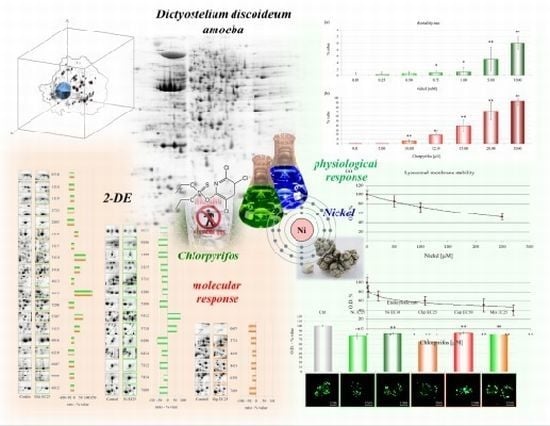
Effects of Nickel, Chlorpyrifos and Their Mixture on the Dictyostelium discoideum Proteome
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Results
2.1. Experimental Design and Physiological Responses in D. discoideum Cells Exposed to Nickel, CHP and Their Mixture
2.1.1. Mortality Rate
2.1.2. Lysosomal Membrane Stability
2.1.3. Endocytic Rate
2.2. Effects of the Toxicants on the D. discoideum Proteome
2.2.1. Nickel
2.2.2. Chlorpyrifos
2.2.3. Mixture
3. Discussion
3.1. Nickel
3.2. Chlorpyrifos
3.3. Mixture
4. Experimental Section
4.1. Dictyostelium Growth and Treatments
4.2. Mortality Rate, Lysosomal Membrane Stability and Endocytic Rate
4.3. Cell Lysis and Protein Extraction
4.4. 2-DE Gel Electrophoresis
4.5. Image Analysis
4.6. Automated ProteinSspot Picking and In-Gel Digestion
4.7. Protein Identification by Nano-LC/Q-TOF MS/MS
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Information
ijms-13-15679-s001.pdf ijms-13-15679-s002.pdf ijms-13-15679-s003.pdf ijms-13-15679-s004.pdf ijms-13-15679-s005.pdfAcknowledgments
References
- Cedergreen, N.; Streibig, J.C. Can the choice of endpoint lead to contradictory results of mixture-toxicity experiments. Environ. Toxicol. Chem 2005, 24, 1676–1683. [Google Scholar]
- Amorim, M.J.B.; Pereira, C.; Menezes-Oliveira, V.B.; Campos, B.; Soares, A.M.V.M.; Loureiro, S. Assessing single and joint effects of chemicals on the survival and reproduction of Folsomia candida (Collembola) in soil. Environ. Pollut 2012, 160, 145–152. [Google Scholar]
- Altenburger, R.; Scholz, S.; Schmitt-Jansen, M.; Busch, W.; Escher, B.I. Mixture toxicity revisited from a toxicogenomic perspective. Environ. Sci. Technol 2012, 46, 2508–2522. [Google Scholar]
- Rager, J.E.; Lichtveld, K.; Ebersviller, S.; Smeester, L.; Jaspers, I.; Sexton, K.G.; Fry, R.C. A toxicogenomic comparison of primary and photochemically altered air pollutant mixtures. Environ. Health Persp 2011, 119, 1583–1589. [Google Scholar]
- Finne, E.F.; Cooper, G.A.; Koop, B.F.; Hylland, K.; Tollefsen, K.E. Toxicogenomic responses in rainbow trout (Oncorhynchus mykiss) hepatocytes exposed to model chemicals and a synthetic mixture. Aquat. Toxicol 2007, 81, 293–303. [Google Scholar]
- Quandt, S.A.; Chen, H.; Grzywacz, J.G.; Vallejos, Q.M.; Galvan, L.; Arcury, T.A. Cholinesterase depression and its association with pesticide exposure across the agricultural season among Latino farmworkers in North Carolina. Environ. Health Persp 2010, 118, 635–639. [Google Scholar]
- Schröder, P.; Collins, C.D.; Markert, B.; Wünschmann, S. Bioindicators and Biomonitors: Use of Organisms to Observe the Influence of Chemicals on the Environment. In Organic Xenobiotics and Plants; Springer Netherlands: Dordrecht, The Netherlands, 2011; Volume 8, pp. 217–236. [Google Scholar]
- Coogan, T.P.; Latta, D.M.; Snow, E.T.; Costa, M. Toxicity and carcinogenicity of nickel compounds. Crit. Rev. Toxicol 1989, 19, 341–384. [Google Scholar]
- US Environmental Protection Agency, Ambient Water Quality Criteria for Nickel; Office of Water Regulations and Standards: Washington, DC, USA, 1986; EPA/440/5-86/004.
