Asymmetric Dimethylarginine, Endothelial Dysfunction and Renal Disease
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Nitric Oxide and the Kidney
- Reduced glomerular blood flow, together with an increase in the vascular resistance of the afferent and efferent arterioles;
- Reduced ultrafiltration, renal blood flow and glomerular filtration rate (GFR);
- Decreased secretion of renin, a hormone involved in the sodium and water balance in the body;
- Reduced ability to excrete sodium under normal conditions;
- Increased blood pressure and deterioration in renal function;
- Lack of stimulation for Na+ and HCO3− transport in the nephron proximal tubules mediated by cGMP;
- Production of oxygen reactive species;
- Production of nitric peroxide when exposed to superoxide anions.
2.1. Endothelial Dysfunction and Oxidative Stress in Kidney Disease
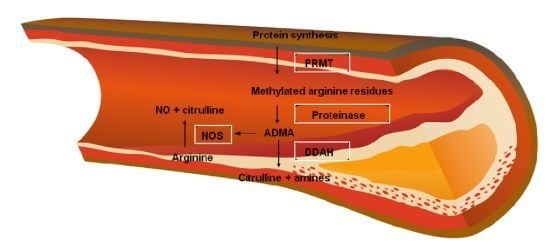
2.2. Arginine-Nitric Oxide Metabolism
3. ADMA as a Cardiovascular Risk Factor
Relationship between ADMA and Homocysteine (Role of the DDAH Enzyme)
4. Asymmetric Dimethylarginine in Kidney Disease
- Higher levels of protein methylation;
- Increased rate of protein turnover;
- Impaired activity of DDAH, which degrades ADMA;
- Impaired renal excretion.
4.1. Asymmetric Dimethylarginine and Proteinuria
4.2. Asymmetric Dimethlylarginine after Renal Transplantation
5. Treatments to Reduce ADMA Levels
5.1. Statins
5.2. Arginine
6. Conclusions
Acknowledgements
Abbreviations
| ADMA | asymmetric dimethylarginine |
| Arg | l-arginine |
| cGMP | cyclic guanosine monophosphate |
| Citr | citrulline |
| cNOS | constitutive nitric oxide synthase |
| CRP | C reactive protein |
| DDAH | dimethylarginine dimethylaminohydrolase |
| eNOS | endothelial nitric oxide synthase |
| GFR | glomerular filtration rate |
| Hcys | homocysteine |
| iNOS | inducible oxide nitric synthase |
| LDL | low density lipoproteins |
| NMMA | N-monomethyl-l-arginine |
| nNOS | neuronal oxide nitric synthase |
| NO | nitric oxide |
| NOS | nitric oxide synthase |
| PRMT | protein arginine methyltransferase |
| RTx | renal transplantation |
| SDMA | symmetric dimethylarginine |
References
- Clarke, R.; Daly, L.; Robinson, K.; Naughten, E.; Cahalane, S.; Fowler, B.; Graham, I. Hyperhomocysteinemia: An independent risk factor for vascular disease. N. Engl. J. Med 1991, 324, 1149–1155. [Google Scholar]
- Aldámiz-Echevarria, L.; Sanjurjo, P.; Vallo, A.; Aquino, L.; Perez-Nanclares, G.; Gimeno, P.; Rueda, M.; Ruiz, I.; Urreizti, R.; Rodriguez-Soriano, J. Hyperhomocysteinemia in children with renal transplants. Pediatr. Nephrol 2002, 17, 718–723. [Google Scholar]
- Nitsch, D.D.; Ghilardi, N.; Muhl, H.; Nitsch, C.; Brune, B.; Pfeilschifter, J. Apoptosis and expression of inducible nitric oxide synthase are mutually exclusive in renal mesangial cell. Am. J. Pathol 1997, 150, 889–900. [Google Scholar]
- Tojo, A.; Welch, W.J.; Bremen, V.; Kimoto, M.; Kimura, K.; Omata, M.; Ogawa, T.; Vallance, P.; Wilcox, C.S. Colocalization of demethylating enzymes and NOS and functional effects of methylarginines in rat kidney. Kidney Int 1997, 52, 1593–1601. [Google Scholar]
- Holmqvist, B.; Olsson, C.F.; Svensson, M.L.; Svanborg, C.; Forsell, J.; Alm, P. Expression of nitric oxide synthase isoforms in the mouse kidney: Cellular localization and influence by lipopolysaccharide and Toll-like receptor 4. J. Mol. Histol 2005, 36, 499–516. [Google Scholar]
- Morrisey, J.J.; McCracken, R.; Kaneto, H.; Vehaskari, M.; Montani, D.; Klahr, S. Location of an inducible nitric oxide synthase mRNA in the normal kidney. Kidney Int 1994, 45, 998–1005. [Google Scholar]
- Raij, L.; Shultz, P.J. Endothelium-Derived relaxing factor, nitric oxide: Effects on and production by mesangial cells and glomerulus. J. Am. Soc. Nephrol 1993, 3, 1435–1441. [Google Scholar]
- Perticone, F.; Maio, R.; Perticone, M.; Sciacqua, A.; Shehaj, E.; Naccarato, P.; Sesti, G. Endothelial dysfunction and subsequent decline in glomerular filtration rate in hypertensive patients. Circulation 2010, 122, 379–384. [Google Scholar]
- Crespo, M.; Campistol, J.M. Disfunción endotelial en transplante renal. Nefrología 2003, 23, 52–58. [Google Scholar]
- Caló, L.A.; Dall’ Amico, R.; Pagnin, E.; Bertipaglia, L.; Zacchello, G.; Davis, P.A. Oxidative stress and post-transplant hypertension in pediatric kidney-transplanted patients. J. Pediatr 2006, 149, 53–57. [Google Scholar]
- Sahin, G.; Akay, O.M.; Bal, C.; Yalcin, A.U.; Gulbas, Z. The effect of calcineurin inhibitors on endothelial and platelet function in renal transplant patients. Clin. Nephrol 2011, 76, 218–225. [Google Scholar]
