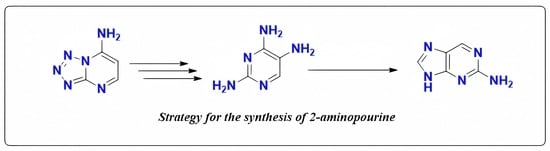
Reconstructive Methodology in the Synthesis of 2-Aminopurine
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Results
2.1. Synthesis
2.2. Crystallography
3. Materials and Methods
3.1. Chemical Experiment
3.2. Crystallography Experiment
4. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Nagatsugi, F.; Uemura, K.; Nakashima, S.; Maeda, M.; Sasaki, S. 2-Aminopurine Derivatives with C6-Substituted Olefin as Novel Cross-Linking Agents and the Synthesis of the Corresponding β-Phosphoramidite Precursors. Tetrahedron 1997, 53, 3035–3044. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ts’o, P.O.P. Basic Principles in Nucleic Acid Chemistry V1; Elsevier Science: Oxford, UK, 1974; ISBN 9780323144001. [Google Scholar]
- Jean, J.M.; Hall, K.B. 2-Aminopurine Fluorescence Quenching and Lifetimes: Role of Base Stacking. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2001, 98, 37–41. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Perry, C.M.; Wagstaff, A.J. Famciclovir: A Review of Its Pharmacological Properties and Therapeutic Efficacy in Herpesvirus Infections. Drugs 1995, 50, 396–415. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Boyd, M.R.; Safrin, S.; Kern, E.R. Penciclovir: A Review of Its Spectrum of Activity, Selectivity, and Cross-Resistance Pattern. Antivir. Chem. Chemother. 1993, 4, 3–11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wagstaff, A.J.; Faulds, D.; Goa, K.L. Aciclovir: A Reappraisal of Its Antiviral Activity, Pharmacokinetic Properties and Therapeutic Efficacy. Drugs 1994, 47, 153–205. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Matthews, T.; Boehme, R. Antiviral Activity and Mechanism of Action of Ganciclovir. Clin. Infect. Dis. 1988, 10, S490–S494. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Melroy, J.; Nair, V. The antiviral activity, mechanism of action, clinical significance and resistance of abacavir in the treatment of pediatric AIDS. Curr. Pharm. Des. 2005, 11, 3847–3852. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhao, C.; Shi, C.; Yang, S.; Wang, F. Method for Synthesizing 2-Aminopurine. Patent CN116063306, 5 May 2023. [Google Scholar]
- Guo, H.; Rao, W.; Niu, H.; Wang, D.; Qu, G. Dehalogenations of 6-Chloropurine, 6-Chloropurine Nucleosides and 6-Bromopurine Nucleosides under Microwave Irradiation in Water. Chin. J. Chem. 2010, 18, 361–364. [Google Scholar]
- Jongejan, H.; Kos, N.J.; Van Der Plas, H.C. A 15N Study of the Ammonia-induced Deamination of 1-aminopurinium Salts. Recl. Trav. Chim. Pays-Bas 1986, 105, 337–340. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saladino, R.; Neri, V.; Crestini, C.; Costanzo, G.; Graciotti, M.; Di Mauro, E. Synthesis and Degradation of Nucleic Acid Components by Formamide and Iron Sulfur Minerals. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2008, 130, 15512–15518. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kos, N.J.; Jongejan, H.; Van Der Plas, H.C. Deamination, Involving Ring Opening, in Reactions of 1-Aminopurinium Mesitylenesulfonates with Methanolic Amonia. Tetrahedron 1987, 43, 4841–4848. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saladino, R.; Botta, G.; Delfino, M.; Di Mauro, E. Meteorites as Catalysts for Prebiotic Chemistry. Chem. A Eur. J. 2013, 19, 16916–16922. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Abdullah, Z.; Bakar, M.; Din, E.; Rani, N.; Salleg, N.; Leong, G.; Ling, L.; Aiyub, Z. Synthesis and fluorescence characteristic of 2-substituted and 6-substituted purines. Malays. J. Sci. 2008, 12, 251–256. [Google Scholar]
