Putative Genes Involved in Saikosaponin Biosynthesis in Bupleurum Species
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Biological Effects of Bupleurum Saikosaponins
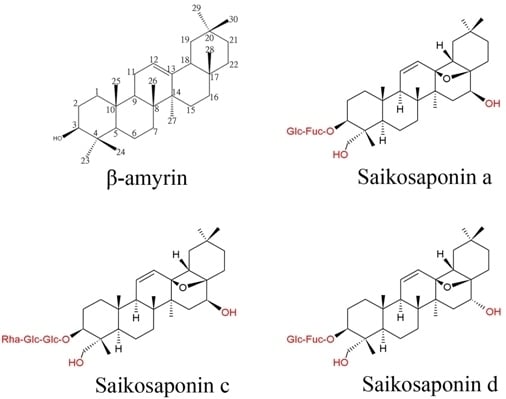
3. Putative Biosynthetic Pathway of Saikosaponins in Bupleurum
4. Identification and Characterization of Genes Involved in Bupleurum Saikosaponin Biosynthesis
4.1. The Oxidosqualene Cyclase (OSC) Genes
4.2. The Cytochrome P450 Monooxygenases/Hydroxylases Genes
4.3. The UDP-Glycosyltransferase Genes
4.4. Genes Involved in Reactions Upstream of the First Committed Step
5. Unique and Overlapping Expression Patterns of Genes Involved in Saikosaponin Biosynthesis
6. Functional Characterization of ERF Genes Extracted from B. kaoi
7. Conclusions
Acknowledgments
Conflict of Interest
References
- Ashour, M.L.; Wink, M. Genus Bupleurum: A review of its phytochemistry, pharmacology and modes of action. J. Pharm. Pharmacol 2011, 63, 305–332. [Google Scholar]
- Mabberley, D.J. Mabberley’s Plant-Book: A Portable Dictionary of Plants, Their Classification and Uses, 3rd ed.; Cambridge University Press: New York, NY, USA, 2008; p. 1021. [Google Scholar]
- Franssen, S.U.; Shrestha, R.P.; Bräutigam, A.; Bornberg-Bauer, E.; Weber, A.P.M. Comprehensive transcriptome analysis of the highly complex Pisum sativum genome. BMC Genomics 2011, 12, 227. [Google Scholar]
- Higashi, Y.; Saito, K. Network analysis for gene discovery in plant specialized metabolism. Plant Cell Environ. 2013. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saito, K.; Hirai, M.Y.; Yonekura-Sakakibara, K. Decoding genes with coexpression 603 networks and metabolomics—‘Majority report by precogs’. Trends Plant Sci 2008, 13, 36–43. [Google Scholar]
- Yang, C.Q.; Fang, X.; Wu, X.M.; Mao, Y.B.; Wang, L.J.; Chen, X.Y. Transcriptional regulation of plant secondary metabolism. J. Integr. Plant Biol 2012, 54, 703–712. [Google Scholar]
- Lin, W.Y.; Chen, L.R.; Lin, T.Y. Rapid authentication of Bupleurum species using an array of immobilized sequence-specific oligonucleotide probes. Planta Med 2008, 74, 464–469. [Google Scholar]
- Yen, M.H.; Weng, T.C.; Liu, S.Y.; Chai, C.Y.; Lin, C.C. The hepatoprotective effect of Bupleurum kaoi, an endemic plant to Taiwan, against dimethylnitrosamine-induced hepatic fibrosis in rats. Biol. Pharm. Bull 2005, 28, 442–448. [Google Scholar]
- Ebata, N.; Nakajima, K.; Hayashi, K.; Okada, M.; Maruno, M. Saponins from the root of Bupleurum falcatum. Phytochemistry 1996, 41, 895–901. [Google Scholar]
- Pistelli, L.; Bilia, A.R.; Marsili, A.; De Tommasi, N.; Manunta, A. Triterpenoid saponins from Bupleurum fruticosum. J. Nat. Prod 1993, 56, 240–244. [Google Scholar]
- Ding, J.K.; Fujino, H.; Kasai, R.; Fujimoto, N.; Tanaka, O.; Zhou, J.; Matsuura, H.; Fuwa, T. Chemical evaluation of Bupleurum species collected in Yunnan, China. Chem. Pharm. Bull 1986, 34, 1158–1167. [Google Scholar]
- Lin, X.; Xue, L.; Zhang, H.; Zhu, C. Determination of saikosaponins a, c, and d in Bupleurum Chinese DC from different areas by capillary zone electrophoresis. Anal. Bioanal. Chem 2005, 382, 1610–1615. [Google Scholar]
