CXCR4/CXCL12 in Non-Small-Cell Lung Cancer Metastasis to the Brain
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. NSCLC Metastasis to the Brain
3. CXCR4 and CXCR12 in NSCLC Metastasis to the Brain
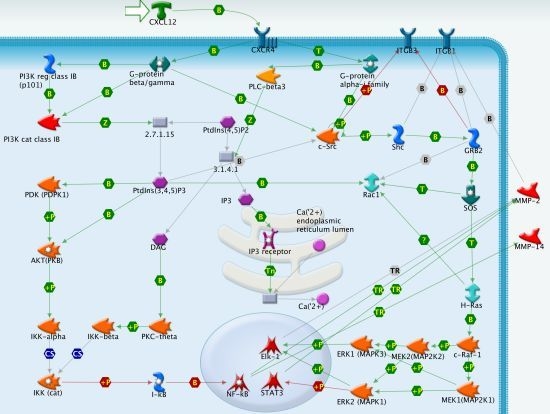
3.1. CXCR4 Signaling in NSCLC Metastasis
3.2. CXCL12 and CXCR4 Expression in NSCLC
4. Antagonist of CXCR4-Mediated Brain Metastasis
5. Conclusions
- Conflict of InterestThe authors declare no conflict of interest.
References
- Ono, S.J.; Nakamura, T.; Miyazaki, D.; Ohbayashi, M.; Dawson, M.; Toda, M. Chemokines: Roles in leukocyte development, trafficking, and effector function. J. Allergy Clin. Immunol 2003, 111, 1185–1199. [Google Scholar]
- Mukaida, N.; Baba, T. Chemokines in tumor development and progression. Exp. Cell Res 2012, 318, 95–102. [Google Scholar]
- Keeley, E.C.; Mehrad, B.; Strieter, R.M. Chemokines as mediators of tumor angiogenesis and neovascularization. Exp. Cell Res 2011, 317, 685–690. [Google Scholar]
- Gerber, P.A.; Hippe, A.; Buhren, B.A.; Muller, A.; Homey, B. Chemokines in tumor-associated angiogenesis. Biol. Chem 2009, 390, 1213–1223. [Google Scholar]
- Zlotnik, A.; Yoshie, O. Chemokines: A new classification system and their role in immunity. Immunity 2000, 12, 121–127. [Google Scholar]
- Zaballos, A.; Gutierrez, J.; Varona, R.; Ardavin, C.; Marquez, G. Cutting edge: Identification of the orphan chemokine receptor GPR-9-6 as CCR9, the receptor for the chemokine TECK. J. Immunol 1999, 162, 5671–5675. [Google Scholar]
- Yoshida, T.; Imai, T.; Kakizaki, M.; Nishimura, M.; Takagi, S.; Yoshie, O. Identification of single C motif-1/lymphotactin receptor XCR1. J. Biol. Chem 1998, 273, 16551–16554. [Google Scholar]
- Homey, B.; Wang, W.; Soto, H.; Buchanan, M.E.; Wiesenborn, A.; Catron, D.; Muller, A.; McClanahan, T.K.; Dieu-Nosjean, M.C.; Orozco, R.; et al. Cutting edge: The orphan chemokine receptor G protein-coupled receptor-2 (GPR-2, CCR10) binds the skin-associated chemokine CCL27 (CTACK/ALP/ILC). J. Immunol 2000, 164, 3465–3470. [Google Scholar]
- Schweickart, V.L.; Epp, A.; Raport, C.J.; Gray, P.W. CCR11 is a functional receptor for the monocyte chemoattractant protein family of chemokines. J. Biol. Chem 2000, 275, 9550–9556. [Google Scholar]
- Sun, X.; Cheng, G.; Hao, M.; Zheng, J.; Zhou, X.; Zhang, J.; Taichman, R.S.; Pienta, K.J.; Wang, J. CXCL12/CXCR4/CXCR7 chemokine axis and cancer progression. Cancer Metastasis Rev 2010, 29, 709–722. [Google Scholar]
- Teicher, B.A.; Fricker, S.P. CXCL12 (SDF-1)/CXCR4 pathway in cancer. Clin. Cancer Res 2010, 16, 2927–2931. [Google Scholar]
- Hinton, C.V.; Avraham, S.; Avraham, H.K. Role of the CXCR4/CXCL12 signaling axis in breast cancer metastasis to the brain. Clin. Exp. Metastasis 2010, 27, 97–105. [Google Scholar]
- Arya, M.; Ahmed, H.; Silhi, N.; Williamson, M.; Patel, H.R. Clinical importance and therapeutic implications of the pivotal CXCL12-CXCR4 (chemokine ligand-receptor) interaction in cancer cell migration. Tumour Biol 2007, 28, 123–131. [Google Scholar]
- Tashiro, K.; Tada, H.; Heilker, R.; Shirozu, M.; Nakano, T.; Honjo, T. Signal sequence trap: A cloning strategy for secreted proteins and type I membrane proteins. Science 1993, 261, 600–603. [Google Scholar]