- Trapp, A.; Weis, M. The impact of immunosuppression on endothelial function. J. Cardiovasc. Pharmacol 2005, 45, 81–87. [Google Scholar]
- Morris, S.T.; McMurray, J.J.V.; Rodger, R.S.; Farmer, R.; Jardine, A.G. Endothelial dysfunction in renal transplant recipients maintained on cyclosporine. Kidney Int 2000, 57, 1100–1106. [Google Scholar]
- Schmidt, R.J.; Yokota, S.; Tracy, T.S.; Sorkin, M.I.; Baylis, C. Nitric oxide production is low in end-stage renal disease patients on peritoneal dialysis. Am. J. Physiol 1999, 276, 794–797. [Google Scholar]
- Loscalzo, J. l-Arginine and atherothrombosis. J. Nutr 2004, 134, 2798S–2800S. [Google Scholar]
- Vallance, P.; Leiper, J. Cardiovascular biology of the asymmetric dimethylarginine: Dimethylarginine dimethylaminohydrolase pathway. Arterioescler. Thromb. Vasc. Biol 2004, 24, 1023–1030. [Google Scholar]
- Böger, R.H.; Sydow, K.; Borlak, J.; Thum, T.; Lenzen, H.; Schubert, B.; Tsikas, D.; Bode-Boger, S.M. LDL cholesterol upregulates synthesis of asymmetrical dimethylarginine in human endothelial cells: Involvement of S-adenosylmethionine-dependent methyltransferases. Circ. Res 2000, 87, 99–105. [Google Scholar]
- Tojo, A.; Welch, W.J.; Bremer, V.; Kimoto, M.; Kimura, K.; Omata, M.; Ogawa, T.; Vallance, P.; Wilcox, C.S. Colocalization of demethylating enzymes and NOS and functional effects of methylarginines in rat kidney. Kidney Int 1997, 52, 1593–1601. [Google Scholar]
- Kielstein, J.T.; Salpeter, S.R.; Bode-Boeger, S.M.; Cooke, J.P.; Fliser, D. Symmetric dimethylarginine (SDMA) as endogenous marker of renal function—A meta-analysis. Nephrol. Dial. Transpl 2006, 21, 2446–2451. [Google Scholar]
- Kielstein, J.T.; Zoccali, C. Asymmetric dimethylarginine: A novel marker of risk and a potential target for therapy in chronic kidney disease. Curr. Opin. Nephrol. Hypertens 2008, 17, 609–615. [Google Scholar]
- Kiechl, S.; Lee, T.; Santer, P.; Thompson, G.; Tsimikas, S.; Egger, G.; Holt, D.W.; Willeit, J.; Xu, Q.; Mayr, M. Asymmetric and symmetric dimethylarginines are of similar predictive value for cardiovascular risk in the general population. Atherosclerosis 2009, 205, 261–265. [Google Scholar]
- Oner-Iyidogan, Y.; Oner, P.; Kocak, H.; Gurdol, F.; Bekpinar, S.; Unlucerci, Y.; Caliskan, Y.; Cetinalp-Demircan, P.; Kocak, T.; Turkmen, A. Dimethylarginines and inflammation markers in patients with chronic kidney disease undergoing dialysis. Clin. Exp. Med 2009, 9, 235–241. [Google Scholar]
- Schepers, E.; Barreto, D.V.; Liabeuf, S.; Glorieux, G.; Eloot, S.; Barreto, F.C.; Massy, Z.; Vanholder, R. European Uremic Toxin Work Group (EUTox). Symmetric dimethylarginine as a proinflammatory agent in chronic kidney disease. Clin. J. Am. Soc. Nephrol 2011, 6, 2374–2383. [Google Scholar]
- Brooks, E.R.; Langman, C.B.; Wang, S.; Price, H.E.; Hodges, A.L.; Darling, L.; Yang, A.Z.; Smith, F.A. Methylated arginine derivatives in children and adolescents with chronic kidney disease. Pediatr. Nephrol 2009, 24, 129–134. [Google Scholar]
- Bode-Böger, S.M.; Scalera, F.; Kielstein, J.T.; Martens-Lobenhoffer, J.; Breithardt, G.; Fobker, M.; Reinecke, H. Symmetrical dimethylarginine: A new combined parameter for renal function and extent of coronary artery disease. J. Am. Soc. Nephrol 2006, 17, 1128–1134. [Google Scholar]
- Schepers, E.; Glorieux, G.; Dou, L.; Cerini, C.; Gayrard, N.; Louvet, L.; Maugard, C.; Preus, P.; Rodriguez-Ortiz, M.; Argiles, A.; et al. European Uremic Toxin Work Group (EUTox). Guanidino compounds as cause of cardiovascular damage in chronic kidney disease: An in vitro evaluation. Blood Purif 2010, 30, 277–287. [Google Scholar]
- Nijveldt, R.J.; Teerlink, T.; van Guldener, C.; Prins, H.A.; van Lambalgen, A.A.; Stehouwer, C.D.; Rauwerda, J.A.; van Leeuwen, P.A. Handling of asymmetrical dimethylarginine and symmetrical dimethylarginine by the rat kidney under basal conditions and during endotoxaemia. Nephrol. Dial. Transpl 2003, 18, 2542–2550. [Google Scholar]
- Leiper, J.M.; Santa María, J.; Chubb, A.; MacAllister, R.J.; Charles, I.G.; Whitley, G.S.; Vallance, P. Identification of two human dimethylarginine dimethylaminohydrolases with distinct tissue distributions and homology with microbial arginine deiminases. Biochem. J 1999, 343, 209–214. [Google Scholar]
- Torondel, B.; Nandi, M.; Kelly, P.; Wojciak-Stothard, B.; Fleming, I.; Leiper, J. Adenoviral-Mediated overexpression of DDAH improves vascular tone regulation. Vasc. Med 2010, 15, 205–213. [Google Scholar]
- Sydow, K.; Fortmann, S.P.; Fair, J.M.; Varady, A.; Hlatky, M.A.; Go, A.S.; Iribarren, C.; Tsao, P.S. ADVANCE Investigators. Distribution of asymmetric dimethylarginine among 980 healthy, older adults of different ethnicities. Clin. Chem 2010, 56, 111–120. [Google Scholar]
