Lycocasine A, a Lycopodium Alkaloid from Lycopodiastrum casuarinoides and Its Acid-Sensing Ion Channel 1a Inhibitory Activity
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Results and Discussion
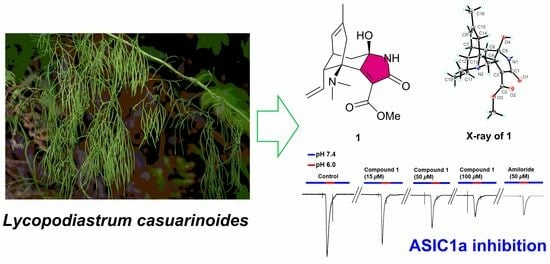
2.1. Structure Elucidation
2.2. ASIC1a Inhibitory Activity
2.3. Molecular Docking
3. Materials and Methods
3.1. General Experimental Procedures
3.2. Plant Material
3.3. Extraction and Isolation
Lycocasine A (1)
3.4. Crystallographic Data of Lycocasine A (1)
3.5. Cell Transfection and Electrophysiological Recordings
3.6. Molecular Docking
4. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Smith, M.H.; Berman, J.R. What is rheumatoid arthritis? JAMA 2022, 327, 1194. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, Y.; Chen, F. Acid-sensing ion channel-1a in articular chondrocytes and synovial fibroblasts: A novel therapeutic target for rheumatoid arthritis. Front. Immunol. 2021, 11, 580936. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhou, R.-P.; Liang, H.-Y.; Hu, W.-R.; Ding, J.; Li, S.-F.; Chen, Y.; Zhao, Y.-J.; Lu, C.; Chen, F.-H.; Hu, W. Modulators of ASIC1a and its potential as a therapeutic target for age-related diseases. Ageing Res. Rev. 2023, 83, 101785. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baron, A.; Lingueglia, E. Pharmacology of acid-sensing ion channels—Physiological and therapeutical perspectives. Neuropharmacology 2015, 94, 19–35. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mankia, K.; Emery, P. Palindromic rheumatism as part of the rheumatoid arthritis continuum. Nat. Rev. Rheumatol. 2019, 15, 687–695. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, G.-P.; Dai, S.; Chen, R.-S. A Dictionary of the Traditional Chinese Medicine, 2nd ed.; Shanghai Scientific & Technical Publishers: Shanghai, China, 2006; pp. 1–3874. [Google Scholar]
- Liu, Y.; Wang, Q.; Xie, Z.; Zheng, D.-K.; Li, J.; Tan, G.-S. Lycopodiastrum casuarinoides: An overview of their phytochemicals, biological activities, structure-activity relationship, biosynthetic pathway and 13C NMR data. Fitoterapia 2023, 165, 105425. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xiong, J.; Meng, W.-J.; Zhang, H.-Y.; Zou, Y.; Wang, W.-X.; Wang, X.-Y.; Yang, Q.-L.; Osman, E.E.A.; Hu, J.-F. Lycofargesiines A–F, further Lycopodium alkaloids from the club moss Huperzia fargesii. Phytochemistry 2019, 162, 183–192. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Thamnarak, W.; Thaisaeng, W.; Batsomboon, P.; Eurtivong, C.; Wannarit, N.; Ruchirawat, S.; Thasana, N. Phlegcarines A–C, three Lycopodium alkaloids from Phlegmariurus carinatus (Desv. ex Poir.) Ching. Phytochemistry 2023, 206, 113553. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Eric, S.; Harald, S.; Alan, R.S.; Hovenkamp, P.; Prado, J.; Rouhan, G.; Salino, A.; Sundue, M.; Almeida, T.E.; Parris, B.; et al. A community-derived classification for extant lycophytes and ferns. J. Syst. Evol. 2016, 54, 563–603. [Google Scholar]
