Sphingomyelin in High-Density Lipoproteins: Structural Role and Biological Function
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Structural Role of Sphingomyelin in HDL
2.1. Distribution into HDL Subclasses
2.2. Source of Sphingomyelin
2.3. Interaction of SM with Apolipoproteins
2.4. Different SM Species
2.5. Metabolic Fate of HDL Sphingomyelin
3. Contribution of Sphingomyelin to the Biological Function of HDL
3.1. Reverse Cholesterol Transport
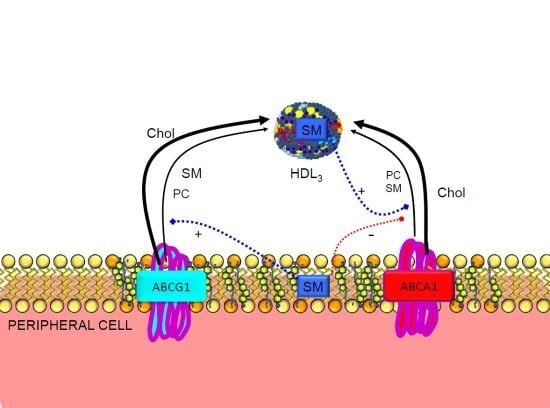
3.2. Regulation of ABCA1
3.3. Regulation of Plasma Enzymes
3.4. SR-BI in Lipid Transfer to the Cells
4. Factors Influencing HDL-SM
4.1. Aging and Sex
4.2. Lifestyle
4.3. Pharmacological Agents
4.4. Changes in HDL-SM Affected by Pathological Conditions
5. Conclusions
Acknowledgments
Abbreviations
| APO | apolipoprotein |
| CHD | coronary heart disease |
| CM | chylomicrons |
| HDL | high-density lipoproteins |
| LCAT | lecithin–cholesterol acyltransferase |
| LDL | low-density lipoproteins |
| PC | phosphatidylcholine |
| SM | sphingomyelin |
| VLDL | very low-density lipoprotein |
Conflict of Interest
References
- Vaisar, T.; Pennathur, S.; Green, P.S.; Gharib, S.A.; Hoofnagle, A.N.; Cheung, M.C.; Byun, J.; Vuletic, S.; Kassim, S.; Singh, P.; et al. Shotgun proteomics implicates protease inhibition and complement activation in the antiinflammatory properties of HDL. J. Clin. Invest 2007, 117, 746–756. [Google Scholar]
- Lou-Bonafonte, J.M.; Fito, M.; Covas, M.I.; Farras, M.; Osada, J. HDL-related mechanisms of olive oil protection in cardiovascular disease. Curr. Vasc. Pharmacol 2012, 10, 392–409. [Google Scholar]
- Gotto, A.M., Jr. High-density lipoproteins: Biochemical and metabolic factors. Am. J. Cardiol 1983, 52, 2B–4B. [Google Scholar]
- Rosenson, R.S.; Brewer, H.B., Jr; Chapman, M.J.; Fazio, S.; Hussain, M.M.; Kontush, A.; Krauss, R.M.; Otvos, J.D.; Remaley, A.T.; Schaefer, E.J. HDL measures, particle heterogeneity, proposed nomenclature, and relation to atherosclerotic cardiovascular events. Clin. Chem. 2011, 57, 392–410. [Google Scholar]
- Kontush, A.; Therond, P.; Zerrad, A.; Couturier, M.; Negre-Salvayre, A.; de Souza, J.A.; Chantepie, S.; Chapman, M.J. Preferential sphingosine-1-phosphate enrichment and sphingomyelin depletion are key features of small dense HDL3 particles: Relevance to antiapoptotic and antioxidative activities. Arterioscler. Thromb. Vasc. Biol 2007, 27, 1843–1849. [Google Scholar]
- Hofer, G.; Lichtenberg, D.; Kostner, G.M.; Hermetter, A. Oxidation of fluorescent glycero- and sphingophospholipids in human plasma lipoproteins: Alkenylacyl subclasses are preferred targets. Clin. Biochem 1996, 29, 445–450. [Google Scholar]
- Chong, C.P.; Lin, T.Y.; Chang, C.L.; Yang, Y.L.; Tsai, M.H.; Yu, Y.S.; Liu, M.Y. Micellar electrokinetic chromatography profiles of human high-density lipoprotein phospholipids. Electrophoresis 2011, 32, 1241–1251. [Google Scholar]
- Khovidhunkit, W.; Kim, M.S.; Memon, R.A.; Shigenaga, J.K.; Moser, A.H.; Feingold, K.R.; Grunfeld, C. Effects of infection and inflammation on lipid and lipoprotein metabolism: Mechanisms and consequences to the host. J. Lipid Res 2004, 45, 1169–1196. [Google Scholar]
- Navab, M.; Reddy, S.T.; van Lenten, B.J.; Anantharamaiah, G.M.; Fogelman, A.M. The role of dysfunctional HDL in atherosclerosis. J. Lipid Res 2009, 50, S145–S149. [Google Scholar]
- Hammad, S.M.; Pierce, J.S.; Soodavar, F.; Smith, K.J.; Al Gadban, M.M.; Rembiesa, B.; Klein, R.L.; Hannun, Y.A.; Bielawski, J.; Bielawska, A. Blood sphingolipidomics in healthy humans: Impact of sample collection methodology. J. Lipid Res 2010, 51, 3074–3087. [Google Scholar]
- Rodriguez, C.; Gonzalez-Diez, M.; Badimon, L.; Martinez-Gonzalez, J. Sphingosine-1-phosphate: A bioactive lipid that confers high-density lipoprotein with vasculoprotection mediated by nitric oxide and prostacyclin. Thromb. Haemost 2009, 101, 665–673. [Google Scholar]
- Hoofnagle, A.N.; Vaisar, T.; Mitra, P.; Chait, A. HDL lipids and insulin resistance. Curr. Diab. Rep 2010, 10, 78–86. [Google Scholar]
- Yetukuri, L.; Soderlund, S.; Koivuniemi, A.; Seppanen-Laakso, T.; Niemela, P.S.; Hyvonen, M.; Taskinen, M.R.; Vattulainen, I.; Jauhiainen, M.; Oresic, M. Composition and lipid spatial distribution of HDL particles in subjects with low and high HDL-cholesterol. J. Lipid Res 2010, 51, 2341–2351. [Google Scholar]
- Moher, D.; Liberati, A.; Tetzlaff, J.; Altman, D.G.; The, P.G. Preferred reporting items for systematic reviews and meta-analyses: The PRISMA Statement. PLoS Med 2009, 6, e1000097. [Google Scholar]
- Skipski, V.P.; Barclay, M.; Barclay, R.K.; Fetzer, V.A.; Good, J.J.; Archibald, F.M. Lipid composition of human serum lipoproteins. Biochem. J 1967, 104, 340–352. [Google Scholar]
- Daerr, W.H.; Greten, H. In vitro modulation of the distribution of normal human plasma high density lipoprotein subfractions through the lecithin: Cholesterol acyltransferase reaction. Biochim. Biophys. Acta 1982, 710, 128–133. [Google Scholar]
- Darr, W.H.; Windler, E.E.; Stephan, K.U.; Walli, A.K.; Greten, H. Characterization and catabolism of rat very high density lipoproteins. J. Lipid Res 1985, 26, 672–683. [Google Scholar]
- Davidson, W.S.; Sparks, D.L.; Lund-Katz, S.; Phillips, M.C. The molecular basis for the difference in charge between pre-beta- and alpha-migrating high density lipoproteins. J. Biol. Chem 1994, 269, 8959–8965. [Google Scholar]
- Marques-Vidal, P.; Jauhiainen, M.; Metso, J.; Ehnholm, C. Transformation of high density lipoprotein 2 particles by hepatic lipase and phospholipid transfer protein. Atherosclerosis 1997, 133, 87–95. [Google Scholar]
- Maldonado, E.N.; Casanave, E.B.; Aveldano, M.I. Major plasma lipids and fatty acids in four HDL mammals. Comp. Biochem. Physiol. Part A 2002, 132, 297–303. [Google Scholar]
