Bioresorbable Drug-Eluting Magnesium-Alloy Scaffold for Treatment of Coronary Artery Disease
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Potential Benefits of a Transient Scaffold
3. Magnesium as a Component for BRS
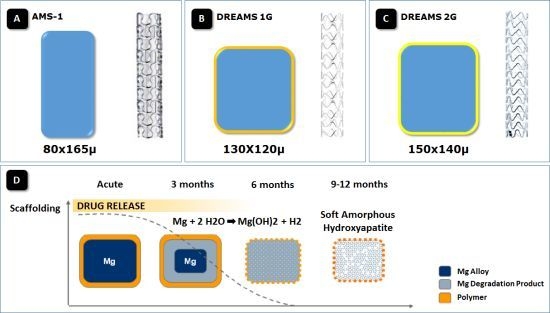
4. The First Generation Magnesium BRS
5. The Paclitaxel-Eluting Absorbable Metal Scaffold (DREAMS)
6. The Sirolimus-Eluting Absorbable Metal Scaffold (DREAMS 2nd Generation)
7. Conclusions
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Gruntzig, A. Transluminal dilatation of coronary-artery stenosis. Lancet 1978, 1, 263. [Google Scholar]
- Ormiston, J.A.; Stewart, F.M.; Roche, A.H.; Webber, B.J.; Whitlock, R.M.; Webster, M.W. Late regression of the dilated site after coronary angioplasty: A 5-year quantitative angiographic study. Circulation 1997, 96, 468–474. [Google Scholar]
- Sigwart, U.; Puel, J.; Mirkovitch, V.; Joffre, F.; Kappenberger, L. Intravascular stents to prevent occlusion and restenosis after transluminal angioplasty. N. Engl. J. Med 1987, 316, 701–706. [Google Scholar]
- Roubin, G.S.; Cannon, A.D.; Agrawal, S.K.; Macander, P.J.; Dean, L.S.; Baxley, W.A.; Breland, J. Intracoronary stenting for acute and threatened closure complicating percutaneous transluminal coronary angioplasty. Circulation 1992, 85, 916–927. [Google Scholar]
- Schatz, R.A.; Baim, D.S.; Leon, M.; Ellis, S.G.; Goldberg, S.; Hirshfeld, J.W.; Cleman, M.W.; Cabin, H.S.; Walker, C.; Stagg, J.; et al. Clinical experience with the Palmaz-Schatz coronary stent. Initial results of a multicenter study. Circulation 1991, 83, 148–161. [Google Scholar]
- Serruys, P.W.; Keane, D. The bailout stent. Is a friend in need always a friend indeed? Circulation 1993, 88, 2455–2457. [Google Scholar]
- Sousa, J.E.; Costa, M.A.; Abizaid, A.; Abizaid, A.S.; Feres, F.; Pinto, I.M.; Seixas, A.C.; Staico, R.; Mattos, L.A.; Sousa, A.G.; et al. Lack of neointimal proliferation after implantation of sirolimus-coated stents in human coronary arteries: A quantitative coronary angiography and three-dimensional intravascular ultrasound study. Circulation 2001, 103, 192–195. [Google Scholar]
- Rensing, B.J.; Vos, J.; Smits, P.C.; Foley, D.P.; van den Brand, M.J.; van der Giessen, W.J.; de Feijter, P.J.; Serruys, P.W. Coronary restenosis elimination with a sirolimus eluting stent: First European human experience with 6-month angiographic and intravascular ultrasonic follow-up. Eur. Heart J 2001, 22, 2125–2130. [Google Scholar]
- Morice, M.C.; Serruys, P.W.; Sousa, J.E.; Fajadet, J.; Ban Hayashi, E.; Perin, M.; Colombo, A.; Schuler, G.; Barragan, P.; Guagliumi, G.; et al. A randomized comparison of a sirolimus-eluting stent with a standard stent for coronary revascularization. N. Engl. J. Med 2002, 346, 1773–1780. [Google Scholar]
- Finn, A.V.; Joner, M.; Nakazawa, G.; Kolodgie, F.; Newell, J.; John, M.C.; Gold, H.K.; Virmani, R. Pathological correlates of late drug-eluting stent thrombosis: Strut coverage as a marker of endothelialization. Circulation 2007, 115, 2435–2441. [Google Scholar]
- Joner, M.; Finn, A.V.; Farb, A.; Mont, E.K.; Kolodgie, F.D.; Ladich, E.; Kutys, R.; Skorija, K.; Gold, H.K.; Virmani, R. Pathology of drug-eluting stents in humans: Delayed healing and late thrombotic risk. J. Am. Coll. Cardiol 2006, 48, 193–202. [Google Scholar]