- Brix, K.V.; Keithly, J.T.; DeForest, D.K.; Laughlin, T. Acute and chronic toxicity of nickel to rainbow trout (Oncorhynchus mykiss). Environ. Toxicol. Chem 2004, 23, 2221–2228. [Google Scholar]
- Banni, M.; Jebali, J.; Guerbej, H.; Dondero, F.; Boussetta, H.; Viarengo, A. Mixture toxicity assessment of nickel and chlorpyrifos in the sea bass Dicentrarchus labrax. Arch. Environ. Contam. Toxicol 2011, 60, 124–131. [Google Scholar]
- Keithly, J.; Brooker, J.A.; DeForest, D.K.; Wu, B.K.; Brix, K.V. Acute and chronic toxicity of nickel to a cladoceran (Ceriodaphnia dubia) and an amphipod (Hyalella azteca). Environ. Toxicol. Chem 2004, 23, 691–696. [Google Scholar]
- Majorel, C.; Hannibal, L.; Soupe, M.-E.; Carriconde, F.; Ducousso, M.; Lebrun, M.; Jourand, P. Tracking nickel-adaptive biomarkers in Pisolithus albus from New Caledonia using a transcriptomic approach. Mol. Ecol 2012, 21, 2208–2223. [Google Scholar]
- Macomber, L.; Hausinger, R.P. Mechanisms of nickel toxicity in microorganisms. Metallomics 2011, 3, 1153–1162. [Google Scholar]
- Yusuf, M.; Fariduddin, Q.; Hayat, S.; Ahmad, A. Nickel: An overview of uptake, essentiality and toxicity in plants. Bull. Environ. Contam. Toxicol 2011, 86, 1–17. [Google Scholar]
- Lemus, R.; Abdelghani, A. Chlorpyrifos: An unwelcome pesticide in our homes. Rev. Environ. Health 2000, 15, 421–433. [Google Scholar]
- Eaton, D.L.; Daroff, R.B.; Autrup, H.; Bridges, J.; Buffler, P.; Costa, L.G.; Coyle, J.; McKhann, G.; Mobley, W.C.; Nadel, L.; et al. Review of the toxicology of chlorpyrifos with an emphasis on human exposure and neurodevelopment. Crit. Rev. Toxicol 2008, 38, 1–125. [Google Scholar]
- Amaroli, A.; Trielli, F.; Bianco, B.; Giordano, S.; Moggia, E.; Corrado, M.U.D. Effects of time-variant extremely low-frequency (ELF) electromagnetic fields (EMF) on cholinesterase activity in Dictyostelium discoideum (Protista). Chem. Biol. Interact 2005, 157, 355–356. [Google Scholar]
- Qiao, D.; Seidler, F.J.; Slotkin, T.A. Developmental neurotoxicity of chlorpyrifos modeled in vitro: Comparative effects of metabolites and other cholinesterase inhibitors on DNA synthesis in PC12 and C6 cells. Environ. Health Persp 2001, 109, 909–913. [Google Scholar]
- Richards, S.M.; Kendall, R.J. Biochemical effects of chlorpyrifos on two developmental stages of Xenopus laevis. Environ. Toxicol. Chem 2002, 21, 1826–1835. [Google Scholar]
- Whitney, K.D.; Seidler, F.J.; Slotkin, T.A. Developmental neurotoxicity of chlorpyrifos—Cellular mechanisms. Toxicol. Appl. Pharmacol 1995, 134, 53–62. [Google Scholar]
- Narra, M.R.; Begum, G.; Rajender, K.; Rao, J.V. Sub-lethal effect of chlorpyrifos on protein metabolism of the food fish Clarias batrachus and monitoring of recovery. Toxicol. Environ. Chem 2011, 93, 1650–1658. [Google Scholar]
- Demir, F.; Uzun, F.G.; Durak, D.; Kalender, Y. Subacute chlorpyrifos-induced oxidative stress in rat erythrocytes and the protective effects of catechin and quercetin. Pestic. Biochem. Physiol 2011, 99, 77–81. [Google Scholar]
- Jiang, W.; Duysen, E.G.; Hansen, H.; Shlyakhtenko, L.; Schopfer, L.M.; Lockridge, O. Mice treated with chlorpyrifos or chlorpyrifos oxon have organophosphorylated tubulin in the brain and disrupted microtubule structures, suggesting a role for tubulin in neurotoxicity associated with exposure to organophosphorus agents. Toxicol. Sci 2010, 115, 183–193. [Google Scholar]