- Tang, Y.; Xiong, J.; Zhang, J.-J.; Wang, W.; Zhang, H.-Y.; Hu, J.-F. Annotinolides A–C, three lycopodane-derived 8,5-lactones with polycyclic skeletons from Lycopodium annotinum. Org. Lett. 2016, 18, 4376–4379. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, X.-J.; Liu, Y.-B.; Li, L.; Yu, S.-S.; Lv, H.-N.; Ma, S.-G.; Bao, X.-Q.; Zhang, D.; Qu, J.; Li, Y. Lycojaponicumins D and E: Two new alkaloids from Lycopodium japonicum. Org. Lett. 2012, 14, 5688–5691. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xia, D.; Wang, Z.-H.; Jiang, J.-M.; Yang, X.-W.; Gao, Y.; Xu, Y.-Y.; Chang, L.-Y.; Zhu, D.; Zhao, B.-J.; Zhu, X.-L.; et al. Lycojapomines A–E: Lycopodium alkaloids with anti-renal fibrosis potential from Lycopodium japonicum. Org. Lett. 2022, 24, 4684–4688. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hirasawa, Y.; Mitsui, C.; Uchiyama, N.; Hakamatsuka, T.; Morita, H. Hupercumines A and B, Lycopodium alkaloids from Huperzia cunninghamioides, inhibiting acetylcholinesterase. Org. Lett. 2018, 20, 1384–1387. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, L.-L.; Zhou, Z.-B.; Zhu, X.-L.; Yuan, F.-Y.; Miyamoto, T.; Pan, K. Lycocasuarines A–C, Lycopodium alkaloids from Lycopodiastrum casuarinoides. Tetrahedron Lett. 2017, 58, 4827–4831. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, L.-L.; Hao, L.-J.; Zhou, Z.-B.; Zhu, X.-L.; Shi, Z.-H.; Miyamoto, T.; Pan, K. Lycodine-type alkaloids and their glycosides from Lycopodiastrum casuarinoides. Phytochemistry 2018, 154, 63–72. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, D.-B.; Chen, J.-J.; Song, Q.-Y.; Zhang, L.; Gao, K. Lycodine-type alkaloids from Lycopodiastrum casuarinoides and their acetylcholinesterase inhibitory activity. Molecules 2014, 19, 9999–10010. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, H.-B.; Hu, J.; Li, J.-X.; Hao, S.-H. Cytotoxic lycodine alkaloids from the aerial parts of Lycopodiastrum casuarinoides. J. Asian Nat. Prod. Res. 2020, 22, 217–224. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wu, J.-C.; Wang, Q.-Y.; Tao, Y.-J.; Jiang, J.-H.; Liu, Y.; Huang, G.-L.; Zhan, R.; Liu, B.; Chen, Y.-G. Two new lycodine alkaloids from Lycopodiastrum casuarinoides. Helv. Chim. Acta 2014, 97, 1719–1722. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hirasawa, Y.; Kato, E.; Kobayashi, J.; Kawahara, N.; Goda, Y.; Shiro, M.; Morita, H. Lycoparins A-C, new alkaloids from Lycopodium casuarinoides inhibiting acetylcholinesterase. Bioorg. Med. Chem. 2008, 16, 6167–6171. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qu, S.-M.; Shan, B.-H.; Wang, H.-T.; Wang, S. Lycodine type alkaloids from Lycopodiastrum casuarinoides with cytotoxic and cholinesterase inhibitory activities. Fitoterapia 2018, 131, 86–90. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Y.; Xu, P.-S.; Ren, Q.; Chen, X.; Zhou, G.; Li, D.; Li, X.-M.; Xu, K.-P.; Yu, X.; Tan, G.-S. Lycodine-type alkaloids from Lycopodiastrum casuarinoides and their cholinesterase inhibitory activities. Fitoterapia 2018, 130, 203–209. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tang, Y.; Fu, Y.; Xiong, J.; Li, M.; Ma, G.-L.; Yang, G.-X.; Wei, B.-G.; Zhao, Y.; Zhang, H.-Y.; Hu, J.-F. Casuarinines A–J, lycodine-type alkaloids from Lycopodiastrum casuarinoides. J. Nat. Prod. 2013, 76, 1475–1484. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jiang, S.; Li, W.-Y.; Gao, B.-B.; Ou, Y.-F.; Yuan, Z.-F.; Zhao, Q.-S. Casuattimines A–N, fourteen new Lycopodium alkaloids from Lycopodiastrum casuarinoides with Cav3.1 channel inhibitory activity. Bioorg. Chem. 2024, 142, 106962. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tan, Q.; Hu, K.; Li, X.-N.; Yang, X.-Z.; Sun, H.-D.; Puno, P.