A Stable Fe-Zn Modified Sludge-Derived Biochar for Diuron Removal: Kinetics, Isotherms, Mechanism, and Practical Research
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Results and Discussion
2.1. Biochar Characterization
2.2. Adsorptive Processes
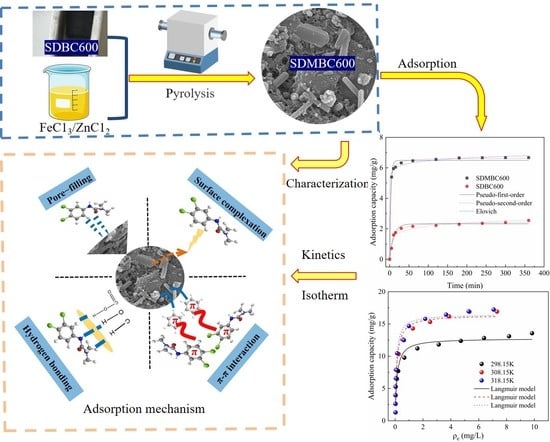
2.2.1. Adsorption Kinetics
2.2.2. Adsorption Isotherms
2.3. Factors Affecting Diuron Adsorption
2.3.1. Effects of Diuron Concentration and Solution Temperature
2.3.2. Effects of Solution pH and Coexisting Substances
2.4. Adsorption Mechanism
2.5. Practical Research
2.5.1. Adsorption of Pesticide Mixture in Solution
2.5.2. Adsorption in Real Water
2.5.3. Stability and Regeneration
3. Materials and Methods
3.1. Reagents and Materials
3.2. Preparation of Adsorbent
3.3. Characterization of the Adsorbent
3.4. Adsorption Experiments
4. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Liu, J.; Morales-Narváez, E.; Vicent, T.; Merkoçi, A.; Zhong, G.-H. Microorganism-decorated nanocellulose for efficient diuron removal. Chem. Eng. J. 2018, 354, 1083–1091. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Al-Shaalan, N.H.; Ali, I.; ALOthman, Z.A.; Al-Wahaibi, L.H.; Alabdulmonem, H. High performance removal and simulation studies of diuron pesticide in water on MWCNTs. J. Mol. Liq. 2019, 289, 111039. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thomas, K. The environmental fate and behaviour of antifouling paint booster biocides: A review. Biofouling 2001, 17, 73–86. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saleh, A.; Molaei, S.; Fumani, N.S.; Abedi, E. Antifouling paint booster biocides (Irgarol 1051 and diuron) in marinas and ports of Bushehr, Persian Gulf. Mar. Pollut. Bull. 2016, 105, 367–372. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kaonga, C.C.; Takeda, K.; Sakugawa, H. Antifouling agents and Fenitrothion contamination in seawater, sediment, plankton, fish and selected marine animals from the Seto Inland Sea, Japan. Geochem. J. 2015, 49, 23–37. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Silva Moretto, J.A.; Rueda Furlan, J.P.; Tonelli Fernandes, A.F.; Bauermeister, A.; Lopes, N.P.; Stehling, E.G. Alternative biodegradation pathway of the herbicide diuron. Int. Biodeterior. Biodegrad. 2019, 143, 104716. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khongthon, W.; Jovanovic, G.; Yokochi, A.; Sangvanich, P.; Pavarajarn, V. Degradation of diuron via an electrochemical advanced oxidation process in a microscale-based reactor. Chem. Eng. J. 2016, 292, 298–307. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Commission, E. Socio-Economic Impacts of the Identification of Priority Hazardous Substances Under the Water Framework Directive. Dir.-Gen. Environ. 2000. Available online: https://ec.europa.eu/environment/enveco/economics_policy/pdf/studies/haz_sub_report.pdf (accessed on 27 February 2023).