- Blaton, V.; Vercaemst, R.; Rosseneu, M.; Mortelmans, J.; Jackson, R.L.; Gotto, A.M., Jr; Peeters, H. Characterization of baboon plasma high-density lipoproteins and of their major apoproteins. Biochemistry 1977, 16, 2157–2163. [Google Scholar]
- McConathy, W.J.; Alaupovic, P. Studies on the isolation and partial characterization of apolipoprotein D and lipoprotein D of human plasma. Biochemistry 1976, 15, 515–520. [Google Scholar]
- Krimbou, L.; Tremblay, M.; Jacques, H.; Davignon, J.; Cohn, J.S. In vitro factors affecting the concentration of gamma-LpE in human plasma. J. Lipid Res 1998, 39, 861–872. [Google Scholar]
- Duverger, N.; Ghalim, N.; Theret, N.; Fruchart, J.C.; Castro, G. Lipoproteins containing apolipoprotein A-IV: Composition and relation to cholesterol esterification. Biochim. Biophys. Acta 1994, 1211, 23–28. [Google Scholar]
- Atmeh, R.F.; Kana’an, B.M.; Massad, T.T. Isolation of high density lipoprotein subclasses by electrofiltration and their chemical components. Prep. Biochem. Biotechnol 2009, 39, 248–265. [Google Scholar]
- Nanjee, M.N.; Cooke, C.J.; Olszewski, W.L.; Miller, N.E. Lipid and apolipoprotein concentrations in prenodal leg lymph of fasted humans. Associations with plasma concentrations in normal subjects, lipoprotein lipase deficiency, and LCAT deficiency. J. Lipid Res 2000, 41, 1317–1327. [Google Scholar]
- Sloop, C.H.; Dory, L.; Roheim, P.S. Interstitial fluid lipoproteins. J. Lipid Res 1987, 28, 225–237. [Google Scholar]
- Worgall, T.S. Sphingolipid synthetic pathways are major regulators of lipid homeostasis. Adv. Exp. Med. Biol 2011, 721, 139–148. [Google Scholar]
- Hussain, M.M.; Jin, W.; Jiang, X.C. Mechanisms involved in cellular ceramide homeostasis. Nutr. Metab 2012, 9, 71. [Google Scholar]
- Maric, J.; Kiss, R.S.; Franklin, V.; Marcel, Y.L. Intracellular lipidation of newly synthesized apolipoprotein A-I in primary murine hepatocytes. J. Biol. Chem 2005, 280, 39942–39949. [Google Scholar]
- Subbaiah, P.V.; Gesquiere, L.R.; Wang, K. Regulation of the selective uptake of cholesteryl esters from high density lipoproteins by sphingomyelin. J. Lipid Res 2005, 46, 2699–2705. [Google Scholar]
- Bielicki, J.K.; Johnson, W.J.; Glick, J.M.; Rothblat, G.H. Efflux of phospholipid from fibroblasts with normal and elevated levels of cholesterol. Biochim. Biophys. Acta 1991, 1085, 7–14. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, W.; Asztalos, B.; Roheim, P.S.; Wong, L. Characterization of phospholipids in pre-alpha HDL: Selective phospholipid efflux with apolipoprotein A-I. J. Lipid Res 1998, 39, 1601–1607. [Google Scholar]
- Sorci-Thomas, M.G.; Owen, J.S.; Fulp, B.; Bhat, S.; Zhu, X.; Parks, J.S.; Shah, D.; Jerome, W.G.; Gerelus, M.; Zabalawi, M.; et al. Nascent high density lipoproteins formed by ABCA1 resemble lipid rafts and are structurally organized by three apoA-I monomers. J. Lipid Res 2012, 53, 1890–1909. [Google Scholar]
- Choi, H.Y.; Karten, B.; Chan, T.; Vance, J.E.; Greer, W.L.; Heidenreich, R.A.; Garver, W.S.; Francis, G.A. Impaired ABCA1-dependent lipid efflux and hypoalphalipoproteinemia in human Niemann-Pick type C disease. J. Biol. Chem 2003, 278, 32569–32577. [Google Scholar]
- Toledo, J.D.; Cabaleiro, L.V.; Garda, H.A.; Gonzalez, M.C. Effect of reconstituted discoidal high-density lipoproteins on lipid mobilization in RAW 264.7 and CHOK1 cells. J. Cell. Biochem 2011, 113, 1208–1216. [Google Scholar]
- Savion, N.; Greemland, M.; Kotev-Emeth, S.; Thilo-Korner, D.G. Metabolism of cholesterol and phospholipids in cultured human vascular smooth muscle cells: Differences between artery and vein-derived cells and the effect of oxygen partial pressure. Eur. J. Cell. Biol 1991, 55, 305–311. [Google Scholar]
- Francis, G.A.; Tsujita, M.; Terry, T.L. Apolipoprotein AI efficiently binds to and mediates cholesterol and phospholipid efflux from human but not rat aortic smooth muscle cells. Biochemistry 1999, 38, 16315–16322. [Google Scholar]
- Massey, J.B.; Hickson-Bick, D.; Via, D.P.; Gotto, A.M., Jr; Pownall, HJ. Fluorescence assay of the specificity of human plasma and bovine liver phospholipid transfer proteins. Biochim. Biophys. Acta 1985, 835, 124–131. [Google Scholar]
- Schifferer, R.; Liebisch, G.; Bandulik, S.; Langmann, T.; Dada, A.; Schmitz, G. ApoA-I induces a preferential efflux of monounsaturated phosphatidylcholine and medium chain sphingomyelin species from a cellular pool distinct from HDL(3) mediated phospholipid efflux. Biochim. Biophys. Acta 2007, 1771, 853–863. [Google Scholar]
- Fukuda, M.; Nakano, M.; Sriwongsitanont, S.; Ueno, M.; Kuroda, Y.; Handa, T. Spontaneous reconstitution of discoidal HDL from sphingomyelin-containing model membranes by apolipoprotein A-I. J. Lipid Res 2007, 48, 882–889. [Google Scholar]
- Sparks, D.L.; Frank, P.G.; Neville, T.A. Effect of the surface lipid composition of reconstituted LPA-I on apolipoprotein A-I structure and lecithin: Cholesterol acyltransferase activity. Biochim. Biophys. Acta 1998, 1390, 160–172. [Google Scholar]
- Rye, K.A.; Hime, N.J.; Barter, P.J. The influence of sphingomyelin on the structure and function of reconstituted high density lipoproteins. J. Biol. Chem 1996, 271, 4243–4250. [Google Scholar]
- Lottin, H.; Motta, C.; Simard, G. Differential effects of glycero- and sphingo-phospholipolysis on human high-density lipoprotein fluidity. Biochim. Biophys. Acta 1996, 1301, 127–132. [Google Scholar]
- Slotte, J.P.; Gronberg, L. Oxidation of cholesterol in low density and high density lipoproteins by cholesterol oxidase. J. Lipid Res 1990, 31, 2235–2242. [Google Scholar]
- Subbaiah, P.V.; Subramanian, V.S.; Wang, K. Novel physiological function of sphingomyelin in plasma. Inhibition of lipid peroxidation in low density lipoproteins. J. Biol. Chem 1999, 274, 36409–36414. [Google Scholar]
