Mixtures of l-Amino Acids as Reaction Medium for Formation of Iron Nanoparticles: The Order of Addition into a Ferrous Salt Solution Matters
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Results and Discussion
2.1. Single l-Amino Acid Mediating NZVI Formation
2.2. Influence of Arg and/or Glu on Ferrous Ions in Solution
2.3. Effect of Sodium Borohydride on Arg and/or Glu–Verification Based on SERS Measurements
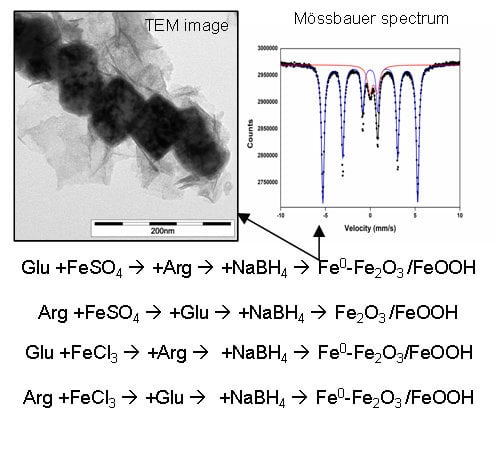
2.4. Impact of l-Amino Acids Mixtures on NZVI Generation
3. Experimental Section
3.1. Chemicals
3.2. Syntheses of Iron Particles Mediated by a Single l-Amino Acid
3.3. Syntheses of Iron Particles Mediated by Mixtures of l-Amino Acids
3.4. Characterization by Mössbauer Spectroscopy
3.5. Magnetization Measurements
3.6. Characterization by X-Ray Powder Diffraction (XRD)
3.7. Characterization by Transmission Electron Microscopy (TEM)
3.8. Synthesis of Silver Nanoparticles for Surface-Enhanced Raman Scattering Spectroscopy (SERS)
3.9. UV-Vis and SERS Spectral Measurements
4. Conclusions











| Sample | T (K) | Bext (T) | Component | δ ± 0.01 (mm/s) | ΔEQ ± 0.01 (mm/s) | Bhf ± 0.3 (T) | Beff ± 0.3 (T) | RA ± 1 (%) | Assignment |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Fe2ArgBH | 300 | 0 | Doublet | 0.35 | 0.79 | - | - | 40 | Fe3+ iron oxide–superparamagnetic state |
| Sextet | 0.34 | 0.02 | 36.4 | - | 60 | Fe3+ iron oxide–blocked state | |||
| 5 | 5 | Sextet | 0.39 | −0.03 | - | 51.3 | 52 | γ-Fe2O3–tetrahedral sites | |
| Sextet | 0.48 | −0.02 | - | 46.9 | 38 | γ-Fe2O3–octahedral sites | |||
| Sextet | 0.10 | 0.00 | - | 32.4 | 10 | Iron | |||
| Fe2GluBH | 300 | 0 | Doublet | 0.36 | 0.78 | - | - | 14 | Fe3+ iron oxide/oxyhydroxide shell |
| Sextet | 0.00 | 0.00 | 32.8 | - | 86 | Iron core | |||
| Fe2pH10BH | 300 | 0 | Doublet | 0.35 | 0.70 | - | - | 100 | Fe3+ iron oxide/oxyhydroxide |
| Fe3ArgBH | 300 | 0 | Doublet | 0.36 | 0.75 | - | - | 57 | Fe3+ iron oxide/oxyhydroxide shell |
| Sextet | 0.01 | −0.02 | 30.4 * | - | 43 | Iron core | |||
| Fe3GluBH | 300 | 0 | Doublet | 0.36 | 0.74 | - | - | 20 | Fe3+ iron oxide/ oxyhydroxide |
| Sextet | 0.00 | 0.00 | 33.1 | - | 80 | Iron core | |||
| Fe2Arg | 300 | 0 | Doublet | 1.26 | 3.19 | - | - | 38 | Fe2+ component |
| Doublet | 0.37 | 0.56 | - | - | 62 | Fe3+ component | |||
| Fe2Glu | 300 | 0 | Doublet | 1.26 | 3.18 | - | - | 87 | Fe2+ component |
| Doublet | 0.39 | 0.43 | - | - | 13 | Fe3+ component | |||
| Fe2ArgGluBH_f | 300 | 0 | Doublet | 0.31 | 0.70 | - | - | 52 | Fe3+ iron oxide/ oxyhydroxide–superparamagnetic state |
| Sextet | 0.31 | 0.00 | 30.6 | - | 48 | Fe3+ iron oxide/ oxyhydroxide–relaxation component | |||
| Fe2ArgGluBH_o | 300 | 0 | Doublet | 0.35 | 0.75 | - | - | 55 | Fe3+ iron oxide/ oxyhydroxide superparamagnetic state |
| Singlet | 0.35 | - | - | - | 45 | Fe3+ iron oxide/ oxyhydroxide–relaxation component | |||
| Fe2GluArgBH_f | 300 | 0 | Doublet | 0.36 | 0.77 | - | - | 21 | Fe3+ iron oxide/ oxyhydroxide shell |
| Sextet | 0.01 | 0.00 | 32.5 | - | 16 | Iron core | |||
| Sextet | 0.04 | −0.05 | 30.1 * | - | 63 | Iron core-to-shell layers | |||
| Fe2GluArgBH_o | 300 | 0 | Doublet | 0.36 | 0.79 | - | - | 29 | Fe3+ iron oxide/ oxyhydroxide shell |
| Sextet | 0.00 | 0.00 | 33.1 | - | 34 | Iron core | |||
