Identification of Oxidative Stress Related Proteins as Biomarkers for Lung Cancer and Chronic Obstructive Pulmonary Disease in Bronchoalveolar Lavage
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Results
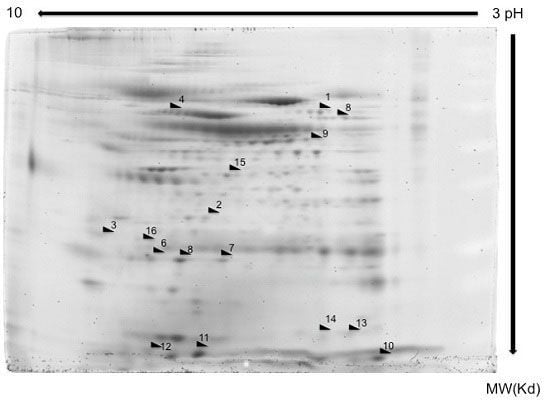
2.1. Proteome Profiles of Comparison of LC and/or COPD
2.2. Western Blotting
3. Discussion
4. Materials and Methods
4.1. Patients and Samples
4.2. Sample Treatment
4.3. 2D-PAGE
4.4. Image Analysis and Mass Spectrometry
4.5. Protein Identification by Mass Spectrometry
4.6. Functional Analysis of the Identified Proteins
4.7. Western Blot
4.8. Bioinformatics
Acknowledgments
References
- Jemal, A.; Bray, F.; Center, M.M.; Ferlay, J.; Ward, E.; Forman, D. Global cancer statistics. CA Cancer J. Clin 2011, 61, 69–90. [Google Scholar]
- Yao, H.; Rahman, I. Current concepts on the role of inflammation in COPD and lung cancer. Curr. Opin. Pharmacol 2009, 9, 375–383. [Google Scholar]
- Pryor, W.A.; Hales, B.J.; Premovic, P.I.; Church, D.F. The radicals in cigarette tar: Their nature and suggested physiological implications. Science 1983, 220, 425–427. [Google Scholar]
- Yoshida, T.; Tuder, R.M. Pathobiology of cigarette smoke-induced chronic obstructive pulmonary disease. Physiol. Rev 2007, 87, 1047–1082. [Google Scholar]
- Psarras, S.; Caramori, G.; Contoli, M.; Papadopoulos, N.; Papi, A. Oxidants in asthma and in chronic obstructive pulmonary disease (COPD). Curr. Pharm. Des 2005, 11, 2053–2062. [Google Scholar]
- Lee, G.; Walser, T.C.; Dubinett, S.M. Chronic inflammation, chronic obstructive pulmonary disease, and lung cancer. Curr. Opin. Pulm. Med 2009, 15, 303–307. [Google Scholar]
- Ghezzi, P.; Bonetto, V. Redox proteomics: Identification of oxidatively modified proteins. Proteomics 2003, 3, 1145–1153. [Google Scholar]
- Hermans, C.; Dong, P.; Robin, M.; Jadoul, M.; Bernard, A.; Bersten, A.D.; Doyle, I.R. Determinants of serum levels of surfactant proteins A and B and Clara cell protein CC16. Biomarkers 2003, 8, 461–471. [Google Scholar]
- Baraibar, M.A.; Hyzewicz, J.; Rogowska-Wrzesinska, A.; Ladouce, R.; Roepstorff, P.; Mouly, V.; Friguet, B. Oxidative stress-induced proteome alterations target different cellular pathways in human myoblasts. Free Radic. Biol. Med 2011, 51, 1522–1532. [Google Scholar]
- Plymoth, A.; Yang, Z.; Lofdahl, C.G.; Ekberg-Jansson, A.; Dahlback, M.; Fehniger, T.E.; Marko-Varga, G.; Hancock, W.S. Rapid proteome analysis of bronchoalveolar lavage samples of lifelong smokers and never-smokers by micro-scale liquid chromatography and mass spectrometry. Clin. Chem 2006, 52, 671–679. [Google Scholar]
- Kelsen, S.G.; Duan, X.; Ji, R.; Perez, O.; Liu, C.; Merali, S. Cigarette smoke induces an unfolded protein response in the human lung: A proteomic approach. Am. J. Respir. Cell Mol. Biol 2008, 38, 541–550. [Google Scholar]
- Pinto-Plata, V.; Toso, J.; Lee, K.; Bilello, J.; Mullerova, H.; De Souza, M.; Vessey, R.; Celli, B. Use of proteomic patterns of serum biomarkers in patients with chronic obstructive pulmonary disease: Correlation with clinical parameters. Proc. Am. Thorac. Soc 2006, 3, 465–466. [Google Scholar]
