Quantitative and Chemical Fingerprint Analysis for the Quality Evaluation of Isatis indigotica based on Ultra-Performance Liquid Chromatography with Photodiode Array Detector Combined with Chemometric Methods
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Results and Discussion
2.1. Optimization of UPLC Conditions
2.2. Optimization of Extraction Methods
2.3. Method Validation of Quantitative Analysis
2.3.1. Calibration Curves, LOD, and LOQ
2.3.2. Precision, Reproducibility, Stability, and Recovery
2.4. Sample Analysis
2.5. UPLC Fingerprint of Radix Isatidis
2.5.1. Similarity Analysis (SA)
2.5.2. Hierarchical Cluster Analysis (HCA)
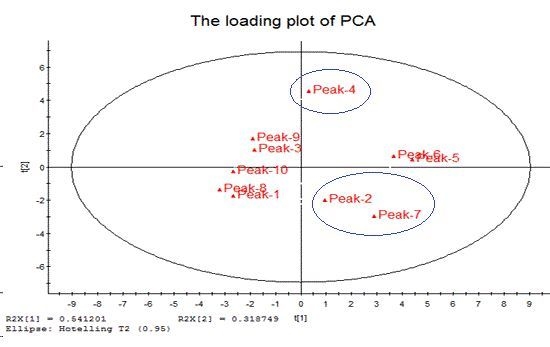
2.5.3. Principal Component Analysis (PCA)
3. Experimental Section
3.1. Materials, Reagents, and Chemicals
3.2. Instrumentation and Chromatographic Condition
3.3. Preparation of Standard Solution
3.4. Preparation of Sample Solution
3.5. Method Validation
3.6. Data Analysis
4. Conclusions
Acknowledgments
References
- Pharmacopoeia of People’s Republic of China, The State Pharmacopoeia Committee of People’s Republic of China; Chemical Industry Press: Beijing, China, 2010; Volume 1, pp. 20–21.
- State Administration of Traditional Chinese Medicine of the People’s Republic of China, Chinese Materia Medica (No.21); Shanghai Scientific & Technical Publishers: Shanghai, China, 1999.
- Wu, P.Y.; Wang, J.M. Botanical study on “Da Qing Ye”, “Ban Lan Gen” and “Qing Dai”. Acta Univer. Tradit. Med. Sin. Pharmacol. Shanghai 1996, 10, 50–52. [Google Scholar]
- Wu, Q.Z.; Wang, Y.L. Comparative analysis of chemical constituents in north-banlangen and south-banlangen. Strait Pharm. J 2007, 19, 82–83. [Google Scholar]
- Qin, H.Z.; Shi, B.; Li, S.Y.; Fan, X.J.; Song, D.Z.; Xian, H.M. Comparing research in Antiviral action of Rhizoma et Radix Baphicacanthis Cusiae and Radix Isatidis against a virus. Chin. Arch. Tradit. Chin. Med 2009, 27, 168–169. [Google Scholar]
- Xu, Y.S.; Sun, J.; He, S.Q. Effect of three kinds of Radix isatidis preparation on the expression of nucleoprotein of influenza virus. Shandong Med. J 2010, 50, 8. [Google Scholar]
- Liu, S.; Chen, W.S.; Qiao, C.Z.; Zheng, S.Q.; Zeng, M.; Zhang, H.M. Antiviral action of Radix Isatidis and Folium Isatidis from different germplasm against influenza A virus. Acad. J. Sec. Mil. Med. Univ 2000, 21, 204–206. [Google Scholar]
- Lin, C.W.; Tsai, F.J.; Tsai, C.H.; Lai, C.C.; Wan, L.; Ho, T.Y.; Hsieh, C.C.; Chao, P.D. Anti-SARS coronavirus 3C-like protease effects of Isatis indigotica root and plant-derived phenolic compounds. Antiviral Res 2005, 68, 36–42. [Google Scholar]
- Sun, H.H. Establishment of a Mouse Model for Pandemic H1N1 Influenza Virus and Study on Effect of Banlangen Granules on Mice Challenged with Pandemic H1N1 Influenza Virus; Peaking Union Medical College: Beijing, China, 2010; pp. 39–49. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, Y.T.; Yang, Z.F.; Zhao, H.S.; Qin, S.; Guan, W.D. Screening of anti-H1N1 active constituents from Radix Isatidis. J. Guangzhou Uni. Tradit. Chin. Med 2011, 28, 419–422. [Google Scholar]
- Sun, H.H.; Deng, W.; Zhan, L.J.; Xu, L.L.; Li, F.D.; Nv, Q.; Zhu, H. Effect of Banlangen Granules on mice challenged with a/California/7/2009. Chin. J. Comp. Med 2010, 20, 53–56. [Google Scholar]