- Dondero, F.; Banni, M.; Negri, A.; Boatti, L.; Dagnino, A.; Viarengo, A. Interactions of a pesticide/heavy metal mixture in marine bivalves: A transcriptomic assessment. BMC Genomics 2011, 12, 195. [Google Scholar]
- Moore, M.N.; Farrar, S.V. Effects of polynuclear aromatic-hydrocarbons on lysosomal membranes in mollusks. Mar. Environ. Res 1985, 17, 222–225. [Google Scholar]
- Viarengo, A.; Nott, J.A. Mechanisms of heavy-metal cation homeostasis in marine-invertebrates. Comp. Biochem. Physiol. C 1993, 104, 355–372. [Google Scholar]
- Loewe, S.; Muischnek, H. Effect of combinations: Mathematical basis of problem. Arch. Exp. Pathol. Pharmacol 1926, 114, 313–326. [Google Scholar]
- Hughes, J.E.; DeLange, K.L.; Welker, D.L. Dictyostelium discoideum cobB mutants show reduced heavy metal accumulation associated with gene amplification. Mol. Gen. Genet 1996, 253, 65–73. [Google Scholar]
- Karthikeyan, J.; Bavani, G. Effect of cadmium on lactate dehyrogenase isoenzyme, succinate dehydrogenase and NA(+)-K+-ATPase in liver tissue of rat. J. Environ. Biol 2009, 30, 895–898. [Google Scholar]
- Espartero, J.; Pintortoro, J.A.; Pardo, J.M. Differential accumulation of S-adenosylmethionine synthetase transcripts in response to salt stress. Plant Mol. Biol 1994, 25, 217–227. [Google Scholar]
- Mayne, M.B.; Coleman, J.R.; Blumwald, E. Differential expression during drought conditioning of a root-specific S-adenosylmethionine synthetase from jack pine (Pinus banksiana Lamb) seedlings. Plant Cell Environ 1996, 19, 958–966. [Google Scholar]
- Ahsan, N.; Lee, D.-G.; Alam, I.; Kim, P.J.; Lee, J.J.; Ahn, Y.-O.; Kwak, S.-S.; Lee, I.-J.; Bahk, J.D.; Kang, K.Y.; et al. Comparative proteomic study of arsenic-induced differentially expressed proteins in rice roots reveals glutathione plays a central role during As stress. Proteomics 2008, 8, 3561–3576. [Google Scholar]
- Hubberstey, A.V.; Mottillo, E.P. Cyclase-associated proteins: CAPacity for linking signal transduction and actin polymerization. FASEB J 2002, 16, 487–499. [Google Scholar]
- Sultana, H.; Rivero, F.; Blau-Wasser, R.; Schwager, S.; Balbo, A.; Bozzaro, S.; Schleicher, M.; Noegel, A.A. Cyclase-associated protein is essential for the functioning of the endo-lysosomal system and provides a link to the actin cytoskeleton. Traffic 2005, 6, 930–946. [Google Scholar]
- Sun, Y.; Ou, Y.; Cheng, M.; Ruan, Y.; van der Hoorn, F.A. Binding of nickel to testicular glutamate-ammonia ligase inhibits Its enzymatic activity. Mol. Reprod. Dev 2011, 78, 104–115. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, B.L.; Zhang, Y.Q.; Dagher, M.C.; Shacter, E. Rho GDP dissociation inhibitor protects cancer cells against drug-induced apoptosis. Cancer Res 2005, 65, 6054–6062. [Google Scholar]
- Hartwig, A. Zinc finger proteins as potential targets for toxic metal ions: Differential effects on structure and function. Antioxid. Redox Signal 2001, 3, 625–634. [Google Scholar]
- Ahsan, N.; Lee, D.-G.; Lee, S.-H.; Kang, K.Y.; Lee, J.J.; Kim, P.J.; Yoon, H.-S.; Kim, J.-S.; Lee, B.-H. Excess copper induced physiological and proteomic changes in germinating rice seeds. Chemosphere 2007, 67, 1182–1193. [Google Scholar]
- Bhatt, I.; Tripathi, B.N. Plant peroxiredoxins: Catalytic mechanisms, functional significance and future perspectives. Biotechnol. Adv 2011, 29, 850–859. [Google Scholar]
- Bonin, S.; Larese, F.F.; Trevisan, G.; Avian, A.; Rui, F.; Stanta, G.; Bovenzi, M. Gene expression changes in peripheral blood mononuclear cells in occupational exposure to nickel. Exp. Dermatol 2011, 20, 147–148. [Google Scholar]