- Merkel, D.; Rist, W.; Seither, P.; Weith, A.; Lenter, M.C. Proteomic study of human bronchoalveolar lavage fluids from smokers with chronic obstructive pulmonary disease by combining surface-enhanced laser desorption/ionization-mass spectrometry profiling with mass spectrometric protein identification. Proteomics 2005, 5, 2972–2980. [Google Scholar]
- Casado, B.; Iadarola, P.; Pannell, L.K.; Luisetti, M.; Corsico, A.; Ansaldo, E.; Ferrarotti, I.; Boschetto, P.; Baraniuk, J.N. Protein expression in sputum of smokers and chronic obstructive pulmonary disease patients: A pilot study by CapLC-ESI-Q-TOF. J. Proteome Res 2007, 6, 4615–4623. [Google Scholar]
- Hoagland, L.F.M., IV; Campa, M.J.; Gottlin, E.B.; Herndon, J.E., II; Patz, E.F., Jr. Haptoglobin and posttranslational glycan-modified derivatives as serum biomarkers for the diagnosis of nonsmall cell lung cancer. Cancer 2007, 110, 2260–2268. [Google Scholar]
- Jessie, K.; Pang, W.W.; Haji, Z.; Rahim, A.; Hashim, O.H. Proteomic analysis of whole human saliva detects enhanced expression of interleukin-1 receptor antagonist, thioredoxin and lipocalin-1 in cigarette smokers compared to non-smokers. Int. J. Mol. Sci 2010, 11, 4488–4505. [Google Scholar]
- Brower, V. Biomarker studies abound for early detection of lung cancer. J. Natl. Cancer Inst 2009, 101, 11–13. [Google Scholar]
- Kang, S.M.; Sung, H.J.; Ahn, J.M.; Park, J.Y.; Lee, S.Y.; Park, C.S.; Cho, J.Y. The Haptoglobin beta chain as a supportive biomarker for human lung cancers. Mol. Biosyst 2011, 7, 1167–1175. [Google Scholar]
- Tian, T.; Hao, J.; Xu, A.; Luo, C.; Liu, C.; Huang, L.; Xiao, X.; He, D. Determination of metastasis-associated proteins in non-small cell lung cancer by comparative proteomic analysis. Cancer Sci 2007, 98, 1265–1274. [Google Scholar]
- Luo, C.; Urgard, E.; Vooder, T.; Metspalu, A. The role of COX-2 and Nrf2/ARE in anti-inflammation and antioxidative stress: Aging and anti-aging. Med. Hypotheses 2011, 77, 174–178. [Google Scholar]
- Kakolyris, S.; Giatromanolaki, A.; Koukourakis, M.; Powis, G.; Souglakos, J.; Sivridis, E.; Georgoulias, V.; Gatter, K.C.; Harris, A.L. Thioredoxin expression is associated with lymph node status and prognosis in early operable non-small cell lung cancer. Clin. Cancer Res 2001, 7, 3087–3091. [Google Scholar]
- Holmgren, A.; Lu, J. Thioredoxin and thioredoxin reductase: Current research with special reference to human disease. Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun 2010, 396, 120–124. [Google Scholar]
- Malmberg, K.J. Effective immunotherapy against cancer: A question of overcoming immune suppression and immune escape? Cancer Immunol. Immunother 2004, 53, 879–892. [Google Scholar]
- Kim, S.J.; Miyoshi, Y.; Taguchi, T.; Tamaki, Y.; Nakamura, H.; Yodoi, J.; Kato, K.; Noguchi, S. High thioredoxin expression is associated with resistance to docetaxel in primary breast cancer. Clin. Cancer Res 2005, 11, 8425–8430. [Google Scholar]
- Lillig, C.H.; Holmgren, A. Thioredoxin and related molecules—From biology to health and disease. Antioxid. Redox. Signal 2007, 9, 25–47. [Google Scholar]
- Jones, D.T.; Pugh, C.W.; Wigfield, S.; Stevens, M.F.; Harris, A.L. Novel thioredoxin inhibitors paradoxically increase hypoxia-inducible factor-alpha expression but decrease functional transcriptional activity, DNA binding, and degradation. Clin. Cancer Res 2006, 12, 5384–5394. [Google Scholar]
