Influence of “Glow Discharge Plasma” as an External Stimulus on the Self-Assembly, Morphology and Binding Affinity of Gold Nanoparticle-Streptavidin Conjugates
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Results and Discussion
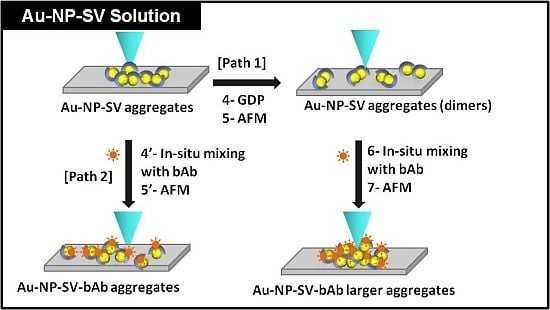
2.1. GDP Treatment of Au-NP-SV and Its in Situ Mixing with Biotinylated Antibody (bAb)
2.1.1. The Influence of GDP on Au-NP-SV Binding
2.1.2. The Influence of GDP on SV-bAb Binding
3. Experimental Section
3.1. Gold Nanoparticles-Streptavidin Conjugates (Au-NP-SV)
3.2. Glow Discharge Plasma (GDP)
3.3. Sample Preparation
3.4. Atomic Force Microscopy (AFM)
4. Conclusions
Acknowledgments
References
- Whitesides, G.M.; Mathias, J.P.; Seto, C.T. Molecular self-assembly and nanochemistry: A chemical strategy for the synthesis of nanostructures. Sci. New Ser 1991, 254, 1312–1319. [Google Scholar]
- Salta, M.; Wharton, J.A.; Stoodley, P.; Dennington, S.P.; Goodes, L.R.; Werwinski, S.; Wood, R.J.K.; Stokes, K.R. Designing biomimetic antifouling surfaces. R. Soc. Lond. Philos. Trans. Biol. Sci 2010, 368, 4729–4754. [Google Scholar]
- Rana, D.; Matsuura, T. Surface modifications for antifouling membranes. Chem. Rev 2010, 110, 2448–2471. [Google Scholar]
- Murugan, R.; Ramakrishna, S. Nano-featured scaffolds for tissue engineering: A review of spinning methodologies. Tissue Eng 2006, 12, 435–447. [Google Scholar]
- Qian, Y.; Zhang, Y.X.; Wang, H.W.; Brash, J.; Chen, H. Anti-fouling bioactive surfaces. Acta Biomater 2011, 7, 1550–1557. [Google Scholar]
- Li, Y.; Dong, M.D.; Otzen, D.E.; Yao, Y.H.; Liu, B.; Besenbacher, F.; Mamdouh, W. Influence of tunable external stimuli on the self-assembly of guanosine supramolecular nanostructures studied by Atomic Force Microscope. Langmuir 2009, 25, 13432–13437. [Google Scholar]
- Williamson, J.R.; Raghuraman, M.K.; Cech, T.R. Monovalent cation-induced structure of telomeric DNA: The G-quartet model. Cell 1989, 59, 871–880. [Google Scholar]
- Fukushima, K.; Iwahashi, H. 1:1 complex of guanine quartet with alkali metal cations detected by electrospray ionization mass spectrometry. Chem. Commun 2000, 11, 895–896. [Google Scholar]
- Moriwaki, H. Complexes of cadmium ion with guanine bases detected by electrospray ionization mass spectrometry. J. Mass Spectrom 2003, 38, 321–327. [Google Scholar]
- Sakamoto, S.; Nakatani, K.; Saito, I.; Yamaguchi, K. Formation and destruction of the guanine quartet in solution observed by cold-spray ionization mass spectrometry. Chem. Commun 2003, 6, 788–789. [Google Scholar]
- Vairamani, M.; Gross, M.L. G-quadruplex formation of thrombin-binding aptamer detected by electrospray ionization mass spectrometry. J. Am. Chem. Soc 2003, 125, 42–43. [Google Scholar]
- Davis, J.T. G-Quartets 40 years later: From 5′-GMP to molecular biology and supramolecular chemistry. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed 2004, 43, 668–698. [Google Scholar]
- Dong, M.D.; Hovgaard, M.B.; Xu, S.L.; Otzen, D.E.; Besenbacher, F. AFM study of glucagon fibrillation via oligomeric structures resulting in interwoven fibrils. Nanotechnology 2006, 17, 4003–4009. [Google Scholar]
- Ghosh, S.K.; Pal, T. Interparticle coupling effect on the surface plasmon resonance of gold nanoparticles: From theory to applications. Chem. Rev 2007, 107, 4797–4862. [Google Scholar]