- Cheng, Y.; Li, X.; Chen, J.W.; He, L.W.; Wang, Y.Y. A study on antiviral effects of the active parts from Radix Isatidis. J. Nanjing TCM Univ 2011, 27, 155–157. [Google Scholar]
- Ye, W.Y.; Li, Y.; Guo, J.W. Screening of 11 antiviral effect constituents from Radix Isatidis. J. Emerg. Tradit. Chin. Med 2011, 20, 1172–1774. [Google Scholar]
- Li, X.M. Remarkable progresses in studies on antiviral mechanism researches of Radix Isatidis (Baiyunshan, Guangdong). China News of TCM 2011, 8. [Google Scholar]
- Liu, S.Y. Tucking up veil the Antiviral causes of Radix Isatidis. China News of TCM 2011, A13. [Google Scholar]
- Liu, Y.H.; Wu, X.Y.; Fang, J.G.; Xie, W. Chemical constituents from Radix Isatidis. Cent. South Pharm 2003, 5, 302–305. [Google Scholar]
- Fang, J.G.; Wang, S.B.; Xu, H.; Liu, Y.H.; Liu, Y.W. Chemical constituents from Radix Isatidis. Chin. Tradit. Herb. Drugs 2004, 35, 845–846. [Google Scholar]
- He, L.W.; Li, X.; Chen, J.W.; Sun, D.D.; Ju, W.Z.; Wang, C.H. Chemical constituents from water extract of Radix isatidis. Acta Pharm. Sin 2006, 41, 1193–1196. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, Y.Y.; Li, X.; Chen, J.W.; Chen, Y.; Wang, S. Study on Chemical constituents from water extract of Radix isatidis. Res. Pract. Chin. Med 2009, 23, 54–56. [Google Scholar]
- Lee, K.C.; Cheuk, M.W.; Chan, W. Determination of glucosinolates in traditional Chinese herbs by high-performance liquid chromatography and electrospray ionization mass spectrometry. Anal. Bioanal. Chem 2006, 386, 2225–2232. [Google Scholar]
- Xu, L.H.; Huang, F.; Chen, T.; Wu, J. Antivirus constituents of radix of Isatidis indigotica. Chin. J. Nat. Med 2005, 3, 359–360. [Google Scholar]
- Deng, X.Y.; Gao, G.H.; Zheng, S.N.; Li, F.M. Qualitative and quantitative of flavonoids in the leaves of Isatis indigatica Fort. by ultra-performance liquid chromatography with PDA and electrospray ionization tandem mass spectrometry detection. J. Pharm. Biomed. Anal 2008, 48, 562–567. [Google Scholar]
- Ye, W.T.; Ou-Yang, H.F.; Li, X.L. Study on quality standard of CO Banlangen Granules. Clin. Med. Eng 2010, 4, 51–52. [Google Scholar]
- Kong, W.J.; Zhao, Y.L.; Shan, L.M.; Xiao, X.H.; Guo, W.Y. Investigation on the spectrum-effect relationships of ETOAc extract from Radix isatidis based on HPLC fingerprints and microcalorimetry. J. Chromatogr. B 2008, 1, 109–144. [Google Scholar]
- Kong, W.J.; Zhao, Y.L.; Shan, L.M.; Xiao, X.H.; Guo, W.Y. Thermochemical studies on the quantity-antibacterial effect relationship of four organic Accids from Radix Isatidis on Escherichia coli growth. Biol. Pharm. Bull 2008, 31, 1301–1305. [Google Scholar]
- Kong, W.J.; Zhao, Y.L.; Shan, L.M.; Xiao, X.H.; Guo, W.Y.; Wang, J.B. Determination of salicylic acid in total acid extraction of Radix Isatidis by HPLC. Cent. South Pharm 2008, 2, 137–140. [Google Scholar]
- Fan, L.F.; Zhang, L.T.; Yuan, Z.F.; Xu, H.J.; He, W. HPLC determination the contents of indigo and indirubin in Radix Isatidis. Chin. J. Pharm. Anal 2008, 4, 540–543. [Google Scholar]
- Na, G.X.; Fang, P. Research overview in degradation of glucosinolates. Food Sci 2008, 29, 350–354. [Google Scholar]