- Kubrak, O.I.; Husak, V.V.; Rovenko, B.M.; Poigner, H.; Mazepa, M.A.; Kriews, M.; Abele, D.; Lushchak, V.I. Tissue specificity in nickel uptake and induction of oxidative stress in kidney and spleen of goldfish Carassius auratus, exposed to waterborne nickel. Aquat. Toxicol 2012, 118, 88–96. [Google Scholar]
- Lynn, S.; Yew, F.H.; Chen, K.S.; Jan, K.Y. Reactive oxygen species are involved in nickel inhibition of DNA repair. Environ. Mol. Mutagen 1997, 29, 208–216. [Google Scholar]
- Randhawa, V.K.; Zhou, F.Z.; Jin, X.L.; Nalewajko, C.; Kushner, D.J. Role of oxidative stress and thiol antioxidant enzymes in nickel toxicity and resistance in strains of the green alga Scenedesmus acutus f. alternans. Can. J. Microbiol 2001, 47, 987–993. [Google Scholar]
- Fang, H.-Y.; Chang, C.-L.; Hsu, S.-H.; Huang, C.-Y.; Chiang, S.-F.; Chiou, S.-H.; Huang, C.-H.; Hsiao, Y.-T.; Lin, T.-Y.; Chiang, I.P.; et al. ATPase family AAA domain-containing 3A is a novel anti-apoptotic factor in lung adenocarcinoma cells. J. Cell Sci 2010, 123, 1171–1180. [Google Scholar]
- Berger, W.; Steiner, E.; Grusch, M.; Elbling, L.; Micksche, M. Vaults and the major vault protein: Novel roles in signal pathway regulation and immunity. Cell Mol. Life Sci 2009, 66, 43–61. [Google Scholar]
- Ryu, S.J.; Park, S.C. Targeting major vault protein in senescence-associated apoptosis resistance. Expert Opin. Ther. Targets 2009, 13, 479–484. [Google Scholar]
- Baviskar, S.N.; Shields, M.S. RNAi silenced Dd-grp94 (Dictyostelium discoideum glucose-regulated protein 94 kDa) cell lines in Dictyostelium exhibit marked reduction in growth rate and delay in development. Gene Expr 2010, 15, 75–87. [Google Scholar]
- Mani, A.; Gelmann, E.P. The ubiquitin-proteasome pathway and its role in cancer. J. Clin. Oncol 2005, 23, 4776–4789. [Google Scholar]
- Oliveira, I.C.; Coruzzi, G.M. Carbon and amino acids reciprocally modulate the expression of glutamine synthetase in arabidopsis. Plant Physiol 1999, 121, 301–309. [Google Scholar]
- Reddy, P.S.; Bhagyalakshmi, A. Fenitrothion-induced alterations in ammonia metabolism in the crab, Oziotelphusa-senex-senex Fabricius. Pestic. Sci 1992, 35, 249–254. [Google Scholar]
- Lukaszewicz-Hussain, A.; Moniuszko-Jakoniuk, J. Chlorfenvinphos, an organophosphate insecticide, affects liver mitochondria antioxidative enzymes, glutathione and hydrogen peroxide concentration. Pol. J. Environ. Stud 2004, 13, 397–401. [Google Scholar]
- Almeida, J.R.; Oliveira, C.; Gravato, C.; Guilhermino, L. Linking behavioural alterations with biomarkers responses in the European seabass Dicentrarchus labrax L. exposed to the organophosphate pesticide fenitrothion. Ecotoxicology 2010, 19, 1369–1381. [Google Scholar]
- Lee, S.M.; Koh, H.J.; Park, D.C.; Song, B.J.; Huh, T.L.; Park, J.W. Cytosolic NADP(+)-dependent isocitrate dehydrogenase status modulates oxidative damage to cells. Free Radic. Biol. Med 2002, 32, 1185–1196. [Google Scholar]
- Noguer, T.; Marty, J.L. High sensitive bienzymic sensor for the detection of dithiocarbamate fungicides. Anal. Chim. Acta 1997, 347, 63–70. [Google Scholar]
- Marty, J.L.; Noguer, T. Bienzyme amperometric sensor for the detection of dithiocarbamate fungicides. Analysis 1993, 21, 231–233. [Google Scholar]
- Marty, J.L.; Mionetto, N.; Noguer, T.; Ortega, F.; Roux, C. Enzyme sensors for the detection of pesticides. Biosens. Bioelectron 1993, 8, 273–280. [Google Scholar]