- Ceccarelli, J.; Delfino, L.; Zappia, E.; Castellani, P.; Borghi, M.; Ferrini, S.; Tosetti, F.; Rubartelli, A. The redox state of the lung cancer microenvironment depends on the levels of thioredoxin expressed by tumor cells and affects tumor progression and response to prooxidants. Int. J. Cancer 2008, 123, 1770–1778. [Google Scholar]
- Chaiswing, L.; Bourdeau-Heller, J.M.; Zhong, W.; Oberley, T.D. Characterization of redox state of two human prostate carcinoma cell lines with different degrees of aggressiveness. Free Radic. Biol. Med 2007, 43, 202–215. [Google Scholar]
- Iwasawa, S.; Yamano, Y.; Takiguchi, Y.; Tanzawa, H.; Tatsumi, K.; Uzawa, K. Upregulation of thioredoxin reductase 1 in human oral squamous cell carcinoma. Oncol. Rep 2011, 25, 637–644. [Google Scholar]
- Lincoln, D.T.; Al-Yatama, F.; Mohammed, F.M.; Al-Banaw, A.G.; Al-Bader, M.; Burge, M.; Sinowatz, F.; Singal, P.K. Thioredoxin and thioredoxin reductase expression in thyroid cancer depends on tumour aggressiveness. Anticancer Res 2010, 30, 767–775. [Google Scholar]
- Nguyen, P.; Awwad, R.T.; Smart, D.D.; Spitz, D.R.; Gius, D. Thioredoxin reductase as a novel molecular target for cancer therapy. Cancer Lett 2006, 236, 164–174. [Google Scholar]
- Welsh, S.J.; Bellamy, W.T.; Briehl, M.M.; Powis, G. The redox protein thioredoxin-1 (Trx-1) increases hypoxia-inducible factor 1alpha protein expression: Trx-1 overexpression results in increased vascular endothelial growth factor production and enhanced tumor angiogenesis. Cancer Res 2002, 62, 5089–5095. [Google Scholar]
- Jin, Z.G.; Melaragno, M.G.; Liao, D.F.; Yan, C.; Haendeler, J.; Suh, Y.A.; Lambeth, J.D.; Berk, B.C. Cyclophilin A is a secreted growth factor induced by oxidative stress. Circ. Res 2000, 87, 789–796. [Google Scholar]
- Pan, H.; Luo, C.; Li, R.; Qiao, A.; Zhang, L.; Mines, M.; Nyanda, A.M.; Zhang, J.; Fan, G.H. Cyclophilin A is required for CXCR4-mediated nuclear export of heterogeneous nuclear ribonucleoprotein A2, activation and nuclear translocation of ERK1/2, and chemotactic cell migration. J. Biol. Chem 2008, 283, 623–637. [Google Scholar]
- Zhu, C.; Wang, X.; Deinum, J.; Huang, Z.; Gao, J.; Modjtahedi, N.; Neagu, M.R.; Nilsson, M.; Eriksson, P.S.; Hagberg, H.; et al. Cyclophilin A participates in the nuclear translocation of apoptosis-inducing factor in neurons after cerebral hypoxia-ischemia. J. Exp. Med 2007, 204, 1741–1748. [Google Scholar]
- Peng, Y.; Li, X.; Wu, M.; Yang, J.; Liu, M.; Zhang, W.; Xiang, B.; Wang, X.; Li, G.; Shen, S. New prognosis biomarkers identified by dynamic proteomic analysis of colorectal cancer. Mol. Biosyst 2012, 8, 3077–3088. [Google Scholar]
- Strange, R.C.; Spiteri, M.A.; Ramachandran, S.; Fryer, A.A. Glutathione-S-transferase family of enzymes. Mutat. Res 2001, 482, 21–26. [Google Scholar]
- Matsumoto, A.; Okado, A.; Fujii, T.; Fujii, J.; Egashira, M.; Niikawa, N.; Taniguchi, N. Cloning of the peroxiredoxin gene family in rats and characterization of the fourth member. FEBS Lett 1999, 443, 246–250. [Google Scholar]