- Assmann, G.; Sokoloski, E.A.; Brewer, H.B., Jr. 31P nuclear magnetic resonance spectroscopy of native and recombined lipoproteins. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 1974, 71, 549–553. [Google Scholar]
- Assmann, G.; Highet, R.J.; Sokoloski, E.A.; Brewer, H.B., Jr. 13C nuclear magnetic resonance spectroscopy of native recombined lipoproteins. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 1974, 71, 3701–3705. [Google Scholar]
- Stoffel, W.; Metz, P. Chemical studies on the structure of human serum high-density lipoprotein (HDL). Photochemical crosslinking of azido-labelled lipids in HDL. Hoppe-Seyler’s. Z. Physiol. Chem 1982, 363, 19–31. [Google Scholar]
- Tam, S.P.; Breckenridge, W.C. Apolipoprotein and lipid distribution between vesicles and HDL-like particles formed during lipolysis of human very low density lipoproteins by perfused rat heart. J. Lipid Res 1983, 24, 1343–1357. [Google Scholar]
- Stoffel, W.; Darr, W.; Salm, K.P. Lipid-protein interactions between human apolipoprotein A-I and defined sphingomyelin species. A 13C-NMR spectroscopic study. Hoppe-Seyler’s Z. Physiol. Chem 1977, 358, 1–11. [Google Scholar]
- Stoffel, W.; Darr, W.; Salm, K.P. Chemical proof of lipid-protein interactions by crosslinking photosensitive lipids to apoproteins. Intermolecular cross-linkage between high-density apolipoprotein A-I and lecithins and sphingomyelins. Hoppe.-Seyler’s Z. Physiol. Chem 1977, 358, 453–462. [Google Scholar]
- Swaney, J.B. Reconstitution of apolipoprotein A-I from human high density lipoprotein with bovine brain sphingomyelin. J. Biol. Chem 1983, 258, 1254–1259. [Google Scholar]
- Assmann, G.; Brewer, H.B., Jr. Lipid-protein interactions in high density lipoproteins. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 1974, 71, 989–993. [Google Scholar]
- Stoffel, W.; Zierenberg, O.; Tunggal, B.; Schreiber, E. 13C nuclear magnetic resonance spectroscopic evidence for hydrophobic lipid-protein interactions in human high density lipoproteins. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 1974, 71, 3696–3700. [Google Scholar]
- Ibdah, J.A.; Lund-Katz, S.; Phillips, M.C. Molecular packing of high-density and low-density lipoprotein surface lipids and apolipoprotein A-I binding. Biochemistry 1989, 28, 1126–1133. [Google Scholar]
- Forte, T.M.; Bielicki, J.K.; Goth-Goldstein, R.; Selmek, J.; McCall, M.R. Recruitment of cell phospholipids and cholesterol by apolipoproteins A-II and A-I: Formation of nascent apolipoprotein-specific HDL that differ in size, phospholipid composition, and reactivity with LCAT. J. Lipid Res 1995, 36, 148–157. [Google Scholar]
- Molotkovsky, J.G.; Manevich, Y.M.; Gerasimova, E.N.; Molotkovskaya, I.M.; Polessky, V.A.; Bergelson, L.D. Differential study of phosphatidylcholine and sphingomyelin in human high-density lipoproteins with lipid-specific fluorescent probes. Eur. J. Biochem 1982, 122, 573–579. [Google Scholar]
- Lindholm, E.M.; Bielicki, J.K.; Curtiss, L.K.; Rubin, E.M.; Forte, T.M. Deletion of amino acids Glu146->Arg160 in human apolipoprotein A-I (ApoA-ISeattle) alters lecithin: Cholesterol acyltransferase activity and recruitment of cell phospholipid. Biochemistry 1998, 37, 4863–4868. [Google Scholar]
- Fox, T.E.; Bewley, M.C.; Unrath, K.A.; Pedersen, M.M.; Anderson, R.E.; Jung, D.Y.; Jefferson, L.S.; Kim, J.K.; Bronson, S.K.; Flanagan, J.M.; et al. Circulating sphingolipid biomarkers in models of type 1 diabetes. J. Lipid Res 2011, 52, 509–517. [Google Scholar]
- Laurila, P.P.; Surakka, I.; Sarin, A.P.; Yetukuri, L.; Hyotylainen, T.; Soderlund, S.; Naukkarinen, J.; Tang, J.; Kettunen, J.; Mirel, D.B.; et al. Genomic, transcriptomic, and lipidomic profiling highlights the role of inflammation in individuals with low high-density lipoprotein cholesterol. Arterioscler. Thromb. Vasc. Biol 2013, 33, 847–857. [Google Scholar]
- Kuksis, A.; Myher, J.J.; Geher, K.; Breckenridge, W.C.; Jones, G.J.; Little, J.A. Lipid class and molecular species interrelationships among plasma lipoproteins of normolipemic subjects. J. Chromatogr 1981, 224, 1–23. [Google Scholar]
- Myher, J.J.; Kuksis, A.; Breckenridge, W.C.; Little, J.A. Differential distribution of sphingomyelins among plasma lipoprotein classes. Can. J. Biochem 1981, 59, 626–636. [Google Scholar]
- Kuksis, A.; Myher, J.J.; Geher, K.; Breckenridge, W.C.; Little, J.A. Lipid class and molecular species interrelationships among plasma lipoproteins of type III and type IV hyperlipemic subjects. J. Chromatogr 1982, 230, 231–252. [Google Scholar]
- Breckenridge, W.C.; Dolphin, P.J.; Tan, M.H. Distribution of the molecular species of phospholipids in human umbilical cord blood. Lipids 1984, 19, 337–340. [Google Scholar]
- Wu, C.Y.; Peng, Y.N.; Chiu, J.H.; Ho, Y.L.; Chong, C.P.; Yang, Y.L.; Liu, M.Y. Characterization of in vitro modified human high-density lipoprotein particles and phospholipids by capillary zone electrophoresis and LC ESI-MS. J. Chromatogr. B 2009, 877, 3495–3505. [Google Scholar]
- Stubiger, G.; Aldover-Macasaet, E.; Bicker, W.; Sobal, G.; Willfort-Ehringer, A.; Pock, K.; Bochkov, V.; Widhalm, K.; Belgacem, O. Targeted profiling of atherogenic phospholipids in human plasma and lipoproteins of hyperlipidemic patients using MALDI-QIT-TOF-MS/MS. Atherosclerosis 2012, 224, 177–186. [Google Scholar]
- Fernando-Warnakulasuriya, G.J.; Eckerson, M.L.; Clark, W.A.; Wells, M.A. Lipoprotein metabolism in the suckling rat: Characterization of plasma and lymphatic lipoproteins. J. Lipid Res 1983, 24, 1626–1638. [Google Scholar]
- Bentejac, M.; Bugaut, M.; Delachambre, M.C.; Lecerf, J. Utilization of high-density lipoprotein sphingomyelin by the developing and mature brain in the rat. J. Neurochem 1989, 52, 1495–1500. [Google Scholar]
- Bentejac, M.; Bugaut, M.; Delachambre, M.C.; Lecerf, J. Time-course of utilization of (stearic or lignoceric acid)sphingomyelin from high-density lipoprotein by rat tissues. Biochim. Biophys. Acta 1990, 1043, 134–142. [Google Scholar]
