Supercritical Fluid Extraction of Bacterial and Archaeal Lipid Biomarkers from Anaerobically Digested Sludge
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Results and Discussion
2.1. Model Fitting and Statistical Analysis
2.2. The Effects of Pressure, Temperature and Modifier Concentration on the Total Amount of RQ
2.3. The Effects of Pressure, Temperature and Modifier Concentration on the Total Amount of PLFA
2.4. The Effects of Pressure, Temperature and Modifier Concentration on the Total Amount of PLEL
2.5. Multiple-Response Optimization
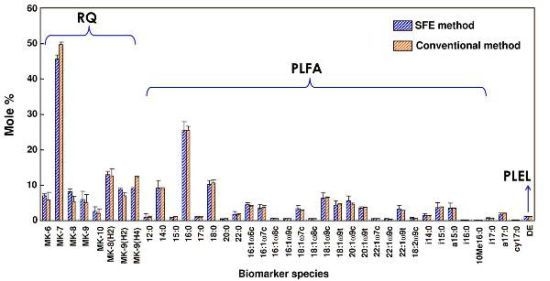
2.6. Comparison of Supercritical CO2 Extraction and Organic Solvent Extraction
3. Experimental Section
3.1. Chemicals and Standards
3.2. Sample Preparation
3.3. Organic Solvent Extraction
3.4. Supercritical Fluid Extraction
3.5. Lipid Fractionation and Derivatization Procedures
3.6. UPLC Analysis of RQ Extracted from Anaerobically Digested Sludge
3.7. Gas Chromatography Analysis of PLFA and PLEL Extracted from Anaerobically Digested Sludge
3.8. Experimental Design
4. Conclusions
Acknowledgment
References
- Sekiguchi, Y.; Kamagata, Y.; Harada, H. Recent advances in methane fermentation technology. Curr. Opin. Biotechnol 2001, 12, 277–282. [Google Scholar]
- Rittmann, B.E. Microbial ecology to manage processes in environmental biotechnology. Trends Biotechnol 2006, 24, 261–266. [Google Scholar]
- Narihiro, T.; Sekiguchi, Y. Microbial communities in anaerobic digestion processes for waste and wastewater treatment: A microbiological update. Curr. Opin. Biotechnol 2007, 18, 273–278. [Google Scholar]
- White, D.C.; Davis, W.M.; Nickels, J.S.; King, J.D.; Bobbie, R.J. Determination of the sedimentary microbial biomass by extractable lipid phosphate. Oecologia 1979, 40, 51–62. [Google Scholar]
- Zelles, L. Fatty acid patterns of phospholipids and lipopolysaccharides in the characterisation of microbial communities in soil: A review. Biol. Fertil. Soils 1999, 29, 111–129. [Google Scholar]
- White, D.C.; Ringelberg, D.B.; Hedrick, D.B.; Nivens, D.E. Rapid Identification of Microbes from Clinical and Environmental Matrices by Mass Spectrometry. In Mass Spectrometry for the Characterization of Microorganisms; Fenselau, C., Ed.; ACS symposium series 541; American Chemical Society: Washington, DC, USA, 1993; pp. 8–17. [Google Scholar]
- Green, C.T.; Scow, K.M. Analysis of phospholipid fatty acids (PLFA) to characterize microbial communities in aquifers. Hydrogeol. J 2000, 8, 126–141. [Google Scholar]
- Hedrick, D.B.; White, D.C. Microbial respiratory quinones in the environment: A sensitive liquid chromatographic method. J. Microbiol. Methods 1986, 5, 243–254. [Google Scholar]
- Hiraishi, A. Isoprenoid quinones as biomarkers of microbial populations in the environment. J. Biosci. Bioeng 1999, 88, 449–460. [Google Scholar]
- Collins, M.D.; Jones, D. Distribution of isoprenoid quinone structural types in bacteria and their taxonomic implications. Microbiol. Rev 1981, 45, 316–354. [Google Scholar]
- Joergensen, R.G.; Wichern, F. Quantitative assessment of the fungal contribution to microbial tissue in soil. Soil Biol. Biochem 2008, 40, 2977–2991. [Google Scholar]
- Smith, C.A.; Phiefer, C.B.; Macnaughton, S.J.; Peacock, A.; Burkhalter, R.S.; Kirkegaard, R.; White, D.C. Quantitative lipid biomarker detection of unculturable microbes and chlorine exposure in water distribution system biofilms. Water Res 2000, 34, 2683–2688. [Google Scholar]
- Gattinger, A. Phospholipid etherlipid and phospholipid fatty acid fingerprints in selected euryarchaeotal monocultures for taxonomic profiling. FEMS Microbiol. Lett 2002, 213, 133–139. [Google Scholar]