- Huang, H.Q.; Zhang, X.; Xu, Z.X.; Su, J.; Yan, S.K.; Zhang, W.D. Fast determination of saikosaponins in Bupleurum by rapid resolution liquid chromatography with evaporative light scattering detection. J. Pharm. Biomed. Anal 2009, 49, 1048–1055. [Google Scholar]
- Barrero, A.F.; Haïdour, A.; Sedqui, A.; Mansour, A.I.; Rodríguez-Garcia, I.; Löpez, A.; Muñoz-Dorado, M. Saikosaponins from roots of Bupleurum gibraltaricum and Bupleurum spinosum. Phytochemistry 2000, 54, 741–745. [Google Scholar]
- Fujioka, T.; Yoshida, K.; Shibao, H.; Nagao, T.; Yoshida, M.; Matsunaga, K.; Takata, J.; Karube, Y.; Iwase, Y.; Okabe, H.; et al. Antiproliferative constituents from Umbelliferae plants. IX. New triterpenoid glycosides from the fruits of Bupleurum rotundifolium. Chem. Pharm. Bull 2006, 54, 1694–1704. [Google Scholar]
- Luo, S.Q.; Lin, L.Z.; Cordell, G.A. Saikosaponin derivatives from Bupleurum wenchuanense. Phytochemistry 1993, 33, 1197–1205. [Google Scholar]
- Guinea, M.C.; Parellada, J.; Lacaille-Dubois, M.A.; Wagner, H. Biologically active triterpene saponins from Bupleurum fruticosum. Planta Med 1994, 60, 163–167. [Google Scholar]
- Yamamoto, M.; Kumagai, A.; Yamamura, Y. Structure and actions of saikosaponins isolated from Bupleurum falcatum L. I. Anti-inflammatory action of saikosaponins. Arzneimittelforschung 1975, 25, 1021–1023. [Google Scholar]
- Abe, H.; Sakaguchi, M.; Yamada, M.; Arichi, S.; Odashima, S. Pharmacological actions of saikosaponins isolated from Bupleurum falcatum. 1. Effects of saikosaponins on liver function. Planta Med 1980, 40, 366–372. [Google Scholar]
- Abe, H.; Orita, M.; Konishi, H.; Arichi, S.; Odashima, S. Effects of saikosaponin-d on enhanced CCl4-hepatotoxicity by phenobarbitone. J. Pharm. Pharmacol 1985, 37, 555–559. [Google Scholar]
- Sun, H.X. Haemolytic activities and adjuvant effect of Bupleurum chinense saponins on the immune responses to ovalbumin in mice. Vaccine 2006, 24, 1324–1331. [Google Scholar]
- Navarro, P.; Giner, R.M.; Recio, M.C.; Manez, S.; Cerda-Nicolas, M.; Rios, J.L. In vivo anti-inflammatory activity of saponins from Bupleurum rotundifolium. Life Sci 2001, 68, 1199–1206. [Google Scholar]
- Bermejo, P.; Abad, M.J.; Silván, A.M.; Sanz, A.; Fernández, L.; Sánchez, S.; Díaz, A.M. In vivo and in vitro antiinflammatory activity of saikosaponins. Life Sci 1998, 63, 1147–1156. [Google Scholar]
- Ushio, Y.; Abe, H. The effects of saikosaponin on macrophage functions and lymphocyte proliferation. Planta Med 1991, 57, 511–514. [Google Scholar]
- Wong, V.K.; Zhou, H.; Cheung, S.S.; Li, T.; Liu, L. Mechanistic study of saikosaponin-d (Ssd) on suppression of murine T lymphocyte activation. J. Cell. Biochem 2009, 107, 303–315. [Google Scholar]
- Park, K.H.; Park, J.; Koh, D.; Lim, Y. Effect of saikosaponin-A, a triterpenoid glycoside, isolated from Bupleurum falcatum on experimental allergic asthma. Phytother. Res 2002, 16, 359–363. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, P.; Ren, J.; Tang, J.; Zhang, D.; Li, B.; Li, Y. Estrogen-like activities of saikosaponin-d in vitro: A pilot study. Eur. J. Pharmacol 2010, 626, 159–165. [Google Scholar]
