Artificial Intelligence Sensing: Effective Flavor Blueprinting of Tea Infusions for a Quality Control Perspective
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Results and Discussion
2.1. Tea infusion Volatile Profiling by IS-SPME-GC-MS
2.2. Key Aroma Marker Quantitation by Standard Addition (SA) and IS-SPME-GC-MS
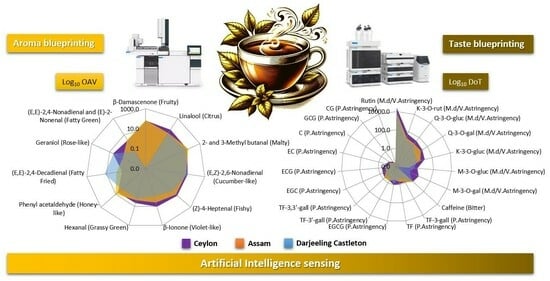
2.3. Aroma Blueprinting by AI Smelling Based on Sensomics
2.4. Taste-Active Compounds’ and Quality Markers’ Accurate Quantitative Profiling by LC-UV/DAD
2.5. Taste Blueprinting by AI Tasting Based on Sensomics
3. Materials and Methods
3.1. Reference Compounds and Solvents
3.2. Reference Solutions and Calibration Mixtures
3.3. Tea Infusions: Samples and Preparation
3.4. Automated in-Solution Solid-Phase Microextraction: Devices and Sampling Conditions
3.5. Automated IS-SPME-GC-MS Instrumental Set-Up and Analysis Conditions
3.6. LC-UV/DAD Instrumental Set-Up and Analysis Conditions
3.7. Data Acquisition and Data Processing
3.8. Method Validation Parameters
3.9. Method Validation Results: Precision and Accuracy
4. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Zhang, L.; Cao, Q.Q.; Granato, D.; Xu, Y.Q.; Ho, C.T. Association between chemistry and taste of tea: A review. Trends Food Sci. Technol. 2020, 101, 139–149. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Morimoto, J.; Rosso, M.C.; Kfoury, N.; Bicchi, C.; Cordero, C.; Robbat, A.; Cialiè Rosso, M.; Kfoury, N.; Bicchi, C.; Cordero, C.; et al. Untargeted/targeted 2D gas chromatography/mass spectrometry detection of the total volatile tea metabolome. Molecules 2019, 24, 3757. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Magagna, F.; Cordero, C.; Cagliero, C.; Liberto, E.; Rubiolo, P.; Sgorbini, B.; Bicchi, C. Black tea volatiles fingerprinting by comprehensive two-dimensional gas chromatography—Mass spectrometry combined with high concentration capacity sample preparation techniques: Toward a fully automated sensomic assessment. Food Chem. 2017, 225, 276–287. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Alcázar, A.; Ballesteros, O.; Jurado, J.M.; Pablos, F.; Martín, M.J.; Vilches, J.L.; Navalón, A. Differentiation of green, white, black, Oolong, and Pu-erh teas according to their free amino acids content. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2007, 55, 5960–5965. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhao, Y.; Chen, P.; Lin, L.; Harnly, J.M.; Yu, L.L.; Li, Z. Tentative identification, quantitation, and principal component analysis of green pu-erh, green, and white teas using UPLC/DAD/MS. Food Chem. 2011, 126, 1269–1277. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yang, Z.; Baldermann, S.; Watanabe, N. Recent studies of the volatile compounds in tea. Food Res. Int. 2013, 53, 585–599. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Atoui, A.K.; Mansouri, A.; Boskou, G.; Kefalas, P. Tea and herbal infusions: Their antioxidant activity and phenolic profile. Food Chem. 2005, 89, 27–36. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Del Rio, D.; Calani, L.; Scazzina, F.; Jechiu, L.; Cordero, C.; Brighenti, F. Bioavailability of catechins from ready-to-drink tea. Nutrition 2010, 26, 528–533. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Del Rio, D.; Calani, L.; Cordero, C.; Salvatore, S.; Pellegrini, N.; Brighenti, F. Bioavailability and catabolism of green tea flavan-3-ols in humans. Nutrition 2010, 26, 1110–1116. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wheeler, D.S.; Wheeler, W.J. The Medicinal Chemistry of Tea. Drug Dev. Res. 2004, 61, 45–65. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Prescott, J. Multisensory processes in flavour perception and their influence on food choice. Curr. Opin. Food Sci. 2015, 3, 47–52. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bondarovich, H.A.; Giammarino, A.S.; Renner, J.A.; Shephard, F.W.; Shingler, A.J.; Gianturco, M.A. Volatiles in tea Some Aspects of the Chemistry of Tea. A Contribution to the Knowledge of the Volatile Constituents. J. Agric. Food Chem. 1967, 15, 36–47. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kawakami, M.; Ganguly, S.N.; Baneijee, J.; Kobayashi, A. Aroma Composition of Oolong Tea and Black Tea by Brewed Extraction Method and Characterizing Compounds of Darjeeling Tea Aroma. J. Agric. Food Chem. 1995, 43, 200–207. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kumazawa, K.; Masuda, H. Change in the flavor of black tea drink during heat processing. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2001, 49, 3304–3309. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lv, H.P.; Zhong, Q.S.; Lin, Z.; Wang, L.; Tan, J.F.; Guo, L. Aroma characterisation of Pu-erh tea using headspace-solid phase microextraction combined with GC/MS and GC-olfactometry. Food Chem. 2012, 130, 1074–1081. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, S.; He, C.; Li, Y.; Yu, Z.; Chen, Y.; Wang, Y.; Ni, D. The formation of aroma quality of dark tea during pile-fermentation based on multi-omics. LWT 2021, 147, 111491. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Togari, N.; Kobayashi, A.; Aishima, T. Pattern recognition applied to gas chromatographic profiles of volatile components in three tea categories. Food Res. Int. 1995, 28, 495–502. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, C.; Lv, S.; Wu, Y.; Gao, X.; Li, J.; Zhang, W.; Meng, Q. Oolong tea made from tea plants from different locations in Yunnan and Fujian, China showed similar aroma but different taste characteristics. Springerplus 2016, 5, 576. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, L.; Zeng, Z.; Zhao, C.; Kong, H.; Lu, X.; Xu, G. A comparative study of volatile components in green, oolong and black teas by using comprehensive two-dimensional gas chromatography-time-of-flight mass spectrometry and multivariate data analysis. J. Chromatogr. A 2013, 1313, 245–252. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vitzthum, O.G.; Werkhoff, P.; Hubert, P. New Volatile Constituents of Black Tea Aroma. J. Agric. Food Chem. 1975, 23, 999–1003. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schuh, C.; Schieberle, P. Characterization of the key aroma compounds in the beverage prepared from Darjeeling black tea: Quantitative differences between tea leaves and infusion. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2006, 54, 916–924. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cordero, C.; Kiefl, J.; Reichenbach, S.E.; Bicchi, C. Characterization of odorant patterns by comprehensive two-dimensional gas chromatography: A challenge in omic studies. TrAC Trends Anal. Chem. 2019, 113, 364–378. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Scharbert, S.; Hofmann, T. Molecular Definition of Black Tea Taste by Means of Quantitative Studies, Taste Reconstitution, and Omission Experiments. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2005, 53, 5377–5384. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Borse, B.; Jagan Mohan Rao, L.; Nagalakshmi, S.; Krishnamurthy, N. Fingerprint of black teas from India: Identification of the regio-specific characteristics. Food Chem. 2002, 79, 419–424. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, L.F.; Lee, J.Y.; Chung, J.O.; Baik, J.H.; So, S.; Park, S.K. Discrimination of teas with different degrees of fermentation by SPME-GC analysis of the characteristic volatile flavour compounds. Food Chem. 2008, 109, 196–206. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Flaig, M.; Qi, S.C.; Wei, G.; Yang, X.; Schieberle, P. Characterisation of the key aroma compounds in a Longjing green tea infusion (Camellia sinensis) by the sensomics approach and their quantitative changes during processing of the tea leaves. Eur. Food Res. Technol. 2020, 246, 2411–2425. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Flaig, M.; Qi, S.; Wei, G.; Yang, X.; Schieberle, P. Characterization of the Key Odorants in a High-Grade Chinese Green Tea Beverage (Camellia sinensis; Jingshan cha) by Means of the Sensomics Approach and Elucidation of Odorant Changes in Tea Leaves Caused by the Tea Manufacturing Process. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2020, 68, 5168–5179. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nicolotti, L.; Mall, V.; Schieberle, P. Characterization of Key Aroma Compounds in a Commercial Rum and an Australian Red Wine by Means of a New Sensomics-Based Expert System (SEBES)—An Approach to Use Artificial Intelligence in Determining Food Odor Codes. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2019, 67, 4011–4022. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cordero, C.; Canale, F.; Rio, D.D.; Bicchi, C. Identification, quantitation, and method validation for flavan-3-ols in fermented ready-to-drink teas from the Italian market using HPLC-UV/DAD and LC-MS/MS. J. Sep. Sci. 2009, 32, 3643–3651. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Squara, S.; Caratti, A.; Fina, A.; Liberto, E.; Spigolon, N.; Genova, G.; Castello, G.; Cincera, I.; Bicchi, C.; Cordero, C. Artificial Intelligence decision-making tools based on comprehensive two-dimensional gas chromatography data: The challenge of quantitative volatilomics in food quality assessment. J. Chromatogr. A 2023, 1700, 464041. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cordero, C.; Kiefl, J.; Schieberle, P.; Reichenbach, S.E.; Bicchi, C. Comprehensive two-dimensional gas chromatography and food sensory properties: Potential and challenges. Anal. Bioanal. Chem. 2015, 407, 169–191. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dunkel, A.; Steinhaus, M.; Kotthoff, M.; Nowak, B.; Krautwurst, D.; Schieberle, P.; Hofmann, T. Nature’s chemical signatures in human olfaction: A foodborne perspective for future biotechnology. Angew. Chemie—Int. Ed. 2014, 53, 7124–7143. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ruosi, M.R.; Cordero, C.; Cagliero, C.; Rubiolo, P.; Bicchi, C.; Sgorbini, B.; Liberto, E. A Further Tool To Monitor the Coffee Roasting Process: Aroma Composition and Chemical Indices. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2012, 60, 11283–11291. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nicolotti, L.; Cordero, C.; Cagliero, C.; Liberto, E.; Sgorbini, B.; Rubiolo, P.; Bicchi, C. Quantitative fingerprinting by headspace-Two-dimensional comprehensive gas chromatography-mass spectrometry of solid matrices: Some challenging aspects of the exhaustive assessment of food volatiles. Anal. Chim. Acta 2013, 798, 115–125. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cordero, C.; Cagliero, C.; Liberto, E.; Nicolotti, L.; Rubiolo, P.; Sgorbini, B.; Bicchi, C. High concentration capacity sample preparation techniques to improve the informative potential of two-dimensional comprehensive gas chromatography–mass spectrometry: Application to sensomics. J. Chromatogr. A 2013, 1318, 1–11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stilo, F.; Cordero, C.; Sgorbini, B.; Bicchi, C.; Liberto, E. Highly Informative Fingerprinting of Extra-Virgin Olive Oil Volatiles: The Role of High Concentration-Capacity Sampling in Combination with Comprehensive Two-Dimensional Gas Chromatography. Separations 2019, 6, 34. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sgorbini, B.; Cagliero, C.; Liberto, E.; Rubiolo, P.; Bicchi, C.; Cordero, C. Strategies for Accurate Quantitation of Volatiles from Foods and Plant-Origin Materials: A Challenging Task. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2019, 67, 1619–1630. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schieberle, P.; Hofmann, T. Mapping the combinatorial code of food flavors by means of molecular sensory science approach. In Food Flavors: Chemical, Sensory and Technological Properties; CRC Press: Boca Raton, FL, USA, 2011; pp. 413–438. ISBN 9781439814925. [Google Scholar]
- McLafferty, F.W. Wiley Registry of Mass Spectral Data, 12th ed.; John Wiley & Sons Ltd.: Hoboken, NJ, USA, 2020. [Google Scholar]
- NIST/EPA/NIH Mass Spectral Library with Search Program Data Version: NIST v17; Mass Spectrometry Data Center, NIST: Gaithersburg, MD, USA, 2017.