- Perticone, F.; Sciacqua, A.; Maio, R.; Perticone, M.; Galiano Leone, G.; Bruni, R.; Di Cello, S.; Pascale, A.; Talarico, G.; Greco, L.; et al. Endothelial dysfunction, ADMA and insulin resistance in essential hypertension. Int. J. Cardiol 2010, 142, 236–241. [Google Scholar]
- Wilcken, D.E.; Sim, A.S.; Wang, J.; Wang, X.L. Asymmetric dimethylarginine (ADMA) in vascular, renal and hepatic disease and the regulatory role of l-arginine on its metabolism. Mol. Genet. Metab 2007, 91, 309–317. [Google Scholar]
- Sibal, L.; Agarwal, S.C.; Home, P.D.; Boger, R.H. The role of asymmetric dimethylarginine (adma) in endothelial dysfunction and cardiovascular disease. Curr. Cardiol. Rev 2010, 6, 82–90. [Google Scholar]
- Cardounel, A.J.; Cui, H.; Samouilov, A.; Johnson, W.; Kearns, P.; Tsai, A.L.; Berka, V.; Zweier, J.L. Evidence for the pathophysiological role of endogenous methylarginines in regulation of endothelial NO production and vascular function. J. Biol. Chem 2007, 282, 879–887. [Google Scholar]
- Böger, R.H. Asymmetric dimethylarginine (ADMA): A novel risk marker in cardiovascular medicine and beyond. Ann. Med 2006, 38, 126–136. [Google Scholar]
- Bermúdez, V.; Bermúdez, F.; Acosta, G.; Acosta, A.; Añez, J.; Andara, C.; Leal, E.; Cano, C.; Manuel, V.; Hernández, R.; et al. Molecular mechanisms of endothelial dysfunction: From nitric oxide synthesis to ADMA inhibition. Am. J. Ther 2008, 15, 326–333. [Google Scholar]
- Laakso, M. Hyperglycemia and cardiovascular disease in type 2 diabetes. Diabetes 1999, 48, 937–942. [Google Scholar]
- Miyazaki, H.; Matsuoka, H.; Cooke, J.P.; Usui, M.; Ueda, S.; Okuda, S.; Imaizumi, T. Endogenous nitric oxide synthase inhibitor: A novel marker of atherosclerosis. J. Cardiol 1999, 33, 105–106. [Google Scholar]
- Stühlinger, M.C.; Abbasi, F.; Chu, J.W.; Lamendola, C.; McLaughlin, T.L.; Cooke, J.P.; Reaven, G.M.; Tsao, P.S. Relationship between insulin resistance and an endogenous nitric oxide synthase inhibitor. JAMA J. Am. Med. Assoc 2002, 287, 1420–1426. [Google Scholar]
- Tarnow, L.; Hovind, P.; Teerlink, T.; Stehouwer, C.D.; Parving, H.H. Elevated plasma asymmetric dimethylarginine as a marker of cardiovascular morbidity in early diabetic nephropathy in type 1 diabetes. Diabetes Care 2004, 27, 765–769. [Google Scholar]
- Andreozzi, F.; Presta, I.; Mannino, G.C.; Scarpelli, D.; Di Silvestre, S.; Di Pietro, N.; Succurro, E.; Sciacqua, A.; Pandolfi, A.; Consoli, A.; et al. A functional variant of the dimethylarginine dimethylaminohydrolase-2 gene is associated with insulin sensitivity. PLoS One 2012, 7, e36224. [Google Scholar]
- Goonasekera, C.D.; Rees, D.D.; Woolard, P.; Frend, A.; Shah, V.; Dillon, M.J. Nitric oxide synthase inhibitors and hypertension in children and adolescents. J. Hypertens 1997, 15, 901–909. [Google Scholar]
- Ueda, S.; Yamagishi, S.; Kaida, Y.; Okuda, S. Asymmetric dimethylarginine may be a missing link between cardiovascular disease and chronic kidney disease. Nephrology 2007, 12, 582–590. [Google Scholar]
- Mallamaci, F.; Zoccali, C. Clinical implications of elevated asymmetric dimethylarginine in chronic kidney disease and end-stage renal disease. J. Ren. Nutr 2009, 19, 25–28. [Google Scholar]
- Alsagaff, M.Y.; Thaha, M.; Aminuddin, M.; Yogiarto, R.M.; Yogiantoro, M.; Tomino, Y. Asymmetric dimethylarginine: A novel cardiovascular risk factor in end-stage renal disease. J. Int. Med. Res 2012, 40, 340–349. [Google Scholar]
- Stühlinger, M.C.; Tsao, P.S.; Her, J.H.; Kimoto, M.; Balint, R.F.; Cooke, J.P. Homocysteine impairs the nitric oxide synthase pathway: Role of asymmetric dimethylarginine. Circulation 2001, 104, 2569–2575. [Google Scholar]
- Lu, T.M.; Ding, Y.A.; Leu, H.B.; Yin, W.H.; Sheu, W.H.; Chu, K.M. Effect of rosuvastatin on plasma levels of asymmetric dimethylarginine in patients with hypercholesterolemia. Am. J. Cardiol 2004, 94, 157–161. [Google Scholar]
- Hasanošlu, A.; Okur, I.; Oren, A.C.; Biberošlu, G.; Oktar, S.; Eminošlu, F.T.; Tümer, L. The levels of asymmetric dimethylarginine, homocysteine and carotid intima-media thickness in hypercholesterolemic children. Turk. J. Pediatr 2011, 53, 522–527. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, W.Z.; Venardos, K.; Chin-Dusting, J.; Kaye, D.M. Adverse effects of cigarette smoke on NO bioavailability: Role of arginine metabolism and oxidative stress. Hypertension 2006, 48, 278–485. [Google Scholar]
- Napora, M.; Graczykowska, A.; Próchniewska, K.; Zdrojewski, Z.; Całka, A.; Górny, J.; Stompór, T. Relationship between serum asymmetric dimethylarginine and left ventricular structure and function in patients with end-stage renal disease treated with hemodialysis. Pol. Arch. Med. Wewn 2012, 122, 226–234. [Google Scholar]