- Gazizov, D.A.; Fedotov, V.V.; Chistyakov, K.A.; Gorbunov, E.B.; Rusinov, G.L.; Charushin, V.N. Access to Azolopyrimidine-6,7-Diamines as a Valuable “Building-Blocks” to Develop New Fused Heteroaromatic Systems. Tetrahedron 2021, 89, 132172. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lyapustin, D.N.; Fedotov, V.V.; Ulomsky, E.N.; Rusinov, V.L.; Chupakhin, O.N. Recent Advances in the Chemistry of Two-Carbon Nitro-Containing Synthetic Equivalents. Russ. Chem. Rev. 2023, 92, RCR5077. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zubarev, V.Y.; Ostrovskii, V.A. Methods for the Synthesis of Mono- and Polynuclear NH-Tetrazoles. (Review). Chem. Heterocycl. Compd. 2000, 36, 759–774. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aksenov, A.V.; Aksenov, D.A.; Aksenov, N.A.; Skomorokhov, A.A.; Aleksandrova, E.V.; Rubin, M. Preparation of Spiro[Indole-3,5′-Isoxazoles] via Grignard Conjugate Addition/Spirocyclization Sequence. RSC Adv. 2021, 11, 1783–1793. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hannser, A.; Stumer, C. Organic Syntheses Based on Name Reactions; Pergamon: Eindhoven, The Netherlands, 2002; p. 443. [Google Scholar]
- Dolomanov, O.V.; Bourhis, L.J.; Gildea, R.J.; Howard, J.A.K.; Puschmann, H. OLEX2: A Complete Structure Solution, Refinement and Analysis Program. J. Appl. Crystallogr. 2009, 42, 339–341. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sheldrick, G.M. Crystal Structure Refinement with SHELXL. Acta Crystallogr. C Struct. Chem. 2015, 71, 3–8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]






| No. | Solvent 2 | Reducing Agent | X, Equiv | Reaction Condition 3 | Yield, % 5 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| entry 1 | EtOH | Na2S•9H2O | 1.0 | 60 °C, 0.1 h | 32% |
| entry 2 | HCl | Fe | 8.0 | 60 °C, 2 h | - |
| entry 3 | AcOH | Zn | 10.0 | reflux, 2 h | - |
| entry 4 | AcOH | Ph3P | 1.0 | reflux, 2 h | 77% |
| entry 5 | AcOH | Cu | 1.0 | reflux, 0.2 h | - |
| entry 6 | THF | Ph3P | 1.0 | reflux, 2 h | - |
| entry 7 | H2O | Na2S2O4 | 8.0 | reflux, 0.2 h | - |
| entry 8 | NH4OH, EtOH | Zn | 4.0 | 70 °C, 1 h | - |
| entry 9 | EtOH | 6 H2/Pd | - | 4 50 °C, 4 h | - |
| No. | Solvent 2 | Reducing Agent | X, Equiv | Reaction Condition 3 | Yield, % 5 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| entry 1 | H2O | Na2S2O4 | 6.0 | reflux, 0.2 h | 59 |
| entry 2 | TEOF, AcOH | Fe | 10.0 | 130 °C, 5 h | - |
| entry 3 | HCl | Sn | 2.0 | 110 °C, 1 h | - |
| entry 4 | DMF | 6 H2/Pd | 0.05 | 4 100 °C, 4 h | 75 |
| No. | Solvent 2 | Formylation Agent | mL, Qty/Equiv | Reaction Condition 3 | Yield, % 4 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| entry 1 | - | HCOOH | 6.0/45.0 | reflux, 3 h | - |
| entry 2 | - | TEOF | 6.0/45.0 | reflux, 3h | - |
| entry 3 | AcOH | TEOF | 1.0/3.0 | reflux, 3 h | - |
| entry 4 | AcOH | TEOF | 1.0/5.0 | reflux, 3 h | - |
| entry 5 | N-Formylmorpholine | HCOOH | 1.0/6.5 | reflux, 3 h | - |
| entry 6 | Ac2O | TEOF | 3.0/25.0 | reflux, 2 h | 41 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Neymash, A.O.; Ulomsky, E.N.; Fedotov, V.V.; Aminov, S.V.; Lyapustin, D.N.; Gorbunov, E.B.; Ishimnikov, V.A.; Slepukhin, P.A.; Rusinov, V.L. Reconstructive Methodology in the Synthesis of 2-Aminopurine. Molecules 2024, 29, 134. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules29010134
Neymash AO, Ulomsky EN, Fedotov VV, Aminov SV, Lyapustin DN, Gorbunov EB, Ishimnikov VA, Slepukhin PA, Rusinov VL. Reconstructive Methodology in the Synthesis of 2-Aminopurine. Molecules. 2024; 29(1):134. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules29010134
Chicago/Turabian StyleNeymash, Artyom O., Evgeny N. Ulomsky, Victor V. Fedotov, Semen V. Aminov, Daniil N. Lyapustin, Evgeny B. Gorbunov, Vladislav A. Ishimnikov, Pavel A. Slepukhin, and Vladimir L. Rusinov. 2024. "Reconstructive Methodology in the Synthesis of 2-Aminopurine" Molecules 29, no. 1: 134. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules29010134
APA StyleNeymash, A. O., Ulomsky, E. N., Fedotov, V. V., Aminov, S. V., Lyapustin, D. N., Gorbunov, E. B., Ishimnikov, V. A., Slepukhin, P. A., & Rusinov, V. L. (2024). Reconstructive Methodology in the Synthesis of 2-Aminopurine. Molecules, 29(1), 134. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules29010134