| Sextet | 0.00 | 0.00 | 25.2 * | - | 37 | Iron core-to-shell layers | |||
| Fe3ArgGluBH | 300 | 0 | Doublet | 0.36 | 0.75 | - | - | 61 | Fe3+ iron oxide/ oxyhydroxide shell |
| Sextet | 0.00 | −0.03 | 32.9 | - | 39 | Iron core | |||
| Fe3GluArgBH | 300 | 0 | Doublet | 0.37 | 0.69 | - | - | 63 | Fe3+ iron oxide/ oxyhydroxide shell |
| Sextet | 0.01 | −0.04 | 32.9 | - | 37 | Iron core | |||
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Papaefthymiou, G.C. Nanoparticle magnetism. Nano Today 2009, 4, 438–447. [Google Scholar]
- Gupta, A.K.; Gupta, M. Synthesis and surface engineering of iron oxide nanoparticles for biomedical applications. Biomaterials 2005, 26, 3995–4021. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, L.; Fang, M. Nanomaterials in pollution trace detection and environmental improvement. Nano Today 2010, 5, 128–142. [Google Scholar]
- Noubactep, C.; Care, S.; Crane, R. Nanoscale metallic iron for environmental remediation: prospects and limitations. Water Air Soil Pollut 2012, 223, 1363–1382. [Google Scholar]
- Machala, L.; Zboril, R.; Gedanken, A. Amorphous iron(III) oxide—A review. J. Phys. Chem. B 2007, 111, 4003–4018. [Google Scholar]
- Machala, L.; Tucek, J.; Zboril, R. Polymorphous transformations of nanometric iron(III) oxide: A review. Chem. Mater 2011, 23, 3255–3272. [Google Scholar]
- Cornell, R.M.; Schwertmann, U. The Iron Oxides. Structure, Properties, Reactions, Occurences and Uses, 2nd ed; Wiley-VCH: Weinheim, Germany, 2003; pp. 59–94. [Google Scholar]
- Siskova, K.; Tucek, J.; Machala, L.; Otyepkova, E.; Filip, J.; Safarova, K.; Pechousek, J.; Zboril, R. Air-stable nZVI formation mediated by glutamic acid: Solid-state storable material exhibiting 2D chain morphology and high reactivity in aqueous environment. J. Nanopart. Res 2012, 14, 1–13. [Google Scholar]
- Siskova, K.M.; Straska, J.; Krizek, M.; Tucek, J.; Machala, L.; Zboril, R. Formation of zero-valent iron nanoparticles mediated by amino acids. Procedia Environ. Sci 2013, 18, 809–817. [Google Scholar]
- Greenwood, N.N.; Gibb, T.C. Mössbauer Spectroscopy, 1st ed.; Chapman and Hall Ltd.: London, UK, 1971; pp. 1–110. [Google Scholar]
- Vertes, A.; Korecz, L.; Burger, K. Mössbauer Spectroscopy, 1st ed; Elsevier Scientific Publishing Company: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 1979; pp. 13–122. [Google Scholar]
- Kuhn, L.T.; Bojesen, A.; Timmermann, L.; Nielsen, M.M.; Morup, S. Structural and magnetic properties of core-shell iron-iron oxide nanoparticles. J. Phys 2002, 14, 13551–13567. [Google Scholar]
- Sun, Y.-P.; Li, X.-Q.; Cao, J.; Zhang, W.-X.; Wang, H.P. Characterization of zero-valent iron nanoparticles. Adv. Colloid Interface Sci 2006, 120, 47–56. [Google Scholar]
- Nadagouda, M.N.; Castle, A.B.; Murdock, R.C.; Hussain, S.M.; Varma, R.S. In vitro biocompatibility of nanoscale zerovalent iron particles (NZVI) synthesized using tea polyphenols. Green Chem 2010, 12, 114–122. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, Q.; Snyder, S.; Kim, J.; Choi, H. Aqueous ethanol modified nanoscale zerovalent iron in bromate reduction: Synthesis, characterization, and reactivity. Environ. Sci. Technol 2009, 43, 3292–3299. [Google Scholar]