- Cook, S.; Ladich, E.; Nakazawa, G.; Eshtehardi, P.; Neidhart, M.; Vogel, R.; Togni, M.; Wenaweser, P.; Billinger, M.; Seiler, C.; et al. Correlation of intravascular ultrasound findings with histopathological analysis of thrombus aspirates in patients with very late drug-eluting stent thrombosis. Circulation 2009, 120, 391–399. [Google Scholar]
- Serruys, P.W.; Garcia-Garcia, H.M.; Onuma, Y. From metallic cages to transient bioresorbable scaffolds: Change in paradigm of coronary revascularization in the upcoming decade? Eur. Heart J 2012, 33, 16b–25b. [Google Scholar]
- Vormann, J. Magnesium: Nutrition and metabolism. Mol. Aspects Med 2003, 24, 27–37. [Google Scholar]
- Song, G. Control of biodegradation of biocompatible magnesium alloy. Corros. Sci 2007, 49, 1696–1701. [Google Scholar]
- Chawla, S.L.; Gupta, R.K. Materials Selection for Corrosion Control; ASM International: Materials Park, OH, USA, 1993. [Google Scholar]
- Sawyer, P.N.; Srinivasan, S. The role of electrochemical surface properties in thrombosis at vascular interfaces: Cumulative experience of studies in animals and man. Bull. N. Y. Acad. Med 1972, 48, 235–256. [Google Scholar]
- Anstall, H.B.; Hayward, G.H.; Huntsman, R.G.; Weitzman, D.; Lehmann, H. The effect of magnesium on blood coagulation in human subjects. Lancet 1959, 1, 814–815. [Google Scholar]
- Rukshin, V.; Shah, P.K.; Cercek, B.; Finkelstein, A.; Tsang, V.; Kaul, S. Comparative antithrombotic effects of magnesium sulfate and the platelet glycoprotein IIb/IIIa inhibitors tirofiban and eptifibatide in a canine model of stent thrombosis. Circulation 2002, 105, 1970–1975. [Google Scholar]
- Rukshin, V.; Azarbal, B.; Shah, P.K.; Tsang, V.T.; Shechter, M.; Finkelstein, A.; Cercek, B.; Kaul, S. Intravenous magnesium in experimental stent thrombosis in swine. Arterioscler. Thromb. Vasc. Biol 2001, 21, 1544–1549. [Google Scholar]
- Moravej, M.; Mantovani, D. Biodegradable metals for cardiovascular stent application: Interests and new opportunities. Int. J. Mol. Sci 2011, 12, 4250–4270. [Google Scholar]
- Erbel, R.; di Mario, C.; Bartunek, J.; Bonnier, J.; de Bruyne, B.; Eberli, F.R.; Erne, P.; Haude, M.; Heublein, B.; Horrigan, M.; et al. Temporary scaffolding of coronary arteries with bioabsorbable magnesium stents: A prospective, non-randomised multicentre trial. Lancet 2007, 369, 1869–1875. [Google Scholar]
- Waksman, R.; Pakala, R.; Kuchulakanti, P.K.; Baffour, R.; Hellinga, D.; Seabron, R.; Tio, F.O.; Wittchow, E.; Hartwig, S.; Harder, C.; et al. Safety and efficacy of bioabsorbable magnesium alloy stents in porcine coronary arteries. Catheter. Cardiovasc. Interv 2006, 68, 607–617, discussion 618–609. [Google Scholar]
- Bose, D.; Eggebrecht, H.; Haude, M.; Schmermund, A.; Erbel, R. First absorbable metal stent implantation in human coronary arteries. Am. Heart Hosp. J 2006, 4, 128–130. [Google Scholar]
- Bose, D.; Eggebrecht, H.; Erbel, R. Absorbable metal stent in human coronary arteries: Imaging with intravascular ultrasound. Heart 2006, 92, 892. [Google Scholar]
- Waksman, R.; Erbel, R.; di Mario, C.; Bartunek, J.; de Bruyne, B.; Eberli, F.R.; Erne, P.; Haude, M.; Horrigan, M.; Ilsley, C.; et al. Early- and long-term intravascular ultrasound and angiographic findings after bioabsorbable magnesium stent implantation in human coronary arteries. JACC Cardiovasc. Interv 2009, 2, 312–320. [Google Scholar]
