Effects of Sorafenib on C-Terminally Truncated Androgen Receptor Variants in Human Prostate Cancer Cells
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Results and Discussion
2.1. Sorafenib Inhibits Canonical AR-Signalling in PCa Cells
2.2. Effect of Sorafenib on Constitutively Active, C-Terminally Truncated AR-Mutant Q640X
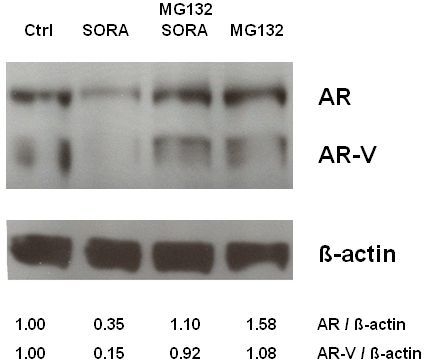
2.3. Sorafenib Induces Proteasomal Degradation of AR and AR-V Splice Variants in 22Rv1 Cells
2.4. Sorafenib Does not Modulate the Subcellular Distribution of AR and ARΔLBD in PCa Cells
2.5. Inhibition of Cell Proliferation after Sorafenib-Treatment in PCa Cell Lines
3. Experimental Section
3.1. Plasmids and Chemicals
3.2. Cell Culture
3.3. Reporter Gene Assays
3.4. Nuclear Translocation Assay
3.5. Proliferation Assay
3.6. Western Blot Analysis and Immunodetection of AR and ARΔLBD
3.7. Statistical Analysis
4. Conclusions
Acknowledgments
- Conflict of InterestThe authors declare no conflict of interest.
References
- Jemal, A.; Bray, F.; Center, M.M.; Ferlay, J.; Ward, E.; Forman, D. Global cancer statistics. CA Cancer J. Clin 2011, 61, 69–90. [Google Scholar]
- Bluemn, E.G.; Nelson, P.S. The androgen/androgen receptor axis in prostate cancer. Curr. Opin. Oncol 2012, 24, 251–257. [Google Scholar]
- Feldman, B.J.; Feldman, D. The development of androgen-independent prostate cancer. Nat. Rev. Cancer 2001, 1, 34–45. [Google Scholar]
- Locke, J.A.; Guns, E.S.; Lubik, A.A.; Adomat, H.H.; Hendy, S.C.; Wood, C.A.; Ettinger, S.L.; Gleave, M.E.; Nelson, C.C. Androgen levels increase by intratumoral de novo steroidogenesis during progression of castration-resistant prostate cancer. Cancer Res 2008, 68, 6407–6415. [Google Scholar]
- Haile, S.; Sadar, M.D. Androgen receptor and its splice variants in prostate cancer. Cell Mol. Life Sci 2011, 68, 3971–3981. [Google Scholar]
- Ceraline, J.; Cruchant, M.D.; Erdmann, E.; Erbs, P.; Kurtz, J.E.; Duclos, B.; Jacqmin, D.; Chopin, D.; Bergerat, J.P. Constitutive activation of the androgen receptor by a point mutation in the hinge region: A new mechanism for androgen-independent growth in prostate cancer. Int. J. Cancer 2004, 108, 152–157. [Google Scholar]
- Libertini, S.J.; Tepper, C.G.; Rodriguez, V.; Asmuth, D.M.; Kung, H.J.; Mudryj, M. Evidence for calpain-mediated androgen receptor cleavage as a mechanism for androgen independence. Cancer Res 2007, 67, 9001–9005. [Google Scholar]
- Hornberg, E.; Ylitalo, E.B.; Crnalic, S.; Antti, H.; Stattin, P.; Widmark, A.; Bergh, A.; Wikstrom, P. Expression of androgen receptor splice variants in prostate cancer bone metastases is associated with castration-resistance and short survival. PLoS One 2011, 6, e19059. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, X.; Morrissey, C.; Sun, S.; Ketchandji, M.; Nelson, P.S.; True, L.D.; Vakar-Lopez, F.; Vessella, R.L.; Plymate, S.R. Androgen receptor variants occur frequently in castration resistant prostate cancer metastases. PLoS One 2011, 6, e27970. [Google Scholar]
- Harada, N.; Inoue, K.; Yamaji, R.; Nakano, Y.; Inui, H. Androgen deprivation causes truncation of the C-terminal region of androgen receptor in human prostate cancer LNCaP cells. Cancer Sci 2012, 103, 1022–1027. [Google Scholar]