- Bleul, C.C.; Farzan, M.; Choe, H.; Parolin, C.; Clark-Lewis, I.; Sodroski, J.; Springer, T.A. The lymphocyte chemoattractant SDF-1 is a ligand for LESTR/fusin and blocks HIV-1 entry. Nature 1996, 382, 829–833. [Google Scholar]
- Oberlin, E.; Amara, A.; Bachelerie, F.; Bessia, C.; Virelizier, J.L.; Arenzana-Seisdedos, F.; Schwartz, O.; Heard, J.M.; Clark-Lewis, I.; Legler, D.F.; et al. The CXC chemokine SDF-1 is the ligand for LESTR/fusin and prevents infection by T-cell-line-adapted HIV-1. Nature 1996, 382, 833–835. [Google Scholar]
- Feng, Y.; Broder, C.C.; Kennedy, P.E.; Berger, E.A. HIV-1 entry cofactor: Functional cDNA cloning of a seven-transmembrane, G protein-coupled receptor. Science 1996, 272, 872–877. [Google Scholar]
- Kucia, M.; Jankowski, K.; Reca, R.; Wysoczynski, M.; Bandura, L.; Allendorf, D.J.; Zhang, J.; Ratajczak, J.; Ratajczak, M.Z. CXCR4-SDF-1 signalling, locomotion, chemotaxis and adhesion. J. Mol. Histol 2004, 35, 233–245. [Google Scholar]
- Ghosh, M.C.; Makena, P.S.; Gorantla, V.; Sinclair, S.E.; Waters, C.M. CXCR4 regulates migration of lung alveolar epithelial cells through activation of Rac1 and matrix metalloproteinase-2. Am. J. Physiol. Lung Cell Mol. Physiol 2012, 302, L846–L856. [Google Scholar]
- Wald, O.; Izhar, U.; Amir, G.; Kirshberg, S.; Shlomai, Z.; Zamir, G.; Peled, A.; Shapira, O.M. Interaction between neoplastic cells and cancer-associated fibroblasts through the CXCL12/CXCR4 axis: Role in non-small cell lung cancer tumor proliferation. J. Thorac. Cardiovasc. Surg 2011, 141, 1503–1512. [Google Scholar]
- Liu, Y.; Wang, B.; Wang, J.; Wan, W.; Sun, R.; Zhao, Y.; Zhang, N. Down-regulation of PKCzeta expression inhibits chemotaxis signal transduction in human lung cancer cells. Lung Cancer 2009, 63, 210–218. [Google Scholar]
- Huang, Y.C.; Hsiao, Y.C.; Chen, Y.J.; Wei, Y.Y.; Lai, T.H.; Tang, C.H. Stromal cell-derived factor-1 enhances motility and integrin up-regulation through CXCR4, ERK and NF-κB-dependent pathway in human lung cancer cells. Biochem. Pharmacol 2007, 74, 1702–1712. [Google Scholar]
- Oonakahara, K.; Matsuyama, W.; Higashimoto, I.; Kawabata, M.; Arimura, K.; Osame, M. Stromal-derived factor-1α/CXCL12-CXCR 4 axis is involved in the dissemination of NSCLC cells into pleural space. Am. J. Respir. Cell Mol. Biol 2004, 30, 671–677. [Google Scholar]
- Kijima, T.; Maulik, G.; Ma, P.C.; Tibaldi, E.V.; Turner, R.E.; Rollins, B.; Sattler, M.; Johnson, B.E.; Salgia, R. Regulation of cellular proliferation, cytoskeletal function, and signal transduction through CXCR4 and c-Kit in small cell lung cancer cells. Cancer Res 2002, 62, 6304–6311. [Google Scholar]
- Murdoch, C.; Monk, P.N.; Finn, A. Functional expression of chemokine receptor CXCR4 on human epithelial cells. Immunology 1999, 98, 36–41. [Google Scholar]
- Sun, Y.X.; Schneider, A.; Jung, Y.; Wang, J.; Dai, J.; Cook, K.; Osman, N.I.; Koh-Paige, A.J.; Shim, H.; Pienta, K.J.; et al. Skeletal localization and neutralization of the SDF-1(CXCL12)/CXCR4 axis blocks prostate cancer metastasis and growth in osseous sites in vivo. J. Bone Miner. Res 2005, 20, 318–329. [Google Scholar]
- Domanska, U.M.; Kruizinga, R.C.; Nagengast, W.B.; Timmer-Bosscha, H.; Huls, G.; de Vries, E.G.; Walenkamp, A.M. A review on CXCR4/CXCL12 axis in oncology: No place to hide. Eur. J. Cancer 2013, 49, 219–230. [Google Scholar]