- Sanderson, G.W.; Selvendran, R.R. The organic acids in tea plants. A study of the non-volatile organic acids separated on silica gel. J. Sci. Food Agric. 1965, 16, 251–258. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sai, V.; Chaturvedula, P.; Prakash, I. The aroma, taste, color and bioactive constituents of tea. J. Med. Plants Res. 2011, 5, 2110–2124. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Leibniz-LSB@TUM Odorant Database. Available online: https://www.leibniz-lsb.de/en/databases/leibniz-lsbtum-odorant-database/odorantdb/ (accessed on 2 January 2024).
- Preininger, M.; Grosch, W. Evaluation of Key Odorants of the Neutral Volatiles of Emmentaler Cheese by the Calculation of Odour Activity Values. LWT—Food Sci. Technol. 1994, 27, 237–244. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hofmann, T. Identification of the Astringent Taste Compounds in Black Tea Infusions by Combining Instrumental Analysis and Human Bioresponse Identification of the Astringent Taste Compounds in Black Tea Infusions by Combining Instrumental Analysis and Human. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2016, 52, 3498–3508. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Eurachem. Eurachem Guide: The Fitness for Purpose of Analytical Methods—A Laboratory Guide to Method Validation and Related Topics; Eurachem: Gembloux, Belgium, 2014; ISBN 0-94948926-12-0. [Google Scholar]
- European Commission. Commission Implementing Regulation (EU) 2021/808 of 22 March 2021 on the performance of analytical methods for residues of pharmacologically active substances used in food-producing animals and on the interpretation of results as well as on the methods to be used for sampling and repealing Decisions 2002/657/EC and 98/179/EC (Text with EEA relevance). Off. J. Eur. Union 2021, 180, 84–109. [Google Scholar]
- ISO/IEC 17025:2017; General Requirements for the Competence of Testing and Calibration Laboratories. ISO: Geneva, Switzerland, 2017.