- Ginzberg, I.; Barel, G.; Ophir, R.; Tzin, E.; Tanami, Z.; Muddarangappa, T.; de Jong, W.; Fogelman, E. Transcriptomic profiling of heat-stress response in potato periderm. J. Exp. Bot 2009, 60, 4411–4421. [Google Scholar]
- Doran, B.; Gherbesi, N.; Hendricks, G.; Flavell, R.A.; Davis, R.J.; Gangwani, L. Deficiency of the zinc finger protein ZPR1 causes neurodegeneration. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2006, 103, 7471–7475. [Google Scholar]
- Gangwani, L. Deficiency of the zinc finger protein ZPR1 causes defects in transcription and cell cycle progression. J. Biol. Chem 2006, 281, 40330–40340. [Google Scholar]
- Cairo, G.; Pietrangelo, A. Iron regulatory proteins in pathobiology. Biochem. J 2000, 352, 241–250. [Google Scholar]
- Sax, C.M.; Salamon, C.; Kays, W.T.; Guo, J.; Yu, F.S.X.; Cuthbertson, R.A.; Piatigorsky, J. Transketolase is a major protein in the mouse cornea. J. Biol. Chem 1996, 271, 33568–33574. [Google Scholar]
- Singh, P.K.; Rai, S.; Pandey, S.; Agrawal, C.; Shrivastava, A.K.; Kumar, S.; Rai, L.C. Cadmium and UV-B induced changes in proteome and some biochemical attributes of Anabaena sp. PCC7120. Phykos 2012, 42, 39–50. [Google Scholar]
- Gerke, V.; Moss, S.E. Annexins and membrane dynamics. BBA-Mol. Cell Res 1997, 1357, 129–154. [Google Scholar]
- Gerke, V.; Creutz, C.E.; Moss, S.E. Annexins: Linking Ca2+ signalling to membrane dynamics. Nat. Rev. Mol. Cell Biol 2005, 6, 449–461. [Google Scholar]
- Rhee, H.J.; Kim, G.Y.; Huh, J.W.; Kim, S.W.; Na, D.S. Annexin I is a stress protein induced by heat, oxidative stress and a sulfhydryl-reactive agent. Eur. J. Biochem 2000, 267, 3220–3225. [Google Scholar]
- Sacre, S.M.; Moss, S.E. Intracellular localization of endothelial cell annexins is differentially regulated by oxidative stress. Exp. Cell Res 2002, 274, 254–263. [Google Scholar]
- Tanaka, T.; Akatsuka, S.; Ozeki, M.; Shirase, T.; Hiai, H.; Toyokuni, S. Redox regulation of annexin 2 and its implications for oxidative stress-induced renal carcinogenesis and metastasis. Oncogene 2004, 23, 3980–3989. [Google Scholar]
- Gorecka, K.M.; Konopka-Postupolska, D.; Hennig, J.; Buchet, R.; Pikula, S. Peroxidase activity of annexin 1 from Arabidopsis thaliana. Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun 2005, 336, 868–875. [Google Scholar]
- Jami, S.K.; Clark, G.B.; Turlapati, S.A.; Handley, C.; Roux, S.J.; Kirti, P.B. Ectopic expression of an annexin from Brassica juncea confers tolerance to abiotic and biotic stress treatments in transgenic tobacco. Plant Physiol. Biochem 2008, 46, 1019–1030. [Google Scholar]
- Forsthoefel, N.R.; Cushman, M.A.F.; Cushman, J.C. Posttranscriptional and Posttranslational Control of Enolase Expression in the Facultative Crassulacean Acid Metabolism Plant Mesembryanthemum crystallinum L. Plant Physiol 1995, 108, 1185–1195. [Google Scholar]
- Yang, H.S.; Henning, D.; Valdez, B.C. Functional interaction between RNA helicase II Gu alpha and ribosomal protein L4. FEBS J 2005, 272, 3788–3802. [Google Scholar]
- Spycher, S.E.; TabatabaVakili, S.; Odonnell, V.B.; Palomba, L.; Azzi, A. Aldose reductase induction: A novel response to oxidative stress of smooth muscle cells. FASEB J 1997, 11, 181–188. [Google Scholar]
- Marsano, F.; Boatti, L.; Ranzato, E.; Cavaletto, M.; Magnelli, V.; Dondero, F.; Viarengo, A. Effects of mercury on Dictyostelium discoideum: Proteomics reveals the molecular mechanisms of physiological adaptation and toxicity. J. Proteome Res 2010, 9, 2839–2854. [Google Scholar]