- Zoccali, C.; Mallamaci, F.; Maas, R.; Benedetto, F.A.; Tripepi, G.; Malatino, L.S.; Cataliotti, A.; Bellanuova, I.; Böger, R. Left ventricular hypertrophy, cardiac remodeling and asymmetric dimethylarginine (ADMA) in hemodialysis patients. Kidney Int 2002, 62, 339–345. [Google Scholar]
- Shi, B.; Ni, Z.; Zhou, W.; Yu, Z.; Gu, L.; Mou, S.; Fang, W.; Wang, Q.; Cao, L.; Yan, Y.; et al. Circulating levels of asymmetric dimethylarginine are an independent risk factor for left ventricular hypertrophy and predict cardiovascular events in pre-dialysis patients with chronic kidney disease. Eur. J. Intern. Med 2010, 21, 444–448. [Google Scholar]
- Chen, Y.; Li, Y.; Zhang, P.; Traverse, J.H.; Hou, M.; Xu, X.; Kimoto, M.; Bache, R.J. Dimethylarginine dimethylaminohydrolase and endothelial dysfunction in failing hearts. Am. J. Physiol. Heart. Circ. Physiol 2005, 289, 2212–2219. [Google Scholar]
- Notsu, Y.; Nabika, T.; Bokura, H.; Suyama, Y.; Kobayashi, S.; Yamaguchi, S.; Masuda, J. Evaluation of asymmetric dimethylarginine and homocysteine in microangiopathy-related cerebral damage. Am. J. Hypertens 2009, 22, 257–262. [Google Scholar]
- Lang, D.; Kredan, M.B.; Moat, S.J.; Hussain, S.A.; Powell, C.A.; Bellamy, M.F.; Powers, H.J.; Lewis, M.J. Homocysteine-induced inhibition of endothelium-dependent relaxation in rabbit aorta: Role for superoxide anions. Arterioscler. Thromb. Vasc. Biol 2000, 20, 422–427. [Google Scholar]
- Dayal, S.; Rodionov, R.N.; Arning, E.; Bottiglieri, T.; Kimoto, M.; Murry, D.J.; Cooke, J.P.; Faraci, F.M.; Lentz, S.R. Tissue-Specific downregulation of dimethylarginine dimethylaminohydrolase in hyperhomocysteinemia. Am. J. Physiol. Heart Circ. Physiol 2008, 295, 816–825. [Google Scholar]
- Van Guldener, C.; Nanayakkara, P.W.; Stehouwer, C.D.A. Homocysteine and asymmetric dimethylarginine (ADMA): Biochemically linked but differently related to vascular disease in chronic kidney disease. Clin. Chem. Lab. Med 2007, 45, 1683–1687. [Google Scholar]
- Young, J.M.; Terrin, N.; Wang, X.; Greene, T.; Beck, G.J.; Kusek, J.W.; Collins, A.J.; Sarnak, M.J.; Menon, V. Asymmetric dimethylarginine and mortality in stages 3 to 4 chronic kidney disease. Clin. J. Am. Soc. Nephrol 2009, 4, 1115–1120. [Google Scholar]
- Ito, A.; Tsao, P.S.; Adimoolam, S.; Kimoto, M.; Ogawa, T.; Cooke, J.P. Novel mechanism for endothelial dysfunction: Dysregulation of dimethylarginine dimethylaminohydrolase. Circulation 1999, 99, 3092–3095. [Google Scholar]
- Feng, M.; Liu, L.; Guo, Z.; Xiong, Y. Gene transfer of dimethylarginine dimethylaminohydrolase-2 improves the impairments of DDAH/ADMA/NOS/NO pathway in endothelial cells induced by lysophosphatidylcholine. Eur. J. Pharmacol 2008, 584, 49–56. [Google Scholar]
- Rocha, M.S.; Teerlink, T.; Janssen, M.C.; Kluijtmans, L.A.; Smulders, Y.; Jakobs, C.; Tavares de Almeida, I.; Rivera, I.; Castro, R.; Blom, H.J. Asymmetric dimethylarginine in adults with cystathionine β-synthase deficiency. Atherosclerosis 2012, 222, 509–511. [Google Scholar]
- Schnabel, R.; Blankenberg, S.; Lubos, E.; Lackner, K.J.; Rupprecht, H.J.; Espinola-Klein, C.; Jachmann, N.; Post, F.; Peetz, D.; Bickel, C.; et al. Asymmetric dimethylarginine and the risk of cardiovascular events and death in patients with coronary artery disease: Results from the AtheroGene Study. Circ. Res 2005, 97, 53–59. [Google Scholar]
- Kielstein, J.T.; Böger, R.H.; Bode-Böger, S.M.; Frölich, J.C.; Haller, H.; Ritz, E.; Fliser, D. Marked increase of asymmetric dimethylarginine in patients with incipient primary chronic renal disease. J. Am. Soc. Nephrol 2002, 13, 170–176. [Google Scholar]
- Kielstein, J.T.; Böger, R.H.; Bode-Böger, S.M.; Schäffer, J.; Barbey, M.; Koch, K.M.; Frölich, J.C. Asymmetric dimethylarginine plasma concentrations differ in patients with end-stage renal disease: Relationship to treatment method and atherosclerotic disease. J. Am. Soc. Nephrol 1999, 10, 594–600. [Google Scholar]
- Jacobi, J.; Tsao, P.S. Asymmetrical dimethylarginine in renal disease: Limits of variation or variation limits? A systematic review. Am. J. Nephrol 2008, 28, 224–237. [Google Scholar]
- Tripepi, G.; Mattace Raso, F.; Sijbrands, E.; Seck, M.S.; Maas, R.; Boger, R.; Witteman, J.; Rapisarda, F.; Malatino, L.; Mallamaci, F.; et al. Inflammation and asymmetric dimethylarginine for predicting death and cardiovascular events in ESRD patients. Clin. J. Am. Soc. Nephrol 2011, 6, 1714–1721. [Google Scholar]
- Dobrian, A.D. ADMA and NOS regulation in chronic renal disease: Beyond the old rivalry for l-arginine. Kidney Int 2012, 81, 722–724. [Google Scholar]
