Hexane Fraction of Adenophora triphylla var. japonica Root Extract Inhibits Angiogenesis and Endothelial Cell-Induced Erlotinib Resistance in Lung Cancer Cells
Abstract
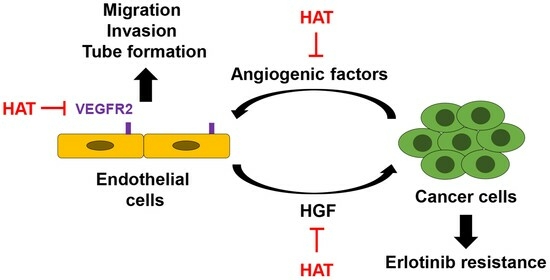
:1. Introduction
2. Results
2.1. Investigation of AT Root Fractions with Anti-Angiogenic Effects
2.2. Effects of HAT on the Angiogenic Capacity of HUVECs
2.3. Effects of HAT on the VEGFR2 Signaling Pathway in HUVECs
2.4. Binding of HAT Constituents to VEGFR2 Kinase Domain
2.5. Effects of HAT on Cancer-Cell-Induced Chemotaxis of HUVECs
2.6. Effects of HAT on EC-Induced EGFR TKI Resistance in Cancer Cells
3. Discussion
4. Materials and Methods
4.1. Preparation of HAT
4.2. Cell Culture
4.3. MTT Assay
4.4. Transwell Assay
4.5. Tube Formation Assay
4.6. Reverse Transcription Quantitative Polymerase Chain Reaction (RT-qPCR)
4.7. Western Blot
4.8. Co-Culture
4.9. Molecular Docking Analysis
4.10. Gas Chromatography–Mass Spectrometry (GC/MS)
4.11. Statistical Analyses
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Sung, H.; Ferlay, J.; Siegel, R.L.; Laversanne, M.; Soerjomataram, I.; Jemal, A.; Bray, F. Global Cancer Statistics 2020: GLOBOCAN Estimates of Incidence and Mortality Worldwide for 36 Cancers in 185 Countries. CA A Cancer J. Clin. 2021, 71, 209–249. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, Y.L.; Yuan, J.Q.; Wang, K.F.; Fu, X.H.; Han, X.R.; Threapleton, D.; Yang, Z.Y.; Mao, C.; Tang, J.L. The prevalence of EGFR mutation in patients with non-small cell lung cancer: A systematic review and meta-analysis. Oncotarget 2016, 7, 78985–78993. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Paez, J.G.; Jänne, P.A.; Lee, J.C.; Tracy, S.; Greulich, H.; Gabriel, S.; Herman, P.; Kaye, F.J.; Lindeman, N.; Boggon, T.J.; et al. EGFR mutations in lung cancer: Correlation with clinical response to gefitinib therapy. Science 2004, 304, 1497–1500. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chong, C.R.; Jänne, P.A. The quest to overcome resistance to EGFR-targeted therapies in cancer. Nat. Med. 2013, 19, 1389–1400. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tang, Z.H.; Lu, J.J. Osimertinib resistance in non-small cell lung cancer: Mechanisms and therapeutic strategies. Cancer Lett. 2018, 420, 242–246. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Prager, G.W.; Poettler, M. Angiogenesis in cancer. Basic mechanisms and therapeutic advances. Hamostaseologie 2012, 32, 105–114. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Baluk, P.; Hashizume, H.; McDonald, D.M. Cellular abnormalities of blood vessels as targets in cancer. Curr. Opin. Genet. Dev. 2005, 15, 102–111. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Le, X.; Nilsson, M.; Goldman, J.; Reck, M.; Nakagawa, K.; Kato, T.; Ares, L.P.; Frimodt-Moller, B.; Wolff, K.; Visseren-Grul, C.; et al. Dual EGFR-VEGF Pathway Inhibition: A Promising Strategy for Patients with EGFR-Mutant NSCLC. J. Thorac. Oncol. 2021, 16, 205–215. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Girard, N. New Strategies and Novel Combinations in EGFR TKI-Resistant Non-small Cell Lung Cancer. Curr. Treat. Options Oncol. 2022, 23, 1626–1644. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, S.E.; Lee, E.H.; Lee, T.J.; Kim, S.W.; Kim, B.H. Anti-obesity effect and action mechanism of Adenophora triphylla root ethanol extract in C57BL/6 obese mice fed a high-fat diet. Biosci. Biotechnol. Biochem. 2013, 77, 544–550. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, D.; Kim, K.Y. Adenophora triphylla var. japonica Inhibits Candida Biofilm Formation, Increases Susceptibility to Antifungal Agents and Reduces Infection. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2021, 22, 12523. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kang, M.; Ha, I.J.; Chun, J.; Kang, S.S.; Kim, Y.S. Separation of two cytotoxic saponins from the roots of Adenophora triphylla var. japonica by high-speed counter-current chromatography. Phytochem. Anal. 2013, 24, 148–154. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chun, J.; Kang, M.; Kim, Y.S. A triterpenoid saponin from Adenophora triphylla var. japonica suppresses the growth of human gastric cancer cells via regulation of apoptosis and autophagy. Tumour Biol. 2014, 35, 12021–12030. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lee, I.S.; Yang, E.J.; Kim, H.S.; Chung, S.K.; Furukawa, F.; Nishikawa, A. Suppressive effects of Adenophora triphylla extracts on in vitro tumor cell growth and in vivo gastric epithelial proliferation. Anticancer Res. 2000, 20, 3227–3231. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Park, H.J.; Park, S.H. Hexane fraction of Adenophora triphylla var. japonica root extract induces apoptosis of human lung cancer cells by inactivating Src/STAT3 pathway. Nat. Prod. Res. 2023, 37, 2924–2928. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Park, S.H. Ethyl Acetate Fraction of Adenophora triphylla var. japonica Inhibits Migration of Lewis Lung Carcinoma Cells by Suppressing Macrophage Polarization toward an M2 Phenotype. J. Pharmacopunct. 2019, 22, 253–259. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Claesson-Welsh, L.; Welsh, M. VEGFA and tumour angiogenesis. J. Intern. Med. 2013, 273, 114–127. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jiang, B.H.; Liu, L.Z. PI3K/PTEN signaling in angiogenesis and tumorigenesis. Adv. Cancer Res. 2009, 102, 19–65. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Eliceiri, B.P.; Paul, R.; Schwartzberg, P.L.; Hood, J.D.; Leng, J.; Cheresh, D.A. Selective requirement for Src kinases during VEGF-induced angiogenesis and vascular permeability. Mol. Cell 1999, 4, 915–924. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Luo, W.; Slebos, R.J.; Hill, S.; Li, M.; Brábek, J.; Amanchy, R.; Chaerkady, R.; Pandey, A.; Ham, A.J.; Hanks, S.K. Global impact of oncogenic Src on a phosphotyrosine proteome. J. Proteome Res. 2008, 7, 3447–3460. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Roussos, E.T.; Condeelis, J.S.; Patsialou, A. Chemotaxis in cancer. Nat. Rev. Cancer 2011, 11, 573–587. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peyri, N.; Berard, M.; Fauvel-Lafeve, F.; Trochon, V.; Arbeille, B.; Lu, H.; Legrand, C.; Crepin, M. Breast tumor cells transendothelial migration induces endothelial cell anoikis through extracellular matrix degradation. Anticancer Res. 2009, 29, 2347–2355. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Ou, J.; Guan, D.; Yang, Y. Non-contact co-culture with human vascular endothelial cells promotes epithelial-to-mesenchymal transition of cervical cancer SiHa cells by activating the NOTCH1/LOX/SNAIL pathway. Cell. Mol. Biol. Lett. 2019, 24, 39. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Morgillo, F.; Della Corte, C.M.; Fasano, M.; Ciardiello, F. Mechanisms of resistance to EGFR-targeted drugs: Lung cancer. ESMO Open 2016, 1, e000060. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nakano, N.; Morishita, R.; Moriguchi, A.; Nakamura, Y.; Hayashi, S.I.; Aoki, M.; Kida, I.; Matsumoto, K.; Nakamura, T.; Higaki, J.; et al. Negative regulation of local hepatocyte growth factor expression by angiotensin II and transforming growth factor-beta in blood vessels: Potential role of HGF in cardiovascular disease. Hypertension 1998, 32, 444–451. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yuan, L.; Mao, Y.; Luo, W.; Wu, W.; Xu, H.; Wang, X.L.; Shen, Y.H. Palmitic acid dysregulates the Hippo-YAP pathway and inhibits angiogenesis by inducing mitochondrial damage and activating the cytosolic DNA sensor cGAS-STING-IRF3 signaling mechanism. J. Biol. Chem. 2017, 292, 15002–15015. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bito, T.; Koseki, K.; Asano, R.; Ueda, N.; Yamada, T.; Yabuta, Y.; Ichiyanagi, T.; Ishihara, A.; Watanabe, K.; Watanabe, F. 5-hydroxymethyl-2-furaldehyde purified from Japanese pear (Pyrus pyrifolia Nakai cv. Nijisseiki) juice concentrate inhibits melanogenesis in B16 mouse melanoma cells. Biosci. Biotechnol. Biochem. 2020, 84, 2374–2384. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chellian, R.; Pandy, V.; Mohamed, Z. Pharmacology and toxicology of α- and β-Asarone: A review of preclinical evidence. Phytomedicine 2017, 32, 41–58. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khajeh, S.; Ganjavi, M.; Panahi, G.; Zare, M.; Zare, M.; Tahami, S.M.; Razban, V. D-allose: Molecular Pathways and Therapeutic Capacity in Cancer. Curr. Mol. Pharmacol. 2023, 16, 801–810. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abraham, A.; Kattoor, A.J.; Saldeen, T.; Mehta, J.L. Vitamin E and its anticancer effects. Crit. Rev. Food Sci. Nutr. 2019, 59, 2831–2838. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Z.; Han, Z.; Tao, J.; Wang, J.; Liu, X.; Zhou, W.; Xu, Z.; Zhao, C.; Wang, Z.; Tan, R.; et al. Role of endothelial-to-mesenchymal transition induced by TGF-β1 in transplant kidney interstitial fibrosis. J. Cell. Mol. Med. 2017, 21, 2359–2369. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gao, B.; Saba, T.M.; Tsan, M.F. Role of alpha(v)beta(3)-integrin in TNF-alpha-induced endothelial cell migration. Am. J. Physiol.-Cell Physiol. 2002, 283, C1196–C1205. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Adjuto-Saccone, M.; Soubeyran, P.; Garcia, J.; Audebert, S.; Camoin, L.; Rubis, M.; Roques, J.; Binétruy, B.; Iovanna, J.L.; Tournaire, R. TNF-α induces endothelial-mesenchymal transition promoting stromal development of pancreatic adenocarcinoma. Cell Death Dis. 2021, 12, 649. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mehta, V.B.; Besner, G.E. HB-EGF promotes angiogenesis in endothelial cells via PI3-kinase and MAPK signaling pathways. Growth Factors 2007, 25, 253–263. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yano, S.; Yamada, T.; Takeuchi, S.; Tachibana, K.; Minami, Y.; Yatabe, Y.; Mitsudomi, T.; Tanaka, H.; Kimura, T.; Kudoh, S.; et al. Hepatocyte growth factor expression in EGFR mutant lung cancer with intrinsic and acquired resistance to tyrosine kinase inhibitors in a Japanese cohort. J. Thorac. Oncol. 2011, 6, 2011–2017. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Umeguchi, H.; Sueoka-Aragane, N.; Kobayashi, N.; Nakamura, T.; Sato, A.; Takeda, Y.; Hayashi, S.; Sueoka, E.; Kimura, S. Usefulness of plasma HGF level for monitoring acquired resistance to EGFR tyrosine kinase inhibitors in non-small cell lung cancer. Oncol. Rep. 2015, 33, 391–396. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Raghav, K.P.; Gonzalez-Angulo, A.M.; Blumenschein, G.R., Jr. Role of HGF/MET axis in resistance of lung cancer to contemporary management. Transl. Lung Cancer Res. 2012, 1, 179–193. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Das, S.K.; Deka, S.J.; Paul, D.; Gupta, D.D.; Das, T.J.; Maravi, D.K.; Tag, H.; Hui, P.K. In-silico based identification of phytochemicals from Houttuynia cordata Thunb. as potential inhibitors for overexpressed HER2 and VEGFR2 cancer genes. J. Biomol. Struct. Dyn. 2022, 40, 6857–6867. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qian, K.; Zheng, X.X.; Wang, C.; Huang, W.G.; Liu, X.B.; Xu, S.D.; Liu, D.K.; Liu, M.Y.; Lin, C.S. β-Sitosterol Inhibits Rheumatoid Synovial Angiogenesis Through Suppressing VEGF Signaling Pathway. Front. Pharmacol. 2022, 12, 816477. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kangsamaksin, T.; Chaithongyot, S.; Wootthichairangsan, C.; Hanchaina, R.; Tangshewinsirikul, C.; Svasti, J. Lupeol and stigmasterol suppress tumor angiogenesis and inhibit cholangiocarcinoma growth in mice via downregulation of tumor necrosis factor-α. PLoS ONE 2017, 12, e0189628. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Min, T.R.; Park, H.J.; Ha, K.T.; Chi, G.Y.; Choi, Y.H.; Park, S.H. Suppression of EGFR/STAT3 activity by lupeol contributes to the induction of the apoptosis of human non small cell lung cancer cells. Int. J. Oncol. 2019, 55, 320–330. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]







| Compound | Binding Residues in Kinase Domain | Binding ΔG |
|---|---|---|
| Lupeol | ALA866, VAL848, LEU840, LEU1035 | −8.5 |
| β-sitosterol | ALA866, VAL848, LEU840, LEU1035, CYS1045 | −7.9 |
| Sorafenib | ALA866, VAL848, LEU840, LEU1035, LYS868, ASP1046, CYS919, PHE1047 | −8.0 |
| Sunitinib | ALA866, VAL848, LEU840, ALA881, GLU885, LEU882, LYS868, GLY846, PHE918 | −7.2 |
| Gene | Sequence (5′→3′) | AT 1 (°C) |
|---|---|---|
| TGF-β | F: CCT GTC TGC ACT ATT CCT TT R: TTA TCA GAG TCC CTG CAT CT | 55 |
| TNF-α | F: CAC CAC GCT CTT CTG TCT ACT G R: GGG CTA CAG GCT TGT CAC TC | 58 |
| EGF | F: AAG AAT GGG GGT CAA CCA GT R: TGA AGT TGG TTG CAT TGA CC | 50 |
| HGF | F: GGG CTG AAA AGA TTG GAT CA R: TTG TAT TGG TGG GTG CTT CA | 55 |
| CCL2 | F: CCC CAG TCA CCT GCT GTT AT R: TGG AAT CCT GAA CCC ACT TC | 55 |
| CXCL1 | F: GAA AGC TTG CCT CAA TCC TG R: CAT TAG GCA CAA TCC AGG TG | 55 |
| CXCL12 | F: ATG AAC GCC AAG GTC GTG R: CTT CGG GTC AAT GCA CAC TT | 55 |
| ACTB (β-actin) | F: GTC TCC TCT GAC TTC AAC AGC G R: ACC ACC CTG TTG CTG TAG CCA A | 55 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Park, H.-J.; Jeong, J.-H.; Choi, Y.-H.; Park, S.-H. Hexane Fraction of Adenophora triphylla var. japonica Root Extract Inhibits Angiogenesis and Endothelial Cell-Induced Erlotinib Resistance in Lung Cancer Cells. Molecules 2024, 29, 597. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules29030597
Park H-J, Jeong J-H, Choi Y-H, Park S-H. Hexane Fraction of Adenophora triphylla var. japonica Root Extract Inhibits Angiogenesis and Endothelial Cell-Induced Erlotinib Resistance in Lung Cancer Cells. Molecules. 2024; 29(3):597. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules29030597
Chicago/Turabian StylePark, Hyun-Ji, Jae-Hoon Jeong, Yung-Hyun Choi, and Shin-Hyung Park. 2024. "Hexane Fraction of Adenophora triphylla var. japonica Root Extract Inhibits Angiogenesis and Endothelial Cell-Induced Erlotinib Resistance in Lung Cancer Cells" Molecules 29, no. 3: 597. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules29030597
APA StylePark, H. -J., Jeong, J. -H., Choi, Y. -H., & Park, S. -H. (2024). Hexane Fraction of Adenophora triphylla var. japonica Root Extract Inhibits Angiogenesis and Endothelial Cell-Induced Erlotinib Resistance in Lung Cancer Cells. Molecules, 29(3), 597. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules29030597