- Sun, Y.; Cai, T.T.; Zhou, X.B.; Xu, Q. Saikosaponin a inhibits the proliferation and activation of T cells through cell cycle arrest and induction of apoptosis. Int. Immunopharmacol 2009, 9, 978–983. [Google Scholar]
- Han, N.R.; Kim, H.M.; Jeong, H.J. Inactivation of cysteine-aspartic acid protease (caspase)-1 by saikosaponin A. Biol. Pharm. Bull 2011, 34, 817–823. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, Q.; Zheng, X.L.; Yang, L.; Shi, F.; Gao, L.B.; Zhong, Y.J.; Sun, H.; He, F.; Lin, Y.; Wang, X. Reactive oxygen species-mediated apoptosis contributes to chemosensitization effect of saikosaponins on cisplatin-induced cytotoxicity in cancer cells. J. Exp. Clin. Cancer Res 2010, 29, 159–166. [Google Scholar]
- Ahn, B.Z.; Yoon, Y.D.; Lee, Y.H.; Kim, B.H.; Sok, D.E. Inhibitory effect of bupleuri radix saponins on adhesion of some solid tumor cells and relation to hemolytic action: Screening of 232 herbal drugs for anti-cell adhesion. Planta Med 1998, 64, 220–224. [Google Scholar]
- Kodama, Y.; Xiaochuan, L.; Tsuchiya, C.; Ohizumi, Y.; Yoshida, M.; Nakahata, N. Dual effect of saikogenin D: In vitro inhibition of prostaglandin E2 production and elevation of intracellular free Ca2+ concentration in C6 rat glioma cells. Planta Med 2003, 69, 765–767. [Google Scholar]
- Abe, I.; Rohmer, M.; Prestwich, G.D. Enzymatic cyclization of squalene and oxidosqualene to sterols and triterpenes. Chem. Rev 1993, 93, 2189–2206. [Google Scholar]
- Abe, I. Enzymatic synthesis of cyclic triterpenes. Nat. Prod. Rep 2007, 24, 1311–1331. [Google Scholar]
- Haralampidis, K.; Trojanowska, M.; Osbourn, A.E. Biosynthesis of triterpenoid saponins in plants. Adv. Biochem. Eng. Biotechnol 2002, 75, 31–49. [Google Scholar]
- Suzuki, H.; Achnine, L.; Xu, R.; Matsuda, S.P.T.; Dixon, R.A. A genomics approach to the early stages of triterpene saponin biosynthesis in Medicago truncatula. Plant J 2002, 32, 1033–1048. [Google Scholar]
- Suzuki, H.; Reddy, M.S.S.; Naoumkina, M.; Aziz, N.; May, G.D.; Huhman, D.V.; Sumner, L.W.; Blount, J.W.; Mendes, P.; Dixon, R.A. Methyl jasmonate and yeast elicitor induce differential transcriptional and metabolic re-programming in cell suspension cultures of the model legume Medicago truncatula. Planta 2005, 220, 696–707. [Google Scholar]
- Hérold, M.C.; Henry, M. UDP-glucuronosyltransferase activity is correlated to saponin production in Gypsophila paniculata root in vitro cultures. Biotechnol. Lett 2001, 23, 335–337. [Google Scholar]
- Mizutani, M.; Ohta, D. Diversification of P450 genes during land plant evolution. Annu. Rev. Plant Biol 2010, 61, 291–315. [Google Scholar]
- Sato, S.; Nakamura, Y.; Kaneko, T.; Asamizu, E.; Kato, T.; Nakao, M.; Sasamoto, S.; Watanabe, A.; Ono, A.; Kawashima, K.; et al. Genome structure of the legume, Lotus japonicus. DNA Res 2008, 15, 227–239. [Google Scholar]
- Li, L.; Cheng, H.; Gai, J.; Yu, D. Genome-wide identification and characterization of putative cytochrome P450 genes in the model legume Medicago truncatula. Planta 2007, 226, 109–123. [Google Scholar]
- Nelson, D.R.; Schuler, M.A.; Paquette, S.M.; Werck-Reichhart, D; Bak, S. Comparative genomics of rice and Arabidopsis. Analysis of 727 cytochrome P450 genes and pseudogenes from a monocot and a dicot. Plant Physiol 2004, 135, 756–772. [Google Scholar]