- Kajimoto, H.; Kai, H.; Aoki, H.; Yasuoka, S.; Anegawa, T.; Aoki, Y.; Ueda, S.; Okuda, S.; Imaizumi, T. Inhibition of eNOS phosphorylation mediates endothelial dysfunction in renal failure: New effect of asymmetric dimethylarginine. Kidney Int 2012, 81, 762–768. [Google Scholar]
- Zoccali, C.; Kielstein, J.T. Asymmetric dimethylarginine: A new player in the pathogenesis of renal disease? Curr. Opin. Nephrol. Hypertens 2006, 15, 314–320. [Google Scholar]
- Kielstein, J.T.; Martens-Lobenhoffer, J.; Vollmer, S.; Bode-Böger, S.M. l-Arginine, ADMA, SDMA, creatinine, MDRD formula: Detour to renal function testing. J. Nephrol 2008, 21, 959–961. [Google Scholar]
- Chen, G.F.; Moningka, N.C.; Sasser, J.M.; Zharikov, S.; Cunningham, M., Jr; Tain, Y.L.; Schwartz, I.F.; Baylis, C. Arginine and asymmetric dimethylarginine in puromycin aminonucleoside-induced chronic kidney disease in the rat. Am. J. Nephrol. 2012, 35, 40–48. [Google Scholar]
- Busch, M.; Fleck, C.; Wolf, G.; Stein, G. Asymmetrical (ADMA) and symmetrical dimethylarginine (SDMA) as potential risk factors for cardiovascular and renal outcome in chronic kidney disease—Possible candidates for paradoxical epidemiology? Amino Acids 2006, 30, 225–232. [Google Scholar]
- Muscheites, J.; Meyer, A.A.; Drueckler, E.; Wigger, M.; Fischer, D.C.; Kundt, G.; Kienast, W.; Haffner, D. Assessment of the cardiovascular system in pediatric chronic kidney disease: A pilot study. Pediatr. Nephrol 2008, 23, 2233–2239. [Google Scholar]
- Lu, T.M.; Chung, M.Y.; Lin, C.C.; Hsu, C.P.; Lin, S.J. Asymmetric dimethylarginine and clinical outcomes in chronic kidney disease. Clin. J. Am. Soc. Nephrol 2011, 6, 1566–1572. [Google Scholar]
- Marescau, B.; Nagels, G.; Possemiers, I.; de Broe, M.E.; Because, I.; Billiouw, J.M.; Lornoy, W.; de Deyn, P.P. Guanidino compounds in serum and urine of nondialyzed patients with chronic renal insufficiency. Metabolism 1997, 46, 1024–1031. [Google Scholar]
- Pi, J.; Kumagai, Y.; Sun, G.; Shimojo, N. Improved method for simultaneous determination of l-arginine and its mono- and dimethylated metabolites in biological samples by high-performance liquid chromatography. J. Chromatogr. B 2000, 742, 199–203. [Google Scholar]
- Tsikas, D.; Schubert, B.; Gutzki, F.M.; Sandmann, J.; Frölich, J.C. Quantitative determination of circulating and urinary asymmetric dimethylarginine (ADMA) in humans by gas chromatography-tandem mass spectrometry as methyl ester tri(N-pentafluoropropionyl) derivative. J. Chromatogr. B 2003, 798, 87–99. [Google Scholar]
- Martens-Lobenhoffer, J.; Krug, O.; Bode-Böger, S.M. Determination of arginine and asymmetric dimethylarginine (ADMA) in human plasma by liquid chromatography/mass spectrometry with the isotope dilution technique. J. Mass. Spectrom 2004, 39, 1287–1294. [Google Scholar]
- Schwedhelm, E.; Tan-Andresen, J.; Maas, R.; Riederer, U.; Schulze, F.; Böger, R.H. Liquid chromatography-tandem mass spectrometry method for the analysis of asymmetric dimethylarginine in human plasma. Clin. Chem 2005, 51, 1268–1271. [Google Scholar]
- Martens-Lobenhoffer, J.; Krug, O.; Bode-Böger, S.M. Fast and efficient determination of arginine, symmetric dimethylarginine, and asymmetric dimethylarginine in biological fluids by hydrophilic-Interaction liquid chromatography–electrospray tandem mass spectrometry. Clin. Chem 2006, 52, 488–493. [Google Scholar]
- Wilcken, D.E.; Wang, J.; Sim, A.S.; Green, K.; Wilcken, B. Asymmetric dimethylarginine in homocystinuria due to cystathionine beta-synthase deficiency: Relevance of renal function. J. Inherit. Metab. Dis 2006, 29, 30–37. [Google Scholar]
- Bishop, M.J.; Crow, B.; Norton, D.; Paliakov, E.; George, J.; Bralley, J.A. Direct analysis of un-derivatized asymmetric dimethylarginine (ADMA) and l-arginine from plasma using mixed-mode ion-exchange liquid chromatography-tandem mass spectrometry. J. Chromatogr. B 2007, 859, 164–169. [Google Scholar]
- Schwedhelm, E.; Maas, R.; Tan-Andresen, J.; Schulze, F.; Riederer, U.; Böger, R.H. High-Throughput liquid chromatographic-tandem mass spectrometric determination of arginine and dimethylated arginine derivatives in human and mouse plasma. J. Chromatogr. B 2007, 851, 211–219. [Google Scholar]
- Weaving, G.; Rocks, B.F.; Bailey, M.P.; Titheradge, M.A. Arginine and methylated arginines in human plasma and urine measured by tandem mass spectrometry without the need for chromatography or sample derivatisation. J. Chromatogr. B 2008, 874, 27–32. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, W.; Zhou, C.; Xie, J.; Chen, B.; Chang, L. Serum asymmetric dimethylarginine and endothelial function after renal transplantation. J. Cent. South Univ. (Med. Sci.) 2009, 34, 289–294. [Google Scholar]