- Bligh, E.G.; Dyer, W.J. A rapid method of total lipid extraction and purification. Can. J. Biochem. Physiol 1959, 37, 911–917. [Google Scholar]
- Geyer, R.; Peacock, A.D.; White, D.C.; Lytle, C.; Van Berkel, G.J. Atmospheric pressure chemical ionization and atmospheric pressure photoionization for simultaneous mass spectrometric analysis of microbial respiratory ubiquinones and menaquinones. J. Mass Spectrom 2004, 39, 922–929. [Google Scholar]
- Nishihara, M.; Koga, Y. Extraction and composition of polar lipids from the archaebacterium, Methanobacterium thermoautotrophicum: Effective extraction of tetraether lipids by an acidified solvent. J. Biochem 1987, 101, 997–1005. [Google Scholar]
- White, P.M. Pressurized liquid extraction of soil microbial phospholipid and neutral lipid fatty acids. J. Agric. Food Chem 2009, 57, 7171–7177. [Google Scholar]
- Pinkart, H.C.; Devereux, R.; Chapman, P.J. Rapid separation of microbial lipids using solid phase extraction columns. J. Microbiol. Methods 1998, 34, 9–15. [Google Scholar]
- Cescut, J.; Severac, E.; Molina-Jouve, C.; Uribelarrea, J.L. Optimizing pressurized liquid extraction of microbial lipids using the response surface method. J. Chromatogr. A 2011, 1218, 373–379. [Google Scholar]
- Pourmortazavi, S.M.; Hajimirsadeghi, S.S. Supercritical fluid extraction in plant essential and volatile oil analysis. J. Chromatogr. A 2007, 1163, 2–24. [Google Scholar]
- Irvan; Atsuta, Y.; Saeki, T.; Daimon, H.; Fujie, K. Supercritical carbon dioxide extraction of ubiquinones and menaquinones from activated sludge. J. Chromatogr. A 2006, 1113, 14–19. [Google Scholar]
- Hanif, M.; Atsuta, Y.; Fujie, K.; Daimon, H. Supercritical fluid extraction of microbial phospholipid fatty acids from activated sludge. J. Chromatogr. A 2010, 1217, 6704–6708. [Google Scholar]
- White, D.C.; Lytle, C.A.; Gan, Y.M.; Piceno, Y.M.; Wimpee, M.H.; Peacock, A.D.; Smith, C.A. Flash detection/identification of pathogens, bacterial spores and bioterrorism agent biomarkers from clinical and environmental matrices. J. Microbiol. Methods 2002, 48, 139–147. [Google Scholar]
- Hawthorne, S.B.; Miller, D.J.; Nivens, D.E.; White, D.C. Supercritical fluid extraction of polar analytes using in situ chemical derivatization. Anal. Chem 1992, 64, 405–412. [Google Scholar]
- Gharaibeh, A.A.; Voorhees, K.J. Characterization of lipid fatty acids in whole-cell microorganisms using in situ supercritical fluid derivatization/extraction and GC/MS. Anal. Chem 1996, 68, 2805–2810. [Google Scholar]
- Hedrick, D.B.; Guckert, J.B.; White, D.C. Archaebacterial ether lipid diversity analyzed by supercritical fluid chromatography: Integration with a bacterial lipid protocol. J. Lipid Res 1991, 32, 659–666. [Google Scholar]
- Hoogerbrugge, R.; Stolker, A.A.M.; Barendregt, A.; Hogendoorn, E.A. A systematic approach for optimisation of supercritical-fluid extraction of polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons from earthworms. Anal. Bioanal. Chem 2003, 377, 715–722. [Google Scholar]
- Marsili, R.; Callahan, D. Comparison of a liquid solvent extraction technique and supercritical fluid extraction for the determination of α- and β-carotene in vegetable. J. Chromatogr. Sci 1993, 31, 422–428. [Google Scholar]
- Roop, R.K.; Akgerman, A.; Dexter, B.J.; Irvin, T.R. Extraction of phenol from water with supercritical carbon dioxide. J. Supercrit. Fluids 1989, 2, 51–56. [Google Scholar]
- Design-Expert Software, V6, User’s Guide, Technical Manual; Stat-Ease Inc.: Minneapolis, MN, USA, 2009.