- Seki, H.; Ohyama, K.; Sawai, S.; Mizutani, M.; Ohnishi, T.; Sudo, H.; Akashi, T.; Aoki, T.; Saito, K.; Muranaka, T. Licorice β-amyrin 11-oxidase, a cytochrome P450 with a key role in the biosynthesis of the triterpene sweetener glycyrrhizin. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2008, 105, 14204–14209. [Google Scholar]
- Seki, H.; Sawai, S.; Ohyama, K.; Mizutani, M.; Ohnishi, T.; Sudo, H.; Fukushima, E.O.; Akashi, T.; Aoki, T.; Saito, K.; et al. Triterpene functional genomics in licorice for identification of CYP72A154 involved in the biosynthesis of glycyrrhizin. Plant Cell 2011, 23, 4112–4123. [Google Scholar]
- Shibuya, M.; Hoshino, M.; Katsube, Y.; Hayashi, H.; Kushiro, T.; Ebizuka, Y. Identification of β-amyrin and sophoradiol 24-hydroxylase by expressed sequence tag mining and functional expression assay. FEBS J 2006, 273, 948–959. [Google Scholar]
- Achnine, L.; Huhman, D.V.; Farag, M.A.; Sumner, L.W.; Blount, J.W.; Dixon, R.A. Genomics-based selection and functional characterization of triterpene glycosyltransferases from the model legume Medicago truncatula. Plant J 2005, 41, 875–887. [Google Scholar]
- van der Fits, L.; Memelink, J. ORCA3, a jasmonate-responsive transcriptional regulator of plant primary and secondary metabolism. Science 2000, 289, 295–297. [Google Scholar]
- Aoyagi, H.; Kobayashi, Y.; Yamada, K.; Yokoyama, M.; Kusakari, K.; Tanaka, H. Efficient production of saikosaponins in Bupleurum falcatum root fragments combined with signal transducers. Appl. Microbiol. Biotechnol 2001, 57, 482–488. [Google Scholar]
- Gundlach, H.; Muller, M.J.; Kutchan, T.M.; Zenk, M.H. Jasmonic acid is a signal transducer in elicitor-induced plant cell cultures. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 1992, 89, 2389–2393. [Google Scholar]
- Chen, L.R.; Chen, Y.J.; Lee, C.Y.; Lin, T.Y. MeJA-induced transcriptional changes in adventitious roots of Bupleurum kaoi. Plant Sci 2007, 173, 12–24. [Google Scholar]
- Sui, C.; Zhang, J.; Wei, J.; Chen, S.; Li, Y.; Xu, J.; Jin, Y.; Xie, C.; Gao, Z.; Chen, H.; et al. Transcriptome analysis of Bupleurum chinense focusing on genes involved in the biosynthesis of saikosaponins. BMC Genomics 2011, 12, 539. [Google Scholar]
- Kim, Y.S.; Cho, J.H.; Park, S.; Han, J.Y.; Back, K.; Choi, Y.E. Gene regulation patterns in triterpene biosynthetic pathway driven by overexpression of squalene synthase and methyl jasmonate elicitation in Bupleurum falcatum. Planta 2011, 233, 343–355. [Google Scholar]
- Sun, C.; Li, Y.; Wu, Q.; Luo, H.M.; Sun, Y.Z.; Song, J.Y.; Lui, E.; Chen, S.L. De novo sequencing and analysis of the American ginseng root transcriptome using a GS FLX Titanium platform to discover putative genes involved in ginsenoside biosynthesis. BMC Genomics 2010, 11, 262. [Google Scholar]
- Sawai, S.; Saito, K. Triterpenoid biosynthesis and engineering in plants. Front. Plant Sci 2011, 2, 25. [Google Scholar]
- Naoumkina, M.A.; Modolo, L.V.; Huhman, D.V.; Urbanczyk-Wochniak, E.; Tang, Y.H.; Sumner, L.W.; Dixon, R.A. Genomic and coexpression analyses predict multiple genes involved in triterpene saponin biosynthesis in Medicago truncatula. Plant Cell 2010, 22, 850–866. [Google Scholar]