-T. Cytotoxic C-20 non-oxygenated ent-kaurane diterpenoids from Isodon wardii. Bioorg. Chem. 2023, 135, 106512. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, C.; Liu, J.-W.; Guo, L.-L.; Xiong, F.; Ran, X.-Q.; Guo, Y.-R.; Yao, Y.-G.; Hao, X.-J.; Luo, R.-C.; Zhang, Y. Monoterpenoid indole alkaloid dimers from Kopsia arborea inhibit cyclin-dependent kinase 5 and tau phosphorylation. Phytochemistry 2022, 203, 113392. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, Z.-L.; Cao, W.-Y.; Zhou, G.-X.; Wichtl, M. A sesquiterpene lactam from Artractylodes macrocephala. Phytochemistry 1997, 45, 765–767. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, C.-P.; Xu, J.-B.; Zhao, J.-X.; Xu, C.-H.; Dong, L.; Ding, J.; Yue, J.-M. Diterpenoids from Croton laui and their cytotoxic and antimicrobial activities. J. Nat. Prod. 2014, 77, 1013–1020. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, J.-S.; Huang, M.-F. The alkaloids huperzines C and D and huperzinine from Lycopodiastrum casuarinoides. Phytochemistry 1994, 37, 1759–1761. [Google Scholar]
- Shen, Y.-C.; Chen, C.-H. Alkaloids from Lycopodium casuarinoides. J. Nat. Prod. 1994, 57, 824–826. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ying, Y.-M.; Yu, H.-F.; Tong, C.-P.; Shan, W.-G.; Zhan, Z.-J. Spiroinonotsuoxotriols A and B, two highly rearranged triterpenoids from Inonotus obliquus. Org. Lett. 2020, 22, 3377–3380. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, Q.-Q.; Song, Q.-Y.; Jiang, K.; Li, G.-D.; Wei, W.-J.; Li, Y.; Gao, K. Spirochensilides A and B, two new rearranged triterpenoids from Abies chensiensis. Org. Lett. 2015, 17, 2760–2763. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Peng, X.-G.; Liu, J.; Gao, Y.; Cheng, F.; Chang, J.-L.; Chen, J.; Duan, F.-F.; Ruan, H.-L. Pchaeglobolactone A, spiropchaeglobosin A, and pchaeglobosals A and B: Four rearranged cytochalasans from Chaetomium globosum P2-2-2. Org. Lett. 2020, 22, 9665–9669. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhao, Q.; Xiao, L.-G.; Bi, L.-S.; Si, Y.; Zhang, X.-M.; Chen, J.-H.; Liu, H.-Y. Hedychins E and F: Labdane-type norditerpenoids with anti-inflammatory activity from the rhizomes of Hedychium forrestii. Org. Lett. 2022, 24, 6936–6939. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, W.; Wang, R.-M.; Pan, Y.-H.; Zhao, Y.-Y.; Yuan, F.-Y.; Huang, D.; Tang, G.-H.; Bi, H.-C.; Yin, S. Crotonpenoids A and B, two highly modified clerodane diterpenoids with a tricyclo[7.2.1.02,7]dodecane core from Croton yanhuii: Isolation, structural elucidation, and biomimetic semisynthesis. Org. Lett. 2020, 22, 4435–4439. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Luan, X.; Xu, Z.; Yuan, S. Studies of the alkaloids of Phlegmariurus fordii (Baker) Ching. Junshi Yixue Kexueyuan Yuankan 2002, 26, 138. [Google Scholar]
- Yin, S.; Fan, C.-Q.; Wang, X.-N.; Yue, J.-M. Lycodine-type alkaloids from Lycopodium casuarinoides. Helv. Chim. Acta 2006, 89, 138–143. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, J.-S.; Zhu, Y.-L.; Yu, C.-M.; Zhou, Y.-Z.; Han, Y.-Y.; Wu, F.-W.; Qi, B.-F. The structures of huperzine A and B, two new alkaloids exhibiting marked anticholinesterase activity. Can. J. Chem. 1986, 64, 837–839. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nakashima, T.T.; Singer, P.P.; Browne, L.M.; Ayer, W.A. Carbon-13 nuclear magnetic resonance studies of some Lycopodium alkaloids. Can. J. Chem. 1975, 53, 1936–1942. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gu, L.; Yang, Y.; Sun, Y.; Zheng, X. Puerarin inhibits acid-sensing ion channels and protects against neuron death induced by acidosis. Planta Med. 2010, 76, 583–588. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Osmakov, D.I.; Koshelev, S.G.; Palikov, V.A.; Palikova, Y.A.; Shaykhutdinova, E.R.; Dyachenko, I.A.; Andreev, Y.A.; Kozlov, S.A. Alkaloid lindoldhamine inhibits acid-sensing ion channel 1a and reveals anti-inflammatory properties. Toxins 2019, 11, 542. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, W.-N.; Wu, P.-F.; Chen, X.-L.; Zhang, Z.; Gu, J.; Yang, Y.-J.; Xiong, Q.-J.; Ni, L.; Wang, F.; Chen, J.-G. Sinomenine protects against ischaemic brain injury: Involvement of co-inhibition of acid-sensing ion channel 1a and L-type calcium channels. Br. J. Pharmacol. 2011, 164, 1445–1459. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, Y.; Ma, J.; DesJarlais, R.L.; Hagan, R.; Rech, J.; Lin, D.; Liu, C.; Miller, R.; Schoellerman, J.; Luo, J.; et al. Molecular mechanism and structural basis of small-molecule modulation of the gating of acid-sensing ion channel 1. Commun. Biol. 2021, 4, 174. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yu, X.; Wei, L.-H.; Zhang, J.-K.; Chen, T.-R.; Jin, Q.; Wang, Y.-N.; Zhang, S.-J.; Dou, T.-Y.; Cao, Y.-F.; Guo, W.-Z.; et al. Anthraquinones from Cassiae semen as thrombin inhibitors: In vitro and in silico studies. Phytochemistry 2019, 165, 112025. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]







| No. | 1 | |
|---|---|---|
| δH | δC | |
| 1 | 166.0 | |
| 2 | 165.3 | |
| 3 | 126.9 | |
| 4 | 160.2 | |
| 5 | 87.0 | |
| 6a | 2.03, br d (13.7) | 40.7 |
| 6b | 1.54, br dd (13.7, 5.2) | |
| 7 | 2.31, m | 38.7 |
| 8 | 5.48, br d (6.3) | 124.3 |
| 10a | 5.15, br d (17.5) | 116.5 |
| 10b | 5.11, br d (10.7) | |
| 11 | 6.10, ddd (17.5, 10.7, 7.1) | 138.5 |
| 12 | 2.66, br d (7.1) | 49.1 |
| 13 | 62.5 | |
| 14a | 2.10, d (17.9) | 30.6 |
| 14b | 2.06, d (17.9) | |
| 15 | 133.4 | |
| 16 | 1.59, s | 22.2 |
| N-Me(a) | 2.04, s | 41.5 |
| N-Me(b) | 2.03, s | 36.2 |
| OMe | 3.66, s | 51.4 |
| NH | 8.76, s | |
| OH | 5.74, br s |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Jiang, S.; Li, W.-Y.; Gao, B.-B.; Zhao, Q.-S. Lycocasine A, a Lycopodium Alkaloid from Lycopodiastrum casuarinoides and Its Acid-Sensing Ion Channel 1a Inhibitory Activity. Molecules 2024, 29, 1581. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules29071581
Jiang S, Li W-Y, Gao B-B, Zhao Q-S. Lycocasine A, a Lycopodium Alkaloid from Lycopodiastrum casuarinoides and Its Acid-Sensing Ion Channel 1a Inhibitory Activity. Molecules. 2024; 29(7):1581. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules29071581
Chicago/Turabian StyleJiang, Shuai, Wen-Yan Li, Bei-Bei Gao, and Qin-Shi Zhao. 2024. "Lycocasine A, a Lycopodium Alkaloid from Lycopodiastrum casuarinoides and Its Acid-Sensing Ion Channel 1a Inhibitory Activity" Molecules 29, no. 7: 1581. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules29071581
APA StyleJiang, S., Li, W.-Y., Gao, B.-B., & Zhao, Q.-S. (2024). Lycocasine A, a Lycopodium Alkaloid from Lycopodiastrum casuarinoides and Its Acid-Sensing Ion Channel 1a Inhibitory Activity. Molecules, 29(7), 1581. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules29071581