FOXO1 Content Is Reduced in Cystic Fibrosis and Increases with IGF-I Treatment
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Results
2.1. Findings in CFBE41o- and 16HBE14o- Cells
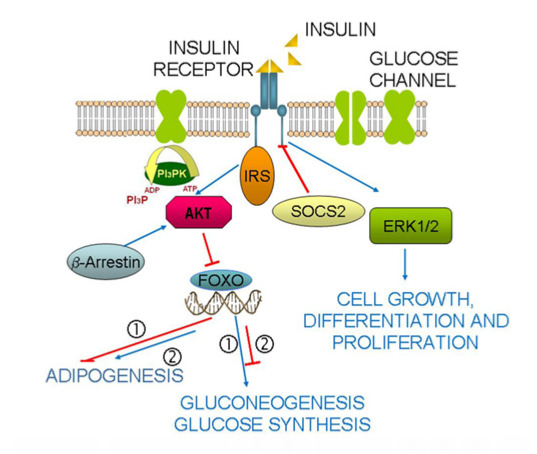
2.1.1. Insulin Receptor
2.1.2. Insulin Signal Transduction





2.1.3. Effect of Treatment of 16HBE14o- Cells with a Cystic Fibrosis Transmembrane Conductance Regulator (CFTR) Inhibitor and CFTR Gene Silencing