- Watts, D.J.; Ashworth, J.M. Growth of myxameobae of the cellular slime mould Dictyostelium discoideum in axenic culture. Biochem. J 1970, 119, 171–174. [Google Scholar]
- Sussman, M. Cultivation and synchronous morphogenesis of Dictyostelium under controlled experimental conditions. Methods Cell Biol 1987, 28, 9–29. [Google Scholar]
- Dondero, F.; Jonsson, H.; Rebelo, M.; Pesce, G.; Berti, E.; Pons, G.; Viarengo, A. Cellular responses to environmental contaminants in amoebic cells of the slime mould Dictyostelium discoideum. Comp. Biochem. Physiol. C Toxicol. Pharmacol 2006, 143, 150–157. [Google Scholar]
- Neuhoff, V.; Arold, N.; Taube, D.; Ehrhardt, W. Improved staining of proteins in polyacrylamide gels including isoelectric focusing gels with clear background at nanogram sensitivity using Coomassie Brilliant Blue G-250 and R-250. Electrophoresis 1988, 9, 255–262. [Google Scholar]
- Matrix Science. Available online: http://www.matrixscience.com/ accessed on 1 June 2012.
- National Center for Biotechnology Information. Available online: http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/ accessed on 1 July 2012.
- Powlesland, C.; George, J. Acute and chronic toxicity of nickel to larvae of Chironomus riparis (Meigen). Environ. Pollut. A 1986, 42, 47–64. [Google Scholar]
- Burlando, B.; Evangelisti, V.; Dondero, F.; Pons, G.; Camakaris, J.; Viarengo, A. Occurrence of Cu-ATPase in Dictyostelium: Possible role in resistance to copper. Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun 2002, 291, 476–483. [Google Scholar]
- Gayatri, R.; Chatterjee, S. Phagocytic-activity of dictyostelium amoebae treated with an organochlorine pesticide. Cell Biol. Internat 1993, 17, 349–352. [Google Scholar]
- Yin, L.; Mano, J.; Wang, S.; Tsuji, W.; Tanaka, K. The involvement of lipid peroxide-derived aldehydes in aluminum toxicity of tobacco roots. Plant Physiol 2010, 152, 1406–1417. [Google Scholar]
- Costa, P.M.; Chicano-Galvez, E.; Barea, J.L.; DelValls, T.A.; Costa, M.H. Alterations to proteome and tissue recovery responses in fish liver caused by a short-term combination treatment with cadmium and benzo a pyrene. Environ. Pollut 2010, 158, 3338–3346. [Google Scholar]
- Zhou, Q.; Wu, C.G.; Dong, B.; Li, F.H.; Liu, F.Q.; Xiang, J.H. Proteomic analysis of acute responses to copper sulfate stress in larvae of the brine shrimp, Artemia sinica. Chin. J. Oceanol. Limnol 2010, 28, 224–232. [Google Scholar]








| Spot n° | Protein ID | gi | DDB | Ratio (% value) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 0013 | 60S acidic ribosomal protein P2 | gi|133059 | DDB0191484 | −45.3 |
| 0106 | LIM-type zinc finger-containing protein | gi|7107412 | DDB0201567 | −55.7 |
| 1108 | Rho GDP-dissociation inhibitor | gi|66803106 | DDB0216235 | −55.5 |
| 1115 | Actin-related protein 2/3 complex, subunit 5 | gi|66806101 | DDB0191138 | −41.5 |
| 3711 | Glutamate-ammonia ligase | gi|60469746 | DDB0231551 | −35.6 |
| 4106 | Peroxiredoxin | gi|28828367 | DDB0231647 | −31.2 |
| Dihydropteridine reductase | gi|66823097 | DDB0237752 | ||
| 5108 | Hypothetical protein DDBDRAFT_0206195 | gi|66815899 | DDB0206195 | −48.5 |
| Peroxiredoxin | gi|66821043 | DDB0231647 | ||
| 5412 | S-adenosylmethionine synthetase | gi|66803080 | DDB0230070 | 83.8 |
| 5718 | Succinate dehydrogenase | gi|66813780 | DDB0214886 | 61.2 |
| 6106 | Similar to ribosomal protein | gi|66821505 | DDB0167610 | −62.4 |
| 6414 | S-adenosyl-methionine synthetase | gi|60463691 | DDB0230070 | −35.4 |