- Patrussi, L.; Baldari, C.T. The CXCL12/CXCR4 axis as a therapeutic target in cancer and HIV-1 infection. Curr. Med. Chem 2011, 18, 497–512. [Google Scholar]
- Furusato, B.; Mohamed, A.; Uhlen, M.; Rhim, J.S. CXCR4 and cancer. Pathol. Int 2010, 60, 497–505. [Google Scholar]
- Petrushev, B.; Tomuleasa, C.; Susman, S.; Sorisau, O.; Aldea, M.; Kacso, G.; Buiga, R.; Irimie, A. The axis of evil in the fight against cancer. Rom. J. Intern. Med 2011, 49, 319–325. [Google Scholar]
- Dela Cruz, C.S.; Tanoue, L.T.; Matthay, R.A. Lung cancer: Epidemiology, etiology, and prevention. Clin. Chest. Med 2011, 32, 605–644. [Google Scholar]
- Molina, J.R.; Yang, P.; Cassivi, S.D.; Schild, S.E.; Adjei, A.A. Non-small cell lung cancer: Epidemiology, risk factors, treatment, and survivorship. Mayo. Clin. Proc 2008, 83, 584–594. [Google Scholar]
- Steliga, M.A.; Dresler, C.M. Epidemiology of lung cancer: Smoking, secondhand smoke, and genetics. Surg. Oncol. Clin. N. Am 2011, 20, 605–618. [Google Scholar]
- Sher, T.; Dy, G.K.; Adjei, A.A. Small cell lung cancer. Mayo. Clin. Proc 2008, 83, 355–367. [Google Scholar]
- Quint, L.E.; Tummala, S.; Brisson, L.J.; Francis, I.R.; Krupnick, A.S.; Kazerooni, E.A.; Iannettoni, M.D.; Whyte, R.I.; Orringer, M.B. Distribution of distant metastases from newly diagnosed non-small cell lung cancer. Ann. Thorac. Surg 1996, 62, 246–250. [Google Scholar]
- Figlin, R.A.; Piantadosi, S.; Feld, R. Intracranial recurrence of carcinoma after complete surgical resection of stage I, II, and III non-small-cell lung cancer. N. Engl. J. Med 1988, 318, 1300–1305. [Google Scholar]
- Jacobs, R.H.; Awan, A.; Bitran, J.D.; Hoffman, P.C.; Little, A.G.; Ferguson, M.K.; Weichselbaum, R.; Golomb, H.M. Prophylactic cranial irradiation in adenocarcinoma of the lung. A possible role. Cancer 1987, 59, 2016–2019. [Google Scholar]
- Eberhardt, W.; Wilke, H.; Stamatis, G.; Stuschke, M.; Harstrick, A.; Menker, H.; Krause, B.; Mueller, M.R.; Stahl, M.; Flasshove, M.; et al. Preoperative chemotherapy followed by concurrent chemoradiation therapy based on hyperfractionated accelerated radiotherapy and definitive surgery in locally advanced non-small-cell lung cancer: Mature results of a phase II trial. J. Clin. Oncol 1998, 16, 622–634. [Google Scholar]
- Kumar, P.; Herndon, J., II; Langer, M.; Kohman, L.J.; Elias, A.D.; Kass, F.C.; Eaton, W.L.; Seagren, S.L.; Green, M.R.; Sugarbaker, D.J. Patterns of disease failure after trimodality therapy of nonsmall cell lung carcinoma pathologic stage IIIA (N2). Analysis of Cancer and Leukemia Group B Protocol 8935. Cancer 1996, 77, 2393–2399. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, S.Y.; Ye, X.; Ou, W.; Lin, Y.B.; Zhang, B.B.; Yang, H. Risk of cerebral metastases for postoperative locally advanced non-small-cell lung cancer. Lung Cancer 2009, 64, 238–243. [Google Scholar]
- Stuschke, M.; Eberhardt, W.; Pottgen, C.; Stamatis, G.; Wilke, H.; Stuben, G.; Stoblen, F.; Wilhelm, H.H.; Menker, H.; Teschler, H.; et al. Prophylactic cranial irradiation in locally advanced non-small-cell lung cancer after multimodality treatment: Long-term follow-up and investigations of late neuropsychologic effects. J. Clin. Oncol 1999, 17, 2700–2709. [Google Scholar]
- Law, A.; Karp, D.D.; Dipetrillo, T.; Daly, B.T. Emergence of increased cerebral metastasis after high-dose preoperative radiotherapy with chemotherapy in patients with locally advanced nonsmall cell lung carcinoma. Cancer 2001, 92, 160–164. [Google Scholar]