- IUPAC-IUB Commission on Biochemical Nomenclature. The nomenclature of lipids. Biochem. J. 1978, 171, 21–35.
- IUPAC-IUB Commission on Biochemical Nomenclature. The nomenclature of quinones with isoprenoid side-chains. Pure Appl. Chem. 1974, 38, 439–447.
- Virtue, P.; Nichols, P.D.; Boon, P.I. Simultaneous estimation of microbial phospholipid fatty acids and diether lipids by capillary gas chromatography. J. Microbiol. Methods 1996, 25, 177–185. [Google Scholar]
- McKinley, V.L.; Peacock, A.D.; White, D.C. Microbial community PLFA and PHB responses to ecosystem restoration in tallgrass prairie soils. Soil Biol. Biochem 2005, 37, 1946–1958. [Google Scholar]
- Katayama, A.; Funasaka, K.; Fujie, K. Changes in the respiratory quinone profile of a soil treated with pesticides. Biol. Fertil. Soils 2001, 33, 454–459. [Google Scholar]
- Koga, Y.; Nishihara, M.; Morii, H.; Matsushita, M.A. Ether polar lipids of methanogenic bacteria: Structures, comparative aspects, and biosynthesis. Microbiol. Rev 1993, 57, 164–182. [Google Scholar]
- MacNicol, R.D.; Beckett, P.H.T. The distribution of heavy metals between the principal components of digested sewage sludge. Water Res 1989, 23, 199–206. [Google Scholar]
- Okabe, A.; Toyota, K.; Kimura, M. Seasonal variations of phospholipid fatty acid composition in the floodwater of a Japanese paddy field under a long-term fertilizer trial. Soil Sci. Plant Nutr 2000, 46, 177–188. [Google Scholar]
- Montgomery, D.C. Design and Analysis of Experiment, 6th ed.; John Wiley & Sons: New York, NY, USA, 2005; pp. 427–439. [Google Scholar]






| Design matrix | Total amounts b | ||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Factors | Microbial lipid biomarkers extracted | ||||||
| No. | Run a | Pressure (MPa) | Temperature (°C) | Modifier (methanol %, v/v) | RQ (nmol/g) | PLFA (nmol/g) | PLEL (nmol/g) |
| 1 | 10 | −1 (10) | −1 (60) | −1 (5) | 12.32 | 152.88 | 1.21 |
| 2 | 7 | +1 (30) | −1 (60) | −1 (5) | 15.57 | 164.06 | 1.26 |
| 3 | 16 | −1 (10) | +1 (100) | −1 (5) | 10.46 | 350.56 | 3.56 |
| 4 | 23 | +1 (30) | +1 (100) | −1 (5) | 12.26 | 420.13 | 5.52 |
| 5 | 2 | −1 (10) | −1 (60) | +1 (15) | 22.93 | 470.31 | 5.57 |
| 6 | 12 | +1 (30) | −1 (60) | +1 (15) | 25.44 | 510.50 | 6.50 |
| 7 | 22 | −1 (10) | +1 (100) | +1 (15) | 10.34 | 459.38 | 5.72 |
| 8 | 19 | +1 (30) | +1 (100) | +1 (15) | 13.36 | 520.25 | 6.15 |
| 9 | 4 | −1.68 (3.18) | 0 (80) | 0 (10) | 4.97 | 112.14 | 0.89 |
| 10 | 18 | +1.68 (36.82) | 0 (80) | 0 (10) | 18.02 | 470.31 | 5.64 |
| 11 | 13 | 0 (20) | −1.68 (46.36) | 0 (10) | 18.38 | 487.81 | 4.86 |
| 12 | 8 | 0 (20) | +1.68 (113.64) | 0 (10) | 10.92 | 510.50 | 6.48 |
| 13 | 1 | 0 (20) | 0 (80) | −1.68 (1.59) | 6.48 | 125.32 | 0.56 |
| 14 | 9 | 0 (20) | 0 (80) | +1.68 (18.41) | 20.97 | 535.94 | 6.15 |
| 15 | 11 | 0 (20) | 0 (80) | 0 (10) | 23.60 | 610.75 | 7.32 |
| 16 | 21 | 0 (20) | 0 (80) | 0 (10) | 21.08 | 590.25 | 5.95 |
| 17 | 5 | 0 (20) | 0 (80) | 0 (10) | 20.68 | 600.38 | 7.13 |
| 18 | 17 | 0 (20) | 0 (80) | 0 (10) | 15.96 | 560.94 | 8.12 |
| 19 | 3 | 0 (20) | 0 (80) | 0 (10) | 19.41 | 598.63 | 7.51 |
| 20 | 20 | 0 (20) | 0 (80) | 0 (10) | 17.81 | 615.13 | 4.95 |
| 21 | 15 | 0 (20) | 0 (80) | 0 (10) | 21.05 | 430.69 | 5.76 |