| 7112 | Hypothetical protein DDB_0233902 | gi|60475381 | DDB0233902 | −47.7 |
| 7414 | Elongation factor 1 β | gi|10801150 | DDB0191174 | −24.0 |
| 7609 | Cyclase-associated protein | gi|66805581 | DDB0191139 | −49.5 |
| Spot n° | Protein ID | gi | DDB | Ratio (% value) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 0124 | Putative polypeptide-associated complex alpha subunit | gi|66812950 | DDB0233328 | −52.8 |
| 0125 | Cytosolic glycoprotein FP21 | gi|66826197 | DDB0191107 | −52.0 |
| 0526 | RepC-binding protein A | gi|4336714 | DDB0191177 | −50.1 |
| Calreticulin | gi|66810606 | DDB0191384 | ||
| 0721 | Glucose-regulated protein 94 | gi|66814268 | DDB0215015 | −42.0 |
| 1125 | Nascent polypeptide-associated complex alpha subunit | gi|66812950 | DDB0233328 | −18.1 |
| 2334 | N-acyl-l-amino-acid amidohydrolase | gi|66825457 | DDB0201767 | −61.1 |
| 26S proteasome non-ATPase regulatory subunit 6 | gi|66826503 | DDB0232985 | ||
| 2831 | Hypothetical protein DDBDRAFT_0192196 | gi|66799895 | DDB0192196 | −44.8 |
| 3423 | Phosphoglycerate kinase | gi|22711882 | DDB0191349 | −40.4 |
| 3721 | Glutamate-ammonia ligase | gi|66815105 | DDB0231551 | 42.3 |
| Prolyl oligopeptidase | gi|4584573 | DDB0185041 | ||
| 3826 | Major vault protein | gi|66825911 | DDB0191259 | −47.3 |
| 4529 | Actin binding protein | gi|66827977 | DDB0191115 | 112.9 |
| 4732 | AAA ATPase domain-containing protein | gi|66805423 | DDB0231600 | 127.5 |
| 6132 | Peroxiredoxin | gi|66808689 | DDB0238212 | 109.2 |
| 6218 | Putative epimerase | gi|66820416 | DDB0167407 | 41.9 |
| 6223 | Phosphoribosyl pyrophosphate synthetase | gi|66809487 | DDB0237882 | −32.1 |
| Spot n° | Protein ID | gi | DDB | Ratio (% value) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 3711 | Glutamate-ammonia ligase | gi|60469746 | DDB0231551 | −52.2 |
| 7609 | Cyclase-associated protein | gi|66805581 | DDB0191139 | −37.4 |
| 4613 | 26S proteasome ATPase 1 subunit | gi|66826743 | DDB0232964 | −28.4 |
| 6310 | Isocitrate dehydrogenase (NAD+) | gi|66799989 | DDB0231294 | −34.5 |
| 4610 | Aldehyde dehydrogenase | gi|66818493 | DDB0231504 | −28.1 |
| 0605 | ZPR1-type zinc finger-containing protein | gi|66825227 | DDB0304584 | −47.0 |
| Spot n° | Protein ID | gi | DDB | Ratio (% value) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1617 | Protein phosphatase 2C-like domain-containing protein | gi|66809891 | DDB0233767 | −29.1 |
| 2723 | not identified | / | / | 69.4 |
| 3326 | Putative SAM-dependent methyltransferase | gi|60475385 | DDB0233903 | −32.1 |
| 3424 | S-adenosylmethionine synthetase | gi|66803080 | DDB0230070 | −20.6 |
| 3536 | Aldehyde dehydrogenase | gi|66818493 | DDB0231504 | −24.5 |
| 3725 | Tetratricopeptide-like helical domain-containing protein (TPR) stress-induced phosphoprotein 1 | gi|66801325 | DDB0237783 | 59.1 |
| 4432 | β-Alanine synthase | gi|66821393 | DDB0185221 | 33.7 |
| 4642 | Transketolase | gi|66822027 | DDB0266926 | 73.6 |
| 4655 | Succinate dehydrogenase (ubiquinone) | gi|66813780 | DDB0214886 | 44.7 |
| Hypothetical protein DDBDRAFT_0218901 | gi|66807283 | DDB0218901 | ||
| 4730 | Putative iron regulatory protein | gi|66815641 | DDB0229908 | 60.5 |
| 6523 | Annexin VII | gi|66825303 | DDB0191502 | 108.4 |
| 7323 | Phosphopyruvate hydratase | gi|66811048 | DDB0231355 | 125.8 |
| 8432 | 60S ribosomal protein L4 | gi|66817212 | DDB0231241 | −54.4 |