- Hashem, F.A.; Saleh, M.M. Antimicrobial components of some cruciferae plants (Diplotaxis harra Forsk. and Erucaria microcarpa Boiss.). Phytother. Res 1999, 13, 329–332. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, R.; Yang, H.Y.; Yang, Q.W. Study on quality standard of Isatidis Radix. Chin. Tradit. Herb. Drug 2010, 41, 478–480. [Google Scholar]
- Xie, Z.Y.; Shi, Y.H.; Wang, Z.T.; Wang, R.; Li, Y.M. Biotransformation of glucosinolates epiprogoitrin and progoitrin to (R)- and (S)-goitrin in Radix isatidis. J. Agric. Food. Chem 2011, 59, 12467–12472. [Google Scholar]
- Zhou, W.; Xie, M.F.; Zhang, X.Y.; Liu, T.T.; Duan, G.L. Improved liquid chromatography fingerprint of fat-soluble Radix Isatidis extract using multi-wavelength combination technique. J. Sep. Sci 2011, 34, 1123–1132. [Google Scholar]
- Xiao, X.; Luo, G.A.; Wang, Y.M. Fingerprints of Isatidis Radix by HPLC. J. Jiangxi Univ. TCM 2010, 22, 67–69. [Google Scholar]
- Zou, P.; Hong, Y.; Koh, H.L. Chemical fingerprinting of Isatis Indigatica root by RP-HPLC and Hierarchical clustering analysis. J. Pharm. Biomed. Anal 2005, 38, 514–520. [Google Scholar]
- Shi, Y.H.; Xie, Z.Y.; Wu, Y.C.; Li, Y.M.; Wang, R.; Wang, Z.T. Determination of R,S-goitrin of Banlangen preparations by RP-HPLC. Chin. J. Exp. Tradit. Med. Form 2010, 17, 144–146. [Google Scholar]
- Tang, D.Q.; Yang, D.Z.; Tang, A.B.; Gao, Y.Y.; Jiang, X.G.; Mou, J.; Yin, X.X. Simultaneous chemical fingerprint and quantitative analysis of Ginkgo biloba extract by HPLC-DAD. Anal. Bioanal. Chem 2010, 396, 3087–3095. [Google Scholar]
- Wei, H.; Sun, L.N.; Tai, Z.G.; Gao, S.H.; Xu, W.; Chen, W.S. A simple and sensitive HPLC method for the simultaneous determination of 8 bioactive components and fingerprint analysis of Schisandra sphenanthera. Anal. Chim. Acta 2010, 662, 97–104. [Google Scholar]
- Jin, X.F.; Lu, Y.H.; Wei, D.Z.; Wang, Z.T. Chemical fingerprint and quantitative analysis of Salvia plebeian R.Br. by high-performance liquid chromatography. J. Pharm. Biomed. Anal 2008, 48, 100–104. [Google Scholar]
- Li, Y.; Wu, T.; Zhu, J.J.; Wan, L.L.; Yu, Q.; Li, X.X.; Cheng, Z.Z.; Guo, C. Combinative method using HPLC fingerprint and quantitative analyses for quality consistency evaluation of an herbal medicinal preparation produced by different manufactures. J. Pharm. Biomed. Anal 2010, 52, 597–602. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, Y.X.; Li, Q.; Wang, Q.; Li, Y.J.; Ling, J.H.; Liu, L.L.; Chen, X.H.; Bi, K.S. Simultaneous determination of seven bioactive components in Oolong Tea Camellia sinensis: Quality control by chemical composition and HPLC fingerprints. J. Agric. Food Chem 2012, 60, 256–260. [Google Scholar]
- Wu, Q.Y.; Zhou, Y.; Jin, X.; Guan, Y.; Xu, M.; Liu, L.F. Chromatographic fingerprint and the simultaneous determination of five bioactive components of Geranium carolinianum L. water extract by high performance liquid chromatography. Int. J. Mol. Sci 2011, 12, 8740–8749. [Google Scholar]







| Compound | Regression equation (Y = ax + b) a | R b | Linear range (μg mL−1) | LOD a (μg mL−1) | LOQ b (μg mL−1) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Hypoxanthine | Y = 914.32x − 684.64 | 0.9999 | 6.50–130.00 | 0.015 | 0.049 |
| Uridine | Y = 1945.9x + 263.11 | 0.9999 | 4.12–82.40 | 0.012 | 0.041 |