- El-Khoury, J.M.; Bunch, D.R.; Reineks, E.; Jackson, R.; Steinle, R.; Wang, S. A simple and fast liquid chromatography-tandem mass spectrometry method for measurement of underivatized l-arginine, symmetric dimethylarginine, and asymmetric dimethylarginine and establishment of the reference ranges. Anal. Bioanal. Chem 2012, 402, 771–779. [Google Scholar]
- Tain, Y.L.; Huang, L.T. Asymmetric dimethylarginine: Clinical applications in pediatric medicine. J. Formos. Med. Assoc 2011, 110, 70–77. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, S.; Vicente, F.B.; Miller, A.; Brooks, E.R.; Price, H.E.; Smith, F.A. Measurement of arginine derivatives in pediatric patients with chronic kidney disease using high-performance liquid chromatography-tandem mass spectrometry. Clin. Chem. Lab. Med 2007, 45, 1305–1312. [Google Scholar]
- Jehlička, P.; Stožický, F.; Mayer, O., Jr; Varvařovská, J.; Racek, J.; Trefil, L.; Siala, K. Asymmetric dimethylarginine and the effect of folate substitution in children with familial hypercholesterolemia and diabetes mellitus type 1. Physiol. Res. 2009, 58, 179–184. [Google Scholar]
- Heilman, K.; Zilmer, M.; Zilmer, K.; Kool, P.; Tillmann, V. Elevated plasma adiponectin and decreased plasma homocysteine and asymmetric dimethylarginine in children with type 1 diabetes. Scand. J. Clin. Lab. Invest 2009, 69, 85–91. [Google Scholar]
- Huemer, M.; Simma, B.; Mayr, D.; Möslinger, D.; Mühl, A.; Schmid, I.; Ulmer, H.; Bodamer, O.A. Free asymmetric dimethylarginine (ADMA) is low in children and adolescents with classical phenylketonuria (PKU). J. Inherit. Metab. Dis 2012, in press. [Google Scholar]
- Andrade, F.; Rodríguez-Soriano, J.; Prieto, J.A.; Aguirre, M.; Ariceta, G.; Lage, S.; Azcona, I.; Prado, C.; Sanjurjo, P.; Aldámiz-Echevarría, L. Methylation cycle, arginine-creatine pathway and asymmetric dimethylarginine in paediatric renal transplant. Nephrol. Dial. Transpl 2011, 26, 328–336. [Google Scholar]
- Arcos, M.I.; Fujihara, C.K.; Sesso, A.; de Almeida Prado, E.B.; de Almeida Prado, M.J.; de Nucci, G.; Zatz, R. Mechanisms of albuminuria in the chronic nitric oxide inhibition model. Am. J. Physiol. Renal. Physiol 2000, 279, 1060–1066. [Google Scholar]
- Okubo, K.; Hayashi, K.; Wakino, S.; Matsuda, H.; Kubota, E.; Honda, M.; Tokuyama, H.; Yamamoto, T.; Kajiya, F.; Saruta, T. Role of asymmetrical dimethylarginine in renal microvascular endothelial dysfunction in chronic renal failure with hypertension. Hypertens. Res 2005, 28, 181–189. [Google Scholar]
- Kaida, Y.; Ueda, S.; Yamagishi, S.I.; Nakayama, Y.; Ando, R.; Iwatani, R.; Fukami, K.; Okuda, S. Proteinuria elevates asymmetric dimethylarginine levels via protein arginine methyltransferase-1 overexpression in a rat model of nephrotic syndrome. Life Sci 2012, in press. [Google Scholar]
- Caglar, K.; Yilmaz, M.I.; Sonmez, A.; Cakir, E.; Kaya, A.; Acikel, C.; Eyileten, T.; Yenicesu, M.; Oguz, Y.; Bilgi, C.; et al. ADMA, proteinuria, and insulin resistance in non-diabetic stage I chronic kidney disease. Kidney Int 2006, 70, 781–787. [Google Scholar]
- Matsumoto, Y.; Ueda, S.; Yamagishi, S.; Matsuguma, K.; Shibata, R.; Fukami, K.; Matsuoka, H.; Imaizumi, T.; Okuda, S. Dimethylarginine dimethylaminohydrolase prevents progression of renal dysfunction by inhibiting loss of peritubular capillaries and tubulointerstitial fibrosis in a rat model of chronic kidney disease. J. Am. Soc. Nephrol 2007, 18, 1525–1533. [Google Scholar]
- Yilmaz, M.I.; Saglam, M.; Caglar, K.; Cakir, E.; Ozgurtas, T.; Sonmez, A.; Eyileten, T.; Yenicesu, M.; Acikel, C.; Oguz, Y.; et al. Endothelial functions improve with decrease in asymmetric dimethylarginine (ADMA) levels after renal transplantation. Transplantation 2005, 80, 1660–1666. [Google Scholar]
- Zoccali, C. Endothelial damage, asymmetric dimethylarginine and cardiovascular risk in end-stage renal disease. Blood Purif 2002, 20, 469. [Google Scholar]
- Teplan, V.; Schück, O.; Racek, J.; Siroka, R.; Haluzik, M.; Kudla, M.; Vitko, S. Asymmetric dimethylarginine and adiponectin after renal transplantation: Role of obesity. J. Ren. Nutr 2008, 18, 154–157. [Google Scholar]
- Teplan, V.; Malý, J.; Gürlich, R.; Teplan, V., Jr; Kudla, M.; Pit’ha, J.; Racek, J.; Haluzík, M.; Senolt, L.; Stollová, M. Muscle and fat metabolism in obesity after kidney transplantation: No effect of peritoneal dialysis or hemodialysis. J. Ren. Nutr. 2012, 22, 166–170. [Google Scholar]