- Bamberger, M.; Lund-Katz, S.; Phillips, M.C.; Rothblat, G.H. Mechanism of the hepatic lipase induced accumulation of high-density lipoprotein cholesterol by cells in culture. Biochemistry 1985, 24, 3693–3701. [Google Scholar]
- Engelmann, B.; Kogl, C.; Kulschar, R.; Schaipp, B. Transfer of phosphatidylcholine, phosphatidylethanolamine and sphingomyelin from low- and high-density lipoprotein to human platelets. Biochem. J 1996, 315, 781–789. [Google Scholar]
- Bentejac, M.; Lecerf, J.; Bugaut, M.; Delachambre, M.C. Turnover and uptake of double-labelled high-density lipoprotein sphingomyelin in the adult rat. Biochim. Biophys. Acta 1988, 959, 349–360. [Google Scholar]
- Bentejac, M.; Bugaut, M.; Delachambre, M.C.; Lecerf, J. Metabolic fate of sphingomyelin of high-density lipoprotein in rat plasma. Lipids 1990, 25, 653–660. [Google Scholar]
- Illingworth, D.R.; Portman, O.W. Exchange of phospholipids between low and high density lipoproteins of squirrel monkeys. J. Lipid Res 1972, 13, 220–227. [Google Scholar]
- Fournier, N.; Paul, J.L.; Atger, V.; Cogny, A.; Soni, T.; de la Llera-Moya, M.; Rothblat, G.; Moatti, N. HDL phospholipid content and composition as a major factor determining cholesterol efflux capacity from Fu5AH cells to human serum. Arterioscler. Thromb. Vasc. Biol 1997, 17, 2685–2691. [Google Scholar]
- Horter, M.J.; Sondermann, S.; Reinecke, H.; Bogdanski, J.; Woltering, A.; Kerber, S.; Breithardt, G.; Assmann, G.; Von Eckardstein, A. Associations of HDL phospholipids and paraoxonase activity with coronary heart disease in postmenopausal women. Acta Physiol. Scand 2002, 176, 123–130. [Google Scholar]
- Hergenc, G.; Onat, A.; Sari, I.; Yazici, M.; Eryonucu, B.; Can, G. Serum total and high-density lipoprotein phospholipid levels in a population-based study and relationship to risk of metabolic syndrome and coronary disease. Angiology 2008, 59, 26–35. [Google Scholar]
- Stein, Y.; Glangeaud, M.C.; Fainaru, M.; Stein, O. The removal of cholesterol from aortic smooth muscle cells in culture and Landschutz ascites cells by fractions of human high-density apolipoprotein. Biochim. Biophys. Acta 1975, 380, 106–118. [Google Scholar]
- Stein, O.; Vanderhoek, J.; Stein, Y. Cholesterol content and sterol synthesis in human skin fibroblasts and rat aortic smooth muscle cells exposed to lipoprotein-depleted serum and high density apolipoprotein/phospholipid mixtures. Biochim. Biophys. Acta 1976, 431, 347–358. [Google Scholar]
- Stein, O.; Coetzee, G.A.; Stein, Y. Modulation of cytoplasmic cholesteryl ester of smooth muscle cells in culture derived from rat, rabbit and bovine aorta. Biochim. Biophys. Acta 1980, 620, 538–549. [Google Scholar]
- Stein, O.; Dabach, Y.; Hollander, G.; Halperin, G.; Oette, K.; Stein, Y. Cholesterol removal by peritoneal lavage with phospholipid-HDL apoprotein mixtures in hypercholesterolemic hamsters. Biochim. Biophys. Acta 1989, 1006, 144–146. [Google Scholar]
- Zhao, Y.; Sparks, D.L.; Marcel, Y.L. Effect of the apolipoprotein A–I and surface lipid composition of reconstituted discoidal HDL on cholesterol efflux from cultured fibroblasts. Biochemistry 1996, 35, 16510–16518. [Google Scholar]
- Swaney, J.B. Membrane cholesterol uptake by recombinant lipoproteins. Chem. Phys. Lipids 1985, 37, 317–327. [Google Scholar]
- Jian, B.; de la Llera-Moya, M.; Royer, L.; Rothblat, G.; Francone, O.; Swaney, J.B. Modification of the cholesterol efflux properties of human serum by enrichment with phospholipid. J. Lipid Res 1997, 38, 734–744. [Google Scholar]
- Haidar, B.; Mott, S.; Boucher, B.; Lee, C.Y.; Marcil, M.; Genest, J., Jr. Cellular cholesterol efflux is modulated by phospholipid-derived signaling molecules in familial HDL deficiency/Tangier disease fibroblasts. J. Lipid Res 2001, 42, 249–257. [Google Scholar]
- Ma, C.I.; Beckstead, J.A.; Thompson, A.; Hafiane, A.; Wang, R.H.; Ryan, R.O.; Kiss, R.S. Tweaking the cholesterol efflux capacity of reconstituted HDL. Biochem. Cell. Biol 2012, 90, 636–645. [Google Scholar]
- Kobayashi, A.; Takanezawa, Y.; Hirata, T.; Shimizu, Y.; Misasa, K.; Kioka, N.; Arai, H.; Ueda, K.; Matsuo, M. Efflux of sphingomyelin, cholesterol, and phosphatidylcholine by ABCG1. J. Lipid Res 2006, 47, 1791–1802. [Google Scholar]
- Kimura, Y.; Morita, S.Y.; Matsuo, M.; Ueda, K. Mechanism of multidrug recognition by MDR1/ABCB1. Cancer Sci 2007, 98, 1303–1310. [Google Scholar]
- Liu, L.; Bortnick, A.E.; Nickel, M.; Dhanasekaran, P.; Subbaiah, P.V.; Lund-Katz, S.; Rothblat, G.H.; Phillips, M.C. Effects of apolipoprotein A-I on ATP-binding cassette transporter A1-mediated efflux of macrophage phospholipid and cholesterol: Formation of nascent high density lipoprotein particles. J. Biol. Chem 2003, 278, 42976–42984. [Google Scholar]
- Hirayama, H.; Kimura, Y.; Kioka, N.; Matsuo, M.; Ueda, K. ATPase activity of human ABCG1 is stimulated by cholesterol and sphingomyelin. J. Lipid Res 2013, 54, 496–502. [Google Scholar]
- Sano, O.; Kobayashi, A.; Nagao, K.; Kumagai, K.; Kioka, N.; Hanada, K.; Ueda, K.; Matsuo, M. Sphingomyelin-dependence of cholesterol efflux mediated by ABCG1. J. Lipid Res 2007, 48, 2377–2384. [Google Scholar]
- Miller, M.; Zhan, M. Genetic determinants of low high-density lipoprotein cholesterol. Curr. Opin. Cardiol 2004, 19, 380–384. [Google Scholar]
- Marmillot, P.; Patel, S.; Lakshman, M.R. Reverse cholesterol transport is regulated by varying fatty acyl chain saturation and sphingomyelin content in reconstituted high-density lipoproteins. Metabolism 2007, 56, 251–259. [Google Scholar]
- Sanchez, S.A.; Tricerri, M.A.; Gratton, E. Interaction of high density lipoprotein particles with membranes containing cholesterol. J. Lipid Res 2007, 48, 1689–1700. [Google Scholar]