- Phillips, D.R.; Rasbery, J.M.; Bartel, B.; Matsuda, S.P.T. Biosynthetic diversity in plant triterpene cyclization. Curr. Opin. Plant Biol 2006, 9, 305–314. [Google Scholar]
- Sawai, S.; Shindo, T.; Sato, S.; Kaneko, T.; Tabata, S.; Ayabe, S.; Aoki, T. Functional and structural analysis of genes encoding oxidosqualene cyclases of Lotus japonicus. Plant Sci 2006, 170, 247–257. [Google Scholar]
- Iturbe-Ormaetxe, I.; Haralampidis, K.; Papadopoulou, K.; Osbourn, A.E. Molecular cloning and characterization of triterpene synthases from Medicago truncatula and Lotus japonicus. Plant Mol. Biol 2003, 51, 731–743. [Google Scholar]
- Shibuya, M.; Katsube, Y.; Otsuka, M.; Zhang, H.; Tansakul, P.; Xiang, T.; Ebizuka, Y. Identification of a product specific β-amyrin synthase from Arabidopsis thaliana. Plant Physiol. Biochem 2009, 47, 26–30. [Google Scholar]
- Hayashi, H.; Huang, P.; Kirakosyan, A.; Inoue, K.; Hiraoka, N.; Ikeshiro, Y.; Kushiro, T.; Shibuya, M.; Ebizuka, Y. Cloning and characterization of a cDNA encoding β-amyrin synthase involved in glycyrrhizin and soyasaponin biosyntheses in licorice. Biol. Pharm. Bull 2001, 24, 912–916. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, Z.; Guhling, O.; Yao, R.; Li, F.; Yeats, T.H.; Rose, J.K.C.; Jetter, R. Two oxidosqualene cyclases responsible for biosynthesis of tomato fruit cuticular triterpenoids. Plant Physiol 2011, 155, 540–552. [Google Scholar]
- Morita, M.; Shibuya, M.; Kushiro, T.; Masuda, K.; Ebizuka, Y. Molecular cloning and functional expression of triterpene synthases from pea (Pisum sativum) new α-amyrin-producing enzyme is a multifunctional triterpene synthase. Eur. J. Biochem 2000, 267, 3453–3460. [Google Scholar]
- Meesapyodsuk, D.; Balsevich, J.; Reed, D.W.; Covello, P.S. Saponin biosynthesis in Saponaria vaccaria. cDNAs encoding β-amyrin synthase and a triterpene carboxylic acid glucosyltransferase. Plant Physiol 2007, 143, 959–969. [Google Scholar]
- Qi, X.; Bakht, S.; Leggett, M.; Maxwell, C.; Melton, R.; Osbourn, A. A gene cluster for secondary metabolism in oat: implications for the evolution of metabolic diversity in plants. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2004, 101, 8233–8238. [Google Scholar]
- Haralampidis, K.; Bryan, G.; Qi, X.; Papadopoulou, K.; Bakht, S.; Melton, R.; Osbourn, A. A new class of oxidosqualene cyclases directs synthesis of antimicrobial phytoprotectants in monocots. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2001, 98, 13431–13436. [Google Scholar]
- Kushiro, T.; Shibuya, M.; Masuda, K.; Ebizuka, Y. A novel multifunctional triterpene synthase from Arabidopsis thaliana. Tetrahedron Lett 2000, 41, 7705–7710. [Google Scholar]
- Kolesnikova, M.D.; Wilson, W.K.; Lynch, D.A.; Obermeyer, A.C.; Matsuda, S.P.T. Arabidopsis camelliol C synthase evolved from enzymes that make pentacycles. Org. Lett 2007, 9, 5223–5226. [Google Scholar]
- Kushiro, T.; Shibuya, M.; Ebizuka, Y. β-amyrin synthase. Cloning of oxidosqualene cyclase that catalyzes the formation of the most popular triterpene among higher plants. Eur. J. Biochem 1998, 256, 238–244. [Google Scholar]