- Ceresoli, G.L.; Reni, M.; Chiesa, G.; Carretta, A.; Schipani, S.; Passoni, P.; Bolognesi, A.; Zannini, P.; Villa, E. Brain metastases in locally advanced nonsmall cell lung carcinoma after multimodality treatment: Risk factors analysis. Cancer 2002, 95, 605–612. [Google Scholar]
- Mujoomdar, A.; Austin, J.H.; Malhotra, R.; Powell, C.A.; Pearson, G.D.; Shiau, M.C.; Raftopoulos, H. Clinical predictors of metastatic disease to the brain from non-small cell lung carcinoma: Primary tumor size, cell type, and lymph node metastases. Radiology 2007, 242, 882–888. [Google Scholar]
- Chen, A.M.; Jahan, T.M.; Jablons, D.M.; Garcia, J.; Larson, D.A. Risk of cerebral metastases and neurological death after pathological complete response to neoadjuvant therapy for locally advanced nonsmall-cell lung cancer: Clinical implications for the subsequent management of the brain. Cancer 2007, 109, 1668–1675. [Google Scholar]
- Omuro, A.M.; Kris, M.G.; Miller, V.A.; Franceschi, E.; Shah, N.; Milton, D.T.; Abrey, L.E. High incidence of disease recurrence in the brain and leptomeninges in patients with nonsmall cell lung carcinoma after response to gefitinib. Cancer 2005, 103, 2344–2348. [Google Scholar]
- Costa, D.B.; Kobayashi, S. Response of intracranial metastases to epidermal growth factor receptor tyrosine kinase inhibitors: It may all depend on EGFR mutations. J. Clin. Oncol 2008, 26, 686. [Google Scholar]
- Robnett, T.J.; Machtay, M.; Stevenson, J.P.; Algazy, K.M.; Hahn, S.M. Factors affecting the risk of brain metastases after definitive chemoradiation for locally advanced non-small-cell lung carcinoma. J. Clin. Oncol 2001, 19, 1344–1349. [Google Scholar]
- Yokoi, K.; Kamiya, N.; Matsuguma, H.; Machida, S.; Hirose, T.; Mori, K.; Tominaga, K. Detection of brain metastasis in potentially operable non-small cell lung cancer: A comparison of CT and MRI. Chest 1999, 115, 714–719. [Google Scholar]
- Pottgen, C.; Eberhardt, W.; Grannass, A.; Korfee, S.; Stuben, G.; Teschler, H.; Stamatis, G.; Wagner, H.; Passlick, B.; Petersen, V.; et al. Prophylactic cranial irradiation in operable stage IIIA non small-cell lung cancer treated with neoadjuvant chemoradiotherapy: Results from a German multicenter randomized trial. J. Clin. Oncol 2007, 25, 4987–4992. [Google Scholar]
- Ebnet, K.; Vestweber, D. Molecular mechanisms that control leukocyte extravasation: The selectins and the chemokines. Histochem. Cell Biol 1999, 112, 1–23. [Google Scholar]
- Koizumi, K.; Hojo, S.; Akashi, T.; Yasumoto, K.; Saiki, I. Chemokine receptors in cancer metastasis and cancer cell-derived chemokines in host immune response. Cancer Sci 2007, 98, 1652–1658. [Google Scholar]
- Zlotnik, A. Involvement of chemokine receptors in organ-specific metastasis. Contrib. Microbiol 2006, 13, 191–199. [Google Scholar]
- Kakinuma, T.; Hwang, S.T. Chemokines, chemokine receptors, and cancer metastasis. J. Leukoc. Biol 2006, 79, 639–651. [Google Scholar]
- Balkwill, F. Cancer and the chemokine network. Nat. Rev. Cancer 2004, 4, 540–550. [Google Scholar]
- Schrader, A.J.; Lechner, O.; Templin, M.; Dittmar, K.E.; Machtens, S.; Mengel, M.; Probst-Kepper, M.; Franzke, A.; Wollensak, T.; Gatzlaff, P.; et al. CXCR4/CXCL12 expression and signalling in kidney cancer. Br. J. Cancer 2002, 86, 1250–1256. [Google Scholar]