| Compound Name | tR min | ITS | Odor | Ceylon | Assam | Azores | Darjeeling Castleton | Darjeeling Testa Valley | Kenya | Yunnan | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | 3-Methyl butanal * | 2.61 | 541 | Malty | d | d | d | d | d | d | d |
| 2 | 2-Methyl butanal * | 2.70 | 566 | Malty | d | d | d | d | d | d | d |
| 3 | (E)-2-Pentenal | 4.10 | 725 | Green, apple | d | d | nd | nd | d | d | nd |
| 4 | (Z)-2-Penten-1-ol | 4.85 | 788 | - | d | d | nd | nd | d | nd | nd |
| 5 | Hexanal * | 5.19 | 816 | Grassy-green | d | d | d | d | d | d | d |
| 6 | (E)-2-Hexenal | 6.82 | 856 | Bitter, almond | d | d | d | d | d | d | d |
| 7 | 1-Hexanol | 7.65 | 873 | Fruity | nd | nd | nd | nd | d | d | d |
| 8 | 2-Heptanone | 8.40 | 890 | Sweet, fruity | d | d | d | nd | d | nd | nd |
| 9 | (Z)-4-Heptenal * | 8.48 | 896 | Fishy | d | d | nd | d | d | d | d |
| 10 | Heptanal | 8.79 | 899 | Oil, fatty | d | d | d | d | d | d | d |
| 11 | (E)-2-Heptenal | 11.10 | 953 | Fatty, almond-like | d | d | nd | nd | nd | d | nd |
| 12 | Benzaldehyde | 11.10 | 954 | Almond, burnt sugar | d | d | d | d | d | d | d |
| 13 | 6-Methyl-5-hepten-2-one | 12.42 | 984 | Pungent, green | d | d | nd | nd | d | d | nd |
| 14 | (E,Z)-2,4-Heptadienal | 12.79 | 993 | Fatty, rancid | d | d | nd | d | d | d | nd |
| 15 | (E,E)-2,4-Heptadienal | 13.43 | 1008 | Fatty, rancid | d | d | nd | d | d | d | d |
| 16 | Limonene | 14.17 | 1026 | Citrus | d | nd | nd | d | d | d | d |
| 17 | 2,2,6-Trimethyl cyclohexanone | 14.51 | 1030 | - | d | nd | nd | nd | nd | nd | nd |
| 18 | Benzyl alcohol | 14.73 | 1035 | Sweet, fruity | d | d | nd | nd | d | nd | nd |
| 19 | Phenyl acetaldehyde * | 14.90 | 1039 | Honey-like | d | d | d | d | d | d | d |
| 20 | (E)-2-Octenal | 15.67 | 1055 | Green, nut, fat | d | d | nd | nd | d | d | nd |
| 21 | Trans-linalool-3,6-oxide | 16.98 | 1071 | Sweet, floral, citrus | d | d | d | d | d | d | d |
| 22 | Cis-linalool-3,6-oxide | 17.13 | 1087 | d | d | d | d | d | d | d | |
| 23 | Linalool * | 17.67 | 1101 | Citrus | d | d | d | d | d | d | d |
| 24 | Nonanal | 18.03 | 1103 | Fatty, waxy | d | nd | nd | nd | d | nd | d |
| 25 | 2-Phenyl alcohol | 18.30 | 1111 | Honey-like | d | nd | nd | nd | d | d | nd |
| 26 | (E,Z)-2,6-Nonadienal * | 20.12 | 1151 | Cucumber-like | d | d | nd | d | d | d | nd |
| 27 | (E)-2-Nonenal * | 20.43 | 1157 | Fatty, green | d | d | nd | nd | d | d | d |
| 28 | cis-Linalool-3,7-oxide | 20.93 | 1168 | Sweet, floral, citrus | d | d | nd | nd | d | d | nd |
| 29 | trans-Linalool-3,7-oxide | 21.18 | 1173 | d | d | nd | nd | d | d | nd | |
| 30 | Methyl salicylate | 21.95 | 1192 | - | d | d | d | d | d | d | d |
| 31 | Safranal | 22.25 | 1196 | Saffron | d | nd | nd | nd | d | d | nd |