| 22 | 6 | 0 (20) | 0 (80) | 0 (10) | 19.75 | 632.25 | 6.85 |
| 23 | 14 | 0 (20) | 0 (80) | 0 (10) | 20.90 | 590.07 | 7.21 |
| Factor | Coefficient Estimate a | RQ | PLFA | PLEL |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Intercept | β0 | 19.97 | 580.58 | 6.74 |
| x1 (pressure) | β1 | 2.38 ** | 57.42 ** | 0.82 * |
| x2 (temperature) | β2 | −3.10 ** | 35.93 * | 0.65 * |
| x3 (modifier) | β3 | 3.36 ** | 114.48 ** | 1.61 ** |
| x12 (pressure) | β12 | −2.51 ** | −56.87 ** | −1.12 ** |
| x22 (temperature) | β13 | −1.39 | −98.32 | −0.27 |
| x32 (modifier) | β23 | −1.72 * | −84.39 ** | −1.09 ** |
| x1 x2 (pressure × temperature) | β11 | −0.12 | 9.88 | 0.20 |
| x1 x3 (pressure × modifier) | β22 | 0.06 | 2.54 | −0.11 |
| x2 x3 (temperature × modifier) | β33 | −2.44 * | −56.87 * | −0.88 * |
| R2 | 0.86 | 0.90 | 0.88 | |
| Adjusted R2 | 0.76 | 0.83 | 0.80 | |
| Standard Deviation | 2.71 | 69.06 | 1.01 |
| Source | Degrees of freedom | Sum of squares | Mean square | F-value | p-value |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| RQ | |||||
| Model | 9 | 585.95 | 65.11 | 8.84 | 0.0003 ** |
| Residual | 13 | 95.75 | 7.37 | ||
| Lack of fit | 5 | 57.72 | 11.54 | 2.43 | 0.1269 |
| Pure error | 8 | 38.02 | 4.75 | ||
| Corrected total | 22 | 681.70 | |||
| PLFA | |||||
| Model | 9 | 5.42 × 105 | 6.02 × 104 | 12.63 | <0.0001 ** |
| Residual | 13 | 6.20 × 104 | 4.77 × 103 | ||
| Lack of fit | 5 | 3.34 × 104 | 6.69 × 103 | 1.88 | 0.2042 |
| Pure error | 8 | 2.85 × 104 | 3.56 × 103 | ||
| Corrected total | 22 | 6.04 × 105 | |||
| PLEL | |||||
| Model | 9 | 96.84 | 10.76 | 10.57 | 0.0001** |
| Residual | 13 | 13.24 | 1.02 | ||
| Lack of fit | 5 | 5.23 | 1.05 | 1.05 | 0.4536 |
| Pure error | 8 | 8.01 | 1.00 | ||
| Corrected total | 22 | 110.08 | |||
© 2012 by the authors; licensee Molecular Diversity Preservation International, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open-access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/3.0/).
Share and Cite
Hanif, M.; Atsuta, Y.; Fujie, K.; Daimon, H. Supercritical Fluid Extraction of Bacterial and Archaeal Lipid Biomarkers from Anaerobically Digested Sludge. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2012, 13, 3022-3037. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms13033022
Hanif M, Atsuta Y, Fujie K, Daimon H. Supercritical Fluid Extraction of Bacterial and Archaeal Lipid Biomarkers from Anaerobically Digested Sludge. International Journal of Molecular Sciences. 2012; 13(3):3022-3037. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms13033022
Chicago/Turabian StyleHanif, Muhammad, Yoichi Atsuta, Koichi Fujie, and Hiroyuki Daimon. 2012. "Supercritical Fluid Extraction of Bacterial and Archaeal Lipid Biomarkers from Anaerobically Digested Sludge" International Journal of Molecular Sciences 13, no. 3: 3022-3037. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms13033022
APA StyleHanif, M., Atsuta, Y., Fujie, K., & Daimon, H. (2012). Supercritical Fluid Extraction of Bacterial and Archaeal Lipid Biomarkers from Anaerobically Digested Sludge. International Journal of Molecular Sciences, 13(3), 3022-3037. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms13033022