- Reyes-Cervantes, A.; Robles-Morales, D.L.; Téllez-Jurado, A.; Huerta-Ochoa, S.; Jiménez-González, A.; Medina-Moreno, S.A. Evaluation in the performance of the biodegradation of herbicide diuron to high concentrations by Lysinibacillus fusiformis acclimatized by sequential batch culture. J. Environ. Manag. 2021, 291, 112688. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, X.C.; Zhou, Y.Y.; Zhang, J.C.; Tang, L.; Luo, L.; Zeng, G.M. Iron Containing Metal-Organic Frameworks: Structure, Synthesis, and Applications in Environmental Remediation. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2017, 9, 20255–20275. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chin, S.X.; Lau, K.S.; Zakaria, S.; Chia, C.H.; Wongchoosuk, C. Chitosan Fibers Loaded with Limonite as a Catalyst for the Decolorization of Methylene Blue via a Persulfate-Based Advanced Oxidation Process. Polymers 2022, 14, 5165. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alshorifi, F.T.; Alswat, A.A.; Mannaa, M.A.; Alotaibi, M.T.; El-Bahy, S.M.; Salama, R.S. Facile and green synthesis of silver quantum dots immobilized onto a polymeric CTS–PEO blend for the photocatalytic degradation of p-Nitrophenol. ACS Omega 2021, 6, 30432–30441. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Beltrán-Flores, E.; Torán, J.; Caminal, G.; Blánquez, P.; Sarrà, M. The removal of diuron from agricultural wastewaters by Trametes versicolor immobilized on pinewood in simple channel reactors. Sci. Total Environ. 2020, 728, 138414. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Taheran, M.; Brar, S.K.; Verma, M.; Surampalli, R.Y.; Zhang, T.C.; Valéro, J.R. Membrane processes for removal of pharmaceutically active compounds (PhACs) from water and wastewaters. Sci. Total Environ. 2016, 547, 60–77. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lau, K.S.; Azmi, N.A.S.; Chin, S.X.; Zakaria, S.; Chia, C.H. Chitosan-Bead-Encapsulated Polystyrene Sulfonate for Adsorption of Methylene Blue and Regeneration Studies: Batch and Continuous Approaches. Polymers 2023, 15, 1269. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Beluci, N.D.C.L.; Dos Santos, T.R.T.; Marcuzzo, J.S.; Bergamasco, R. Facile filtration system to remove Diuron in aqueous solutions. J. Hazard. Mater. 2021, 404, 124163. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lau, K.S.; Chin, S.X.; Khiew, P.S.; Zakaria, S.; Yin, M.L.J.; Key, K.H.M.; Chia, C.H. Enhanced adsorption of anionic phenol red using cationic polyethylenimine-incorporated chitosan beads. J. Porous Mater. 2022, 29, 609–619. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tang, L.; Yu, J.; Pang, Y.; Zeng, G.; Deng, Y.; Wang, J.; Ren, X.; Ye, S.; Peng, B.; Feng, H. Sustainable efficient adsorbent: Alkali-acid modified magnetic biochar derived from sewage sludge for aqueous organic contaminant removal. Chem. Eng. J. 2018, 336, 160–169. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, W.; Zheng, J.; Zheng, P.; Qiu, R. Atrazine immobilization on sludge derived biochar and the interactive influence of coexisting Pb(II) or Cr(VI) ions. Chemosphere 2015, 134, 438–445. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, L.; Liu, X.; Wang, D.; Lin, H.; Huang, L. Removal and reduction of Cr(VI) in simulated wastewater using magnetic biochar prepared by co-pyrolysis of nano-zero-valent iron and sewage sludge. J. Clean. Prod. 2020, 257, 120562. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, Y.; Yu, I.K.M.; Tsang, D.C.W.; Cao, X.; Lin, D.; Wang, L.; Graham, N.J.D.; Alessi, D.S.; Komárek, M.; Ok, Y.S.; et al. Multifunctional iron-biochar composites for the removal of potentially toxic elements, inherent cations, and hetero-chloride from hydraulic fracturing wastewater. Environ. Int. 2019, 124, 521–532. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alshorifi, F.T.; Ali, S.L.; Salama, R.S. Promotional synergistic effect of Cs–Au NPs on the performance of Cs–Au/MgFe2O4 catalysts in catalysis 3, 4-Dihydropyrimidin-2 (1H)-Ones and degradation of RhB Dye. J. Inorg. Organomet. Polym. Mater. 