- Zhou, Y.; Larsen, P.H.; Hao, C.; Yong, V.W. CXCR4 is a major chemokine receptor on glioma cells and mediates their survival. J. Biol. Chem 2002, 277, 49481–49487. [Google Scholar]
- Barbero, S.; Bonavia, R.; Bajetto, A.; Porcile, C.; Pirani, P.; Ravetti, J.L.; Zona, G.L.; Spaziante, R.; Florio, T.; Schettini, G. Stromal cell-derived factor 1α stimulates human glioblastoma cell growth through the activation of both extracellular signal-regulated kinases 1/2 and Akt. Cancer Res 2003, 63, 1969–1974. [Google Scholar]
- Sun, Y.X.; Wang, J.; Shelburne, C.E.; Lopatin, D.E.; Chinnaiyan, A.M.; Rubin, M.A.; Pienta, K.J.; Taichman, R.S. Expression of CXCR4 and CXCL12 (SDF-1) in human prostate cancers (PCa) in vivo. J. Cell Biochem 2003, 89, 462–473. [Google Scholar]
- Scala, S.; Ottaiano, A.; Ascierto, P.A.; Cavalli, M.; Simeone, E.; Giuliano, P.; Napolitano, M.; Franco, R.; Botti, G.; Castello, G. Expression of CXCR4 predicts poor prognosis in patients with malignant melanoma. Clin. Cancer Res 2005, 11, 1835–1841. [Google Scholar]
- Wagner, P.L.; Hyjek, E.; Vazquez, M.F.; Meherally, D.; Liu, Y.F.; Chadwick, P.A.; Rengifo, T.; Sica, G.L.; Port, J.L.; Lee, P.C.; et al. CXCL12 and CXCR4 in adenocarcinoma of the lung: Association with metastasis and survival. J. Thorac. Cardiovasc. Surg 2009, 137, 615–621. [Google Scholar]
- Na, I.K.; Scheibenbogen, C.; Adam, C.; Stroux, A.; Ghadjar, P.; Thiel, E.; Keilholz, U.; Coupland, S.E. Nuclear expression of CXCR4 in tumor cells of non-small cell lung cancer is correlated with lymph node metastasis. Hum. Pathol 2008, 39, 1751–1755. [Google Scholar]
- Imai, H.; Sunaga, N.; Shimizu, Y.; Kakegawa, S.; Shimizu, K.; Sano, T.; Ishizuka, T.; Oyama, T.; Saito, R.; Minna, J.D.; et al. Clinicopathological and therapeutic significance of CXCL12 expression in lung cancer. Int. J. Immunopathol. Pharmacol 2010, 23, 153–164. [Google Scholar]
- Gangadhar, T.; Nandi, S.; Salgia, R. The role of chemokine receptor CXCR4 in lung cancer. Cancer Biol. Ther 2010, 9, 409–416. [Google Scholar]
- Pfeiffer, M.; Hartmann, T.N.; Leick, M.; Catusse, J.; Schmitt-Graeff, A.; Burger, M. Alternative implication of CXCR4 in JAK2/STAT3 activation in small cell lung cancer. Br. J. Cancer 2009, 100, 1949–1956. [Google Scholar]
- Chen, G.; Wang, Z.; Liu, X.Y.; Liu, F.Y. High-level CXCR4 expression correlates with brain-specific metastasis of non-small cell lung cancer. World J. Surg 2011, 35, 56–61. [Google Scholar]
- Su, L.; Zhang, J.; Xu, H.; Wang, Y.; Chu, Y.; Liu, R.; Xiong, S. Differential expression of CXCR4 is associated with the metastatic potential of human non-small cell lung cancer cells. Clin. Cancer Res 2005, 11, 8273–8280. [Google Scholar]
- Spano, J.P.; Andre, F.; Morat, L.; Sabatier, L.; Besse, B.; Combadiere, C.; Deterre, P.; Martin, A.; Azorin, J.; Valeyre, D.; et al. Chemokine receptor CXCR4 and early-stage non-small cell lung cancer: Pattern of expression and correlation with outcome. Ann. Oncol 2004, 15, 613–617. [Google Scholar]
- Burger, M.; Glodek, A.; Hartmann, T.; Schmitt-Graff, A.; Silberstein, L.E.; Fujii, N.; Kipps, T.J.; Burger, J.A. Functional expression of CXCR4 (CD184) on small-cell lung cancer cells mediates migration, integrin activation, and adhesion to stromal cells. Oncogene 2003, 22, 8093–8101. [Google Scholar]