- Wittchow, E.; Adden, N.; Riedmuller, J.; Savard, C.; Waksman, R.; Braune, M. Bioresorbable drug-eluting magnesium-alloy scaffold: Design and feasibility in a porcine coronary model. EuroIntervention 2013, 8, 1441–1450. [Google Scholar]
- Haude, M.; Erbel, R.; Erne, P.; Verheye, S.; Degen, H.; Böse, D.; Vermeersch, P.; Wijnbergen, I.; Weissman, N.; Prati, F.; et al. Safety and performance of the drug-eluting absorbable metal scaffold (DREAMS) in patients with de novo coronary lesions: 12 month results of the prospective, multicentre, first-in-man BIOSOLVE-I trial. Lancet 2013, 381, 836–844. [Google Scholar]
- Colmenarez, H.; Fernandez, C.; Escaned, J. Impact of technological developments in drug-eluting stents on patient-focused outcomes: A pooled direct and indirect comparison of randomised trials comparing first- and second-generation drug-eluting stents. EuroIntervention 2013, in press. [Google Scholar]
- Abizaid, A.; Ormiston, J.A.; Fajadet, J.; Mauri, L.; Schofer, J.; Verheye, S.; Dens, J.; Thuesen, L.; Macours, N.; Qureshi, A.C.; et al. Two-year follow-up of the NEVO RES-ELUTION I (NEVO RES-I) trial: A randomised, multicentre comparison of the NEVO sirolimus-eluting coronary stent with the TAXUS Liberte paclitaxel-eluting stent in de novo native coronary artery lesions. EuroIntervention 2013, 9, 721. [Google Scholar]
- Kollum, M.; Heitzer, T.; Schmoor, C.; Brunner, M.; Witzenbichler, B.; Wiemer, M.; Hoffmann, R.; Gutleben, K.J.; Schultheiss, H.P.; Horstkotte, D.; et al. Intra-individual head-to-head comparison of Sirolimus(R)- and Paclitaxel(R)-eluting stents for coronary revascularization. A randomized, multi-center trial. Int. J. Cardiol 2013, 167, 1552–1559. [Google Scholar]



© 2013 by the authors; licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/3.0/).
Share and Cite
Campos, C.M.; Muramatsu, T.; Iqbal, J.; Zhang, Y.-J.; Onuma, Y.; Garcia-Garcia, H.M.; Haude, M.; Lemos, P.A.; Warnack, B.; Serruys, P.W. Bioresorbable Drug-Eluting Magnesium-Alloy Scaffold for Treatment of Coronary Artery Disease. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2013, 14, 24492-24500. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms141224492
Campos CM, Muramatsu T, Iqbal J, Zhang Y-J, Onuma Y, Garcia-Garcia HM, Haude M, Lemos PA, Warnack B, Serruys PW. Bioresorbable Drug-Eluting Magnesium-Alloy Scaffold for Treatment of Coronary Artery Disease. International Journal of Molecular Sciences. 2013; 14(12):24492-24500. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms141224492
Chicago/Turabian StyleCampos, Carlos M., Takashi Muramatsu, Javaid Iqbal, Yao-Jun Zhang, Yoshinobu Onuma, Hector M. Garcia-Garcia, Michael Haude, Pedro A. Lemos, Boris Warnack, and Patrick W. Serruys. 2013. "Bioresorbable Drug-Eluting Magnesium-Alloy Scaffold for Treatment of Coronary Artery Disease" International Journal of Molecular Sciences 14, no. 12: 24492-24500. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms141224492
APA StyleCampos, C. M., Muramatsu, T., Iqbal, J., Zhang, Y. -J., Onuma, Y., Garcia-Garcia, H. M., Haude, M., Lemos, P. A., Warnack, B., & Serruys, P. W. (2013). Bioresorbable Drug-Eluting Magnesium-Alloy Scaffold for Treatment of Coronary Artery Disease. International Journal of Molecular Sciences, 14(12), 24492-24500. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms141224492