- Chan, S.C.; Li, Y.; Dehm, S.M. Androgen receptor splice variants activate androgen receptor target genes and support aberrant prostate cancer cell growth independent of canonical androgen receptor nuclear localization signal. J. Biol. Chem 2012, 287, 19736–19749. [Google Scholar]
- Mostaghel, E.A.; Marck, B.T.; Plymate, S.R.; Vessella, R.L.; Balk, S.; Matsumoto, A.M.; Nelson, P.S.; Montgomery, R.B. Resistance to CYP17A1 inhibition with abiraterone in castration-resistant prostate cancer: Induction of steroidogenesis and androgen receptor splice variants. Clin. Cancer Res 2011, 17, 5913–5925. [Google Scholar]
- Gioeli, D.; Paschal, B.M. Post-translational modification of the androgen receptor. Mol. Cell Endocrinol 2012, 352, 70–78. [Google Scholar]
- Weigel, N.L.; Moore, N.L. Steroid receptor phosphorylation: A key modulator of multiple receptor functions. Mol. Endocrinol 2007, 21, 2311–2319. [Google Scholar]
- Oh, S.J.; Erb, H.H.; Hobisch, A.; Santer, F.R.; Culig, Z. Sorafenib decreases proliferation and induces apoptosis of prostate cancer cells by inhibition of the androgen receptor and Akt signaling pathways. Endocr. Relat. Cancer 2012, 19, 305–319. [Google Scholar]
- Gaddipati, J.P.; McLeod, D.G.; Heidenberg, H.B.; Sesterhenn, I.A.; Finger, M.J.; Moul, J.W.; Srivastava, S. Frequent detection of codon 877 mutation in the androgen receptor gene in advanced prostate cancers. Cancer Res 1994, 54, 2861–2864. [Google Scholar]
- Streicher, W.; Zengerling, F.; Laschak, M.; Weidemann, W.; Hopfner, M.; Schrader, A.J.; Jentzmik, F.; Schrader, M.; Cronauer, M.V. AR-Q640X, a model to study the effects of constitutively active C-terminally truncated AR variants in prostate cancer cells. World J. Urol 2012, 30, 333–339. [Google Scholar]
- Lapouge, G.; Erdmann, E.; Marcias, G.; Jagla, M.; Monge, A.; Kessler, P.; Serra, S.; Lang, H.; Jacqmin, D.; Bergerat, J.P.; et al. Unexpected paracrine action of prostate cancer cells harboring a new class of androgen receptor mutation—A new paradigm for cooperation among prostate tumor cells. Int. J. Cancer 2007, 121, 1238–1244. [Google Scholar]
- Watson, P.A.; Chen, Y.F.; Balbas, M.D.; Wongvipat, J.; Socci, N.D.; Viale, A.; Kim, K.; Sawyers, C.L. Constitutively active androgen receptor splice variants expressed in castration-resistant prostate cancer require full-length androgen receptor. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2010, 107, 16759–16765. [Google Scholar]
- Chen, S.; Xu, Y.; Yuan, X.; Bubley, G.J.; Balk, S.P. Androgen receptor phosphorylation and stabilization in prostate cancer by cyclin-dependent kinase 1. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2006, 103, 15969–15974. [Google Scholar]
- Rinnab, L.; Schütz, S.V.; Diesch, J.; Schmid, E.; Kufer, R.; Hautmann, R.E.; Spindler, K.D.; Cronauer, M.V. Inhibition of glycogen synthase kinase-3 in androgen-responsive prostate cancer cell lines: Are GSK inhibitors therapeutically useful? Neoplasia 2008, 10, 624–634. [Google Scholar]
- Agoulnik, I.U.; Bingman, W.E., III; Nakka, M.; Li, W.; Wang, Q.; Liu, X.S.; Brown, M.; Weigel, N.L. Target gene-specific regulation of androgen receptor activity by p42/p44 mitogen-activated protein kinase. Mol. Endocrinol. 2008, 22, 2420–2432. [Google Scholar]