- Gold, J.C.; Phillips, M.C. Effects of membrane lipid composition on the kinetics of cholesterol exchange between lipoproteins and different species of red blood cells. Biochim. Biophys. Acta 1990, 1027, 85–92. [Google Scholar]
- Slotte, J.P.; Tenhunen, J.; Porn, I. Effects of sphingomyelin degradation on cholesterol mobilization and efflux to high-density lipoproteins in cultured fibroblasts. Biochim. Biophys. Acta 1990, 1025, 152–156. [Google Scholar]
- Porn, M.I.; Ares, M.P.; Slotte, J.P. Degradation of plasma membrane phosphatidylcholine appears not to affect the cellular cholesterol distribution. J. Lipid Res 1993, 34, 1385–1392. [Google Scholar]
- Ito, J.; Nagayasu, Y.; Yokoyama, S. Cholesterol-sphingomyelin interaction in membrane and apolipoprotein-mediated cellular cholesterol efflux. J. Lipid Res 2000, 41, 894–904. [Google Scholar]
- Ito, J.; Nagayasu, Y.; Ueno, S.; Yokoyama, S. Apolipoprotein-mediated cellular lipid release requires replenishment of sphingomyelin in a phosphatidylcholine-specific phospholipase C-dependent manner. J. Biol. Chem 2002, 277, 44709–44714. [Google Scholar]
- Nagao, K.; Takahashi, K.; Hanada, K.; Kioka, N.; Matsuo, M.; Ueda, K. Enhanced apoA-I-dependent cholesterol efflux by ABCA1 from sphingomyelin-deficient Chinese hamster ovary cells. J. Biol. Chem 2007, 282, 14868–14874. [Google Scholar]
- Yamauchi, Y.; Hayashi, M.; Abe-Dohmae, S.; Yokoyama, S. Apolipoprotein A-I activates protein kinase C alpha signaling to phosphorylate and stabilize ATP binding cassette transporter A1 for the high density lipoprotein assembly. J. Biol. Chem 2003, 278, 47890–47897. [Google Scholar]
- Takahashi, K.; Kimura, Y.; Kioka, N.; Matsuo, M.; Ueda, K. Purification and ATPase activity of human ABCA1. J. Biol. Chem 2006, 281, 10760–10768. [Google Scholar]
- Panousis, C.G.; Zuckerman, S.H. Interferon-gamma induces downregulation of Tangier disease gene (ATP-binding-cassette transporter 1) in macrophage-derived foam cells. Arterioscler. Thromb. Vasc. Biol 2000, 20, 1565–1571. [Google Scholar]
- Tamehiro, N.; Zhou, S.; Okuhira, K.; Benita, Y.; Brown, C.E.; Zhuang, D.Z.; Latz, E.; Hornemann, T.; von Eckardstein, A.; Xavier, R.J.; et al. SPTLC1 binds ABCA1 to negatively regulate trafficking and cholesterol efflux activity of the transporter. Biochemistry 2008, 47, 6138–6147. [Google Scholar]
- Allen, T.M. A study of phospholipid interactions between high-density lipoproteins and small unilamellar vesicles. Biochim. Biophys. Acta 1981, 640, 385–397. [Google Scholar]
- Sweeny, S.A.; Jonas, A. Substrate specificity of human plasma phospholipid transfer protein. Biochim. Biophys. Acta 1985, 835, 279–290. [Google Scholar]
- Singh, D.K.; Gesquiere, L.R.; Subbaiah, P.V. Role of sphingomyelin and ceramide in the regulation of the activity and fatty acid specificity of group V secretory phospholipase A2. Arch. Biochem. Biophys 2007, 459, 280–287. [Google Scholar]
- Subbaiah, P.V.; Liu, M. Role of sphingomyelin in the regulation of cholesterol esterification in the plasma lipoproteins. Inhibition of lecithin-cholesterol acyltransferase reaction. J. Biol. Chem 1993, 268, 20156–20163. [Google Scholar]
- Subbaiah, P.V.; Jiang, X.C.; Belikova, N.A.; Aizezi, B.; Huang, Z.H.; Reardon, C.A. Regulation of plasma cholesterol esterification by sphingomyelin: Effect of physiological variations of plasma sphingomyelin on lecithin-cholesterol acyltransferase activity. Biochim. Biophys. Acta 2012, 1821, 908–913. [Google Scholar]
- Park, T.S.; Panek, R.L.; Rekhter, M.D.; Mueller, S.B.; Rosebury, W.S.; Robertson, A.; Hanselman, J.C.; Kindt, E.; Homan, R.; Karathanasis, S.K. Modulation of lipoprotein metabolism by inhibition of sphingomyelin synthesis in ApoE knockout mice. Atherosclerosis 2006, 189, 264–272. [Google Scholar]
- Gesquiere, L.; Cho, W.; Subbaiah, P.V. Role of group IIa and group V secretory phospholipases A(2) in the metabolism of lipoproteins. Substrate specificities of the enzymes and the regulation of their activities by sphingomyelin. Biochemistry 2002, 41, 4911–4920. [Google Scholar]
- Singh, D.K.; Subbaiah, P.V. Modulation of the activity and arachidonic acid selectivity of group X secretory phospholipase A2 by sphingolipids. J. Lipid Res 2007, 48, 683–692. [Google Scholar]
- Nilsson, A.; Duan, R.D. Absorption and lipoprotein transport of sphingomyelin. J. Lipid Res 2006, 47, 154–171. [Google Scholar]
- Chajek, T.; Aron, L.; Fielding, C.J. Interaction of lecithin:cholesterol acyltransferase and cholesteryl ester transfer protein in the transport of cholesteryl ester into sphingomyelin liposomes. Biochemistry 1980, 19, 3673–3677. [Google Scholar]
- Bolin, D.J.; Jonas, A. Sphingomyelin inhibits the lecithin-cholesterol acyltransferase reaction with reconstituted high density lipoproteins by decreasing enzyme binding. J. Biol. Chem 1996, 271, 19152–19158. [Google Scholar]
- Lee, J.Y.; Badeau, R.M.; Mulya, A.; Boudyguina, E.; Gebre, A.K.; Smith, T.L.; Parks, J.S. Functional LCAT deficiency in human apolipoprotein A-I transgenic, SR-BI knockout mice. J. Lipid Res 2007, 48, 1052–1061. [Google Scholar]
- Rodrigueza, W.V.; Thuahnai, S.T.; Temel, R.E.; Lund-Katz, S.; Phillips, M.C.; Williams, D.L. Mechanism of scavenger receptor class B type I-mediated selective uptake of cholesteryl esters from high density lipoprotein to adrenal cells. J. Biol. Chem 1999, 274, 20344–20350. [Google Scholar]
- Rhainds, D.; Bourgeois, P.; Bourret, G.; Huard, K.; Falstrault, L.; Brissette, L. Localization and regulation of SR-BI in membrane rafts of HepG2 cells. J. Cell. Sci 2004, 117, 3095–3105. [Google Scholar]
- Thuahnai, S.T.; Lund-Katz, S.; Williams, D.L.; Phillips, M.C. Scavenger receptor class B, type I-mediated uptake of various lipids into cells. Influence of the nature of the donor particle interaction with the receptor. J. Biol. Chem 2001, 276, 43801–43808. [Google Scholar]