- Lim, Y.S.; Cha, M.K.; Kim, H.K.; Uhm, T.B.; Park, J.W.; Kim, K.; Kim, I.H. Removals of hydrogen peroxide and hydroxyl radical by thiol-specific antioxidant protein as a possible role in vivo. Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun 1 1993, 92, 273–280. [Google Scholar]
- Gharib, S.A.; Nguyen, E.; Altemeier, W.A.; Shaffer, S.A.; Doneanu, C.E.; Goodlett, D.R.; Schnapp, L.M. Of mice and men: Comparative proteomics of bronchoalveolar fluid. Eur. Respir. J 2010, 35, 1388–1395. [Google Scholar]
- Garcia, M.; Derocq, D.; Pujol, P.; Rochefort, H. Overexpression of transfected cathepsin D in transformed cells increases their malignant phenotype and metastatic potency. Oncogene 1990, 5, 1809–1814. [Google Scholar]
- Rochefort, H.; Capony, F.; Garcia, M.; Cavailles, V.; Freiss, G.; Chambon, M.; Morisset, M.; Vignon, F. Estrogen-induced lysosomal proteases secreted by breast cancer cells: A role in carcinogenesis? J. Cell Biochem 1987, 35, 17–29. [Google Scholar]
- Berchem, G.; Glondu, M.; Gleizes, M.; Brouillet, J.P.; Vignon, F.; Garcia, M.; Liaudet-Coopman, E. Cathepsin-D affects multiple tumor progression steps in vivo: Proliferation, angiogenesis and apoptosis. Oncogene 2002, 21, 5951–5955. [Google Scholar]
- Kim, H.; Kang, H.J.; You, K.T.; Kim, S.H.; Lee, K.Y.; Kim, T.I.; Kim, C.; Song, S.Y.; Kim, H.J.; Lee, C. Suppression of human selenium-binding protein 1 is a late event in colorectal carcinogenesis and is associated with poor survival. Proteomics 2006, 6, 3466–3476. [Google Scholar]
- Zeng, H.; Xu, L.; Xiao, D.; Zhang, H.; Wu, X.; Zheng, R.; Li, Q.; Niu, Y.; Shen, Z.; Li, E. Altered expression of ezrin in esophageal squamous cell carcinoma. J. Histochem. Cytochem 2006, 54, 889–896. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, S.J.; Wu, S.T.; Gokemeijer, J.; Fura, A.; Krishna, M.; Morin, P.; Chen, G.; Price, K.; Wang-Iverson, D.; Olah, T.; et al. Attribution of the discrepancy between ELISA and LC-MS/MS assay results of a PEGylated scaffold protein in post-dose monkey plasma samples due to the presence of anti-drug antibodies. Anal. Bioanal. Chem 2012, 402, 1229–1239. [Google Scholar]
- Nicolay, N.; Callaghan, M.A.; Domegan, L.M.; Oza, A.N.; Marsh, B.J.; Flanagan, P.C.; Igoe, D.M.; O’Donnell, J.M.; O’Flanagan, D.M.; O’Hora, A.P. Epidemiology, clinical characteristics and resource implications of pandemic (H1N1) 2009 in intensive care units in Ireland. Crit. Care. Resusc 2010, 12, 255–261. [Google Scholar]
- Wong, K.K.; Jacks, T.; Dranoff, G. NF-kappaB fans the flames of lung carcinogenesis. Cancer Prev. Res 2010, 3, 403–405. [Google Scholar]
- Di Stefano, A.; Caramori, G.; Oates, T.; Capelli, A.; Lusuardi, M.; Gnemmi, I.; Ioli, F.; Chung, K.F.; Donner, C.F.; Barnes, P.J.; et al. Increased expression of nuclear factor-κB in bronchial biopsies from smokers and patients with COPD. Eur. Respir. J 2002, 20, 556–563. [Google Scholar]
- Nakanishi, C.; Toi, M. Nuclear factor-κB inhibitors as sensitizers to anticancer drugs. Nat. Rev. Cancer 2005, 5, 297–309. [Google Scholar]
- Denlinger, C.E.; Rundall, B.K.; Jones, D.R. Modulation of antiapoptotic cell signaling pathways in non-small cell lung cancer: The role of NF-kappaB. Semin. Thorac. Cardiovasc. Surg 2004, 16, 28–39. [Google Scholar]