| 32 | Decanal | 22.45 | 1200 | Penetrating, waxy | d | nd | nd | nd | d | d | nd |
| 33 | (E,E)-2,4-Nonadienal * | 22.93 | 1215 | Fatty, green | d | d | d | nd | d | d | d |
| 34 | Geraniol * | 24.79 | 1254 | Rose-like | d | d | d | d | d | d | d |
| 35 | Geranial | 25.55 | 1267 | Citrus | d | nd | nd | d | d | d | nd |
| 36 | Trans anethole | 26.35 | 1280 | Sweet | nd | d | nd | d | d | nd | nd |
| 37 | (E,Z)-2,4-Decadienal | 26.54 | 1291 | Deep-fried | d | d | nd | d | d | d | nd |
| 38 | (E,E)-2,4-Decadienal * | 29.64 | 1319 | Fatty, fried | d | d | nd | d | d | d | nd |
| 39 | β-Damascenone | 30.48 | 1381 | Fruity | d | d | nd | nd | d | d | nd |
| 40 | (Z)-Jasmone | 31.01 | 1400 | Floral, sweet, fruity | d | nd | nd | d | d | nd | nd |
| 41 | α-Ionone | 32.24 | 1424 | Violet-like | d | d | nd | d | d | d | d |
| 42 | Geranyl acetone | 33.31 | 1450 | Magnolia, green | d | d | nd | d | d | d | d |
| 43 | β-Ionone * | 34.62 | 1483 | Violet-like | d | d | nd | d | d | d | d |
| 44 | Caffeine | 43.77 | 1841 | - | d | d | d | d | d | d | d |
| Compound Name | Odor Threshold (µg/L) | Ceylon | Assam | Azores | Darjeeling Castleton | Darjeeling Testa Valley | Kenya | Yunnan |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 3-Methyl butanal | 1.2 | 37.00 | 49.12 | 52.32 | 25.22 | 27.45 | 84.89 | 17.02 |
| 2-Methyl butanal | 4.4 | 45.44 | 63.12 | 46.69 | 29.50 | 21.22 | 89.97 | 18.29 |
| Hexanal | 10 | 45.25 | 23.04 | 14.84 | 15.30 | 63.49 | 31.75 | 16.88 |
| (Z)-4-Heptenal | 0.06 | 0.98 | 0.68 | <LOQ | 0.20 | 0.82 | 0.41 | 0.47 |
| Phenyl acetaldehyde | 6.3 | 32.73 | 62.73 | 29.76 | 10.77 | 77.52 | 38.76 | 16.11 |
| Linalool | 0.6 | 25.75 | 9.72 | 10.19 | 7.86 | 54.48 | 27.24 | 0.41 |
| (E,Z)-2,6-Nonadienal | 0.03 | 0.56 | 0.39 | <LOQ | 0.50 | 0.28 | 0.14 | <LOQ |
| (E)-2-Nonenal | 0.4 | 0.40 | 0.24 | <LOQ | 0.02 | 1.21 | 0.60 | 0.15 |
| (E,E)-2,4-Nonadienal | 0.2 | 0.29 | 0.39 | 0.14 | <LOQ | 1.46 | 0.73 | 0.29 |
| Geraniol | 3.2 | 13.20 | 1.07 | 16.38 | 11.31 | 24.83 | 12.41 | 2.78 |
| (E,E)-2,4-Decadienal | 0.16 | 0.51 | 0.15 | <LOQ | 2.29 | 0.21 | 0.11 | <LOQ |
| β-Damascenone | 0.004 | 0.26 | 0.29 | <LOQ | <LOQ | 0.38 | 0.19 | <LOQ |
| β-Ionone | 0.2 | 2.16 | 0.78 | <LOQ | 0.18 | 3.84 | 1.92 | 0.29 |
| Compound Name | TT (µg/L) | Ceylon | Assam | Azores | Darjeeling Castleton | Darjeeling Testa Valley | Kenya | Yunnan |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Epigallocatechin Q (EGC) | 159 | 72.38 | 29.24 | 16.09 | 25.27 | 71.08 | 38.62 | 16.61 |
| Catechin Q (C) | 119 | 10.87 | 8.05 | 4.42 | 7.22 | 13.03 | 11.54 | 9.76 |
| Epicatechin Q (EC) | 270 | 41.97 | 19.07 | 12.99 | 14.16 | 25.80 | 24.90 | 19.84 |
