao, T.; Mo, C.H.; Zhao, H.M.; Li, Y.W.; Li, H.; Cai, Q.Y.; Zhou, D.M.; Wong, M.H. Sorption Kinetics, Isotherms, and Mechanism of Aniline Aerofloat to Agricultural Soils with Various Physicochemical Properties. Ecotoxicol. Environ. Saf. 2018, 154, 84–91. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rudzinski, W.; Plazinski, W. Kinetics of Solute Adsorption at Solid/Solution Interfaces: On the Special Features of the Initial Adsorption Kinetics. Langmuir 2008, 24, 6738–6744. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nguyen, L.N.; Hai, F.I.; Kang, J.; Nghiem, L.D.; Price, W.E.; Guo, W.; Ngo, H.H.; Tung, K.-L. Comparison between Sequential and Simultaneous Application of Activated Carbon with Membrane Bioreactor for Trace Organic Contaminant Removal. Bioresour. Technol. 2013, 130, 412–417. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Kim, S.H.; Shon, H.K.; Ngo, H.H. Adsorption Characteristics of Antibiotics Trimethoprim on Powdered and Granular Activated Carbon. J. Ind. Eng. Chem. 2010, 16, 344–349. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aschermann, G.; Schröder, C.; Zietzschmann, F.; Jekel, M. Organic Micropollutant Desorption in Various Water Matrices - Activated Carbon Pore Characteristics Determine the Reversibility of Adsorption. Chemosphere 2019, 237, 124415. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pan, B.; Zhang, D.; Li, H.; Wu, M.; Wang, Z.; Xing, B. Increased Adsorption of Sulfamethoxazole on Suspended Carbon Nanotubes by Dissolved Humic Acid. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2013, 47, 7722–7728. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mutavdžić Pavlović, D.; Tolić Čop, K.; Barbir, V.; Gotovuša, M.; Lukač, I.; Lozančić, A.; Runje, M. Sorption of Cefdinir, Memantine, Praziquantel and Trimethoprim in Sediment and Soil Samples. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2022, 29, 66841–66857. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kovalova, L.; Siegrist, H.; von Gunten, U.; Eugster, J.; Hagenbuch, M.; Wittmer, A.; Moser, R.; McArdell, C.S. Elimination of Micropollutants during Post-Treatment of Hospital Wastewater with Powdered Activated Carbon, Ozone, and UV. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2013, 47, 7899–7908. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Anielak, A.M.; Styszko, K.; Kłeczek, A.; Łomińska-Płatek, D. Humic Substances—Common Carriers of Micropollutants in Municipal Engineering. Energies 2022, 15, 8496. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mailler, R.; Gasperi, J.; Coquet, Y.; Deshayes, S.; Zedek, S.; Cren-Olivé, C.; Cartiser, N.; Eudes, V.; Bressy, A.; Caupos, E.; et al. Study of a Large Scale Powdered Activated Carbon Pilot: Removals of a Wide Range of Emerging and Priority Micropollutants from Wastewater Treatment Plant Effluents. Water Res. 2015, 72, 315–330. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Burchacka, E.; Pstrowska, K.; Beran, E.; Fałtynowicz, H.; Chojnacka, K.; Kułażyński, M. Antibacterial Agents Adsorbed on Active Carbon: A New Approach for S. Aureus and E. Coli Pathogen Elimination. Pathogens 2021, 10, 1066. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Giannakoudakis, D.A.; Kyzas, G.Z.; Avranas, A.; Lazaridis, N.K. Multi-Parametric Adsorption Effects of the Reactive Dye Removal with Commercial Activated Carbons. J. Mol. Liq. 2016, 213, 381–389. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Viswanadhan, V.N.; Ghose, A.K.; Revankar, G.R.; Robins, R.K. Atomic Physicochemical Parameters for Three Dimensional Structure Directed Quantitative Structure-Activity Relationships. 4. Additional Parameters for Hydrophobic and Dispersive Interactions and Their Application for an Automated Superposition of Certain. J. Chem. Inf. Model. 1989, 29, 163–172. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Meija, J.; Coplen, T.B.; Berglund, M.; Brand, W.A.; De Bièvre, P.; Gröning, M.; Holden, N.E.; Irrgeher, J.; Loss, R.D.; Walczyk, T.; et al. Atomic Weights of the Elements 2013 (IUPAC Technical Report). Pure Appl. Chem. 2016, 88, 265–291. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Babić, S.; Horvat, A.J.M.; Mutavdžić Pavlović, D.; Kaštelan-Macan, M. Determination of PKa Values of Active Pharmaceutical Ingredients. TrAC—Trends Anal. Chem. 2007, 26, 1043–1061. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zrnčić, M.; Babić, S.; Mutavdžić Pavlović, D. Determination of Thermodynamic p K a Values of Pharmaceuticals from Five Different Groups Using Capillary Electrophoresis. J. Sep. Sci. 2015, 38, 1232–1239. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lagergren, S. About the Theory of So-Called Adsorption of Soluble Substances. K. Sven. Vetensk. Handl. 1898, 24, 1–39. [Google Scholar]




| Compound | PAC (g/L) | C0 (mg/L) | qe, exp. (µg/g) | Pseudo-First Order | Pseudo-Second Order | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| qe, calc. (µg/g) | k1 (1/min) | R2 | qe, calc. (µg/g) | k2 (g/µg·min) | R2 | ||||
| DCF | 1 | 5 | 4826 | 206 | 1.61 × 10−4 | 0.135 | 5000 | 4.00 × 10−3 | 1.000 |
| 1 | 15 | 14,729 | 3185 | 2.07 × 10−3 | 0.806 | 14,286 | 6.13 × 10−6 | 1.000 | |
| 1 | 25 | 22,240 | 11,163 | 1.15 × 10−3 | 0.851 | 25,000 | 1.14 × 10−6 | 0.993 | |
| 0.1 | 5 | 31,442 | 127,321 | 6.91 × 10−5 | 0.743 | 33,333 | 1.13 × 10−6 | 0.999 | |
| 0.1 | 15 | 34,852 | 29,971 | 4.61 × 10−4 | 0.430 | 33,333 | 1.29 × 10−6 | 0.996 | |
| 0.1 | 25 | 34,869 | 229,192 | 4.61 × 10−4 | 0.877 | 33,333 | 6.92 × 10−7 | 0.995 | |