- Husselstein-Muller, T.; Schaller, H.; Benveniste, P. Molecular cloning and expression in yeast of 2,3-oxidosqualene-triterpenoid cyclases from Arabidopsis thaliana. Plant Mol. Biol 2001, 45, 75–92. [Google Scholar]
- Nelson, D.R. Cytochrome P450 and the individuality of species. Arch. Biochem. Biophys 1999, 369, 1–10. [Google Scholar]
- Mizutani, M.; Sato, F. Unusual P450 reactions in plant secondary metabolism. Arch. Biochem. Biophys 2011, 507, 194–203. [Google Scholar]
- Fukushima, E.O.; Seki, H.; Ohyama, K.; Ono, E.; Umemoto, N.; Mizutani, M.; Saito, K.; Muranaka, T. CYP716A subfamily members are multifunctional oxidases in triterpenoid biosynthesis. Plant Cell Physiol 2011, 52, 2050–2061. [Google Scholar]
- Shimada, Y.; Fujioka, S.; Miyauchi, N.; Kushiro, M.; Takatsuto, S.; Nomura, T.; Yokota, T.; Kamiya, Y.; Bishop, G.J.; Yoshida, S. Brassinosteroid-6-oxidases from Arabidopsis and tomato catalyze multiple C-6 oxidations in brassinosteroid biosynthesis. Plant Physiol 2001, 126, 770–779. [Google Scholar]
- Fujita, S.; Ohnishi, T.; Watanabe, B.; Yokota, T.; Takatsuto, S.; Fujioka, S.; Yoshida, S.; Sakata, K.; Mizutani, M. Arabidopsis CYP90B1 catalyses the early C-22 hydroxylation of C27, C28 and C29 sterols. Plant J 2006, 45, 765–774. [Google Scholar]
- Mizutani, M. Impacts of diversification of cytochrome P450 on plant metabolism. Biol. Pharm. Bull 2012, 35, 824–832. [Google Scholar]
- Ohnishi, T.; Szatmari, A.M.; Watanabe, B.; Fujita, S.; Bancos, S.; Koncz, C.; Lafos, M.; Shibata, K.; Yokota, T.; Sakata, K.; et al. C-23 hydroxylation by Arabidopsis CYP90C1 and CYP90D1 reveals a novel shortcut in Brassinosteroid biosynthesis. Plant Cell 2006, 18, 3275–3288. [Google Scholar]
- Field, B.; Osbourn, A.E. Metabolic diversification–independent assembly of operon-like gene clusters in different plants. Science 2008, 320, 543–547. [Google Scholar]
- Yonekura-Sakakibara, K. Functional genomics of family 1 glycosyltransferases in Arabidopsis. Plant Biotechnol 2009, 26, 267–274. [Google Scholar]
- Gachon, C.M.M.; Langlois-Meurinne, M.; Saindrenan, P. Plant secondary metabolism glycosyltransferases: The emerging functional analysis. Trends Plant Sci 2005, 10, 542–549. [Google Scholar]
- Hughes, J.; Hughes, M.A. Multiple secondary plant product UDP-glucose glucosyltransferase genes expressed in cassava (Manihot esculenta Crantz) cotyledons. DNA Seq 1994, 5, 41–49. [Google Scholar]
- Tsukamoto, C.; Kikuchi, A.; Harada, K.; Kitamura, K.; Okubo, K. Genetic and chemical polymorphisms of saponins in soybean seed. Phytochemistry 1993, 34, 1351–1356. [Google Scholar]
- Sayama, T.; Ono, E.; Takagi, K.; Takada, Y.; Horikawa, M.; Nakamoto, Y.; Hirose, A.; Sasama, H.; Ohashi, M.; Hasegawa, H.; et al. The Sg-1 glycosyltransferase locus regulates structural diversity of triterpenoid saponins of soybean. Plant Cell 2012, 24, 2123–2138. [Google Scholar]
- Luo, H.; Sun, C.; Sun, Y.; Wu, Q.; Li, Y.; Song, J.; Niu, Y.; Cheng, X.; Xu, H.; Li, C.; et al. Analysis of the transcriptome of Panax notoginseng root uncovers putative triterpene saponin-biosynthetic genes and genetic markers. BMC Genomics 2011, 12, S5. [Google Scholar]