- Durmus, Z.; Kavas, H.; Toprak, M.S.; Baykal, A.; Altincekic, T.G.; Aslan, A.; Bozkurt, A.; Cosgun, S. l-lysine coated iron oxide nanoparticles: Synthesis, structural and conductivity characterization. J. Alloys Compd 2009, 484, 371–376. [Google Scholar]
- Marinescu, G.; Patron, L.; Culita, D.C.; Neagoe, C.; Lepadatu, C.I.; Balint, I.; Bessais, L.; Cizmas, C.B. Synthesis of magnetite nanoparticles in the presence of aminoacids. J. Nanopart. Res 2006, 8, 1045–1051. [Google Scholar]
- Mantion, A.; Gozzo, F.; Schmitt, B.; Stern, W.B.; Gerber, Y.; Robin, A.Y.; Fromm, K.M.; Painsi, M.; Taubert, A. Amino acids in iron oxide mineralization: (incomplete) crystal phase selection is achieved even with single amino acids. J. Phys. Chem. C 2008, 112, 12104–12110. [Google Scholar]
- Sousa, M.H.; Rubim, J.C.; Sobrinho, P.G.; Tourinho, F.A. Biocompatible magnetic fluid precursors based on aspartic and glutamic acid modified maghemite nanostructures. J. Magn. Magn. Mater 2001, 225, 67–72. [Google Scholar]
- Yang, H.-M.; Lee, H.J.; Jang, K.-S.; Park, C.W.; Yang, H.W.; Heo, W.D.; Kim, J.-D. Poly(amino acid)-coated iron oxide nanoparticles as ultra-small magnetic resonance probes. J. Mater. Chem 2009, 19, 4566–4574. [Google Scholar]
- Brown, S. Engineered iron oxide-adhesion mutants of the Escherichia coli phage lambda receptor. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 1992, 89, 8651–8655. [Google Scholar]
- Brown, S.; Sarikaya, M.; Johnson, E. A genetic analysis of crystal growth. J. Mol. Biol 2000, 299, 725–735. [Google Scholar]
- Venkateswara Rao, P.; Holm, R.H. Synthetic analogues of the active sites of iron-sulfur proteins. Chem. Rev 2004, 104, 527–559. [Google Scholar]
- Arakaki, A.; Webb, J.; Matsunaga, T. A novel protein tightly bound to bacterial magnetic particles in Magnetospirillum magneticum strain AMB-1. J. Biol. Chem 2003, 278, 8745–8750. [Google Scholar]
- Prozorov, T.; Mallapragada, S.K.; Narasimhan, B.; Wang, L.; Palo, P.; Nilsen-Hamilton, M.; Williams, T.J.; Bazylinski, D.A.; Prozorov, R.; Canfield, P.C. Protein-mediated synthesis of uniform superparamagnetic magnetite nanocrystals. Adv. Funct. Mater 2007, 17, 951–957. [Google Scholar]
- Matrajt, G.; Blanot, D. Properties of synthetic ferrihydrite as an amino acid adsorbent and a promoter of peptide bond formation. Amino Acids 2004, 26, 153–158. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, Z.; Zhu, H.; Wang, X.; Yang, F.; Yang, X. One-pot green synthesis of biocompatible arginine-stabilized magnetic nanoparticles. Nanotechnology 2009, 20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schneeweiss, O.; Zboril, R.; Mashlan, M.; Petrovsky, E.; Tucek, J. Novel solid-state synthesis of α-Fe and Fe3O4 nanoparticles embedded in a MgO matrix. Nanotechnology 2006, 17, 607–616. [Google Scholar]
- Kneipp, K.; Moskovits, M.; Kneipp, H. Surface-Enhanced Raman Scattering Physics and Applications, 1st ed; Springer-Verlag: Berlin, Germany, 2006; pp. 1–103. [Google Scholar]
- Le Ru, E.; Etchegoin, P. Principles of Surface Enhanced Raman Spectroscopy and Related Plasmonic Effects, 1st ed; Elsevier: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2009; pp. 1–27. [Google Scholar]
- Siskova, K.; Becicka, O.; Masek, V.; Safarova, K.; Zboril, R. Spacer-free SERRS spectra of unperturbed porphyrin detected at 100 fM concentration in Ag hydrosols prepared by modified Tollens method. J. Raman Spectrosc 2012, 43, 689–691. [Google Scholar]