| SMX | 1 | 5 | 4999 | 2085 | 5.07 × 10−3 | 0.987 | 5000 | 8.16 × 10−6 | 0.999 |
| 1 | 15 | 9910 | 11,527 | 6.91 × 10−4 | 0.902 | 11,111 | 8.71 × 10−7 | 0.992 | |
| 1 | 25 | 11,549 | 23,206 | 4.61 × 10−4 | 0.877 | 14,286 | 1.88 × 10−7 | 0.979 | |
| 0.1 | 5 | 19,398 | 43,813 | 2.30 × 10−4 | 0.868 | 20,000 | 4.55 × 10−7 | 0.992 | |
| 0.1 | 15 | 26,490 | 138,038 | 9.21 × 10−5 | 0.784 | 25,000 | 7.41 × 10−8 | 0.996 | |
| 0.1 | 25 | 37,016 | 233,830 | 6.91 × 10−5 | 0.940 | 33,333 | 3.83 × 10−8 | 0.984 | |
| TMP | 1 | 5 | 4992 | 82 | 2.07 × 10−3 | 0.598 | 5000 | 4.00 × 10−7 | 1.000 |
| 1 | 15 | 14,933 | 606 | 1.84 × 10−3 | 0.543 | 14,286 | 4.90 × 10−5 | 1.000 | |
| 1 | 25 | 24,083 | 3151 | 1.15 × 10−3 | 0.657 | 25,000 | 8.00 × 10−6 | 1.000 | |
| 0.1 | 5 | 37,184 | 25,439 | 4.61 × 10−4 | 0.844 | 33,333 | 1.13 × 10−6 | 0.997 | |
| 0.1 | 15 | 33,416 | 126,765 | 6.91 × 10−5 | 0.561 | 33,333 | 1.5 × 10−6 | 0.999 | |
| 0.1 | 25 | 36,425 | 229,826 | 6.91 × 10−5 | 0.917 | 33,333 | 6.43 × 10−7 | 0.989 | |
| Compound | C0 (mg/L) | Intraparticle Diffusion | ||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| First Phase | Second Phase | Third Phase | ||||||||
| kp1 (μg/g min1/2) | C1 | R2 | kp2 (μg/g min1/2) | C2 | R2 | kp3 (μg/g min1/2) | C3 | R2 | ||
| DCF | 5 | 0.402 | 93.03 | 0.921 | 0.078 | 95.45 | 1.000 | −0.006 | 96.751 | 0.979 |
| 15 | 15.657 | 129.49 | 0.996 | 2.322 | 242.66 | 0.999 | −0.013 | 295.08 | 1.000 | |
| 25 | 26.047 | 109.34 | 0.976 | 11.310 | 192.21 | 0.962 | 0.029 | 443.70 | 1.000 | |
| SMX | 5 | 2.596 | 50.37 | 0.985 | 1.926 | 54.95 | 0.962 | 0.074 | 97.16 | 1.000 |
| 15 | 7.479 | 20.77 | 0.977 | 8.644 | −8.99 | 1.000 | 0.187 | 191.09 | 1.000 | |
| 25 | 8.524 | −23.18 | 0.947 | 14.061 | −97.14 | 0.991 | 0.033 | 229.71 | 1.000 | |
| TMP | 5 | 3.813 | 78.36 | 0.889 | 0.348 | 96.39 | 0.995 | 0.020 | 99.15 | 0.781 |
| 15 | 12.055 | 211.25 | 0.958 | 0.958 | 285.80 | 0.998 | 0.072 | 296.07 | 0.938 | |
| 25 | 15.330 | 337.67 | 0.982 | 3.291 | 420.88 | 0.999 | 0.321 | 470.19 | 0.933 | |
| Linear Sorption | Langmuir Isotherm | Freundlich Sorption | |||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Compound | PAC Conc. (g/L) | Kd (mL/g) | R2 | qm (µg/g) | KL (L/mg) | R2 | 1/n | KF (mg/g) (mL/mg)1/n | R2 |
| Individual solutions | |||||||||
| DCF | 0.1 | 1777.9 | 0.895 | 33,333 | 0.300 | 0.963 | 0.281 | 12,673.9 | 0.925 |
| 0.25 | 1949.2 | 0.836 | 33,333 | 0.429 | 0.979 | 0.215 | 14,368.6 | 0.953 | |
| 0.5 | 2980.6 | 0.783 | 25,000 | 2.000 | 0.978 | 0.271 | 14,099.6 | 0.991 | |
| 1 | 7167.1 | 0.855 | 20,000 | 5.000 | 0.946 | 0.574 | 10,802.1 | 0.999 | |
| SMX | 0.1 | 1896.0 | 0.960 | 50,000 | 0.100 | 0.915 | 0.439 | 8918.7 | 0.959 |
| 0.25 | 1634.0 | 0.947 | 33,333 | 0.150 | 0.936 | 0.392 | 7972.1 | 0.967 | |