2022, 32, 3765–3776. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, Y.; Wang, T.; Han, C.; Lv, X.; Bai, L.; Sun, X.; Zhang, P. Facile synthesis of Fe-modified lignin-based biochar for ultra-fast adsorption of methylene blue: Selective adsorption and mechanism studies. Bioresour. Technol. 2022, 344, 126186. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yan, L.; Liu, Y.; Zhang, Y.; Liu, S.; Wang, C.; Chen, W.; Liu, C.; Chen, Z.; Zhang, Y. ZnCl2 modified biochar derived from aerobic granular sludge for developed microporosity and enhanced adsorption to tetracycline. Bioresour. Technol. 2020, 297, 122381. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, F.; Zimmerman, A.R.; Hu, X.; Gao, B. Removal of aqueous Cr(VI) by Zn-and Al-modified hydrochar. Chemosphere 2020, 260, 127610. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, P.; Tang, L.; Wei, X.; Zeng, G.; Zhou, Y.; Deng, Y.; Wang, J.; Xie, Z.; Fang, W. Synthesis and application of iron and zinc doped biochar for removal of p-nitrophenol in wastewater and assessment of the influence of co-existed Pb(II). Appl. Surf. Sci. 2017, 392, 391–401. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tan, Y.; Wan, X.; Zhou, T.; Wang, L.; Yin, X.; Ma, A.; Wang, N. Novel Zn-Fe engineered kiwi branch biochar for the removal of Pb(II) from aqueous solution. J. Hazard. Mater. 2022, 424, 127349. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, T.; Xu, Y.; Huang, Q.; Sun, Y.; Liang, X.; Wang, L.; Qin, X.; Zhao, L. Adsorption characteristics and the removal mechanism of two novel Fe-Zn composite modified biochar for Cd(II) in water. Bioresour. Technol. 2021, 333, 125078. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, Y.Y.; Liu, X.C.; Xiang, Y.J.; Wang, P.; Zhang, J.C.; Zhang, F.F.; Wei, J.H.; Luo, L.; Lei, M.; Tang, L. Modification of biochar derived from sawdust and its application in removal of tetracycline and copper from aqueous solution: Adsorption mechanism and modelling. Bioresour. Technol. 2017, 245, 266–273. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, X.; Shi, J.; Luo, X. Enhanced adsorption of rhodamine B from water by Fe-N co-modified biochar: Preparation, performance, mechanism and reusability. Bioresour. Technol. 2022, 343, 126103. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wan, C.; Li, H.; Zhao, L.; Li, Z.; Zhang, C.; Tan, X.; Liu, X. Mechanism of removal and degradation characteristics of dicamba by biochar prepared from Fe-modified sludge. J. Environ. Manag. 2021, 299, 113602. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lyu, H.; Zhang, Q.; Shen, B. Application of biochar and its composites in catalysis. Chemosphere 2020, 240, 124842. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nguyen, V.-T.; Nguyen, T.-B.; Dat, N.D.; Huu, B.T.; Nguyen, X.-C.; Tran, T.; Bui, M.-H.; Dong, C.-D.; Bui, X.-T. Adsorption of norfloxacin from aqueous solution on biochar derived from spent coffee ground: Master variables and response surface method optimized adsorption process. Chemosphere 2022, 288, 132577. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, Z.; Su, J.; Hu, X.; Ali, A.; Wu, Z. Isolation of biosynthetic crystals by microbially induced calcium carbonate precipitation and their utilization for fluoride removal from groundwater. J. Hazard. Mater. 2021, 406, 124748. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Inyang, H.I.; Onwawoma, A.; Bae, S. The Elovich equation as a predictor of lead and cadmium sorption rates on contaminant barrier minerals. Soil Tillage Res. 2016, 155, 124–132. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Raghav, S.; Kumar, D. Comparative kinetics and thermodynamic studies of fluoride adsorption by two novel synthesized biopolymer composites. Carbohydr. Polym. 2019, 203, 430–440. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Qu, J.; Meng, Q.; Lin, X.; Han, W.; Jiang, Q.; Wang, L.; Hu, Q.; Zhang, L.; Zhang, Y. Microwave-assisted synthesis of β-cyclodextrin functionalized celluloses for enhanced removal of Pb(II) from water: Adsorptive performance and mechanism exploration. Sci. Total Environ. 2021, 752, 141854. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Szewczuk-Karpisz, K.; Tomczyk, A.; Celińska, M.; Sokołowska, Z.; Kuśmierz, M. Carboxin and diuron adsorption mechanism on sunflower husks biochar and goethite in the single/mixed pesticide solutions. Materials 2021, 14, 2584. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dai, Y.; Li, J.; Shan, D. Adsorption of tetracycline in aqueous solution by biochar derived from waste Auricularia auricula dregs. Chemosphere 2020, 238, 124432. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gao, Y.; Li, Y.; Zhang, L.; Huang, H.; Hu, J.; Shah, S.M.; Su, X. Adsorption and removal of tetracycline antibiotics from aqueous solution by graphene oxide. J. Colloid Interface Sci. 2012, 368, 540–546. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barbosa De Andrade, M.; Sestito Guerra, A.C.; Tonial dos Santos, T.R.; Cusioli, L.F.; de Souza Antônio, R.; Bergamasco, R. Simplified synthesis of new GO-α-γ-Fe2O3-Sh adsorbent material composed of graphene oxide decorated with iron oxide nanoparticles applied for removing diuron from aqueous medium. J. Environ. Chem. Eng. 2020, 8, 103903. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhuo, S.-N.; Dai, T.-C.; Ren, H.-Y.; Liu, B.-F. Simultaneous adsorption of phosphate and tetracycline by calcium modified corn stover biochar: Performance and mechanism. Bioresour. Technol. 2022, 359, 127477. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Y.; Azeem, M.; Luo, Y.; Peng, Y.; Feng, C.; Li, R.; Peng, J.; Zhang, L.; Wang, H.; Zhang, Z. Phosphate capture from biogas slurry with magnesium-doped biochar composite derived from Lycium chinensis branch filings: Performance, mechanism, and effect of coexisting ions. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2022, 29, 84873–84885. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cao, Y.; Jiang, S.; Zhang, Y.; Xu, J.; Qiu, L.; Wang, L. Investigation into adsorption characteristics and mechanism of atrazine on nano-MgO modified fallen leaf biochar. J. Environ. Chem. Eng. 2021, 9, 105727. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, L.; Liu, Y.; Liu, S.; Hu, X.; Zeng, G.; Hu, X.; Liu, S.; Liu, S.; Huang, B.; Li, M. Fabrication of β-cyclodextrin/poly (l-glutamic acid) supported magnetic graphene oxide and its adsorption behavior for 17β-estradiol. Chem. Eng. J. 2017, 308, 597–605. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yao, B.; Luo, Z.; Du, S.; Yang, J.; Zhi, D.; Zhou, Y. Sustainable biochar/MgFe2O4 adsorbent for levofloxacin removal: Adsorption performances and mechanisms. Bioresour. Technol. 2021, 340, 125698. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Stathi, P.; Louloudi, M.; Deligiannakis, Y. Effects of dissolved carbonates and carboxylates on the sorption of thiuram disulfide pesticides on humic acids and model surfaces. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2007, 41, 2782–2788. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, W.; Gao, M.; Cao, M.; Dan, J.; Yang, H. Self-propagating synthesis of Zn-loaded biochar for tetracycline elimination. Sci. Total Environ. 2021, 759, 143542. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mei, Y.; Xu, J.; Zhang, Y.; Li, B.; Fan, S.; Xu, H. Effect of Fe–N modification on the properties of biochars and their adsorption behavior on tetracycline removal from aqueous solution. Bioresour. Technol. 2021, 325, 124732. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wu, Y.; Cheng, H.; Pan, D.; Zhang, L.; Li, W.; Song, Y.; Bian, Y.; Jiang, X.; Han, J. Potassium hydroxide-modified algae-based biochar for the removal of sulfamethoxazole: Sorption performance and mechanisms. J. Environ. Manag. 