2.1.4. Winged Helix Forkhead (FOX)O1 Changes after Treatment with IGF-I

2.2. Findings in Normal and Cystic Fibrosis (CF)-Affected Mice
2.2.1. Insulin Signal Transduction


2.2.2. FOXO1 Changes after Treatment with rhIGF-I

3. Discussion
4. Experimental Section
4.1. Cell Lines, Cultures, Insulin and IGF-I Treatments
4.2. Total Protein Content
4.3. Protein Assays in Lysates
4.4. Immunoprecipitation (IP)
4.5. Western Immunoblotting
4.6. CFTR Inhibition and Gene Silencing
4.7. Animal Models and IGF-I Treatment
4.8. Statistical Analysis
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Supplementary Files
Supplementary File 1Acknowledgments
Author Contributions
Conflicts of Interest
References
- O’Shea, D.; O’Connell, J. Cystic fibrosis related diabetes. Curr. Diabetes Rep. 2014, 14, 511–521. [Google Scholar]
- McCormick, J.; Mehta, G.; Olesen, H.V.; Viviani, L.; Macek, M.; Mehta, A.; European Registry Working Group. Comparative demographics of the European cystic fibrois population: A cross-sectional database analysis. Lancet 2010, 375, 1007–1013. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Moran, A.; Dunitz, J.; Nathan, B.; Saeed, A.; Holme, B.; Thomas, W. Cystic fibrosis-related diabetes: Current trends in prevalence, incidence, and mortality. Diabetes Care 2009, 32, 1626–1631. [Google Scholar]
- Tofé, S.; Moreno, J.C.; Máiz, L.; Alonso, M.; Escobar, H.; Barrio, R. Insulin-secretion abnormalities and clinical deterioration related to impaired glucose tolerance in cystic fibrosis. Eur. J. Endocrinol. 2005, 152, 241–247. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lanng, S. Glucose intolerance in cystic fibrosis patients. Paediatr. Respir. Rev. 2001, 2, 253–259. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Moran, A.; Becker, D.; Casella, S.J.; Gottlieb, P.A.; Kirkman, M.S.; Marshall, B.C.; Slovis, B.; CFRD Consensus Conference Committee. Epidemiology, pathophysiology, and prognostic implications of cystic fibrosis-related diabetes: A technical review. Diabetes Care 2010, 33, 2677–2683. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lombardo, F.; de Luca, F.; Rosano, M.; Sferlazzas, C.; Lucanto, C.; Arrigo, T.; Messina, M.F.; Crisafulli, G.; Wasniewska, M.; Valenzise, M.; et al. Natural history of glucose tolerance, beta-cell function and peripheral insulin sensitivity in cystic fibrosis patients with fasting euglycemia. Eur. J. Endocrinol. 2003, 149, 53–59. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Street, M.E.; Ziveri, M.A.; Spaggiari, C.; Viani, I.; Volta, C.; Grzincich, G.L.; Virdis, R.; Bernasconi, S. Inflammation is a Modulator of the IGF-IGFBP System Inducing Reduced Bioactivity of IGFs in Cystic Fibrosis. Eur. J. Endocrinol. 2006, 154, 47–52. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Street, M.E.; Spaggiari, C.; Ziveri, M.A.; Rossi, M.; Volta, C.; Viani, I.; Grzincich, G.L.; Sartori, C.; Zanzucchi, M.; Raia, V.; et al. Insulin production and resistance in cystic fibrosis: Effect of age, disease activity, and genotype. J. Endocrinol. Investig. 2012, 35, 246–253. [Google Scholar]
- Hardin, D.S.; Leblanc, A.; Marshall, G.; Seilheimer, D.K. Mechanisms of insulin resistance in cystic fibrosis. Am. J. Physiol. Endocrinol. Metab. 2001, 281, E1022–E1028. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Taniguchi, C.M.; Emanuelli, B.; Kahn, R. Critical nodes in signalling pathways: Insights into insulin action. Mol. Cell. Biol. 2006, 7, 85–96. [Google Scholar]
- Pessin, J.E.; Saltiel, A.L. Signaling pathways in insulin action: Molecular targets of insulin resistance. J. Clin. Investig. 2000, 106, 165–169. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kitamura, T. The role of FOXO1 in β-cell failure and type 2 diabetes mellitus. Nat. Rev. Endocrinol. 2013, 9, 615–623. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shao, S.; Yang, Y.; Yuan, G.; Zhang, M.; Yu, X. Signaling Molecules involved in Lipid-induced pancreatic Beta-Cell Dysfunction. DNA Cell Biol. 2013, 32, 41–49. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Marshall, B.C.; Butler, S.M.; Stoddard, M. Epidemiology of cystic fibrosis-related diabetes. J. Pediatr. 2005, 146, 681–687. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Luciani, A.; Vilella, V.R.; Esposito, S.; Brunetti-Pierri, N.; Medina, D.; Settembre, C.; Gavina, M.; Pulze, L.; Giardino, I.; Pettoello-Mantovani, M.; et al. Defective CFTR induces aggresome formation and lung inflammation in cystic fibrosis through ROS-mediated autophagy inhibition. Nat. Cell. Biol. 2010, 12, 863–875. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, M.K.; Kim, H.S.; Lee, I.K.; Park, K.G. Endoplasmic reticulum stress and insulin biosynthesis: A review. Exp. Diabetes Res. 2012, 509437. [Google Scholar]
- Li, Q.; Verma, I.M. NFkB regulation in the immune system. Nat. Rev. Immunol. 2002, 2, 725–734. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Berger, M. Inflammatory mediators in cystic fibrosis lung disease. Allergy Asthma Proc. 2002, 23, 19–25. [Google Scholar]
