Mn2Ga2S5 and Mn2Al2Se5 van der Waals Chalcogenides: A Source of Atomically Thin Nanomaterials
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Results and Discussion
2.1. Synthesis and Air Stability
2.2. Crystal Structure
2.3. Magnetic Properties
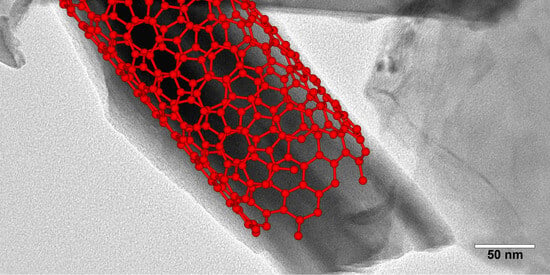
2.4. Morphology and Nanomaterials
3. Materials and Methods
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Brec, R. Review on structural and chemical properties of transition metal phosphorous trisulfides MPS3. Solid State Ion. 1986, 22, 3–30. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Haeuseler, H.; Kwarteng-Acheampong, W. Materials with layered structures II: A new quaternary compound with ZnIn2S4(IIIa)-type structure in the system MnGa2S4MnCr2S4. Mater. Res. Bull. 1989, 24, 939–943. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, H.; Chen, R.; Zhai, K.; Chen, X.; Caretta, L.; Huang, X.; Chopdekar, R.V.; Cao, J.; Sun, J.; Yao, J.; et al. Itinerant ferromagnetism in van der Waals Fe5-xGeTe2 crystals above room temperature. Phys. Rev. B 2020, 102, 064417. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rouxel, J.; Meerschaut, A.; Wiegers, G.A. Chalcogenide misfit layer compounds. J. Alloys Compd. 1995, 229, 144–157. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, B.; Quhe, R.; Yang, J.; Liu, S.; Shi, J.; Lu, J.; Du, H. High-Performance Spin Filters and Spin Field Effect Transistors Based on Bilayer VSe2. Adv. Theory Simul. 2021, 4, 2000238. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Z.; Sapkota, D.; Taniguchi, T.; Watanabe, K.; Mandrus, D.; Morpurgo, A.F. Tunneling Spin Valves Based on Fe3GeTe2/hBN/Fe3GeTe2 van der Waals Heterostructures. Nano Lett. 2018, 18, 4303–4308. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mak, K.F.; Shan, J.; Ralph, D.C. Probing and controlling magnetic states in 2D layered magnetic materials. Nat. Rev. Phys. 2019, 1, 646–661. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Verchenko, V.Y.; Stepanova, A.V.; Bogach, A.V.; Kirsanova, M.A.; Shevelkov, A.V. Cleavable crystals, crystal structure, and magnetic properties of the NbFe1+xTe3 layered van der Waals telluride. Dalton Trans. 2023, 52, 5534. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nicolosi, V.; Chhowalla, M.; Kanatzidis, M.G.; Strano, M.S.; Coleman, J.N. Liquid exfoliation of layered materials. Science 2013, 340, 1226419. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, H.; Ruan, S.; Zeng, Y.J. Intrinsic Van Der Waals Magnetic Materials from Bulk to the 2D Limit: New Frontiers of Spintronics. Adv. Mater. 2019, 31, 1900065. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, G.; Zhu, Y.; Xiang, J.; Yang, T.Y.; Huang, M.; Wang, Z.; Wang, Z.; Liu, P.; Zhang, Y.; Feng, C.; et al. Antisymmetric Magnetoresistance in a van der Waals Antiferromagnetic/Ferromagnetic Layered MnPS3/Fe3GeTe2Stacking Heterostructure. ACS Nano 2020, 14, 12037–12044. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, M.; Tian, Y.; Chen, X.; Sun, Z.; Zhu, X.; Wu, J. Observation of ultra-large Rabi splitting in the plasmon-exciton polaritons at room temperature. Nanophotonics 2023, 12, 3267–3275. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Long, G.; Henck, H.; Gibertini, M.; Dumcenco, D.; Wang, Z.; Taniguchi, T.; Watanabe, K.; Giannini, E.; Morpurgo, A.F. Persistence of Magnetism in Atomically Thin MnPS3 Crystals. Nano Lett. 2020, 20, 2452–2459. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lim, S.Y.; Kim, K.; Lee, S.; Park, J.G.; Cheong, H. Thickness dependence of antiferromagnetic phase transition in Heisenberg-type MnPS3. Curr. Appl. Phys. 2021, 21, 1–5. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kumar, R.; Jenjeti, R.N.; Austeria, M.P.; Sampath, S. Bulk and few-layer MnPS3: A new candidate for field effect transistors and UV photodetectors. J. Mater. Chem. C Mater. 2019, 7, 324–329. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ressouche, E.; Loire, M.; Simonet, V.; Ballou, R.; Stunault, A.; Wildes, A. Magnetoelectric MnPS3 as a candidate for ferrotoroidicity. Phys. Rev. B Condens. Matter Mater. Phys. 2010, 82, 100408(R). [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Z.; Gao, M.; Yu, T.; Zhou, S.; Xu, M.; Hirayama, M.; Arita, R.; Shiomi, Y.; Zhou, W.; Ogawa, N. Real-Space Observation of Ripple-Induced Symmetry Crossover in Ultrathin MnPS3. ACS Nano 2023, 17, 1916–1924. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, S.; Choi, K.Y.; Lee, S.; Park, B.H.; Park, J.G. Tunneling transport of mono- and few-layers magnetic van der Waals MnPS3. APL Mater. 2016, 4, 086108. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, W.; Feng, Y.; Wang, Y.; Zhu, J.; Lian, Z.; Zhang, H.; Li, H.; Wu, Y.; Liu, C.; Wang, Y.; et al. Direct visualization of edge state in even-layer MnBi2Te4 at zero magnetic field. Nat. Commun. 2022, 13, 7714. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ovchinnikov, D.; Huang, X.; Lin, Z.; Fei, Z.; Cai, J.; Song, T.; He, M.; Jiang, Q.; Wang, C.; Li, H.; et al. Intertwined Topological and Magnetic Orders in Atomically Thin Chern Insulator MnBi2Te4. Nano Lett. 2021, 21, 2544–2550. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zeugner, A.; Nietschke, F.; Wolter, A.U.B.; Gaß, S.; Vidal, R.C.; Peixoto, T.R.F.; Pohl, D.; Damm, C.; Lubk, A.; Hentrich, R.; et al. Chemical Aspects of the Candidate Antiferromagnetic Topological Insulator MnBi2Te4. Chem. Mater. 2019, 31, 2795–2806. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, J.; Li, Y.; Du, S.; Wang, Z.; Gu, B.L.; Zhang, S.C.; He, K.; Duan, W.; Xu, Y. Intrinsic magnetic topological insulators in van der Waals layered MnBi2Te4-family materials. Sci. Adv. 2019, 5, eaaw5685. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Deng, Y.; Yu, Y.; Shi, M.Z.; Guo, Z.; Xu, Z.; Wang, J.; Chen, X.H.; Zhang, Y. Quantum anomalous Hall effect in intrinsic magnetic topological insulator MnBi2Te4. Science 2020, 367, 895–900. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, S.; Xu, X.; Zhu, Y.; Niu, R.; Xu, C.; Peng, Y.; Cheng, X.; Jia, X.; Huang, Y.; Xu, X.; et al. Odd-Even Layer-Number Effect and Layer-Dependent Magnetic Phase Diagrams in MnBi2Te4. Phys. Rev. X 2021, 11, 011003. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Verchenko, V.Y.; Kanibolotskiy, A.V.; Chernoukhov, I.V.; Cherednichenko, K.A.; Bogach, A.V.; Znamenkov, K.O.; Sobolev, A.V.; Glazkova, I.S.; Presniakov, I.A.; Shevelkov, A.V. Layered van der Waals Chalcogenides FeAl2Se4, MnAl2S4, and MnAl2Se4: Atomically Thin Triangular Arrangement of Transition-Metal Atoms. Inorg. Chem. 2023, 62, 7557–7565. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Menard, M.C.; Ishii, R.; Higo, T.; Nishibori, E.; Sawa, H.; Nakatsuji, S.; Chan, J.Y. High-resolution synchrotron studies and magnetic properties of frustrated antiferromagnets MAl2S4 (M = Mn2+, Fe 2+, Co2+). Chem. Mater. 2011, 23, 3086–3094. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dotzel, P.; Schäfer, H.; Schön, G. Zur Darstellung und Strukturchemie Ternärer Selenide des Magnesiums mit Indium und Aluminium. Z. Anorg. Allg. Chem. 1976, 426, 260–268. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pardo, M.P.; Fourcroy, P.H.; Flahaut, J. Systeme Ga2S3|MnS diagramme de phase—Etude cristallographique. Mater. Res. Bull. 1975, 10, 665–675. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shen, J.; Xu, X.; He, M.; Liu, Y.; Han, Y.; Qu, Z. Spin freezing in the van der Waals material Mn2Ga2S5. Chin. Phys. B 2022, 31, 067105. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Williams, A.J.; Reifsnyder, A.; Yu, B.; Moore, C.E.; Susner, M.A.; Windl, W.; McComb, D.W.; Goldberger, J.E. Single crystal synthesis and properties of the two-dimensional van der Waals frustrated magnets, Mn2In2Se5 and Mn2Ga2S5. J. Mater. Chem. C Mater. 2024, 12, 1753–1762. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Buschow, K.H.J.; Boer, F.R. Physics of Magnetism and Magnetic Materials; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2003. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schneider, C.A.; Rasband, W.S.; Eliceiri, K.W. NIH Image to ImageJ: 25 years of image analysis. Nat. Methods 2012, 9, 671–675. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]








| Parameter | Value | |
|---|---|---|
| composition | Mn2Ga2S5 | Mn2Al2Se5 |
| formula weight (g/mol) | 409.647 | 558.639 |
| diffractometer | Huber G670 | |
| detector | image plate | |
| radiation | Cu Kα1 | |
| wavelength (Å) | 1.5406 | |
| crystal system | trigonal | |
| space group | Pm1 | |
| unit cell parameters | ||
| a (Å) | 3.71694(3) | 3.89660(4) |
| c (Å) | 15.2237(2) | 15.9912(2) |
| V (Å3) | 182.146(2) | 210.272(4) |
| temperature (K) | 293 | |
| ρcalc (g/cm3) | 3.73 | 4.41 |
| μ (cm−1) | 48.55 | 50.48 |
| 2θ range (deg) | 3–100.3 | 3–100.3 |
| Rp | 0.0255 | 0.0207 |