- Paratore, S.; Banna, G.L.; D’Arrigo, M.; Saita, S.; Iemmolo, R.; Lucenti, L.; Bellia, D.; Lipari, H.; Buscarino, C.; Cunsolo, R.; et al. CXCR4 and CXCL12 immunoreactivities differentiate primary non-small-cell lung cancer with or without brain metastases. Cancer Biomark 2011, 10, 79–89. [Google Scholar]
- Ghosh, M.C.; Collins, G.D.; Vandanmagsar, B.; Patel, K.; Brill, M.; Carter, A.; Lustig, A.; Becker, K.G.; Wood, W.W., III; Emeche, C.D.; et al. Activation of Wnt5A signaling is required for CXC chemokine ligand 12-mediated T-cell migration. Blood 2009, 114, 1366–1373. [Google Scholar]
- Subik, K.; Shu, L.; Wu, C.; Liang, Q.; Hicks, D.; Boyce, B.; Schiffhauer, L.; Chen, D.; Chen, C.; Tang, P.; Xing, L. The ubiquitin E3 ligase WWP1 decreases CXCL12-mediated MDA231 breast cancer cell migration and bone metastasis. Bone 2012, 50, 813–823. [Google Scholar]
- Oh, J.W.; Olman, M.; Benveniste, E.N. CXCL12-mediated induction of plasminogen activator inhibitor-1 expression in human CXCR4 positive astroglioma cells. Biol. Pharm. Bull 2009, 32, 573–577. [Google Scholar]
- Belperio, J.A.; Phillips, R.J.; Burdick, M.D.; Lutz, M.; Keane, M.; Strieter, R. The SDF-1/CXCL 12/CXCR4 biological axis in non-small cell lung cancer metastases. Chest 2004, 125, S156. [Google Scholar]
- Phillips, R.J.; Mestas, J.; Gharaee-Kermani, M.; Burdick, M.D.; Sica, A.; Belperio, J.A.; Keane, M.P.; Strieter, R.M. Epidermal growth factor and hypoxia-induced expression of CXC chemokine receptor 4 on non-small cell lung cancer cells is regulated by the phosphatidylinositol 3-kinase/PTEN/AKT/mammalian target of rapamycin signaling pathway and activation of hypoxia inducible factor-1α. J. Biol. Chem 2005, 280, 22473–22481. [Google Scholar]
- Li, M.; Ransohoff, R.M. Multiple roles of chemokine CXCL12 in the central nervous system: A migration from immunology to neurobiology. Prog. Neurobiol 2008, 84, 116–131. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, Y.; Huang, J.; Li, Y.; Yang, G.Y. Roles of chemokine CXCL12 and its receptors in ischemic stroke. Curr. Drug Targets 2012, 13, 166–172. [Google Scholar]
- Terasaki, M.; Sugita, Y.; Arakawa, F.; Okada, Y.; Ohshima, K.; Shigemori, M. CXCL12/CXCR4 signaling in malignant brain tumors: A potential pharmacological therapeutic target. Brain Tumor. Pathol 2011, 28, 89–97. [Google Scholar]
- Savarin-Vuaillat, C.; Ransohoff, R.M. Chemokines and chemokine receptors in neurological disease: Raise, retain, or reduce? Neurotherapeutics 2007, 4, 590–601. [Google Scholar]
- Fujisawa, N.; Sakao, Y.; Hayashi, S.; Hadden, W.A., 3rd; Harmon, C.L.; Miller, E.J. α-Chemokine growth factors for adenocarcinomas; a synthetic peptide inhibitor for α-chemokines inhibits the growth of adenocarcinoma cell lines. J. Cancer Res. Clin. Oncol. 2000, 126, 19–26. [Google Scholar]
- Galffy, G.; Mohammed, K.A.; Dowling, P.A.; Nasreen, N.; Ward, M.J.; Antony, V.B. Interleukin 8: An autocrine growth factor for malignant mesothelioma. Cancer Res 1999, 59, 367–371. [Google Scholar]
- Burger, J.A.; Peled, A. CXCR4 antagonists: Targeting the microenvironment in leukemia and other cancers. Leukemia 2009, 23, 43–52. [Google Scholar]