| Epigallocatechingallate T,Q (EGCG) | 87.0 | 85.35 | 24.09 | 11.88 | 63.52 | 177.23 | 27.18 | 11.23 |
| Gallocatechingallate Q (GCG) | 179 | 8.64 | 5.49 | 2.84 | 3.16 | 4.73 | 3.54 | 5.44 |
| Epicatechingallate Q (ECG) | 115 | 41.40 | 21.90 | 7.92 | 29.68 | 39.79 | 20.31 | 18.80 |
| Catechingallate Q (CG) | 239 | 5.37 | 5.18 | 3.07 | 5.03 | 3.93 | 3.59 | 2.76 |
| Theaflavin Q (TF) | 9.00 | 7.55 | 4.39 | 2.92 | 2.25 | 2.16 | 4.50 | 2.33 |
| Theaflavin-3-gallate Q (TF3) | 10.7 | 8.81 | 7.77 | 3.70 | 3.17 | 2.89 | 5.90 | 3.65 |
| Theaflavin-3’-gallate Q (TF3’) | 10.7 | 5.28 | 6.64 | 3.76 | 3.47 | >LOQ | 4.92 | 3.67 |
| Theaflavin-3,3’-gallate Q (TF3-3’) | 11.3 | 6.38 | 7.96 | >LOQ | 3.40 | >LOQ | 4.77 | 3.59 |
| Myricetin-3-o-galactoside T (M-3-o-gal) | 1.3 | 2.39 | >LOQ | 0.28 | 0.42 | 0.32 | 1.51 | >LOQ |
| Myricetin-3-o-glucoside T (M-3-o-gluc) | 1.0 | 4.10 | 0.24 | 0.37 | 0.85 | 1.02 | 1.33 | >LOQ |
| Quercetin-3-o-rutinoside T (Rutin) | 0.0009 | 19.58 | 6.68 | 6.39 | 5.16 | 6.34 | 9.55 | 7.63 |
| Quercetin-3-o-galactoside T (Q-3-o-gal) | 0.20 | 4.31 | 2.62 | 1.60 | 1.90 | 2.39 | 4.01 | 1.82 |
| Quercetin-3-o-glucoside T (Q-3-o-gluc) | 0.30 | 9.42 | 3.93 | 1.01 | 0.77 | 1.12 | 5.53 | 2.68 |
| Kaempferol-3-o-rutinoside T (K-3-o-rut) | 0.15 | 8.31 | 3.11 | 4.56 | 1.98 | 3.83 | 6.89 | 3.91 |
| Kaempferol-3-o-glucoside T (K-3-o-gluc) | 0.30 | 4.19 | 1.32 | 1.07 | 0.62 | 1.24 | 3.50 | 1.43 |
| Caffeine T | 97.1 | 250.50 | 290.30 | 143.70 | 241.52 | 265.88 | 263.36 | 228.03 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Caratti, A.; Fina, A.; Trapani, F.; Bicchi, C.; Liberto, E.; Cordero, C.; Magagna, F. Artificial Intelligence Sensing: Effective Flavor Blueprinting of Tea Infusions for a Quality Control Perspective. Molecules 2024, 29, 565. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules29030565
Caratti A, Fina A, Trapani F, Bicchi C, Liberto E, Cordero C, Magagna F. Artificial Intelligence Sensing: Effective Flavor Blueprinting of Tea Infusions for a Quality Control Perspective. Molecules. 2024; 29(3):565. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules29030565
Chicago/Turabian StyleCaratti, Andrea, Angelica Fina, Fulvia Trapani, Carlo Bicchi, Erica Liberto, Chiara Cordero, and Federico Magagna. 2024. "Artificial Intelligence Sensing: Effective Flavor Blueprinting of Tea Infusions for a Quality Control Perspective" Molecules 29, no. 3: 565. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules29030565
APA StyleCaratti, A., Fina, A., Trapani, F., Bicchi, C., Liberto, E., Cordero, C., & Magagna, F. (2024). Artificial Intelligence Sensing: Effective Flavor Blueprinting of Tea Infusions for a Quality Control Perspective. Molecules, 29(3), 565. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules29030565