- Yancey, P.G.; de la Llera-Moya, M.; Swarnakar, S.; Monzo, P.; Klein, S.M.; Connelly, M.A.; Johnson, W.J.; Williams, D.L.; Rothblat, G.H. High density lipoprotein phospholipid composition is a major determinant of the bi-directional flux and net movement of cellular free cholesterol mediated by scavenger receptor BI. J. Biol. Chem 2000, 275, 36596–36604. [Google Scholar]
- Werder, M.; Han, C.H.; Wehrli, E.; Bimmler, D.; Schulthess, G.; Hauser, H. Role of scavenger receptors SR-BI and CD36 in selective sterol uptake in the small intestine. Biochemistry 2001, 40, 11643–11650. [Google Scholar]
- Urban, S.; Zieseniss, S.; Werder, M.; Hauser, H.; Budzinski, R.; Engelmann, B. Scavenger receptor BI transfers major lipoprotein-associated phospholipids into the cells. J. Biol. Chem 2000, 275, 33409–33415. [Google Scholar]
- Berrougui, H.; Khalil, A. Age-associated decrease of high-density lipoprotein-mediated reverse cholesterol transport activity. Rejuvenation Res 2009, 12, 117–126. [Google Scholar]
- Berrougui, H.; Isabelle, M.; Cloutier, M.; Grenier, G.; Khalil, A. Age-related impairment of HDL-mediated cholesterol efflux. J. Lipid Res 2007, 48, 328–336. [Google Scholar]
- Schriewer, H.; Gunnewig, V.; Assmann, G. HDL sphingomyelin determinations in normal individuals and patients with type IV-hyperlipoproteinaemia. J. Clin. Chem. Clin. Biochem 1983, 21, 139–143. [Google Scholar]
- Deevska, G.M.; Sunkara, M.; Morris, A.J.; Nikolova-Karakashian, M.N. Characterization of secretory sphingomyelinase activity, lipoprotein sphingolipid content and LDL aggregation in ldlr-/- mice fed on a high-fat diet. Biosci. Rep 2012, 32, 479–490. [Google Scholar]
- Bladergroen, B.A.; Beynen, A.C.; Geelen, M.J. Dietary pectin lowers sphingomyelin concentration in VLDL and raises hepatic sphingomyelinase activity in rats. J. Nutr 1999, 129, 628–633. [Google Scholar]
- Geelen, M.J.; van Hoorn, D.; Beynen, A.C. Consumption of casein instead of soybean protein produces a transient rise in the concentration of sphingomyelin in VLDL in rats. J. Nutr 1999, 129, 2119–2122. [Google Scholar]
- Geelen, M.J.; Beynen, A.C. Consumption of olive oil has opposite effects on plasma total cholesterol and sphingomyelin concentrations in rats. Br. J. Nutr 2000, 83, 541–547. [Google Scholar]
- Martínez-Beamonte, R.; Navarro, M.A.; Acin, S.; Guillén, N.; Barranquero, C.; Arnal, C.; Surra, J.; Osada, J. Postprandial changes in high density lipoproteins in rats subjected to gavage administration of virgin olive oil. PLoS One 2013. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Z.; Basterr, M.J.; Hailemariam, T.K.; Hojjati, M.R.; Lu, S.; Liu, J.; Liu, R.; Zhou, H.; Jiang, X.C. The effect of dietary sphingolipids on plasma sphingomyelin metabolism and atherosclerosis. Biochim. Biophys. Acta 2005, 1735, 130–134. [Google Scholar]
- Vesper, H.; Schmelz, E.M.; Nikolova-Karakashian, M.N.; Dillehay, D.L.; Lynch, D.V.; Merrill, A.H., Jr. Sphingolipids in food and the emerging importance of sphingolipids to nutrition. J. Nutr 1999, 129, 1239–1250. [Google Scholar]
- Gerasimova, E.; Perova, N.; Ozerova, I.; Polessky, V.; Metelskaya, V.; Sherbakova, I.; Levachev, M.; Kulakova, S.; Nikitin, Y.; Astakhova, T. The effect of dietary n-3 polyunsaturated fatty acids on HDL cholesterol in Chukot residents vs muscovites. Lipids 1991, 26, 261–265. [Google Scholar]
- Myher, J.J.; Kuksis, A.; Shepherd, J.; Packard, C.J.; Morrisett, J.D.; Taunton, O.D.; Gotto, A.M. Effect of saturated and unsaturated fat diets on molecular species of phosphatidylcholine and sphingomyelin of human plasma lipoproteins. Biochim. Biophys. Acta 1981, 666, 110–119. [Google Scholar]
- Sola, R.; Baudet, M.F.; Motta, C.; Maille, M.; Boisnier, C.; Jacotot, B. Effects of dietary fats on the fluidity of human high-density lipoprotein: influence of the overall composition and phospholipid fatty acids. Biochim. Biophys. Acta 1990, 1043, 43–51. [Google Scholar]
- Ottestad, I.; Hassani, S.; Borge, G.I.; Kohler, A.; Vogt, G.; Hyotylainen, T.; Oresic, M.; Bronner, K.W.; Holven, K.B.; Ulven, S.M.; Myhrstad, M.C. Fish oil supplementation alters the plasma lipidomic profile and increases long-chain PUFAs of phospholipids and triglycerides in healthy subjects. PLoS One 2012, 7, e42550. [Google Scholar]
- Tynkkynen, T.; Mursu, J.; Nurmi, T.; Tuppurainen, K.; Laatikainen, R.; Soininen, P. NMR protocol for determination of oxidation susceptibility of serum lipids and application of the protocol to a chocolate study. Metabolomics 2012, 8, 386–398. [Google Scholar]
- Floegel, A.; Stefan, N.; Yu, Z.; Muhlenbruch, K.; Drogan, D.; Joost, H.G.; Fritsche, A.; Haring, H.U.; Hrabe de Angelis, M.; Peters, A.; et al. Identification of serum metabolites associated with risk of type 2 diabetes using a targeted metabolomic approach. Diabetes 2013, 62, 639–648. [Google Scholar]
- Schriewer, H.; Gunnewig, V.; Jung, K.; Assmann, G. The influence of a 100 km run on the composition of HDL. J. Clin. Chem. Clin. Biochem 1982, 20, 533–536. [Google Scholar]
- Marmillot, P.; Munoz, J.; Patel, S.; Garige, M.; Rosse, R.B.; Lakshman, M.R. Long-term ethanol consumption impairs reverse cholesterol transport function of high-density lipoproteins by depleting high-density lipoprotein sphingomyelin both in rats and in humans. Metabolism 2007, 56, 947–953. [Google Scholar]
- Bagdade, J.D.; Dunn, F.L. Improved lipoprotein surface and core lipid composition following intraperitoneal insulin delivery in insulin-dependent diabetes mellitus. Diab. Metab 1996, 22, 420–426. [Google Scholar]
- Bagdade, J.D.; Helve, E.; Taskinen, M.R. Effects of continuous insulin infusion therapy on lipoprotein surface and core lipid composition in insulin-dependent diabetes mellitus. Metabolism 1991, 40, 445–449. [Google Scholar]