- Kohara, A.; Nakajima, C.; Hashimoto, K.; Ikenaga, T.; Tanaka, H.; Shoyama, Y.; Yoshida, S.; Muranaka, T. A novel glucosyltransferase involved in steroid saponin biosynthesis in Solanum aculeatissimum. Plant Mol. Biol 2005, 57, 225–239. [Google Scholar]
- Kohara, A.; Nakajima, C.; Yoshida, S.; Muranaka, T. Characterization and engineering of glycosyltransferases responsible for steroid saponin biosynthesis in Solanaceous plants. Phytochemistry 2007, 68, 478–486. [Google Scholar]
- Kim, T.D.; Han, J.Y.; Huh, G.H.; Choi, Y.E. Expression and functional characterization of three squalene synthase genes associated with saponin biosynthesis in Panax ginseng. Plant Cell Physiol 2011, 52, 125–137. [Google Scholar]
- Kim, Y.S.; Cho, J.H.; Ahn, J.; Hwang, B. Upregulation of isoprenoid pathway genes during enhanced saikosaponin biosynthesis in the hairy roots of Bupleurum falcatum. Mol. Cells 2006, 22, 269–274. [Google Scholar]
- Woo, H.H.; Orbach, M.J.; Hirsch, A.M.; Hawes, M.C. Meristem-localized inducible expression of a UDP-glycosyltransferase gene is essential for growth and development in pea and alfalfa. Plant Cell 1999, 11, 2303–2315. [Google Scholar]
- Sepúlveda-Jiménez, G.; Rueda-Benítez, P.; Porta, H.; Rocha-Sosa, M. A red beet (Beta vulgaris) UDP-glucosyltransferase gene induced by wounding, bacterial infiltration and oxidative stress. J. Exp. Bot 2005, 56, 605–611. [Google Scholar]
- Suttipanta, N.; Pattanaik, S.; Kulshrestha, M.; Patra, B.; Singh, S.K.; Yuan, L. The transcription factor CrWRKY1 positively regulates the terpenoid indole alkaloid biosynthesis in Catharanthus roseus. Plant Physiol 2011, 157, 2081–2093. [Google Scholar]
- Skirycz, A.; Reichelt, M.; Burow, M.; Birkemeyer, C.; Rolcik, J.; Kopka, J.; Zanor, M.I.; Gershenzon, J.; Strnad, M.; Szopa, J.; et al. DOF transcription factor AtDof1.1 (OBP2) is part of a regulatory network controlling glucosinolate biosynthesis in Arabidopsis. Plant J 2006, 47, 10–24. [Google Scholar]
- Celenza, J.L.; Quiel, J.A.; Smolen, G.A.; Merrikh, H.; Silvestro, A.R.; Normanly, J.; Bender, J. The Arabidopsis ATR1 Myb transcription factor controls indolic glucosinolate homeostasis. Plant Physiol 2005, 137, 253–262. [Google Scholar]
- Dubouzet, J.G.; Sakuma, Y.; Ito, Y.; Kasuga, M.; Dubouzet, E.G.; Miura, S.; Seki, M.; Shinozaki, K.; Yamaguchi-Shinozaki, K. OsDREB genes in rice, Oryza sativa L., encode transcription activators that function in drought-, high-salt- and cold-responsive gene expression. Plant J 2003, 33, 751–763. [Google Scholar]
- Nakano, T.; Suzuki, K.; Fujimura, T.; Shinshi, H. Genome-wide analysis of the ERF gene family in Arabidopsis and rice. Plant Physiol 2006, 140, 411–432. [Google Scholar]
- Liu, W.Y.; Chiou, S.J.; Ko, C.Y.; Lin, T.Y. Functional characterization of three ethylene response factor genes from Bupleurum kaoi indicates that BkERFs mediate resistance to Botrytis cinerea. J. Plant Physiol 2011, 168, 375–381. [Google Scholar]
- Ohme-Takagi, M.; Shinshi, H. Ethylene-inducible DNA binding proteins that interact with an ethylene-responsive element. Plant Cell 1995, 7, 173–182. [Google Scholar]