| wRp | 0.0368 | 0.0276 |
| Robs | 0.0776 | 0.0439 |
| wRobs | 0.0951 | 0.0535 |
| Rall | 0.0857 | 0.0452 |
| wRall | 0.0952 | 0.0538 |
| GOF | 2.84 | 1.66 |
| parameters | 29 | 32 |
| constraints | 3 | 5 |
| residual peaks (e−/Å3) | 2.78/−2.06 | 1.37/−1.36 |
| (a) | Mn2Ga2S5 | |||||
| Label | Symmetry | x | y | z | Occupancy | Uiso (Å2) |
| Mn1 | 3m | 1/3 | 2/3 | 0.1024(1) | 0.791(5)Mn + 0.209Ga | 0.0194(6) |
| Ga1 | 3m | 1/3 | 2/3 | 0.6635(1) | 0.791Ga + 0.209Mn | 0.0188(5) |
| S1 | m | 0 | 0 | 0 | 1 | 0.009(1) |
| S2 | 3m | 1/3 | 2/3 | 0.3989(2) | 1 | 0.0049(6) |
| S3 | 3m | 1/3 | 2/3 | 0.8115(2) | 1 | 0.0277(9) |
| (b) | Mn2Al2Se5 | |||||
| Label | Symmetry | x | y | z | Occupancy | Uiso(Å2) |
| Mn1 | 3m | 1/3 | 2/3 | 0.10275(7) | 0.645(1)Mn + 0.355Al | 0.0203(3) |
| Al1 | 3m | 1/3 | 2/3 | 0.65970(4) | 0.645Al + 0.355Mn | 0.0260(3) |
| Se1 | m | 0 | 0 | 0 | 1 | 0.0382(6) |
| Se2 | 3m | 1/3 | 2/3 | 0.39710(6) | 1 | 0.0138(5) |
| Se3 | 3m | 1/3 | 2/3 | 0.81149(6) | 1 | 0.0291(6) |
| (a) | Mn2Ga2S5 | |
| Central Atom | Neighbor Atom | Distance (Å) |
| Mn1 | S1 (×3) | 2.652(1) |
| S3 (×3) | 2.515(2) | |
| Ga1 | S2 (×3) | 2.347(1) |
| S3 (×1) | 2.253(3) | |
| (b) | Mn2Al2Se5 | |
| Central Atom | Neighbor Atom | Distance (Å) |
| Mn1 | Se1 (×3) | 2.7858(6) |
| Se3 (×3) | 2.6347(7) | |
| Al1 | Se2 (×3) | 2.4261(4) |
| Se3 (×1) | 2.427(1) |
| dSAED, Å | dXRD, Å | h | k | l |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 3.25 | 3.22 | 1 | 0 | 0 |
| 1.87 | 1.86 | 2 | 0 | |
| 1.61 | 1.61 | 2 | 0 | 0 |
| 1.23 | 1.22 | 3 | 0 | |
| 1.07 | 1.07 | 3 | 0 | 0 |
| 0.93 | 0.93 | 4 | 0 | |
| 0.89 | 0.89 | 4 | 0 | |
| 0.82 | 0.80 | 4 | 0 | 0 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Chernoukhov, I.V.; Bogach, A.V.; Cherednichenko, K.A.; Gashigullin, R.A.; Shevelkov, A.V.; Verchenko, V.Y. Mn2Ga2S5 and Mn2Al2Se5 van der Waals Chalcogenides: A Source of Atomically Thin Nanomaterials. Molecules 2024, 29, 2026. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules29092026
Chernoukhov IV, Bogach AV, Cherednichenko KA, Gashigullin RA, Shevelkov AV, Verchenko VY. Mn2Ga2S5 and Mn2Al2Se5 van der Waals Chalcogenides: A Source of Atomically Thin Nanomaterials. Molecules. 2024; 29(9):2026. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules29092026
Chicago/Turabian StyleChernoukhov, Ivan V., Alexey V. Bogach, Kirill A. Cherednichenko, Ruslan A. Gashigullin, Andrei V. Shevelkov, and Valeriy Yu. Verchenko. 2024. "Mn2Ga2S5 and Mn2Al2Se5 van der Waals Chalcogenides: A Source of Atomically Thin Nanomaterials" Molecules 29, no. 9: 2026. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules29092026
APA StyleChernoukhov, I. V., Bogach, A. V., Cherednichenko, K. A., Gashigullin, R. A., Shevelkov, A. V., & Verchenko, V. Y. (2024). Mn2Ga2S5 and Mn2Al2Se5 van der Waals Chalcogenides: A Source of Atomically Thin Nanomaterials. Molecules, 29(9), 2026. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules29092026