- Glover, R.D.; Miller, J.M.; Hutchison, J.E. Generation of metal nanoparticles from silver and copper objects: Nanoparticle dynamics on surfaces and potential sources of nanoparticles in the environment. ACS Nano 2011, 5, 8950–8957. [Google Scholar]
- Wu, K.Y.; Chen, W.Y.; Hwang, J.; Wei, H.K.; Kou, C.S.; Lee, C.-Y.; Liu, Y.-L.; Huang, H.Y. Structure modification of highly ordered pyrolytic graphite by Ar plasma beam scanning at different incident angles. Appl. Phys. A Mater. Sci. Proc 2009, 95, 707–712. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, G.; Yang, D.; Sacher, E. X-ray photoelectron spectroscopic analysis of Pt nanoparticles on highly oriented pyrolytic graphite, using symmetric component line shapes. J. Phys. Chem. C 2007, 111, 565–570. [Google Scholar]
- Vesel, A.; Elersic, K.; Mozetic, M. Immobilization of protein streptavidin to the surface of PMMA polymer. Vacuum 2012, 86, 773–775. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, Z.J.; Xie, Y.B.; Liu, C.J. Synthesis and characterization of noble metal (Pd, Pt, Au, Ag) nanostructured materials confined in the channels of mesoporous SBA-15. J. Phys. Chem. C 2008, 112, 19818–19824. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, H.P.; Liu, C.J. Preparation and characterization of SBA-15 supported Pd catalyst for CO oxidation. Appl. Catal. B Environ 2011, 106, 672–680. [Google Scholar]
- Yang, D.-Q.; Sacher, E. Strongly enhanced interaction between evaporated Pt nanoparticles and functionalized multiwalled carbon nanotubes via plasma surface modifications: Effects of physical and chemical defects. J. Phys. Chem. C 2008, 112, 4075–4082. [Google Scholar]
- Allen, M.L.; Aronniemi, M.; Mattila, T.; Alastalo, A.; Ojanperä, K.; Suhonen, M.; Seppä, H. Electrical sintering of nanoparticle structures. Nanotechnology 2008, 19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nakasoa, K.; Shimadaa, M.; Okuyamaa, K.; Deppertb, K. Evaluation of the change in the morphology of gold nanoparticles during sintering. J. Aerosol Sci 2002, 33, 1061–1074. [Google Scholar]
- Hu, A.; Guo, J.Y.; Alarifi, H.; Patane, G.; Zhou, Y.; Compagnini, G.; Xu, C.X. Low temperature sintering of Ag nanoparticles for flexible electronics packaging. Appl. Phys. Lett. 2010, 97, 153117:1–153117:3. [Google Scholar]
- Magdassi, S.; Grouchko, M.; Berezin, O.; Kamyshny, A. Triggering the sintering of silver nanoparticles at room temperature. ACS Nano 2010, 4, 1943–1948. [Google Scholar]
- Chou, K.-S.; Huang, K.-C.; Lee, H.-H. Fabrication and sintering effect on the morphologies and conductivity of nano-Ag particle films by the spin coating method. Nanotechnology 2005, 16, 779–784. [Google Scholar]
- Sokołowska, A.; Szawłowski, J.; Frąckowiak, I.; Rudnicki, J.; Boruszewski, P.; Beer, P.; Olszyna, A. Plasma-chemical surface engineering of wood. J. Ach. Mater. Manuf. Eng 2009, 37, 694–697. [Google Scholar]
- Coutts, M.J.; Cortie, M.B.; Ford, M.J.; McDonagh, A.M. Rapid and controllable sintering of gold nanoparticle inks at room temperature using a chemical agent. J. Phys. Chem. C 2009, 113, 1325–1328. [Google Scholar]
- Chen, Y.; Palmer, R.E.; Wilcoxon, J.P. Sintering of passivated gold nanoparticles under the electron beam. Langmuir 2006, 22, 2851–2855. [Google Scholar]
- Green, N.M. The nature of the biotin-binding site. Biochem. J 1963, 89, 599–609. [Google Scholar]