- Abedini, S.; Meinitzer, A.; Holme, I.; März, W.; Weihrauch, G.; Fellstrøm, B.; Jardine, A.; Holdaas, H. Asymmetrical dimethylarginine is associated with renal and cardiovascular outcomes and all-cause mortality in renal transplant recipients. Kidney Int 2010, 77, 44–50. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, D.L.; Liu, J.; Liu, S.; Zhang, Y.; Liu, W.H. The differences of asymmetric dimethylarginine removal by different dialysis treatments. Ren. Fail 2010, 32, 935–940. [Google Scholar]
- Maas, R. Pharmacotherapies and their influence on asymmetric dimethylargine (ADMA). Vasc. Med 2005, 10, S49–S57. [Google Scholar]
- Goralczyk, T.; Tisonczyk, J.; Fijorek, K.; Undas, A. High tea and vegetable consumption is associated with low ADMA generation in older healthy subjects. Metabolism 2012, 61, 1171–1176. [Google Scholar]
- Saran, R.; Novak, J.E.; Desai, A.; Abdulhayoglu, E.; Warren, J.S.; Bustami, R.; Handelman, G.J.; Barbato, D.; Weitzel, W.; D’Alecy, L.G.; et al. Impact of vitamin E on plasma asymmetric dimethylarginine (ADMA) in chronic kidney disease (CKD): A pilot study. Nephrol. Dial. Transpl 2003, 18, 2415–2420. [Google Scholar]
- Nanayakkara, P.W.; Kiefte-de Jong, J.C.; ter Wee, P.M.; Stehouwer, C.D.; van Ittersum, F.J.; Olthof, M.R.; Teerlink, T.; Twisk, J.W.; van Guldener, C.; Smulders, Y.M. Randomized placebo-controlled trial assessing a treatment strategy consisting of pravastatin, vitamin E, and homocysteine lowering on plasma asymmetric dimethylarginine concentration in mild to moderate CKD. Am. J. Kidney Dis 2009, 53, 41–50. [Google Scholar]
- Teplan, V.; Schück, O.; Racek, J.; Mareckova, O.; Stollova, M.; Hanzal, V.; Malý, J. Reduction of plasma asymmetric dimethylarginine in obese patients with chronic kidney disease after three years of a low-protein diet supplemented with keto-amino acids: A randomized controlled trial. Wien. Klin. Wochenschr 2008, 120, 478–485. [Google Scholar]
- Cupiste, A.; Ghiadoni, L.; D’Alessandro, C.; Cardas, I.; Morelli, E.; Panichi, V.; Locati, D.; Morandi, S.; Saba, A.; Barsotti, G.; et al. Soy protein diet improves endothelial dysfunction in renal transplant patients. Nephrol. Dial. Transpl 2007, 22, 229–234. [Google Scholar]
- Urquhart, B.L.; House, A.A. Assessing plasma total homocysteine in patients with end-stage renal disease. Perit. Dial. Int 2007, 27, 476–488. [Google Scholar]
- Thaha, M.; Widodo, P.W.; Yogiantoro, M.; Tomino, Y. Intravenous N-acetylcysteine during hemodialysis reduces asymmetric dimethylarginine level in end-stage renal disease patients. Clin. Nephrol 2008, 69, 24–32. [Google Scholar]
- Ruiz, M.C.; Moreno, J.M.; Ruiz, N.; Vargas, F.; Asensio, C.; Osuna, A. Effect of statin treatment on oxidative stress and renal function in renal transplantation. Transpl. Proc 2006, 38, 2431–2433. [Google Scholar]
- Trimarchi, H.M.; Brennan, S.; González, J.M.; Suki, W.N. Effects of the statins in kidney transplantation. Medicina (B. Aires) 2000, 60, 457–465. [Google Scholar]
- Panichi, V.; Mantuano, E.; Paoletti, S.; Santi, S.; Manca Rizza, G.; Cutrupi, S.; Pizzini, P.; Spoto, B.; Tripepi, G.; Zoccali, C. Effect of simvastatin on plasma asymmetric dimethylarginine concentration in patients with chronic kidney disease. J. Nephrol 2008, 21, 38–44. [Google Scholar]
- Lim, A.; Manley, K.J.; Roberts, M.A.; Fraenkel, M.B. Fish oil treatment for kidney transplant recipients: A meta-analysis of randomized controlled trials. Transplantation 2007, 83, 831–838. [Google Scholar]
- Beavers, K.M.; Beavers, D.P.; Bowden, R.G.; Wilson, R.L.; Gentile, M. Omega-3 fatty acid supplementation and total homocysteine levels in end-stage renal disease patients. Nephrology (Carlton) 2008, 13, 284–288. [Google Scholar]
- Małyszko, J.; Małyszko, J.S.; Brzósko, S.; Pawlak, K.; Myśliwiec, M. Effects of fluvastatin on homocysteine and serum lipids in kidney allograft recipients. Ann. Transpl 2002, 7, 52–54. [Google Scholar]
- Vos, I.H.; Rabelink, T.J.; Dorland, B.; Loos, R.; van Middelaar, B.; Grone, H.J.; Joles, J.A. l-Arginine supplementation improves function and reduces inflamation in renal allografts. J. Am. Soc. Nephrol 2001, 12, 361–367. [Google Scholar]
- Baylis, C. Arginine, arginine analogs and nitric oxide production in chronic kidney disease. Nat. Clin. Pract. Nephrol 2006, 2, 209–220. [Google Scholar]
- El-Mesallamy, H.O.; Abdel Hamid, S.G.; Gad, M.Z. Oxidative stress and asymmetric dimethylarginine are associated with cardiovascular complications in hemodialysis patients: Improvements by l-arginine intake. Kidney Blood Press. Res 2008, 31, 189–195. [Google Scholar]
- Bodamer, O.A.; Sahoo, T.; Beaudet, A.L.; O’Brien, W.E.; Bottiglieri, T.; Stockler-Ipsiroglu, S.; Wagner, C.; Scaglia, F. Creatine metabolism in combined methylmalonic aciduria and homocystinuria. Ann. Neurol 2005, 57, 557–560. [Google Scholar]