2021, 293, 112912. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, X.; Xu, J.; Luo, X.; Shi, J. Efficient adsorption of dyes from aqueous solution using a novel functionalized magnetic biochar: Synthesis, kinetics, isotherms, adsorption mechanism, and reusability. Bioresour. Technol. 2022, 360, 127526. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moreno-Castilla, C. Adsorption of organic molecules from aqueous solutions on carbon materials. Carbon 2004, 42, 83–94. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Jiang, S.; Yan, L.; Wang, R.; Li, G.; Rao, P.; Ju, M.; Jian, L.; Guo, X.; Che, L. Recyclable nitrogen-doped biochar via low-temperature pyrolysis for enhanced lead(II) removal. Chemosphere 2022, 286, 131666. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]









| Fitting Model | Parameter | SDBC600 | SDMBC600 |
|---|---|---|---|
| Experimental adsorption capacity | qm (mg/g) a | 2.55 | 6.67 |
| Pseudo-first-order | qm (mg/g) b | 2.32 | 6.49 |
| k1 (min−1) | 0.093 | 0.33 | |
| R2 | 0.973 | 0.989 | |
| Pseudo-second-order | qm (mg/g) b | 2.4721 | 6.65 |
| k2 (g/(mg·min)) | 0.0542 | 0.12 | |
| R2 | 0.975 | 0.999 | |
| Elovich | α (g/(mg·min)) | 2.67 | 1.61 × 108 |
| β (g/mg) | 3.10 | 3.84 | |
| R2 | 0.934 | 0.996 |
| Fitting Model | Parameter | Temperature (°C) | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 25 | 35 | 45 | ||
| Langmuir | Qm (mg/g) | 12.8 | 16.4 | 16.5 |
| KL (L/mg) | 7.96 | 8.68 | 11.3 | |
| R2 | 0.955 | 0.935 | 0.971 | |
| Freundlich | KF (mg/g(L/mg)1/n) | 8.87 | 11.8 | 12.3 |
| n | 4.73 | 4.27 | 4.47 | |
| R2 | 0.901 | 0.878 | 0.904 | |
| Sips | qm (mg/g) | 13.7 | 17.6 | 17.7 |
| Ks (L/mg) | 5.81 | 6.26 | 8.20 | |
| m | 0.74 | 0.77 | 0.75 | |
| R2 | 0.964 | 0.942 | 0.979 | |
| Experiment | Parameter |
|---|---|
| Kinetics | C0 = 5 mg/L, V = 0.1 L, m = 0.075 g, t = 0–360 min, and T = 25 °C |
| Isotherm | C0 = 1–20 mg/L, V = 0.1 L, m = 0.075 g, t = 360 min, and T = 25/35/45 °C |
| Diuron initial concentration | C0 = 1–20 mg/L, V = 0.1 L, m = 0.075 g, t = 360 min, and T = 25 °C |
| Temperature | C0 = 10 mg/L, V = 0.1 L, m = 0.075 g, t = 360 min, and T = 20–45 °C |
| Solution pH | C0 = 10 mg/L, V = 0.1 L, m = 0.075 g, t = 360 min, and pH = 2–10 |
| Coexisting ions and HA | C0 = 10 mg/L, V = 0.1 L, m = 0.075 g, t = 360 min, and the concentration of coexisting ions (Cu2+, Ca2+, Cr6+, K+, Mg2+, Pb2+) and HA were 0–20 mg/L. |
| Pesticide mixture | C0 = 0.25/2.5/5 mg/L, V = 0.1 L, m = 0.075 g, t = 360 min, and T = 25 °C |
| Real water | C0 = 10 mg/L, V = 0.1 L, m = 0.075 g, t = 360 min, and T = 25 °C |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Liu, Y.; Ji, X.; Wang, Y.; Zhang, Y.; Zhang, Y.; Li, W.; Yuan, J.; Ma, D.; Sun, H.; Duan, J. A Stable Fe-Zn Modified Sludge-Derived Biochar for Diuron Removal: Kinetics, Isotherms, Mechanism, and Practical Research. Molecules 2023, 28, 2868. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules28062868
Liu Y, Ji X, Wang Y, Zhang Y, Zhang Y, Li W, Yuan J, Ma D, Sun H, Duan J. A Stable Fe-Zn Modified Sludge-Derived Biochar for Diuron Removal: Kinetics, Isotherms, Mechanism, and Practical Research. Molecules. 2023; 28(6):2868. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules28062868
Chicago/Turabian StyleLiu, Yucan, Xianguo Ji, Ying Wang, Yan Zhang, Yanxiang Zhang, Wei Li, Jiang Yuan, Dong Ma, Hongwei Sun, and Jinming Duan. 2023. "A Stable Fe-Zn Modified Sludge-Derived Biochar for Diuron Removal: Kinetics, Isotherms, Mechanism, and Practical Research" Molecules 28, no. 6: 2868. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules28062868
APA StyleLiu, Y., Ji, X., Wang, Y., Zhang, Y., Zhang, Y., Li, W., Yuan, J., Ma, D., Sun, H., & Duan, J. (2023). A Stable Fe-Zn Modified Sludge-Derived Biochar for Diuron Removal: Kinetics, Isotherms, Mechanism, and Practical Research. Molecules, 28(6), 2868. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules28062868