- Hu, R.; Dunn, T.A.; Wei, S.; Isharwal, S.; Veltri, R.W.; Humphreys, E.; Han, M.; Partin, A.W.; Vessella, R.L.; Isaacs, W.B.; et al. Ligand-independent androgen receptor variants derived from splicing of cryptic exons signify hormone-refractory prostate cancer. Cancer Res 2009, 69, 16–22. [Google Scholar]
- Schütz, S.V.; Cronauer, M.V.; Rinnab, L. Inhibition of glycogen synthase kinase-3beta promotes nuclear export of the androgen receptor through a CRM1-dependent mechanism in prostate cancer cell lines. J. Cell Biochem 2010, 109, 1192–1200. [Google Scholar]
- Schütz, S.V.; Schrader, A.J.; Zengerling, F.; Genze, F.; Cronauer, M.V.; Schrader, M. Inhibition of glycogen synthase kinase-3β counteracts ligand-independent activity of the androgen receptor in castration resistant prostate cancer. PLoS One 2011, 6, e25341. [Google Scholar]
- Jain, G.; Voogdt, C.; Tobias, A.; Spindler, K.D.; Moller, P.; Cronauer, M.V.; Marienfeld, R.B. IkappaB kinases modulate the activity of the androgen receptor in prostate carcinoma cell lines. Neoplasia 2012, 14, 178–189. [Google Scholar]
- Mosmann, T. Rapid colorimetric assay for cellular growth and survival: Application to proliferation and cytotoxicity assays. J. Immunol. Methods 1983, 65, 55–63. [Google Scholar]
- Cronauer, M.V.; Ince, Y.; Engers, R.; Rinnab, L.; Weidemann, W.; Suschek, C.V.; Burchardt, M.; Kleinert, H.; Wiedenmann, J.; Sies, H.; et al. Nitric oxide-mediated inhibition of androgen receptor activity: Possible implications for prostate cancer progression. Oncogene 2007, 26, 1875–1884. [Google Scholar]
- Sonpavde, G.; Periman, P.O.; Bernold, D.; Weckstein, D.; Fleming, M.T.; Galsky, M.D.; Berry, W.R.; Zhan, F.; Boehm, K.A.; Asmar, L.; et al. Sunitinib malate for metastatic castration-resistant prostate cancer following docetaxel-based chemotherapy. Ann. Oncol 2009, 21, 319–324. [Google Scholar]
- Dror Michaelson, M.; Regan, M.M.; Oh, W.K.; Kaufman, D.S.; Olivier, K.; Michaelson, S.Z.; Spicer, B.; Gurski, C.; Kantoff, P.W.; Smith, M.R. Phase II study of sunitinib in men with advanced prostate cancer. Ann. Oncol 2009, 20, 913–920. [Google Scholar]
- Araujo, J.C.; Mathew, P.; Armstrong, A.J.; Braud, E.L.; Posadas, E.; Lonberg, M.; Gallick, G.E.; Trudel, G.C.; Paliwal, P.; Agrawal, S.; et al. Dasatinib combined with docetaxel for castration-resistant prostate cancer: Results from a phase 1-2 study. Cancer 2012, 118, 63–71. [Google Scholar]
- Mathew, P.; Thall, P.F.; Bucana, C.D.; Oh, W.K.; Morris, M.J.; Jones, D.M.; Johnson, M.M.; Wen, S.; Pagliaro, L.C.; Tannir, N.M.; et al. Platelet-derived growth factor receptor inhibition and chemotherapy for castration-resistant prostate cancer with bone metastases. Clin. Cancer Res 2007, 13, 5816–5824. [Google Scholar]
- Dahut, W.L.; Scripture, C.; Posadas, E.; Jain, L.; Gulley, J.L.; Arlen, P.M.; Wright, J.J.; Yu, Y.; Cao, L.; Steinberg, S.M.; et al. A phase II clinical trial of sorafenib in androgen-independent prostate cancer. Clin. Cancer Res 2008, 14, 209–214. [Google Scholar]
- Steinbild, S.; Mross, K.; Frost, A.; Morant, R.; Gillessen, S.; Dittrich, C.; Strumberg, D.; Hochhaus, A.; Hanauske, A.R.; Edler, L.; et al. Cancer 2007, 97, 1480–1485.