- Schramm, L.; La, M.; Heidbreder, E.; Hecker, M.; Beckman, J.S.; Lopau, K.; Zimmermann, J.; Rendl, J.; Reiners, C.; Winderl, S.; et al. l-Arginine deficiency and supplementation in experimental acute renal failure and in human kidney transplantation. Kidney Int 2002, 61, 1423–1432. [Google Scholar]
- Schwedhelm, E.; Maas, R.; Freese, R.; Jung, D.; Lukacs, Z.; Jambrecina, A.; Spickler, W.; Schulze, F.; Böger, R.H. Pharmacokinetic and pharmacodynamic properties of oral l-citrulline and l-arginine: Impact on nitric oxide metabolism. Br. J. Clin. Pharmacol 2008, 65, 51–59. [Google Scholar]




| Subjects | Age (Years) | ADMA (μM) | SDMA (μM) | Arg (μM) | Arg/ADMA | Method | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Marescau et al. 1997 [75] | Controls | 23–86 | 0.41 ± 0.09 | 0.38 ± 0.10 | 110 ± 24 | LC-Fluorescence | |
| CKD: CC > 40 | 23–86 | 0.60 ± 0.10 | 0.83 ± 0.22 | 111 ± 24 | LC-Fluorescence | ||
| CKD: CC = 40–20 | 23–86 | 0.72 ± 0.22 | 1.41 ± 0.63 | 119 ± 33 | LC-Fluorescence | ||
| CKD: CC = 20–10 | 23–86 | 0.84 ± 0.15 | 2.24 ± 0.74 | 122 ± 36 | LC-Fluorescence | ||
| CKD: CC < 10 | 23–86 | 0.80 ± 0.14 | 3.17 ± 1.05 | 129 ± 37 | LC-Fluorescence | ||
| Pi et al. 2000 [76] | Controls | 23–35 | 0.30 ± 0.05 | 0.34 ± 0.06 | 60.7 ± 19.0 | LC-Fluorescence | |
| Tsikas et al. 2003 [77] | Controls | 35.6 ± 11.4 | 0.39 ± 0.06 | GC-MS/MS | |||
| Martens-Lobenhoffer et al. 2004 [78] | Controls | 20–56 | 0.36 ± 0.07 | 0.46 ± 0.09 | 63.9 ± 23.9 | LC-MS/MS | |
| CKD | 36–78 | 0.67 ± 0.13 | 3.16 ± 0.91 | 48.1 ± 18.5 | LC-MS/MS | ||
| Schwedhelm et al. 2005 [79] | Controls | >18 | 0.55 ± 0.14 | 0.69 ± 0.23 | 65.6 ± 23.4 | 132 ± 55 | LC-MS/MS |
| Martens-Lobenhoffer et al. 2006 [80] | Controls | 22–32 | 0.37 ± 0.06 | 0.45 ± 0.06 | 60.6 ± 18.3 | LC-MS/MS | |
| Wilcken et al. 2006 [81] | Controls | 34.6 ± 11.7 | 0.49 ± 0.07 | 0.40 ± 0.07 | 87.9 ± 19.5 | 181.9 ± 56.1 | LC-Fluorescence |
| CBS | 34.2 ± 12.6 | 0.55 ± 0.08 | 0.39 ± 0.09 | 73.5 ± 18.8 | 132.9 ± 24.7 | LC-Fluorescence | |
| Bishop et al. 2007 [82] | Controls | >18 | 0.66 ± 0.12 | 87 ± 35 | 142 ± 81 | LC-MS/MS | |
| Schwedhelm et al. 2007 [83] | Controls | >18 | 0.46 ± 0.09 | 0.37 ± 0.07 | 74 ± 19 | 166 ± 50 | LC-MS/MS |
| Weaving et al. 2008 [84] | Controls | 20.9 ± 2.5 | 0.40 ± 0.14 | 0.47 ± 0.06 | 162 ± 76 | SPE-MS/MS | |
| Zhang et al. 2009 [85] | Controls | 46.1 ± 13.2 | 0.49 ± 0.12 | 0.24 ± 0.08 | LC-Fluorescence | ||
| CKD | 45.7 ± 14.2 | 2.36 ± 0.89 | 0.48 ± 0.11 | LC-Fluorescence | |||
| RTx | 45.7 ± 14.2 | 0.70 ± 0.24 | 0.26 ± 0.07 | LC-Fluorescence | |||
| El-Khoury et al. 2012 [86] | Controls | 19–64 | 0.36–0.67 | 0.32–0.65 | 53.1–129.7 | LC-MS/MS |
| Subjects | Age (Years) | ADMA (μM) | SDMA (μM) | Arg (μM) | Arg/ADMA | Method | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Wang et al. 2007 [88] | Controls | 12.6 ± 1.0 | 0.78 ± 0.16 | 0.71 ± 0.23 | 65.3 ± 21.3 | LC-MS/MS | |
| CKD | 11.3 ± 4.7 | 1.10 ± 0.35 | 2.06 ± 1.11 | 57.9 ± 22.1 | LC-MS/MS | ||
| Brooks et al. 2009 [24] | Controls | 11.3 ± 4.7 | 0.8 ± 0.2 | 0.7 ± 0.2 | 65.3 ± 21.3 | 86.8 ± 30.6 | LC-MS/MS |
| CKD | 12.6 ± 1.0 | 1.1 ± 0.3 | 2.1 ± 1.1 | 57.9 ± 22.1 | 62.4 ± 27.7 | LC-MS/MS | |
| Andrade et al. 2011 [92] | Controls | 7–18 | 0.41–0.96 | 56.4–125.4 | 83.0–218.5 | ELISA | |
| RTx | 7–18 | 0.67–1.28 | 52.6–140.3 | 55.4–177.2 | ELISA | ||
| Huemer et al. 2012 [91] | Controls | 11.6 ± 3.7 | 0.64 ± 0.66 | 59 ± 59 | 86 ± 91 | ELISA |
© 2012 by the authors; licensee Molecular Diversity Preservation International, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open-access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/3.0/).
Share and Cite
Aldámiz-Echevarría, L.; Andrade, F. Asymmetric Dimethylarginine, Endothelial Dysfunction and Renal Disease. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2012, 13, 11288-11311. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms130911288
Aldámiz-Echevarría L, Andrade F. Asymmetric Dimethylarginine, Endothelial Dysfunction and Renal Disease. International Journal of Molecular Sciences. 2012; 13(9):11288-11311. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms130911288
Chicago/Turabian StyleAldámiz-Echevarría, Luis, and Fernando Andrade. 2012. "Asymmetric Dimethylarginine, Endothelial Dysfunction and Renal Disease" International Journal of Molecular Sciences 13, no. 9: 11288-11311. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms130911288
APA StyleAldámiz-Echevarría, L., & Andrade, F. (2012). Asymmetric Dimethylarginine, Endothelial Dysfunction and Renal Disease. International Journal of Molecular Sciences, 13(9), 11288-11311. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms130911288