- Shin, H.N.; Moon, H.H.; Ku, J.L. Stromal cell-derived factor-1α and macrophage migration-inhibitory factor induce metastatic behavior in CXCR4-expressing colon cancer cells. Int. J. Mol. Med 2012, 30, 1537–1543. [Google Scholar]
- Liang, Z.; Zhan, W.; Zhu, A.; Yoon, Y.; Lin, S.; Sasaki, M.; Klapproth, J.M.; Yang, H.; Grossniklaus, H.E.; Xu, J.; et al. Development of a unique small molecule modulator of CXCR4. PLoS One 2012, 7, e34038. [Google Scholar]
- Ma, M.; Ye, J.Y.; Deng, R.; Dee, C.M.; Chan, G.C. Mesenchymal stromal cells may enhance metastasis of neuroblastoma via SDF-1/CXCR4 and SDF-1/CXCR7 signaling. Cancer Lett 2011, 312, 1–10. [Google Scholar]
- Zhao, B.C.; Wang, Z.J.; Mao, W.Z.; Ma, H.C.; Han, J.G.; Zhao, B.; Xu, H.M. CXCR4/SDF-1 axis is involved in lymph node metastasis of gastric carcinoma. World J. Gastroenterol 2011, 17, 2389–2396. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, H.; Yang, D.; Wang, K.; Wang, J. Expression and potential role of chemokine receptor CXCR4 in human bladder carcinoma cell lines with different metastatic ability. Mol. Med. Report 2011, 4, 525–528. [Google Scholar]
- Uchida, D.; Onoue, T.; Kuribayashi, N.; Tomizuka, Y.; Tamatani, T.; Nagai, H.; Miyamoto, Y. Blockade of CXCR4 in oral squamous cell carcinoma inhibits lymph node metastases. Eur. J. Cancer 2011, 47, 452–459. [Google Scholar]
- Hassan, S.; Buchanan, M.; Jahan, K.; Aguilar-Mahecha, A.; Gaboury, L.; Muller, W.J.; Alsawafi, Y.; Mourskaia, A.A.; Siegel, P.M.; Salvucci, O.; et al. CXCR4 peptide antagonist inhibits primary breast tumor growth, metastasis and enhances the efficacy of anti-VEGF treatment or docetaxel in a transgenic mouse model. Int. J. Cancer 2011, 129, 225–232. [Google Scholar]
- Richert, M.M.; Vaidya, K.S.; Mills, C.N.; Wong, D.; Korz, W.; Hurst, D.R.; Welch, D.R. Inhibition of CXCR4 by CTCE-9908 inhibits breast cancer metastasis to lung and bone. Oncol. Rep 2009, 21, 761–767. [Google Scholar]
- Tan, C.T.; Chu, C.Y.; Lu, Y.C.; Chang, C.C.; Lin, B.R.; Wu, H.H.; Liu, H.L.; Cha, S.T.; Prakash, E.; Ko, J.Y.; et al. CXCL12/CXCR4 promotes laryngeal and hypopharyngeal squamous cell carcinoma metastasis through MMP-13-dependent invasion via the ERK1/2/AP-1 pathway. Carcinogenesis 2008, 29, 1519–1527. [Google Scholar]
- Kim, S.Y.; Lee, C.H.; Midura, B.V.; Yeung, C.; Mendoza, A.; Hong, S.H.; Ren, L.; Wong, D.; Korz, W.; Merzouk, A.; et al. Inhibition of the CXCR4/CXCL12 chemokine pathway reduces the development of murine pulmonary metastases. Clin. Exp. Metastasis 2008, 25, 201–211. [Google Scholar]
- Kajiyama, H.; Shibata, K.; Terauchi, M.; Ino, K.; Nawa, A.; Kikkawa, F. Involvement of SDF-α/CXCR4 axis in the enhanced peritoneal metastasis of epithelial ovarian carcinoma. Int. J. Cancer 2008, 122, 91–99. [Google Scholar]
- Yoon, Y.; Liang, Z.; Zhang, X.; Choe, M.; Zhu, A.; Cho, H.T.; Shin, D.M.; Goodman, M.M.; Chen, Z.G.; Shim, H. CXC chemokine receptor-4 antagonist blocks both growth of primary tumor and metastasis of head and neck cancer in xenograft mouse models. Cancer Res 2007, 67, 7518–7524. [Google Scholar]
- Uchida, D.; Onoue, T.; Tomizuka, Y.; Begum, N.M.; Miwa, Y.; Yoshida, H.; Sato, M. Involvement of an autocrine stromal cell derived factor-1/CXCR4 system on the distant metastasis of human oral squamous cell carcinoma. Mol. Cancer Res 2007, 5, 685–694. [Google Scholar]