- Shen, H.M.; Tergaonkar, V. NFκB signaling in carcinogenesis and as a potential molecular target for cancer therapy. Apoptosis 2009, 14, 348–363. [Google Scholar]
- Cheng, Q.; Lee, H.H.; Li, Y.; Parks, T.P.; Cheng, G. Upregulation of Bcl-x and Bfl-1 as a potential mechanism of chemoresistance, which can be overcome by NF-κB inhibition. Oncogene 2000, 19, 4936–4940. [Google Scholar]
- Li, Y.; Ahmed, F.; Ali, S.; Philip, P.A.; Kucuk, O.; Sarkar, F.H. Inactivation of nuclear factor kappaB by soy isoflavone genistein contributes to increased apoptosis induced by chemotherapeutic agents in human cancer cells. Cancer Res 2005, 65, 6934–6942. [Google Scholar]
- Osaki, S.; Nakanishi, Y.; Takayama, K.; Pei, X.H.; Ueno, H.; Hara, N. Transfer of IkappaBalpha gene increase the sensitivity of paclitaxel mediated with caspase 3 activation in human lung cancer cell. J. Exp. Clin. Cancer Res 2003, 22, 69–75. [Google Scholar]
- Chen, W.; Wang, X.; Bai, L.; Liang, X.; Zhuang, J.; Lin, Y. Blockage of NF-kappaB by IKKbeta- or RelA-siRNA rather than the NF-κB super-suppressor IkappaBalpha mutant potentiates adriamycin-induced cytotoxicity in lung cancer cells. J. Cell Biochem 2008, 105, 554–561. [Google Scholar]
- Jones, D.R.; Broad, R.M.; Madrid, L.V.; Baldwin, A.S., Jr; Mayo, M.W. Inhibition of NF-κB sensitizes non-small cell lung cancer cells to chemotherapy-induced apoptosis. Ann. Thorac. Surg. 2000, 70, 930–936. [Google Scholar]




| Controls n = 15 | COPD n = 15 | LC n = 15 | LC&COPD n = 15 | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Gender | ||||
| Male | 100.0% (15) | 100.0% (15) | 100.0% (15) | 100.0% (15) |
| Female | 0.0% (0) | 0.0% (0) | 0.0% (0) | 0.0% (0) |
| Average age (range) | 61.3 (41–80) | 61.5 (45–78) | 60.7 (46–69) | 60.7 (49–68) |
| Smoking status Smokers | 73.3% (11) | 53.3% (8) | 53.3% (8) | 80.0% (12) |
| Ex-smokers | 26.7% (4) | 46.7% (7) | 46.7% (7) | 20.0% (3) |
| Packs-year | 21.82 | 32.20 | 35.21 | 30.78 |
| COPD | ||||
| Mild | - | 20.0% (3) | - | 53.3% (8) |
| Moderate | - | 33.3% (5) | - | 26.7% (4) |
| Severe | - | 26.7% (4) | - | - |
| Very severe | - | 20.0% (3) | - | 20.0% (3) |
| Histology | ||||
| Adenocarcinoma | - | - | 73.3% (11) | 66.7% (10) |
| Squamous cell carcinoma | - | - | 26.7% (4) | 33.3% (5) |
| Spot no | Protein name | Protein symbol | Accession no | Protein MW | Protein PI | Peptide count | Protein score | Score C.I. % | Total ion score | Ion C.I. % | COPD | LC | LC/COPD | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | Catalase | CAT | gi|4557014 | 59946.8 | 6.90 | 13 | 310 | 100 | 234 | 100 | Up | 2.5 | - | Up | 2.8 | |
| 2 | Cathepsin D preprotein | CTSD | gi|4503143 | 45036.8 | 6.10 | 8 | 135 | 100 | 95 | 100 | - | Up | 3.0 | . | ||
| 3 | Ezrin | EZR | gi|46249758 | 69312.7 | 5.94 | 18 | 250 | 100 | 175 | 100 | - | Up | 3.0 | - | ||
| 4 | Glutathione reductase | GSR | gi|119583848 | 61464.6 | 8.71 | 7 | 131 | 100 | 108 | 100 | Up | 2.8 | Up | 3.1 | Up | 2.0 |
| 5 | Glutathione S-transferase A1 subunit | GSTA1 | gi|163310943 | 25628.7 | 8.72 | 15 | 384 | 100 | 268 | 100 | Down | 3.0 | Down | 3.2 | Down | 3.8 |
| 6 | Glutathione S-transferase A2 subunit | GSTA2 | gi|257476 | 25589.6 | 8.81 | 7 | 105 | 100 | 70 | 100 | Down | 2.5 | Down | 3.0 | Down | 2.6 |