- Piperi, C.; Kalofoutis, C.; Papapanagiotou, A.; Skenderi, C.; Kalofoutis, A. Comparative analysis of oestrogen and raloxifene effects on the phospholipid composition of high density lipoproteins in healthy postmenopausal women. J. Obstet. Gynaecol 2004, 24, 52–57. [Google Scholar]
- Piperi, C.; Kalofoutis, C.; Skenderi, K.; Economidou, O.; Kalofoutis, A. Beneficial effects of raloxifene and atorvastatin on serum lipids and HDL phospholipids levels of postmenopausal women. J. Obstet. Gynaecol 2004, 24, 414–419. [Google Scholar]
- Bergheanu, S.C.; Reijmers, T.; Zwinderman, A.H.; Bobeldijk, I.; Ramaker, R.; Liem, A.H.; van der Greef, J.; Hankemeier, T.; Jukema, J.W. Lipidomic approach to evaluate rosuvastatin and atorvastatin at various dosages: Investigating differential effects among statins. Curr. Med. Res. Opin 2008, 24, 2477–2487. [Google Scholar]
- Perova, N.V.; Ozerova, I.N.; Paramonova, I.V.; Olfer'ev, A.M.; Akhmedzhanov, N.M.; Pavlova, L.I.; Oganov, R.G. Phospholipid composition of high-density lipoproteins reflects lipolysis of triglyceride-rich lipoproteins during hyperlipidemia. Bull. Exp. Biol. Med 2001, 131, 321–324. [Google Scholar]
- Hammad, S.M. Blood sphingolipids in homeostasis and pathobiology. Adv. Exp. Med. Biol 2011, 721, 57–66. [Google Scholar]
- Yetukuri, L.; Huopaniemi, I.; Koivuniemi, A.; Maranghi, M.; Hiukka, A.; Nygren, H.; Kaski, S.; Taskinen, M.R.; Vattulainen, I.; Jauhiainen, M.; et al. High density lipoprotein structural changes and drug response in lipidomic profiles following the long-term fenofibrate therapy in the FIELD substudy. PLoS One 2011, 6, e23589. [Google Scholar]
- Bagdade, J.D.; Buchanan, W.F.; Pollare, T.; Lithell, H. Effects of hydrochlorothiazide and captopril on lipoprotein lipid composition in patients with essential hypertension. Eur. J. Clin. Pharmacol 1996, 49, 355–359. [Google Scholar]
- Bagdade, J.D.; Subbaiah, P.V. Influence of low estrogen-containing oral contraceptives on lipoprotein phospholipid composition and mononuclear cell membrane fluidity. J. Clin. Endocrinol. Metab 1988, 66, 857–861. [Google Scholar]
- Papapanagiotou, A.; Koufali, M.M.; Zachari, A.; Charalabidou, C.; Kalofoutis, A. Effects of hormone replacement therapy on the phospholipid composition of high density lipoproteins in postmenopausal women. J. Obstet. Gynaecol 2001, 21, 56–61. [Google Scholar]
- von Eckardstein, A.; Crook, D.; Elbers, J.; Ragoobir, J.; Ezeh, B.; Helmond, F.; Miller, N.; Dieplinger, H.; Bennink, H.C.; Assmann, G. Tibolone lowers high density lipoprotein cholesterol by increasing hepatic lipase activity but does not impair cholesterol efflux. Clin. Endocrinol 2003, 58, 49–58. [Google Scholar]
- Park, T.S.; Panek, R.L.; Mueller, S.B.; Hanselman, J.C.; Rosebury, W.S.; Robertson, A.W.; Kindt, E.K.; Homan, R.; Karathanasis, S.K.; Rekhter, M.D. Inhibition of sphingomyelin synthesis reduces atherogenesis in apolipoprotein E-knockout mice. Circulation 2004, 110, 3465–3471. [Google Scholar]
- Lan, W.; Zhu, H.; Zhou, Z.; Ye, C.; Liu, M. 1H NMR investigation on interaction between ibuprofen and lipoproteins. Chem. Phys. Lipids 2007, 148, 105–111. [Google Scholar]
- Jones, J.W.; Ways, P. Abnormalities of high density lipoproteins in abetalipoproteinemia. J. Clin. Invest 1967, 46, 1151–1161. [Google Scholar]
- Barenholz, Y.; Yechiel, E.; Cohen, R.; Deckelbaum, R.J. Importance of cholesterol-phospholipid interaction in determining dynamics of normal and abetalipoproteinemia red blood cell membrane. Cell. Biophys 1981, 3, 115–126. [Google Scholar]
- Herbert, P.N.; Hyams, J.S.; Bernier, D.N.; Berman, M.M.; Saritelli, A.L.; Lynch, K.M.; Nichols, A.V.; Forte, T.M. Apolipoprotein B-100 deficiency. Intestinal steatosis despite apolipoprotein B-48 synthesis. J. Clin. Invest 1985, 76, 403–412. [Google Scholar]
- Leventhal, A.R.; Chen, W.; Tall, A.R.; Tabas, I. Acid sphingomyelinase-deficient macrophages have defective cholesterol trafficking and efflux. J. Biol. Chem 2001, 276, 44976–44983. [Google Scholar]
- Dastani, Z.; Ruel, I.L.; Engert, J.C.; Genest, J., Jr; Marcil, M. Sphingomyelin phosphodiesterase-1 (SMPD1) coding variants do not contribute to low levels of high-density lipoprotein cholesterol. BMC Med. Genet 2007, 8, 79. [Google Scholar]
- Dubois, G.; Mussini, J.M.; Auclair, M.; Battesti, J.; Boutry, J.M.; Kemeny, J.L.; Maziere, J.C.; Turpin, J.C.; Hauw, J.J. Adult sphingomyelinase deficiency: report of 2 patients who initially presented with psychiatric disorders. Neurology 1990, 40, 132–136. [Google Scholar]
- Lee, C.Y.; Lesimple, A.; Larsen, A.; Mamer, O.; Genest, J. ESI-MS quantitation of increased sphingomyelin in Niemann-Pick disease type B HDL. J. Lipid Res 2005, 46, 1213–1228. [Google Scholar]
- Lee, C.Y.; Krimbou, L.; Vincent, J.; Bernard, C.; Larramee, P.; Genest, J., Jr; Marcil, M. Compound heterozygosity at the sphingomyelin phosphodiesterase-1 (SMPD1) gene is associated with low HDL cholesterol. Hum. Genet 2003, 112, 552–562. [Google Scholar]
- Lee, C.Y.; Lesimple, A.; Denis, M.; Vincent, J.; Larsen, A.; Mamer, O.; Krimbou, L.; Genest, J.; Marcil, M. Increased sphingomyelin content impairs HDL biogenesis and maturation in human Niemann-Pick disease type B. J. Lipid Res 2006, 47, 622–632. [Google Scholar]
- Tamasawa, N.; Takayasu, S.; Murakami, H.; Yamashita, M.; Matsuki, K.; Tanabe, J.; Matsui, J.; Satoh, K.; Suda, T. Reduced cellular cholesterol efflux and low plasma high-density lipoprotein cholesterol in a patient with type B Niemann-Pick disease because of a novel SMPD-1 mutation. J. Clin. Lipidol 2012, 6, 74–80. [Google Scholar]
- Yao, J.K.; Herbert, P.N.; Fredrickson, D.S.; Ellefson, R.D.; Heinen, R.J.; Forte, T.; Dyck, P.J. Biochemical studies in a patient with a Tangier syndrome. J. Neuropathol. Exp. Neurol 1978, 37, 138–154. [Google Scholar]