| 0.5 | 1756.3 | 0.902 | 25,000 | 0.444 | 0.956 | 0.380 | 7667.1 | 0.985 | |
| 1 | 1417.6 | 0.937 | 16,667 | 0.300 | 0.912 | 0.520 | 3947.0 | 0.990 | |
| TMP | 0.1 | 2618.9 | 0.833 | 50,000 | 0.400 | 0.951 | 0.178 | 23,576.4 | 0.801 |
| 0.25 | 3712.3 | 0.820 | 50,000 | 0.667 | 0.972 | 0.249 | 21,407.6 | 0.961 | |
| 0.5 | 5939.4 | 0.852 | 33,333 | 1.500 | 0.967 | 0.393 | 16,565.9 | 0.998 | |
| 1 | 19,820.0 | 0.910 | 25,000 | 4.444 | 0.939 | N.A. | N.A. | N.A. | |
| Mixture | |||||||||
| DCF | 0.1 | 1806.2 | 0.852 | 33,333 | 0.375 | 0.987 | 0.203 | 16,008.9 | 0.955 |
| 0.25 | 1063.6 | 0.763 | 16,667 | 1.000 | 1.000 | 0.124 | 11,356.0 | 0.900 | |
| 0.5 | 1348.8 | 0.785 | 16,667 | 1.000 | 0.995 | 0.212 | 9531.0 | 0.962 | |
| 1 | 1390.1 | 0.707 | 12,500 | 1.000 | 0.996 | 0.125 | 9464.5 | 0.823 | |
| SMX | 0.1 | 423.03 | 0.935 | 50,000 | 0.010 | 0.031 | 0.587 | 1222.7 | 0.423 |
| 0.25 | 385.32 | 0.965 | 14,286 | 0.054 | 0.924 | 0.670 | 1012.2 | 0.950 | |
| 0.5 | 280.47 | 0.976 | 10,000 | 0.053 | 0.869 | 0.709 | 629.0 | 0.998 | |
| 1 | 162.16 | 0.868 | 3333 | 0.375 | 0.968 | 0.137 | 1783.6 | 0.652 | |
| TMP | 0.1 | 2442.7 | 0.901 | 50,000 | 0.200 | 0.832 | 0.257 | 17,243.7 | 0.597 |
| 0.25 | 2036.5 | 0.733 | 25,000 | 2.000 | 0.999 | 0.128 | 19,171.9 | 0.964 | |
| 0.5 | 2716.2 | 0.730 | 25,000 | 2.000 | 0.999 | 0.151 | 17,870.4 | 0.955 | |
| 1 | 5636.6 | 0.843 | 25,000 | 2.000 | 0.995 | 0.239 | 14,485.5 | 1.000 | |
| Compound | C0 (mg/L) | qe, exp. (µg/g) | Pseudo-First Order | Pseudo-Second Order | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| qe, calc. (µg/g) | k1 (1/min) | R2 | qe, calc. (µg/g) | k2 (g/µg·min) | R2 | |||
| DCF | 5 | 18,467 | 136,395 | 9.21 × 10−5 | 0.878 | 16,667 | 1.33 × 10−6 | 0.991 |
| 15 | 28,362 | 40,272 | 1.84 × 10−4 | 0.851 | 33,333 | 4.09 × 10−7 | 0.993 | |
| 25 | 15,957 | 242,493 | 2.30 × 10−5 | 0.387 | 16,667 | 1.2 × 10−6 | 0.990 | |
| SMX | 5 | 5716 | 48,865 | 6.909 × 10−5 | 0.801 | 10,000 | 1.81 × 10−7 | 0.890 |
| 15 | 4742 | 147,809 | 1.382 × 10−5 | 0.633 | 5000 | 2.72 × 10−6 | 0.991 | |
| 25 | 35,771 | 237,684 | 6.909 × 10−5 | 0.740 | 33,333 | 2.81 × 10−7 | 0.997 | |
| TMP | 5 | 25,531 | 32,464 | 2.30 × 10−4 | 0.820 | 25,000 | 1.45 × 10−6 | 0.999 |
| 15 | 25,310 | 134,122 | 4.61 × 10−5 | 0.435 | 25,000 | 1.23 × 10−6 | 0.990 | |
| 25 | 25,948 | 239,111 | 4.61 × 10−5 | 0.874 | 25,000 | 5.71 × 10−7 | 0.941 | |
| Linear Sorption | Langmuir Isotherm | Freundlich Sorption | |||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Compound | PAC Conc. (g/L) | Kd (mL/g) | R2 | qm (µg/g) | KL (L/mg) | R2 | 1/n | KF (mg/g) (mL/mg)1/n | R2 |
| Humic acid solution | |||||||||
| DCF | 0.1 | 4521.6 | 0.941 | 100,000 | 0.125 | 0.908 | 0.4568 | 18,012.1 | 0.929 |