- Nakamoto, K. Infrared and Raman Spectra of Inorganic and Coordination Compounds, Part B: Applications in Coordination, Organometallic, and Bioinorganic Chemistry, 6th ed; John Wiley & Sons: Hoboken, NJ, USA, 2009; pp. 1–31. [Google Scholar]
- Munro, C.H.; Smith, W.E.; Garner, M.; Clarkson, J.; White, P.C. Characterization of the surface of a citrate-reduced colloid optimized for use as a substrate for surface-enhanced Raman scattering. Langmuir 1995, 11, 3712–3720. [Google Scholar]
- Siskova, K.; Vlckova, B.; Turpin, P.-Y.; Thorel, A.; Prochazka, M. Laser ablation of silver in aqueous solutions of organic species: Probing Ag nanoparticle-adsorbate systems evolution by surface-enhanced Raman and surface plasmon extinction spectra. J. Phys. Chem. C 2011, 115, 5404–5412. [Google Scholar]
- Nogues, J.; Schuller, I.K. Exchange bias. J. Magn. Magn. Mater 1999, 192, 203–232. [Google Scholar]
- Iglesias, O.; Labarta, A.; Batlle, X. Exchange bias phenomenology and models of core/shell nanoparticles. J. Nanosci. Nanotechnol 2008, 8, 2761–2780. [Google Scholar]
- O’Handley, R.C. Modern Magnetic Materials, Principles and Applications, 1st ed; John Wiley & Sons: New York, NY, USA, 2000; pp. 1–740. [Google Scholar]
- Batlle, X.; Labarta, A. Finite-size effects in fine particles: Magnetic and transport properties. J. Phys 2002, 35, R15–R42. [Google Scholar]
- Pechousek, J.; Jancik, D.; Frydrych, J.; Navarik, J.; Novak, P. Setup of Mössbauer spectrometers at RCPTM. In Mössbauer Spectroscopy in Materials Science; Tucek, J., Machala, L., Eds.; AIP Conference Proceedings: New York, NY, USA, 2012; pp. 186–193. [Google Scholar]
© 2013 by the authors; licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/3.0/).
Share and Cite
Šišková, K.M.; Machala, L.; Tuček, J.; Kašlík, J.; Mojzeš, P.; Zbořil, R. Mixtures of l-Amino Acids as Reaction Medium for Formation of Iron Nanoparticles: The Order of Addition into a Ferrous Salt Solution Matters. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2013, 14, 19452-19473. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms141019452
Šišková KM, Machala L, Tuček J, Kašlík J, Mojzeš P, Zbořil R. Mixtures of l-Amino Acids as Reaction Medium for Formation of Iron Nanoparticles: The Order of Addition into a Ferrous Salt Solution Matters. International Journal of Molecular Sciences. 2013; 14(10):19452-19473. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms141019452
Chicago/Turabian StyleŠišková, Karolína M., Libor Machala, Jiři Tuček, Josef Kašlík, Peter Mojzeš, and Radek Zbořil. 2013. "Mixtures of l-Amino Acids as Reaction Medium for Formation of Iron Nanoparticles: The Order of Addition into a Ferrous Salt Solution Matters" International Journal of Molecular Sciences 14, no. 10: 19452-19473. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms141019452
APA StyleŠišková, K. M., Machala, L., Tuček, J., Kašlík, J., Mojzeš, P., & Zbořil, R. (2013). Mixtures of l-Amino Acids as Reaction Medium for Formation of Iron Nanoparticles: The Order of Addition into a Ferrous Salt Solution Matters. International Journal of Molecular Sciences, 14(10), 19452-19473. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms141019452