- Pruzanski, W.; Stefanski, E.; de Beer, F.C.; de Beer, M.C.; Ravandi, A.; Kuksis, A. Comparative analysis of lipid composition of normal and acute-phase high density lipoproteins. J. Lipid Res 2000, 41, 1035–1047. [Google Scholar]
- Papathanasiou, A.; Kostara, C.; Cung, M.T.; Seferiadis, K.; Elisaf, M.; Bairaktari, E.; Goudevenos, I.A. Analysis of the composition of plasma lipoproteins in patients with extensive coronary heart disease using 1H NMR spectroscopy. Hellenic J. Cardiol 2008, 49, 72–78. [Google Scholar]
- Bagdade, J.D.; Subbaiah, P.V. Abnormal high-density lipoprotein composition in women with insulin-dependent diabetes. J. Lab. Clin. Med 1989, 113, 235–240. [Google Scholar]
- Bagdade, J.D.; Subbaiah, P.V. Whole-plasma and high-density lipoprotein subfraction surface lipid composition in IDDM men. Diabetes 1989, 38, 1226–1230. [Google Scholar]
- Chapkin, R.S.; Haberstroh, B.; Liu, T.; Holub, B.J. Characterization of the individual phospholipids and their fatty acids in serum and high-density lipoprotein of the renal patient on long-term maintenance hemodialysis. J. Lab. Clin. Med 1983, 101, 726–735. [Google Scholar]
- Makinen, V.P.; Tynkkynen, T.; Soininen, P.; Peltola, T.; Kangas, A.J.; Forsblom, C.; Thorn, L.M.; Kaski, K.; Laatikainen, R.; Ala-Korpela, M.; et al. Metabolic diversity of progressive kidney disease in 325 patients with type 1 diabetes (the FinnDiane Study). J. Proteome Res 2012, 11, 1782–1790. [Google Scholar]
- Makinen, V.P.; Tynkkynen, T.; Soininen, P.; Forsblom, C.; Peltola, T.; Kangas, A.J.; Groop, P.H.; Ala-Korpela, M. Sphingomyelin is associated with kidney disease in type 1 diabetes (The FinnDiane Study). Metabolomics 2012, 8, 369–375. [Google Scholar]
- Kuliszkiewicz-Janus, M.; Baczynski, S. Chemotherapy-associated changes in 31P MRS spectra of sera from patients with multiple myeloma. NMR Biomed 1995, 8, 127–132. [Google Scholar]
- Pussinen, P.J.; Jauhiainen, M.; Vilkuna-Rautiainen, T.; Sundvall, J.; Vesanen, M.; Mattila, K.; Palosuo, T.; Alfthan, G.; Asikainen, S. Periodontitis decreases the antiatherogenic potency of high density lipoprotein. J. Lipid Res 2004, 45, 139–147. [Google Scholar]
- Ozerova, I.N.; Perova, N.V.; Shchel’tsyna, N.V.; Mamedov, M.N. Parameters of high-density lipoproteins in patients with arterial hypertension in combination with other components of metabolic syndrome. Bull. Exp. Biol. Med 2007, 143, 320–322. [Google Scholar]
- Francone, O.L.; Subbaiah, P.V.; van Tol, A.; Royer, L.; Haghpassand, M. Abnormal phospholipid composition impairs HDL biogenesis and maturation in mice lacking Abca1. Biochemistry 2003, 42, 8569–8578. [Google Scholar]
- Jeong, T.; Schissel, S.L.; Tabas, I.; Pownall, H.J.; Tall, A.R.; Jiang, X. Increased sphingomyelin content of plasma lipoproteins in apolipoprotein E knockout mice reflects combined production and catabolic defects and enhances reactivity with mammalian sphingomyelinase. J. Clin. Invest 1998, 101, 905–912. [Google Scholar]
- Dong, J.; Liu, J.; Lou, B.; Li, Z.; Ye, X.; Wu, M.; Jiang, X.C. Adenovirus-mediated overexpression of sphingomyelin synthases 1 and 2 increases the atherogenic potential in mice. J. Lipid Res 2006, 47, 1307–1314. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, X.; Dong, J.; Zhao, Y.; Li, Y.; Wu, M. Adenovirus-mediated sphingomyelin synthase 2 increases atherosclerotic lesions in ApoE KO mice. Lipids Health Dis 2011, 10, 7. [Google Scholar]
- Siggins, S.; Bykov, I.; Hermansson, M.; Somerharju, P.; Lindros, K.; Miettinen, T.A.; Jauhiainen, M.; Olkkonen, V.M.; Ehnholm, C. Altered hepatic lipid status and apolipoprotein A–I metabolism in mice lacking phospholipid transfer protein. Atherosclerosis 2007, 190, 114–123. [Google Scholar]
- Li, Z.; Li, Y.; Chakraborty, M.; Fan, Y.; Bui, H.H.; Peake, D.A.; Kuo, M.S.; Xiao, X.; Cao, G.; Jiang, X.C. Liver-specific deficiency of serine palmitoyltransferase subunit 2 decreases plasma sphingomyelin and increases apolipoprotein E levels. J. Biol. Chem 2009, 284, 27010–27019. [Google Scholar]






| Procedure | Categories | |||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Ultracentrifugation (Densities in g/mL) | HDL2b (1.063 to 1.090) | HDL2a (1.090 to 1.120) | HDL3a (1.120 to 1.150) | HDL3b (1.150 to 1.180) | HDL3c (1.180 to 1.210) | |||
| Electrophoretic mobility | preβ-1 | preβ-2 | α-1 | α-2 | α-3 | preα-1 | preα-2 | preα-3c |
| Nuclear magnetic resonance | 26 subtypes | |||||||
| Immune affinity | Lipoparticles containing: APOA1, APOA2, APOA4, APOD, APOE, APOF, APOH, APOJ, APOM, APOA1-APOA2, APOA1-APOA2-APOA4…… | |||||||
© 2013 by the authors; licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/3.0/).
Share and Cite
Martínez-Beamonte, R.; Lou-Bonafonte, J.M.; Martínez-Gracia, M.V.; Osada, J. Sphingomyelin in High-Density Lipoproteins: Structural Role and Biological Function. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2013, 14, 7716-7741. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms14047716
Martínez-Beamonte R, Lou-Bonafonte JM, Martínez-Gracia MV, Osada J. Sphingomyelin in High-Density Lipoproteins: Structural Role and Biological Function. International Journal of Molecular Sciences. 2013; 14(4):7716-7741. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms14047716
Chicago/Turabian StyleMartínez-Beamonte, Roberto, Jose M. Lou-Bonafonte, María V. Martínez-Gracia, and Jesús Osada. 2013. "Sphingomyelin in High-Density Lipoproteins: Structural Role and Biological Function" International Journal of Molecular Sciences 14, no. 4: 7716-7741. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms14047716
APA StyleMartínez-Beamonte, R., Lou-Bonafonte, J. M., Martínez-Gracia, M. V., & Osada, J. (2013). Sphingomyelin in High-Density Lipoproteins: Structural Role and Biological Function. International Journal of Molecular Sciences, 14(4), 7716-7741. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms14047716