| Adenosine | Y = 6870.2x − 3669.6 | 0.9999 | 4.26–85.20 | 0.005 | 0.017 |
| Guanosine | Y = 12618x − 1461.7 | 1.0000 | 3.90–78.00 | 0.017 | 0.045 |
| Progoitrin | Y = 2579.2x − 886.87 | 0.9997 | 2.30–34.50 | 0.563 | 1.875 |
| Epiprogoitrin | Y = 4336.8x − 68.733 | 0.9998 | 2.30–34.50 | 0.708 | 2.100 |
| R,S-goitrin | Y = 1756.6x − 757.89 | 1.0000 | 4.50–90.00 | 0.014 | 0.045 |
| Gluconapin | Y = 1865.8x − 240.44 | 0.9999 | 2.05–30.75 | 0.456 | 1.640 |
| Compound | Precision RSD (%) (n = 6) | Reproducibility RSD (%) (n = 6) | Stability RSD (%) (n = 6) | Recovery (%) (n = 9) Mean ± RSD (%) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Hypoxanthine | 0.15 | 0.46 | 0.22 | 101.5 ± 1.63 |
| Uridine | 0.18 | 0.10 | 0.39 | 101.2 ± 1.33 |
| Adenosine | 0.07 | 0.61 | 0.49 | 101.1 ± 1.11 |
| Guanosine | 0.12 | 1.24 | 1.30 | 100.9 ± 1.72 |
| Progoitrin | 0.11 | 0.19 | 0.24 | 99.5 ± 1.81 |
| Epiprogoitrin | 0.11 | 1.92 | 1.44 | 100.2 ± 1.73 |
| R,S-goitrin | 0.48 | 0.72 | 0.91 | 100.4 ± 0.73 |
| Gluconapin | 0.31 | 0.33 | 0.48 | 103.0 ± 1.14 |
| Name | No.a | Content b (mg g−1) | ||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 c | 2 | 3 | 4 | 5 | 6 | 7 | 9 | Total | ||
| Prepared slices | S-01 | 0.137 | 0.414 | 5.938 | 6.605 | 0.492 | 0.525 | 0.776 | 4.051 | 18.937 |
| S-02 | 0.022 | 0.279 | 1.529 | 1.500 | 0.293 | 0.377 | 0.899 | 0.870 | 5.768 | |
| S-03 | 0.042 | 0.436 | 2.389 | 2.094 | 0.343 | 0.465 | 0.789 | 1.210 | 7.767 | |
| S-04 | 0.024 | 0.283 | 2.465 | 2.293 | 0.342 | 0.336 | 0.414 | 1.190 | 7.347 | |
| S-05 | 0.019 | 0.278 | 3.331 | 3.355 | 0.347 | 0.345 | 0.551 | 1.977 | 10.203 | |
| S-06 | 0.037 | 0.416 | 1.178 | 1.413 | 0.372 | 0.424 | 0.732 | 0.401 | 4.974 | |
| S-07 | 0.021 | 0.384 | 1.416 | 1.750 | 0.336 | 0.347 | 0.483 | 0.574 | 5.310 | |
| S-08 | 0.336 | 0.345 | 1.950 | 2.441 | 0.348 | 0.379 | 0.436 | 0.501 | 6.735 | |
| Crude herbs | S-09 | 0.056 | 0.083 | 5.929 | 6.605 | 0.114 | 0.095 | 0.057 | 10.020 | 22.959 |
| S-10 | 0.022 | 0.057 | 7.345 | 6.565 | 0.127 | 0.132 | 0.083 | 9.458 | 23.790 | |
| S-11 | 0.028 | 0.070 | 5.286 | 6.424 | 0.120 | 0.116 | 0.070 | 10.130 | 22.244 | |
| S-12 | 0.035 | 0.084 | 3.934 | 5.660 | 0.124 | 0.137 | 0.123 | 7.235 | 17.333 | |
| S-13 | 0.048 | 0.057 | 6.396 | 6.534 | 0.105 | 0.135 | 0.062 | 6.747 | 20.084 | |
| S-14 | 0.040 | 0.059 | 5.507 | 6.253 | 0.122 | 0.327 | 0.084 | 9.611 | 22.003 | |
| S-15 | 0.033 | 0.070 | 6.628 | 5.713 | 0.105 | 0.207 | 0.054 | 5.498 | 18.309 | |
| Granules | S-16 | N.D. d | 0.045 | N.D. | N.D. | 0.006 | 0.008 | 0.085 | 0.330 | 0.473 |
| S-17 | 0.004 | 0.022 | N.D. | N.D. | N.D. | N.D. | 0.027 | 0.094 | 0.147 | |
| S-18 | N.D. | 0.058 | N.D. | N.D. | 0.003 | 0.005 | 0.075 | 0.576 | 0.716 | |
| S-19 | N.D. | 0.021 | N.D. | N.D. | 0.001 | N.D. | 0.033 | 0.100 | 0.154 | |
| S-20 | 0.006 | 0.061 | N.D. | N.D. | 0.007 | 0.006 | 0.087 | 0.515 | 0.681 | |
| S-21 | 0.036 | 0.053 | N.D. | 0.102 | 0.012 | 0.010 | 0.067 | 0.169 | 0.448 | |
| Name | No. | Batch No. | Resource | Origins | Similarity |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Prepared Slices | S-01 | 20101121 | Anhui | Isatis indigotica Fort. | 0.991 |
| S-02 | 101001 | Anhui | Isatis indigotica Fort. | 0.933 | |
| S-03 | 8100182 | Anhui | Isatis indigotica Fort. | 0.948 | |