| 0.25 | 4802.4 | 0.783 | 50,000 | 1.000 | 0.994 | 0.2799 | 24,760.4 | 0.896 | |
| 0.5 | 4600.6 | 0.768 | 33,333 | 1.500 | 0.984 | 0.2000 | 20,607.3 | 0.781 | |
| 1 | 12,308.0 | 0.718 | 100,000 | 1.429 | 0.994 | N.A. | N.A. | N.A. | |
| SMX | 0.1 | 2856.7 | 0.878 | 50,000 | 0.250 | 0.919 | 0.2630 | 20,426.7 | 0.863 |
| 0.25 | 3957.7 | 0.792 | 50,000 | 1.000 | 0.983 | 0.1408 | 29,673.2 | 0.651 | |
| 0.5 | 6994.4 | 0.801 | 33,333 | 3.000 | 0.983 | 0.2731 | 22,606.7 | 0.807 | |
| 1 | 11,372.0 | 0.763 | 25,000 | 5.000 | 0.991 | N.A. | N.A. | N.A. | |
| TMP | 0.1 | 2287.9 | 0.860 | 50,000 | 0.286 | 0.976 | 0.2116 | 19,150.8 | 0.900 |
| 0.25 | 2600.1 | 0.791 | 33,333 | 0.750 | 0.992 | 0.1891 | 19,424.7 | 0.958 | |
| 0.5 | 3824.5 | 0.720 | 33,333 | 3.000 | 0.994 | 0.1960 | 19,358.8 | 0.998 | |
| 1 | 31,430.0 | 0.740 | 25,000 | 10.000 | 0.998 | N.A. | N.A. | N.A. | |
| MBR permeate | |||||||||
| DCF | 0.1 | 1553.7 | 0.880 | 33,333 | 0.150 | 0.978 | 0.4160 | 8206.6 | 0.865 |
| 0.25 | 1785.4 | 0.802 | 25,000 | 0.667 | 0.989 | 0.2066 | 14,004.0 | 0.925 | |
| 0.5 | 3273.4 | 0.776 | 50,000 | 1.000 | 0.985 | 0.2785 | 14,831.4 | 0.997 | |
| 1 | 12,011.0 | 0.734 | 25,000 | 1.000 | 0.995 | N.A. | N.A. | N.A. | |
| SMX | 0.1 | 1642.8 | 0.999 | 1,000,000 | 0.002 | 0.028 | 0.9527 | 1843.1 | 0.988 |
| 0.25 | 1349.2 | 0.962 | 33,333 | 0.100 | 0.924 | 0.4976 | 5154.4 | 0.978 | |
| 0.5 | 1874.2 | 0.870 | 25,000 | 0.444 | 0.993 | 0.2650 | 10,690.4 | 0.932 | |
| 1 | 3009.7 | 0.837 | 20,000 | 1.000 | 0.999 | 0.2310 | 11,178.0 | 0.996 | |
| TMP | 0.1 | 9370.2 | 0.875 | 250,000 | 0.057 | 0.225 | 0.8102 | 15,532.7 | 0.647 |
| 0.25 | 6616.8 | 0.690 | 50,000 | 1.000 | 0.974 | 0.2822 | 31,351.0 | 0.754 | |
| 0.5 | 8417.5 | 0.535 | 50,000 | 1.000 | 0.937 | N.A. | N.A. | N.A. | |
| 1 | N.A. | N.A. | N.A. | N.A. | N.A. | N.A. | N.A. | N.A. | |
| Mixed liquor | |||||||||
| DCF | 0.1 | 827.9 | 0.993 | −25,000 | −0.019 | 0.466 | 1.3563 | 299.7 | 0.957 |
| 0.25 | 766.7 | 0.963 | −10,000 | −0.033 | 0.407 | 1.6076 | 148.1 | 0.903 | |
| 0.5 | 235.9 | 0.995 | 50,000 | 0.005 | 0.038 | 0.9064 | 296.5 | 0.952 | |
| 1 | 234.1 | 0.998 | 33,333 | 0.008 | 0.268 | 0.8891 | 312.6 | 0.979 | |
| SMX | 0.1 | 431.5 | 0.965 | −3333 | −0.048 | 0.907 | 1.8270 | 55.0 | 1.000 |
| 0.25 | 233.2 | 0.990 | −33,333 | −0.006 | 0.085 | 1.0983 | 186.3 | 0.954 | |
| 0.5 | 84.0 | 0.892 | 2000 | 0.172 | 0.873 | 0.4847 | 384.3 | 0.707 | |
| 1 | 109.4 | 0.858 | 2500 | 0.118 | 0.552 | 0.6615 | 300.6 | 0.594 | |
| TMP | 0.1 | 3988.7 | 0.976 | 1,250,000 | 0.004 | 0.015 | 1.0055 | 4011.8 | 0.939 |
| 0.25 | 1785.7 | 0.995 | 125,000 | 0.020 | 0.538 | 0.8440 | 2659.3 | 0.980 | |
| 0.5 | 1002.7 | 0.960 | 33,333 | 0.060 | 0.986 | 0.6493 | 2484.4 | 1.000 | |