- Chi, K.N.; Ellard, S.L.; Hotte, S.J.; Czaykowski, P.; Moore, M.; Ruether, J.D.; Schell, A.J.; Taylor, S.; Hansen, C.; Gauthier, I.; et al. A phase II study of sorafenib in patients with chemo-naive castration-resistant prostate cancer. Ann. Oncol 2008, 19, 746–751. [Google Scholar]
- Aragon-Ching, J.B.; Jain, L.; Gulley, J.L.; Arlen, P.M.; Wright, J.J.; Steinberg, S.M.; Draper, D.; Venitz, J.; Jones, E.; Chen, C.C.; et al. Final analysis of a phase II trial using sorafenib for metastatic castration-resistant prostate cancer. Br. J. Urol. Int 2009, 103, 1636–1640. [Google Scholar]
- Safarinejad, M.R. Safety and efficacy of sorafenib in patients with castrate resistant prostate cancer: A Phase II study. Urol. Oncol 2008, 28, 21–27. [Google Scholar]
- Huang, R.; Chen, X.Q.; Huang, Y.; Chen, N.; Zeng, H. The multikinase inhibitor sorafenib induces caspase-dependent apoptosis in PC-3 prostate cancer cells. Asian J. Androl 2010, 12, 527–534. [Google Scholar]
- Ullen, A.; Farnebo, M.; Thyrell, L.; Mahmoudi, S.; Kharaziha, P.; Lennartsson, L.; Grander, D.; Panaretakis, T.; Nilsson, S. Sorafenib induces apoptosis and autophagy in prostate cancer cells in vitro. Int. J. Oncol 2010, 37, 15–20. [Google Scholar]
- Beardsley, E.K.; Hotte, S.J.; North, S.; Ellard, S.L.; Winquist, E.; Kollmannsberger, C.; Mukherjee, S.D.; Chi, K.N. A phase II study of sorafenib in combination with bicalutamide in patients with chemotherapy-naive castration resistant prostate cancer. Invest. New Drugs 2012, 30, 1652–1659. [Google Scholar]





© 2012 by the authors; licensee Molecular Diversity Preservation International, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open-access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/3.0/).
Share and Cite
Zengerling, F.; Streicher, W.; Schrader, A.J.; Schrader, M.; Nitzsche, B.; Cronauer, M.V.; Höpfner, M. Effects of Sorafenib on C-Terminally Truncated Androgen Receptor Variants in Human Prostate Cancer Cells. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2012, 13, 11530-11542. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms130911530
Zengerling F, Streicher W, Schrader AJ, Schrader M, Nitzsche B, Cronauer MV, Höpfner M. Effects of Sorafenib on C-Terminally Truncated Androgen Receptor Variants in Human Prostate Cancer Cells. International Journal of Molecular Sciences. 2012; 13(9):11530-11542. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms130911530
Chicago/Turabian StyleZengerling, Friedemann, Wolfgang Streicher, Andres J. Schrader, Mark Schrader, Bianca Nitzsche, Marcus V. Cronauer, and Michael Höpfner. 2012. "Effects of Sorafenib on C-Terminally Truncated Androgen Receptor Variants in Human Prostate Cancer Cells" International Journal of Molecular Sciences 13, no. 9: 11530-11542. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms130911530
APA StyleZengerling, F., Streicher, W., Schrader, A. J., Schrader, M., Nitzsche, B., Cronauer, M. V., & Höpfner, M. (2012). Effects of Sorafenib on C-Terminally Truncated Androgen Receptor Variants in Human Prostate Cancer Cells. International Journal of Molecular Sciences, 13(9), 11530-11542. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms130911530