Involvement of Bile Acid Metabolism and Gut Microbiota in the Amelioration of Experimental Metabolism-Associated Fatty Liver Disease by Nobiletin
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Results
2.1. NOB Treatment Attenuated HFD-Induced Weight Gain and Insulin Resistance (IR) in Mice
2.2. NOB Treatment Attenuates Lipid Levels in MAFLD Mice
2.3. NOB Treatment Improves Liver Biochemical Indices and Inflammatory Factor Levels in MAFLD Mice
2.4. Effect of NOB Treatment on Histopathology of Liver and Ileum in MAFLD Mice
2.5. NOB Regulates BA Composition in the Feces of MAFLD Mice
2.6. NOB Alters the Composition of Gut Microbes in MAFLD Mice
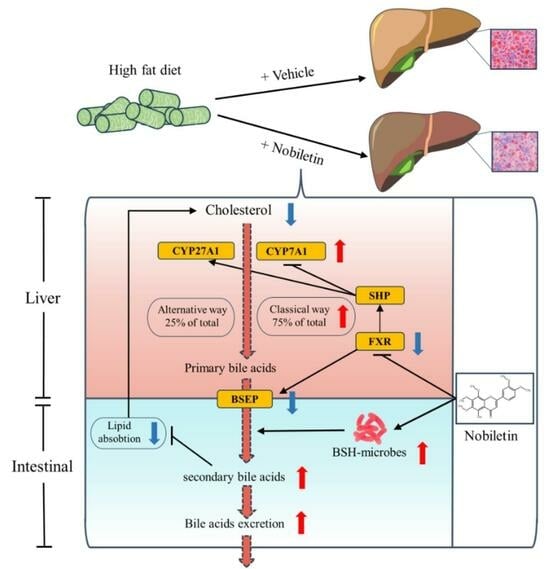
2.7. NOB Reduces Liver Lipid Deposition by Regulating the Key Genes in BA Metabolism
3. Discussion
4. Materials and Methods
4.1. Reagents and Chemicals
4.2. Animal Experimentation
4.3. Biochemical Analysis and Histological Analysis
4.4. Metabolomics Analysis of BA
4.5. Feces Microbiota 16S rRNA Analysis
4.6. mRNA Expression Analysis
4.7. Western Blot
4.8. Statistical Analysis
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Eslam, M.; Sanyal, A.J.; George, J. MAFLD: A Consensus-Driven Proposed Nomenclature for Metabolic Associated Fatty Liver Disease. Gastroenterology 2020, 158, 1999–2014.e1. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bae, S.; George, J.; Qiao, L. From MAFLD to Hepatocellular Carcinoma and Everything in Between. Chin. Med. J. 2022, 135, 547–556. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barchetta, I.; Cimini, F.A.; Cavallo, M.G. Vitamin D and Metabolic Dysfunction-Associated Fatty Liver Disease (MAFLD): An Update. Nutrients 2020, 12, 3302. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nagata, N.; Xu, L.; Kohno, S.; Ushida, Y.; Aoki, Y.; Umeda, R.; Fuke, N.; Zhuge, F.; Ni, Y.; Nagashimada, M.; et al. Glucoraphanin Ameliorates Obesity and Insulin Resistance Through Adipose Tissue Browning and Reduction of Metabolic Endotoxemia in Mice. Diabetes 2017, 66, 1222–1236. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rooks, M.G.; Garrett, W.S. Gut Microbiota, Metabolites and Host Immunity. Nat. Rev. Immunol. 2016, 16, 341–352. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mohr, A.E.; Jager, R.; Carpenter, K.C.; Kerksick, C.M.; Purpura, M.; Townsend, J.R.; West, N.P.; Black, K.; Gleeson, M.; Pyne, D.B.; et al. The Athletic Gut Microbiota. J. Int. Soc. Sports Nutr. 2020, 17, 24. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Khanmohammadi, S.; Kuchay, M.S. Toll-like Receptors and Metabolic (Dysfunction)-Associated Fatty Liver Disease. Pharmacol. Res. 2022, 185, 106507. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Singh, P.; Lembo, A. Emerging Role of the Gut Microbiome in Irritable Bowel Syndrome. Gastroenterol. Clin. N. Am. 2021, 50, 523–545. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ma, S.; Pang, X.; Tian, S.; Sun, J.; Hu, Q.; Li, X.; Lu, Y. The Protective Effects of Sulforaphane on High-Fat Diet-Induced Metabolic Associated Fatty Liver Disease in Mice via Mediating the FXR/LXRalpha Pathway. Food Funct. 2022, 13, 12966–12982. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gottlieb, A.; Canbay, A. Why Bile Acids Are So Important in Non-Alcoholic Fatty Liver Disease (NAFLD) Progression. Cells 2019, 8, 1358. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Huang, F.; Zheng, X.; Ma, X.; Jiang, R.; Zhou, W.; Zhou, S.; Zhang, Y.; Lei, S.; Wang, S.; Kuang, J.; et al. Theabrownin from Pu-Erh Tea Attenuates Hypercholesterolemia via Modulation of Gut Microbiota and Bile Acid Metabolism. Nat. Commun. 2019, 10, 4971. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xiang, J.; Zhang, Z.; Xie, H.; Zhang, C.; Bai, Y.; Cao, H.; Che, Q.; Guo, J.; Su, Z. Effect of Different Bile Acids on the Intestine through Enterohepatic Circulation Based on FXR. Gut Microbes 2021, 13, 1949095. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yoshimoto, S.; Loo, T.M.; Atarashi, K.; Kanda, H.; Sato, S.; Oyadomari, S.; Iwakura, Y.; Oshima, K.; Morita, H.; Hattori, M.; et al. Obesity-Induced Gut Microbial Metabolite Promotes Liver Cancer through Senescence Secretome. Nature 2013, 499, 97–101. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Clifford, B.L.; Sedgeman, L.R.; Williams, K.J.; Morand, P.; Cheng, A.; Jarrett, K.E.; Chan, A.P.; Brearley-Sholto, M.C.; Wahlstrom, A.; Ashby, J.W.; et al. FXR Activation Protects against NAFLD via Bile-Acid-Dependent Reductions in Lipid Absorption. Cell Metab. 2021, 33, 1671–1684.e4. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chavez-Talavera, O.; Tailleux, A.; Lefebvre, P.; Staels, B. Bile Acid Control of Metabolism and Inflammation in Obesity, Type 2 Diabetes, Dyslipidemia, and Nonalcoholic Fatty Liver Disease. Gastroenterology 2017, 152, 1679–1694.e3. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sun, L.; Pang, Y.; Wang, X.; Wu, Q.; Liu, H.; Liu, B.; Liu, G.; Ye, M.; Kong, W.; Jiang, C. Ablation of Gut Microbiota Alleviates Obesity-Induced Hepatic Steatosis and Glucose Intolerance by Modulating Bile Acid Metabolism in Hamsters. Acta Pharm. Sin. B 2019, 9, 702–710. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y.; Jiang, R.; Zheng, X.; Lei, S.; Huang, F.; Xie, G.; Kwee, S.; Yu, H.; Farrar, C.; Sun, B.; et al. Ursodeoxycholic Acid Accelerates Bile Acid Enterohepatic Circulation. Br. J. Pharmacol. 2019, 176, 2848–2863. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wei, J.; Chen, J.; Fu, L.; Han, L.; Gao, X.; Sarhene, M.; Hu, L.; Zhang, Y.; Fan, G. Polygonum Multiflorum Thunb Suppress Bile Acid Synthesis by Activating Fxr-Fgf15 Signaling in the Intestine. J. Ethnopharmacol. 2019, 235, 472–480. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qin, C.; Yuan, Q.; Zhang, S.; He, C.; Wei, X.; Liu, M.; Jiang, N.; Huang, L.; Zhuang, L.; Wang, P. Biomimetic in Vitro Respiratory System Using Smooth Muscle Cells on ECIS Chips for Anti-Asthma TCMs Screening. Anal. Chim. Acta 2021, 1162, 338452. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wen, X.; Zhao, H.; Wang, L.; Wang, L.; Du, G.; Guan, W.; Liu, J.; Cao, X.; Jiang, X.; Tian, J.; et al. Nobiletin Attenuates DSS-Induced Intestinal Barrier Damage through the HNF4alpha-Claudin-7 Signaling Pathway. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2020, 68, 4641–4649. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kim, E.; Nohara, K.; Wirianto, M.; Escobedo, G.J.; Lim, J.Y.; Morales, R.; Yoo, S.H.; Chen, Z. Effects of the Clock Modulator Nobiletin on Circadian Rhythms and Pathophysiology in Female Mice of an Alzheimer’s Disease Model. Biomolecules 2021, 11, 1004. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, S.Z.; Zhang, N.N.; Yang, X.; Huang, T.Q.; Lin, Y.; Jiang, Z.M.; Yi, Y.; Liu, E.H. Nobiletin Ameliorates Nonalcoholic Fatty Liver Disease by Regulating Gut Microbiota and Myristoleic Acid Metabolism. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2023, 71, 7312–7323. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bunbupha, S.; Pakdeechote, P.; Maneesai, P.; Prasarttong, P. Nobiletin Alleviates High-Fat Diet-Induced Nonalcoholic Fatty Liver Disease by Modulating AdipoR1 and Gp91(Phox) Expression in Rats. J. Nutr. Biochem. 2021, 87, 108526. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fan, C.; Ling-Hu, A.; Sun, D.; Gao, W.; Zhang, C.; Duan, X.; Li, H.; Tian, W.; Yu, Q.; Ke, Z. Nobiletin Ameliorates Hepatic Lipid Deposition, Oxidative Stress, and Inflammation by Mechanisms That Involve the Nrf2/NF-kappaB Axis in Nonalcoholic Fatty Liver Disease. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2023, 71, 20105–20117. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Morrow, N.M.; Burke, A.C.; Samsoondar, J.P.; Seigel, K.E.; Wang, A.; Telford, D.E.; Sutherland, B.G.; O’Dwyer, C.; Steinberg, G.R.; Fullerton, M.D.; et al. The Citrus Flavonoid Nobiletin Confers Protection from Metabolic Dysregulation in High-Fat-Fed Mice Independent of AMPK. J. Lipid Res. 2020, 61, 387–402. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jia, W.; Wei, M.; Rajani, C.; Zheng, X. Targeting the Alternative Bile Acid Synthetic Pathway for Metabolic Diseases. Protein Cell 2021, 12, 411–425. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rice, T.A.; Bielecka, A.A.; Nguyen, M.T.; Rosen, C.E.; Song, D.; Sonnert, N.D.; Yang, Y.; Cao, Y.; Khetrapal, V.; Catanzaro, J.R.; et al. Interspecies Commensal Interactions Have Nonlinear Impacts on Host Immunity. Cell Host Microbe 2022, 30, 988–1002.e6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- van Muijlwijk, G.H.; van Mierlo, G.; Jansen, P.; Vermeulen, M.; Bleumink-Pluym, N.; Palm, N.W.; van Putten, J.; de Zoete, M.R. Identification of Allobaculum Mucolyticum as a Novel Human Intestinal Mucin Degrader. Gut Microbes 2021, 13, 1966278. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Han, Y.; Li, L.; Wang, B. Role of Akkermansia Muciniphila in the Development of Nonalcoholic Fatty Liver Disease: Current Knowledge and Perspectives. Front. Med. 2022, 16, 667–685. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fei, N.; Bruneau, A.; Zhang, X.; Wang, R.; Wang, J.; Rabot, S.; Gerard, P.; Zhao, L. Endotoxin Producers Overgrowing in Human Gut Microbiota as the Causative Agents for Nonalcoholic Fatty Liver Disease. mBio 2020, 11, e03263-19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lei, Y.; Tang, L.; Chen, Q.; Wu, L.; He, W.; Tu, D.; Wang, S.; Chen, Y.; Liu, S.; Xie, Z.; et al. Disulfiram Ameliorates Nonalcoholic Steatohepatitis by Modulating the Gut Microbiota and Bile Acid Metabolism. Nat. Commun. 2022, 13, 6862. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tang, B.; Tang, L.; Li, S.; Liu, S.; He, J.; Li, P.; Wang, S.; Yang, M.; Zhang, L.; Lei, Y.; et al. Gut Microbiota Alters Host Bile Acid Metabolism to Contribute to Intrahepatic Cholestasis of Pregnancy. Nat. Commun. 2023, 14, 1305. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yang, Y.N.; Wang, Q.C.; Xu, W.; Yu, J.; Zhang, H.; Wu, C. The Berberine-Enriched Gut Commensal Blautia Producta Ameliorates High-Fat Diet (HFD)-Induced Hyperlipidemia and Stimulates Liver LDLR Expression. Biomed. Pharmacother. 