| 7 | Glutathione S-transferase P | GSTP1 | gi|4504183 | 23569.1 | 5.43 | 10 | 633 | 100 | 541 | 100 | Down | 2.2 | Down | 2.4 | Down | 2.5 |
| 8 | Isocitrate dehydrogenase 1 | IDH1 | gi|89573979 | 42091.0 | 6.19 | 8 | 62 | 100 | 29 | 100 | Up | 2.2 | Up | 2.1 | Up | 2.5 |
| 9 | Leukocyte elastase inhibitor | SERPINB1 | gi|13489087 | 42828.7 | 5.90 | 18 | 403 | 100 | 274 | 100 | Up | 2.7 | Up | 2.6 | Up | 2.5 |
| 10 | Peptidylprolyl isomerase A (Cyclophilin A) | PPIA | gi|1633054 | 18097.9 | 7.82 | 10 | 260 | 100 | 159 | 100 | - | Up | 2.2 | Up | 2.6 | |
| 11 | Peroxiredoxin 1 | PRDX1 | gi|55959887 | 19134.7 | 6.41 | 8 | 170 | 100 | 98 | 100 | Up | 5.0 | - | Up | 4.2 | |
| 12 | Peroxiredoxin 5 | PRDX5 | gi|6166493 | 22261.6 | 8.85 | 11 | 638 | 100 | 537 | 100 | Up | 2.3 | - | Up | 2.4 | |
| 13 | Peroxiredoxin-2 isoform a | PRDX2 | gi|32189392 | 22049.3 | 5.66 | 12 | 451 | 100 | 325 | 100 | Up | 3.0 | - | Up | 2.9 | |
| 14 | Rho GDP-dissociation inhibitor 2 | ARHGDIB | gi|56676393 | 23030.6 | 5.10 | 7 | 215 | 100 | 170 | 100 | Up | 2.9 | Up | 2.6 | Up | 2.3 |
| 15 | Thioredoxin | TXN | gi|135772 | 12345.0 | 7.93 | 10 | 241 | 100 | 203 | 100 | Up | 2.4 | Up | 2.3 | Up | 2.1 |
© 2013 by the authors; licensee Molecular Diversity Preservation International, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/3.0/).
Share and Cite
Pastor, M.D.; Nogal, A.; Molina-Pinelo, S.; Meléndez, R.; Romero-Romero, B.; Mediano, M.D.; López-Campos, J.L.; García-Carbonero, R.; Sanchez-Gastaldo, A.; Carnero, A.; et al. Identification of Oxidative Stress Related Proteins as Biomarkers for Lung Cancer and Chronic Obstructive Pulmonary Disease in Bronchoalveolar Lavage. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2013, 14, 3440-3455. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms14023440
Pastor MD, Nogal A, Molina-Pinelo S, Meléndez R, Romero-Romero B, Mediano MD, López-Campos JL, García-Carbonero R, Sanchez-Gastaldo A, Carnero A, et al. Identification of Oxidative Stress Related Proteins as Biomarkers for Lung Cancer and Chronic Obstructive Pulmonary Disease in Bronchoalveolar Lavage. International Journal of Molecular Sciences. 2013; 14(2):3440-3455. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms14023440
Chicago/Turabian StylePastor, Maria Dolores, Ana Nogal, Sonia Molina-Pinelo, Ricardo Meléndez, Beatriz Romero-Romero, Maria Dolores Mediano, Jose L. López-Campos, Rocío García-Carbonero, Amparo Sanchez-Gastaldo, Amancio Carnero, and et al. 2013. "Identification of Oxidative Stress Related Proteins as Biomarkers for Lung Cancer and Chronic Obstructive Pulmonary Disease in Bronchoalveolar Lavage" International Journal of Molecular Sciences 14, no. 2: 3440-3455. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms14023440
APA StylePastor, M. D., Nogal, A., Molina-Pinelo, S., Meléndez, R., Romero-Romero, B., Mediano, M. D., López-Campos, J. L., García-Carbonero, R., Sanchez-Gastaldo, A., Carnero, A., & Paz-Ares, L. (2013). Identification of Oxidative Stress Related Proteins as Biomarkers for Lung Cancer and Chronic Obstructive Pulmonary Disease in Bronchoalveolar Lavage. International Journal of Molecular Sciences, 14(2), 3440-3455. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms14023440