- Takenaga, M.; Tamamura, H.; Hiramatsu, K.; Nakamura, N.; Yamaguchi, Y.; Kitagawa, A.; Kawai, S.; Nakashima, H.; Fujii, N.; Igarashi, R. A single treatment with microcapsules containing a CXCR4 antagonist suppresses pulmonary metastasis of murine melanoma. Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun 2004, 320, 226–232. [Google Scholar]
- Liang, Z.; Wu, T.; Lou, H.; Yu, X.; Taichman, R.S.; Lau, S.K.; Nie, S.; Umbreit, J.; Shim, H. Inhibition of breast cancer metastasis by selective synthetic polypeptide against CXCR4. Cancer Res 2004, 64, 4302–4308. [Google Scholar]
- Mori, T.; Doi, R.; Koizumi, M.; Toyoda, E.; Ito, D.; Kami, K.; Masui, T.; Fujimoto, K.; Tamamura, H.; Hiramatsu, K.; et al. CXCR4 antagonist inhibits stromal cell-derived factor 1-induced migration and invasion of human pancreatic cancer. Mol. Cancer Ther 2004, 3, 29–37. [Google Scholar]
- Otani, Y.; Kijima, T.; Kohmo, S.; Oishi, S.; Minami, T.; Nagatomo, I.; Takahashi, R.; Hirata, H.; Suzuki, M.; Inoue, K.; et al. Suppression of metastases of small cell lung cancer cells in mice by a peptidic CXCR4 inhibitor TF14016. FEBS Lett 2012, 586, 3639–3644. [Google Scholar]
- De Clercq, E. The AMD3100 story: The path to the discovery of a stem cell mobilizer (Mozobil). Biochem. Pharmacol. 2009, 77, 1655–1664. [Google Scholar]
- Burger, J.A.; Stewart, D.J.; Wald, O.; Peled, A. Potential of CXCR4 antagonists for the treatment of metastatic lung cancer. Expert Rev. Anticancer Ther 2011, 11, 621–630. [Google Scholar]
- Burger, J.A.; Stewart, D.J. CXCR4 chemokine receptor antagonists: Perspectives in SCLC. Expert Opin. Investig. Drugs 2009, 18, 481–490. [Google Scholar]
- Phillips, R.J.; Burdick, M.D.; Lutz, M.; Belperio, J.A.; Keane, M.P.; Strieter, R.M. The stromal derived factor-1/CXCL12-CXC chemokine receptor 4 biological axis in non-small cell lung cancer metastases. Am. J. Respir. Crit. Care Med 2003, 167, 1676–1686. [Google Scholar]
- Fahham, D.; Weiss, I.D.; Abraham, M.; Beider, K.; Hanna, W.; Shlomai, Z.; Eizenberg, O.; Zamir, G.; Izhar, U.; Shapira, O.M.; et al. In vitro and in vivo therapeutic efficacy of CXCR4 antagonist BKT140 against human non-small cell lung cancer. J. Thorac. Cardiovasc. Surg. 2012, 144. [Google Scholar]

© 2013 by the authors; licensee Molecular Diversity Preservation International, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open-access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/3.0/).
Share and Cite
Cavallaro, S. CXCR4/CXCL12 in Non-Small-Cell Lung Cancer Metastasis to the Brain. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2013, 14, 1713-1727. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms14011713
Cavallaro S. CXCR4/CXCL12 in Non-Small-Cell Lung Cancer Metastasis to the Brain. International Journal of Molecular Sciences. 2013; 14(1):1713-1727. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms14011713
Chicago/Turabian StyleCavallaro, Sebastiano. 2013. "CXCR4/CXCL12 in Non-Small-Cell Lung Cancer Metastasis to the Brain" International Journal of Molecular Sciences 14, no. 1: 1713-1727. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms14011713
APA StyleCavallaro, S. (2013). CXCR4/CXCL12 in Non-Small-Cell Lung Cancer Metastasis to the Brain. International Journal of Molecular Sciences, 14(1), 1713-1727. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms14011713