2022, 155, 113749. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Song, Z.; Cai, Y.; Lao, X.; Wang, X.; Lin, X.; Cui, Y.; Kalavagunta, P.K.; Liao, J.; Jin, L.; Shang, J.; et al. Taxonomic Profiling and Populational Patterns of Bacterial Bile Salt Hydrolase (BSH) Genes Based on Worldwide Human Gut Microbiome. Microbiome 2019, 7, 9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, P.; Zheng, L.; Duan, Y.; Gao, Y.; Gao, H.; Mao, D.; Luo, Y. Gut Microbiota Exaggerates Triclosan-Induced Liver Injury via Gut-Liver Axis. J. Hazard. Mater. 2022, 421, 126707. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, G.D.; Pan, A.; Zhang, X.; Cai, Y.Y.; Wang, Q.; Huang, F.Q.; Alolga, R.N.; Li, J.; Qi, L.W.; Liu, Q. Cordyceps Improves Obesity and Its Related Inflammation via Modulation of Enterococcus Cecorum Abundance and Bile Acid Metabolism. Am. J. Chin. Med. 2022, 50, 817–838. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ridlon, J.M.; Harris, S.C.; Bhowmik, S.; Kang, D.J.; Hylemon, P.B. Consequences of Bile Salt Biotransformations by Intestinal Bacteria. Gut Microbes 2016, 7, 22–39. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, L.; Cai, J.; Gonzalez, F.J. The Role of Farnesoid X Receptor in Metabolic Diseases, and Gastrointestinal and Liver Cancer. Nat. Rev. Gastroenterol. Hepatol. 2021, 18, 335–347. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, M.-F.; Xi, Q.-H.; Sheng, Y.; Wang, Y.-M.; Wang, W.-Y.; Chi, C.-F.; Wang, B. Antioxidant Peptides from Monkfish Swim Bladders: Ameliorating NAFLD In Vitro by Suppressing Lipid Accumulation and Oxidative Stress via Regulating AMPK/Nrf2 Pathway. Mar. Drugs 2023, 21, 360. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aron-Wisnewsky, J.; Gaborit, B.; Dutour, A.; Clement, K. Gut Microbiota and Non-Alcoholic Fatty Liver Disease: New Insights. Clin. Microbiol. Infect. 2013, 19, 338–348. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kuchay, M.S.; Choudhary, N.S.; Mishra, S.K. Pathophysiological Mechanisms Underlying MAFLD. Diabetes Metab. Syndr. 2020, 14, 1875–1887. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Roychowdhury, S.; Selvakumar, P.C.; Cresci, G. The Role of the Gut Microbiome in Nonalcoholic Fatty Liver Disease. Med. Sci. 2018, 6, 47. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wieland, A.; Frank, D.N.; Harnke, B.; Bambha, K. Systematic Review: Microbial Dysbiosis and Nonalcoholic Fatty Liver Disease. Aliment. Pharmacol. Ther. 2015, 42, 1051–1063. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bisanz, J.E.; Upadhyay, V.; Turnbaugh, J.A.; Ly, K.; Turnbaugh, P.J. Meta-Analysis Reveals Reproducible Gut Microbiome Alterations in Response to a High-Fat Diet. Cell Host Microbe 2019, 26, 265–272.e4. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, Q.; Li, Y.; Dai, X.; Wang, B.; Zhang, J.; Cao, H. Polysaccharides: The Potential Prebiotics for Metabolic Associated Fatty Liver Disease (MAFLD). Nutrients 2023, 15, 3722. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mazidi, M.; Katsiki, N.; Banach, M. A Higher Flavonoid Intake Is Associated with Less Likelihood of Nonalcoholic Fatty Liver Disease: Results from a Multiethnic Study. J. Nutr. Biochem. 2019, 65, 66–71. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tan, P.; Jin, L.; Qin, X.; He, B. Natural Flavonoids: Potential Therapeutic Strategies for Non-Alcoholic Fatty Liver Disease. Front. Pharmacol. 2022, 13, 1005312. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zeng, S.L.; Li, S.Z.; Xiao, P.T.; Cai, Y.Y.; Chu, C.; Chen, B.Z.; Li, P.; Li, J.; Liu, E.H. Citrus Polymethoxyflavones Attenuate Metabolic Syndrome by Regulating Gut Microbiome and Amino Acid Metabolism. Sci. Adv. 2020, 6, eaax6208. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, X.; Deng, Y.; Tu, Y.; Feng, D.; Liao, W. Nobiletin Mitigates NAFLD via Lipophagy and Inflammation. Food Funct. 2022, 13, 10186–10199. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, S.; Li, X.; Chen, F.; Liu, M.; Ning, L.; Yan, Y.; Zhang, S.; Huang, S.; Tu, C. Nobiletin Mitigates Hepatocytes Death, Liver Inflammation, and Fibrosis in a Murine Model of NASH through Modulating Hepatic Oxidative Stress and Mitochondrial Dysfunction. J. Nutr. Biochem. 2022, 100, 108888. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Geng, W.; Lin, J. Bacterial Bile Salt Hydrolase: An Intestinal Microbiome Target for Enhanced Animal Health. Anim. Health Res. Rev. 2016, 17, 148–158. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Choi, S.B.; Lew, L.C.; Yeo, S.K.; Nair, P.S.; Liong, M.T. Probiotics and the BSH-Related Cholesterol Lowering Mechanism: A Jekyll and Hyde Scenario. Crit. Rev. Biotechnol. 2015, 35, 392–401. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ferrebee, C.B.; Dawson, P.A. Metabolic Effects of Intestinal Absorption and Enterohepatic Cycling of Bile Acids. Acta Pharm. Sin. B 2015, 5, 129–134. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shi, Z.; Chen, G.; Cao, Z.; Wu, F.; Lei, H.; Chen, C.; Song, Y.; Liu, C.; Li, J.; Zhou, J.; et al. Gut Microbiota and Its Metabolite Deoxycholic Acid Contribute to Sucralose Consumption-Induced Nonalcoholic Fatty Liver Disease. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2021, 69, 3982–3991. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rao, A.; Kosters, A.; Mells, J.E.; Zhang, W.; Setchell, K.D.; Amanso, A.M.; Wynn, G.M.; Xu, T.; Keller, B.T.; Yin, H.; et al. Inhibition of Ileal Bile Acid Uptake Protects against Nonalcoholic Fatty Liver Disease in High-Fat Diet-Fed Mice. Sci. Transl. Med. 2016, 8, 357ra122. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, D.Q.; Tazuma, S.; Cohen, D.E.; Carey, M.C. Feeding Natural Hydrophilic Bile Acids Inhibits Intestinal Cholesterol Absorption: Studies in the Gallstone-Susceptible Mouse. Am. J. Physiol. Gastrointest. Liver Physiol. 2003, 285, G494–G502. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wahlstrom, A.; Sayin, S.I.; Marschall, H.U.; Backhed, F. Intestinal Crosstalk between Bile Acids and Microbiota and Its Impact on Host Metabolism. Cell Metab. 2016, 24, 41–50. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yang, Y.; Wu, C. Targeting Gut Microbial Bile Salt Hydrolase (BSH) by Diet Supplements: New Insights into Dietary Modulation of Human Health. Food Funct. 2022, 13, 7409–7422. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, Y.; Chen, K.; Li, F.; Gu, Z.; Liu, Q.; He, L.; Shao, T.; Song, Q.; Zhu, F.; Zhang, L.; et al. Probiotic Lactobacillus Rhamnosus GG Prevents Liver Fibrosis Through Inhibiting Hepatic Bile Acid Synthesis and Enhancing Bile Acid Excretion in Mice. Hepatology 2020, 71, 2050–2066. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gonzalez, F.J.; Jiang, C.; Patterson, A.D. An Intestinal Microbiota-Farnesoid X Receptor Axis Modulates Metabolic Disease. Gastroenterology 2016, 151, 845–859. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kong, B.; Wang, L.; Chiang, J.Y.; Zhang, Y.; Klaassen, C.D.; Guo, G.L. Mechanism of Tissue-Specific Farnesoid X Receptor in Suppressing the Expression of Genes in Bile-Acid Synthesis in Mice. Hepatology 2012, 56, 1034–1043. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhu, R.G.; Sun, Y.D.; Hou, Y.T.; Fan, J.G.; Chen, G.; Li, T.P. Pectin Penta-Oligogalacturonide Reduces Cholesterol Accumulation by Promoting Bile Acid Biosynthesis and Excretion in High-Cholesterol-Fed Mice. Chem. Biol. Interact. 2017, 272, 153–159. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, W.; Zhao, J.; Gui, W.; Sun, D.; Dai, H.; Xiao, L.; Chu, H.; Du, F.; Zhu, Q.; Schnabl, B.; et al. Tauroursodeoxycholic Acid Inhibits Intestinal Inflammation and Barrier Disruption in Mice with Non-Alcoholic Fatty Liver Disease. Br. J. Pharmacol. 2018, 175, 469–484. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, D.; Dun, Y.; Qi, D.; Ripley-Gonzalez, J.W.; Dong, J.; Zhou, N.; Qiu, L.; Zhang, J.; Zeng, T.; You, B.; et al. Intermittent Fasting Activates Macrophage Migration Inhibitory Factor and Alleviates High-Fat Diet-Induced Nonalcoholic Fatty Liver Disease. Sci. Rep. 2023, 13, 13068. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]









| Gene | Sequence 5′ → 3′ (Forward) | Sequence 3′ → 5′ (Forward) |
|---|---|---|
| CYP7A1 | GTGATGTTTGAAGCCGGATATC | TTTATGTGCGGTCTTGAACAAG |
| CYP27A1 | GACCATCGGCACCTTTCCTGAG | GGCACCACACCAGTCACTTCC1 |
| FXR | GCAACCAGTCATGTACAGATTC | TTATTGAAAATCTCCGCCGAAC |
| SHP | GTCCGACTATTCTGTATGCACT | CTACTGTCTTGGCTAGGACATC |
| BSEP | GTGTCTACTTCATGCTTGTGAC | GAGACTTAGATCGTTGACGGAT |
| β-actin | CTACCTCATGAAGATCCTGACC | CACAGCTTCTCTTTGATGTCAC |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Xu, H.; Yuan, M.; Niu, K.; Yang, W.; Jiang, M.; Zhang, L.; Zhou, J. Involvement of Bile Acid Metabolism and Gut Microbiota in the Amelioration of Experimental Metabolism-Associated Fatty Liver Disease by Nobiletin. Molecules 2024, 29, 976. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules29050976
Xu H, Yuan M, Niu K, Yang W, Jiang M, Zhang L, Zhou J. Involvement of Bile Acid Metabolism and Gut Microbiota in the Amelioration of Experimental Metabolism-Associated Fatty Liver Disease by Nobiletin. Molecules. 2024; 29(5):976. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules29050976
Chicago/Turabian StyleXu, Hongling, Mingming Yuan, Kailin Niu, Wei Yang, Maoyuan Jiang, Lei Zhang, and Jing Zhou. 2024. "Involvement of Bile Acid Metabolism and Gut Microbiota in the Amelioration of Experimental Metabolism-Associated Fatty Liver Disease by Nobiletin" Molecules 29, no. 5: 976. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules29050976
APA StyleXu, H., Yuan, M., Niu, K., Yang, W., Jiang, M., Zhang, L., & Zhou, J. (2024). Involvement of Bile Acid Metabolism and Gut Microbiota in the Amelioration of Experimental Metabolism-Associated Fatty Liver Disease by Nobiletin. Molecules, 29(5), 976. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules29050976