- Green, N.M. Avidin. Adv. Protein Chem 1975, 29, 85–133. [Google Scholar]
- Wilchek, M.; Bayer, E.A. The avidin-biotin complex in bioanalytical applications. Anal. Biochem 1988, 171, 1–32. [Google Scholar]
- Wilchek, M.; Bayer, E.A. Avidin-biotin technology ten years on: Has it lived up to its expectations? Trends Biochem. Sci 1989, 14, 408–412. [Google Scholar]
- Livnah, O.; Bayer, E.A.; Wilchek, M.; Sussman, J.L. Three-dimensional structures of avidin and the avidin-biotin complex. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 1993, 90, 5076–5780. [Google Scholar]
- Weber, P.C.; Ohlendorf, D.H.; Wendoloski, J.J.; Salemme, F.R. Structural origins of high-affinity biotin binding to streptavidin. Science 1989, 243, 85–88. [Google Scholar]
- Hermanson, G.T. Bioconjugate Techniques, 1st ed; Academic Press: San Diego, CA, USA, 1996. [Google Scholar]
- Sperling, R.A.; Parak, W.J. Surface modification, functionalization and bioconjugation of colloidal inorganic nanoparticles. Phil. Trans. R. Soc. A 2010, 368, 1333–1383. [Google Scholar]
- Dechancie, J.; Houk, K.N. The origins of femtomolar protein-ligand binding: Hydrogen-bond cooperativity and desolvation energetics in the biotin-(strept)avidin binding site. J. Am. Chem. Soc 2007, 129, 5419–5429. [Google Scholar]
- Liang, X.; Wang, Z.J.; Liu, C.J. Size-controlled synthesis of colloidal gold nanoparticles at room temperature under the influence of glow discharge. Nanoscale Res. Lett 2010, 5, 124–129. [Google Scholar]
- Zou, J.J.; Zhang, Y.P.; Liu, C.J. Reduction of supported noble-metal ions using glow discharge plasma. Langmuir 2006, 22, 11388–11394. [Google Scholar]






© 2012 by the authors; licensee Molecular Diversity Preservation International, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open-access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/3.0/).
Share and Cite
Mamdouh, W.; Li, Y.; Shawky, S.M.; Azzazy, H.M.E.; Liu, C.-J. Influence of “Glow Discharge Plasma” as an External Stimulus on the Self-Assembly, Morphology and Binding Affinity of Gold Nanoparticle-Streptavidin Conjugates. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2012, 13, 6534-6547. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms13066534
Mamdouh W, Li Y, Shawky SM, Azzazy HME, Liu C-J. Influence of “Glow Discharge Plasma” as an External Stimulus on the Self-Assembly, Morphology and Binding Affinity of Gold Nanoparticle-Streptavidin Conjugates. International Journal of Molecular Sciences. 2012; 13(6):6534-6547. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms13066534
Chicago/Turabian StyleMamdouh, Wael, Yingzhi Li, Sherif M. Shawky, Hassan M. E. Azzazy, and Chang-Jun Liu. 2012. "Influence of “Glow Discharge Plasma” as an External Stimulus on the Self-Assembly, Morphology and Binding Affinity of Gold Nanoparticle-Streptavidin Conjugates" International Journal of Molecular Sciences 13, no. 6: 6534-6547. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms13066534
APA StyleMamdouh, W., Li, Y., Shawky, S. M., Azzazy, H. M. E., & Liu, C. -J. (2012). Influence of “Glow Discharge Plasma” as an External Stimulus on the Self-Assembly, Morphology and Binding Affinity of Gold Nanoparticle-Streptavidin Conjugates. International Journal of Molecular Sciences, 13(6), 6534-6547. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms13066534