| Spot n° | Protein ID | gi | DDB | Ratio (% value) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 0510 | Hypothetical protein DDBDRAFT_0187751 | gi|66806459 | DDB0187751 | −44.4 |
| 1114 | Pyruvate dehydrogenase E1 beta subunit | gi|66818919 | DDB0229442 | −50.8 |
| 1119 | Putative delta-24-sterol methyltransferase | gi|60464861 | DDB0237965 | −41.5 |
| 2722 | Clathrin heavy chain | gi|66818048 | DDB0185029 | −60.9 |
| 2803 | Myosin II heavy chain | gi|134047850 | DDB0191444 | −62.2 |
| 3110 | Aldehyde reductase | gi|38637654 | DDB0215363 | 30.1 |
| 3115 | not identified | / | / | −32.9 |
| 3414 | Aldehyde dehydrogenase | gi|66818493 | DDB0231504 | 90.3 |
| 3416 | Phosphoglycerate kinase | gi|22711882 | DDB0191349 | 44.8 |
| 4613 | Glucosamine-6-phosphate isomerase | gi|66808101 | DDB0234127 | −30.6 |
| 4615 | Putative transport protein | gi|166240434 | DDB0235163 | 132.4 |
| 5208 | Isocitrate dehydrogenase (NAD+) | gi|60462281 | DDB0231294 | −52.7 |
| 5307 | S-adenosyl-methionine synthetase | gi|60463691 | DDB0230070 | 68.0 |
| 5415 | 3-phosphoglycerate dehydrogenase | gi|66813238 | DDB0230052 | 43.3 |
| 6016 | Actin binding protein | gi|60468343 | DDB0215335 | −30.0 |
| 6210 | G β-like protein | gi|66820452 | DDB0185122 | −56.7 |
| 6607 | Cyclase-associated protein | gi|66805581 | DDB0191139 | −50.8 |
| 6608 | ATP citrate synthase | gi|66816585 | DDB0235360 | −44.7 |
| 6612 | Aconitase, mitochondrial | gi|60470010 | DDB0230168 | −37.5 |
| gi | Protein ID | Chlorpyrifos | Nickel | Mixture | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| EC25 | EC50 | EC25 | EC50 | |||
| gi|66805581 | cyclase-associated protein | −37.4 | / | −49.5 | / | −50.8 |
| gi|60469746 | glutamate-ammonia ligase | −52.2 | / | −35.6 | / | / |
| gi|66818493 | aldehyde dehydrogenase | −28.1 | −24.5 | / | / | 90.3 |
| gi|60463691 | S-adenosyl-methionine synthetase | / | / | −35.4 | / | 68.0 |
| gi|66803080 | S-adenosylmethionine synthetase | / | −20.6 | 83.8 | / | / |
| gi|22711882 | phosphoglycerate kinase | / | / | / | −40.4 | 44.8 |
| gi|60462281 | isocitrate dehydrogenase (NAD+) | −34.5 | / | / | / | −52.7 |
© 2012 by the authors; licensee Molecular Diversity Preservation International, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open-access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/3.0/).
Share and Cite
Boatti, L.; Robotti, E.; Marengo, E.; Viarengo, A.; Marsano, F. Effects of Nickel, Chlorpyrifos and Their Mixture on the Dictyostelium discoideum Proteome. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2012, 13, 15679-15705. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms131215679
Boatti L, Robotti E, Marengo E, Viarengo A, Marsano F. Effects of Nickel, Chlorpyrifos and Their Mixture on the Dictyostelium discoideum Proteome. International Journal of Molecular Sciences. 2012; 13(12):15679-15705. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms131215679
Chicago/Turabian StyleBoatti, Lara, Elisa Robotti, Emilio Marengo, Aldo Viarengo, and Francesco Marsano. 2012. "Effects of Nickel, Chlorpyrifos and Their Mixture on the Dictyostelium discoideum Proteome" International Journal of Molecular Sciences 13, no. 12: 15679-15705. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms131215679
APA StyleBoatti, L., Robotti, E., Marengo, E., Viarengo, A., & Marsano, F. (2012). Effects of Nickel, Chlorpyrifos and Their Mixture on the Dictyostelium discoideum Proteome. International Journal of Molecular Sciences, 13(12), 15679-15705. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms131215679