| 1 | 822.7 | 0.868 | 14,286 | 0.233 | 0.996 | 0.4847 | 2980.3 | 0.967 | |
| Linear Isotherm | Langmuir Isotherm | Freundlich Isotherm | |||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Compound | PAC Conc. (g/L) | Kd (mL/g) | R2 | qm (µg/g) | KL (L/mg) | R2 | 1/n | KF (mg/g) (mL/mg)1/n | R2 |
| DCF | 0.1 | 2931.5 | 0.8482 | 50,000 | 0.400 | 0.983 | 0.2194 | 23,435.3 | 0.951 |
| 0.25 | 3196.9 | 0.8713 | 50,000 | 0.333 | 0.980 | 0.3342 | 15,739.0 | 0.988 | |
| 0.5 | 2932.1 | 0.7000 | 25,000 | 2.000 | 0.999 | 0.0962 | 20,854.0 | 0.959 | |
| 1 | 2403.6 | 0.6190 | 16,667 | 6.000 | 0.990 | 0.0825 | 13,418.6 | 0.614 | |
| SMX | 0.1 | 2378.1 | 0.8972 | 50,000 | 0.250 | 0.985 | 0.2619 | 18,030.1 | 0.953 |
| 0.25 | 3434.0 | 0.8685 | 50,000 | 0.500 | 0.981 | 0.3040 | 18,300.8 | 0.970 | |
| 0.5 | 5491.8 | 0.8108 | 33,333 | 3.000 | 0.988 | 0.1885 | 23,086.4 | 0.948 | |
| 1 | 7530.7 | 0.7846 | 20,000 | 6.250 | 0.988 | N.A. | N.A. | N.A. | |
| TMP | 0.1 | 2340.0 | 0.8716 | 50,000 | 0.250 | 0.989 | 0.2932 | 16,000.9 | 0.9487 |
| 0.25 | 2567.3 | 0.7911 | 33,333 | 0.750 | 0.991 | 0.2272 | 17,667.8 | 0.9735 | |
| 0.5 | 3896.4 | 0.7282 | 33,333 | 3.000 | 0.996 | 0.1366 | 22,092.6 | 0.9872 | |
| 1 | N.A. | N.A. | N.A. | N.A. | N.A. | N.A. | N.A. | N.A. | |
| Compound | Molecular Formula | Molecular Weight (g/mol) | logKow 1 | pKa1 | pKa2 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Diclofenac | C14H10Cl2NNaO2 | 318.13 | 4.26 | 4.21 2 | |
| Sulfamethoxazole | C10H11N3O3S | 253.28 | 0.79 | 1.83 2 | 5.57 2 |
| Trimethoprim | C14H18N4O3 | 290.32 | 1.28 | 7.10 ± 0.02 3 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Gutiérrez, M.; Verlicchi, P.; Mutavdžić Pavlović, D. Study of the Influence of the Wastewater Matrix in the Adsorption of Three Pharmaceuticals by Powdered Activated Carbon. Molecules 2023, 28, 2098. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules28052098
Gutiérrez M, Verlicchi P, Mutavdžić Pavlović D. Study of the Influence of the Wastewater Matrix in the Adsorption of Three Pharmaceuticals by Powdered Activated Carbon. Molecules. 2023; 28(5):2098. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules28052098
Chicago/Turabian StyleGutiérrez, Marina, Paola Verlicchi, and Dragana Mutavdžić Pavlović. 2023. "Study of the Influence of the Wastewater Matrix in the Adsorption of Three Pharmaceuticals by Powdered Activated Carbon" Molecules 28, no. 5: 2098. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules28052098
APA StyleGutiérrez, M., Verlicchi, P., & Mutavdžić Pavlović, D. (2023). Study of the Influence of the Wastewater Matrix in the Adsorption of Three Pharmaceuticals by Powdered Activated Carbon. Molecules, 28(5), 2098. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules28052098