| S-04 | 100709 | Anhui | Isatis indigotica Fort. | 0.947 | |
| S-05 | 20110213 | Jiangsu | Isatis indigotica Fort. | 0.967 | |
| S-06 | 100713 | Mongolia | Isatis indigotica Fort. | 0.954 | |
| S-07 | 100602 | Mongolia | Isatis indigotica Fort. | 0.954 | |
| S-08 | 101120 | Zhejiang | Isatis indigotica Fort. | 0.967 | |
| Crude herbs | S-09 | 20110224-1 | Shanghai | Isatis indigotica Fort. | 0.777 |
| S-10 | 20110224-2 | Shanghai | Isatis indigotica Fort. | 0.774 | |
| S-11 | 20110224-3 | Shanghai | Isatis indigotica Fort. | 0.752 | |
| S-12 | 20080902 | Harbin | Isatis indigotica Fort. | 0.759 | |
| S-13 | blg-081020 | Henan | Isatis indigotica Fort. | 0.818 | |
| S-14 | 20110205 | Anhui | Isatis indigotica Fort. | 0.820 | |
| S-15 | 20081017 | Hebei | Isatis indigotica Fort. | 0.811 | |
| Granule | S-16 | 090921 | Shanghai | - | - |
| S-17 | 100302 | Shanghai | - | - | |
| S-18 | A0F090 | Guangzhou | - | - | |
| S-19 | L9F043 | Guangzhou | - | - | |
| S-20 | 100303 | Sichuan | - | - | |
| S-21 | 100702 | Sichuan | - | - | |
| Nan-Banlangen | S-22 | 060308-1 | Jiangxi | Baphicacanthus eusia (Nees) Bremek. | - |
| S-23 | 1678-3 | Guizhou | Baphicacanthus eusia (Nees) Bremek. | - | |
| S-24 | 20110923 | Fujian | Baphicacanthus eusia (Nees) Bremek. | - | |
| S-25 | 20111025 | Fujian | Baphicacanthus eusia (Nees) Bremek. | - | |
© 2012 by the authors; licensee Molecular Diversity Preservation International, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open-access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/3.0/).
Share and Cite
Shi, Y.-H.; Xie, Z.-Y.; Wang, R.; Huang, S.-J.; Li, Y.-M.; Wang, Z.-T. Quantitative and Chemical Fingerprint Analysis for the Quality Evaluation of Isatis indigotica based on Ultra-Performance Liquid Chromatography with Photodiode Array Detector Combined with Chemometric Methods. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2012, 13, 9035-9050. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms13079035
Shi Y-H, Xie Z-Y, Wang R, Huang S-J, Li Y-M, Wang Z-T. Quantitative and Chemical Fingerprint Analysis for the Quality Evaluation of Isatis indigotica based on Ultra-Performance Liquid Chromatography with Photodiode Array Detector Combined with Chemometric Methods. International Journal of Molecular Sciences. 2012; 13(7):9035-9050. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms13079035
Chicago/Turabian StyleShi, Yan-Hong, Zhi-Yong Xie, Rui Wang, Shan-Jun Huang, Yi-Ming Li, and Zheng-Tao Wang. 2012. "Quantitative and Chemical Fingerprint Analysis for the Quality Evaluation of Isatis indigotica based on Ultra-Performance Liquid Chromatography with Photodiode Array Detector Combined with Chemometric Methods" International Journal of Molecular Sciences 13, no. 7: 9035-9050. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms13079035
APA StyleShi, Y. -H., Xie, Z. -Y., Wang, R., Huang, S. -J., Li, Y. -M., & Wang, Z. -T. (2012). Quantitative and Chemical Fingerprint Analysis for the Quality Evaluation of Isatis indigotica based on Ultra-Performance Liquid Chromatography with Photodiode Array Detector Combined with Chemometric Methods. International Journal of Molecular Sciences, 13(7), 9035-9050. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms13079035