- Gu, Y.Q.; Wildermuth, M.C.; Chakravarthy, S.; Loh, Y.T.; Yang, C.; He, X.; Han, Y.; Martin, G.B. Tomato transcription factors pti4, pti5, and pti6 activate defense responses when expressed in Arabidopsis. Plant Cell 2002, 14, 817–831. [Google Scholar]
- Guo, Z.J.; Chen, X.J.; Wu, X.L.; Ling, J.Q.; Xu, P. Overexpression of the AP2/EREBP transcription factor OPBP1 enhances disease resistance and salt tolerance in tobacco. Plant Mol. Biol 2004, 55, 607–618. [Google Scholar]
- Lorenzo, O.; Piqueras, R.; Sanchez-Serrano, J.J.; Solano, R. ETHYLENE RESPONSE FACTOR1 integrates signals from ethylene and jasmonate pathways in plant defense. Plant Cell 2003, 15, 165–178. [Google Scholar]
- McGrath, K.C.; Dombrecht, B.; Manners, J.M.; Schenk, P.M.; Edgar, C.I.; Maclean, D.J.; Scheible, W.R.; Udvardi, M.K.; Kazan, K. Repressor-and activator-type ethylene response factors functioning in jasmonate signaling and disease resistance identified via a genome-wide screen of Arabidopsis transcription factor gene expression. Plant Physiol 2005, 139, 949–959. [Google Scholar]
- Berrocal-Lobo, M.; Molina, A.; Solano, R. Constitutive expression of ETHYLENE-RESPONSEFACTOR1 in Arabidopsis confers resistance to several necrotrophic fungi. Plant J 2002, 29, 23–32. [Google Scholar]
- Pre, M.; Atallah, M.; Champion, A.; de Vos, M.; Pieterse, C.M.; Memelink, J. The AP2/ERF domain transcription factor ORA59 integrates jasmonic acid and ethylene signals in plant defense. Plant Physiol 2008, 147, 1347–1357. [Google Scholar]
- Meng, X.; Xu, J.; He, Y.; Yang, K.Y.; Mordorski, B.; Liu, Y.; Zhang, S. Phosphorylation of an ERF transcription factor by Arabidopsis MPK3/MPK6 regulates plant defense gene induction and fungal resistance. Plant Cell 2013, 25, 1126–1142. [Google Scholar]
- Yu, Z.X.; Li, J.X.; Yang, C.Q.; Hu, W.L.; Wang, L.J.; Chen, X.Y. The jasmonate-responsive AP2/ERF transcription factors AaERF1 and AaERF2 positively regulate artemisinin biosynthesis in Artemisia annua L. Mol. Plant 2012, 5, 353–365. [Google Scholar]





© 2013 by the authors; licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution license ( http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/3.0/).
Share and Cite
Lin, T.-Y.; Chiou, C.-Y.; Chiou, S.-J. Putative Genes Involved in Saikosaponin Biosynthesis in Bupleurum Species. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2013, 14, 12806-12826. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms140612806
Lin T-Y, Chiou C-Y, Chiou S-J. Putative Genes Involved in Saikosaponin Biosynthesis in Bupleurum Species. International Journal of Molecular Sciences. 2013; 14(6):12806-12826. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms140612806
Chicago/Turabian StyleLin, Tsai-Yun, Chung-Yi Chiou, and Shu-Jiau Chiou. 2013. "Putative Genes Involved in Saikosaponin Biosynthesis in Bupleurum Species" International Journal of Molecular Sciences 14, no. 6: 12806-12826. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms140612806
APA StyleLin, T.-Y., Chiou, C.-Y., & Chiou, S.-J. (2013). Putative Genes Involved in Saikosaponin Biosynthesis in Bupleurum Species. International Journal of Molecular Sciences, 14(6), 12806-12826. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms140612806