- Aguirre, V.; Werner, E.D.; Giraud, J.; Lee, Y.H.; Shoelson, S.E.; White, M.F. Phosphorylation of Ser307 in insulin receptor substrate-1 blocks interactions with the insulin receptor and inhibits insulin action. J. Biol. Chem. 2002, 277, 1531–1537. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ozes, O.N.; Akca, H.; Mayo, L.D.; Gustin, J.A.; Maehama, T.; Dixon, J.E.; Donner, D.B. A phosphatidylinositol 3-kinase/Akt/mTOR pathway mediates and PTEN antagonizes tumor necrosis factor inhibition of insulin signalling through insulin receptor substrate-1. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2001, 98, 4640–4645. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Senn, J.J.; Klover, P.J.; Nowak, I.A.; Mooney, R.A. Interleukin-6 induces cellular insulin resistance in hepatocytes. Diabetes 2002, 51, 3391–3399. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mooney, R.A.; Senn, J.; Cameron, S.; Inamdar, N.; Boivin, L.M.; Shang, Y.; Furlanetto, R.W. Suppressors of cytokine signaling-1 and -6 associate with and inhibit the insulin receptor. A potential mechanism for cytokine-mediated insulin resistance. J. Biol. Chem. 2001, 276, 25889–25893. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zadjali, F.; Santana-Farre, R.; Vesterlund, M.; Carow, B.; Mirecki-Garrido, M.; Hernandez-Hernandez, I.; Flodström-Tullberg, M.; Parini, P.; Rottenberg, M.; Norstedt, G.; et al. SOCS2 deletion protects against hepatic steatosis but worsens insulin resistance in high-fat-diet-fed mice. FASEB J. 2012, 26, 3282–3291. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Feng, X.; Wang, W.; Liu, J.; Liu, Y. β-Arrestins: Multifunctional signalling adaptors in type 2 diabetes. Mol. Biol. Rep. 2011, 38, 2517–2528. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- DeWire, S.M.; Ahn, S.; Lefkowitz, R.J.; Shenoy, S.K. Beta-arrestins and cell signaling. Annu. Rev. Physiol. 2007, 69, 483–510. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Manson, M.E.; Corey, D.A.; White, N.M.; Kelley, T.J. cAMP-mediated regulation of cholesterol accumulation in cystic fibrosis and Niemann-Pick type C cells. Am. J. Physiol. Lung Cell. Mol. Physiol. 2008, 295, L809–L819. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- DeFronzo, R.A.; Tripathy, D. Skeletal muscle insulin resistance is the primary defect in type 2 diabetes. Diabetes Care 2009, 32, S157–S163. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Silveira, L.R.; Fiamoncini, J.; Hirabara, S.M.; Procópio, J.; Cambiaghi, T.D.; Pinheiro, C.H.; Lopes, L.R.; Curi, R. Updating the effects of fatty acids on skeletal muscle. J. Cell. Physiol. 2008, 217, 1–12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- McDonald, A.; Williams, R.M.; Regan, F.M.; Semple, R.K.; Dunger, D.B. IGF-I treatment of insulin resistance. Eur. J. Endocrinol. 2007, 157, 51–56. [Google Scholar]
- Savage, M.O.; Camacho-Hübner, C.; Dunger, D.B. Therapeutic applications of the insulin-like growth factors. Growth Horm. IGF Res. 2004, 14, 301–308. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Street, M.E.; Viani, I.; Ziveri, M.A.; Volta, C.; Smerieri, A.; Bernasconi, S. Impairment of insulin receptor signal transduction in placentas of intra-uterine growth-restricted newborns and its relationship with fetal growth. Eur. J. Endocrinol. 2011, 164, 45–52. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lu, M.; Wan, M.; Leavens, K.F.; Chu, Q.; Monks, B.R.; Fernandez, S.; Ahima, R.S.; Ueki, K.; Kahn, C.R.; Birnbaum, M.J. Insulin regulates liver metabolism in vivo in the absence of hepatic Akt and Foxo1. Nat. Med. 2012, 18, 388–396. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Van der Vos, K.E.; Coffer, P.J. FOXO-binding partners: It takes two to tango. Oncogene 2008, 27, 2289–2299. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hardin, D.S.; Ahn, C.; Rice, J.; Rice, M.; Rosenblatt, R. Elevated gluconeogenesis and lack of suppression by insulin contribute to cystic fibrosis-related diabetes. J. Investig. Med. 2008, 56, 567–573. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Zhang, K.; Li, L.; Qi, Y.; Zhu, X.; Gan, B.; DePinho, R.A.; Averitt, T.; Guo, S. Hepatic suppression of Foxo1 and Foxo3 causes hypoglycemia and hyperlipidemia in mice. Endocrinology 2012, 153, 631–646. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hardin, D.S.; LeBlanc, A.; Para, L.; Seilheimer, D.K. Hepatic insulin resistance and defects in substrate utilization in cystic fibrosis. Diabetes 1999, 48, 1082–1087. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gentzsch, M.; Choudry, A.; Chang, X.; Pagano, R.E.; Riordan, J.R. Misassembled mutant ΛF508 CFTR in the distal secretory pathway alters cellular lipid trafficking. J. Cell. Sci. 2007, 120, 447–455. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yang, X.; Zhou, G.; Ren, T.; Li, H.; Zhang, Y.; Yin, D.; Qian, H.; Li, Q. β-arrestin prevents cell apoptosis through pro-apoptotic ERK1 /2 and p38 MAPKs and anti-apoptotic Akt pathways. Apoptosis 2012, 17, 1019–1026. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bost, F.; Aouadi, M.; Caron, L.; Even, P.; Belmonte, N.; Prot, M.; Dani, C.; Hofman, P.; Pagès, G.; Pouysségur, J.; et al. The extracellular signal-regulated kinase isoform ERK1 is specifically required for in vitro and in vivo adipogenesis. Diabetes 2005, 54, 402–411. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Martel, G.; Rousseau, S. TPL2 signalling: From Toll-like receptors-mediated ERK1/ERK2 activation to Cystic Fibrosis lung disease. Int. J. Biochem. Cell Biol. 2014, 52, 146–151. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mohan, K.; Miller, H.; Dyce, P.; Grainger, R.; Hughes, R.; Vora, J.; Ledson, M.; Walshaw, M. Mechanisms of glucose intolerance in cystic fibrosis. Diabet. Med. 2009, 26, 582–588. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gupta, D.; Leahy, A.A.; Mongan, N.; Peshavaria, M.; Jetton, T.L.; Leahy, J.L. Peroxisome proliferator-activated receptor γ (PPARγ) and its target genes are downstream effectors of FoxO1 protein in islet β-cells: Mechanism of β-cell compensation and failure. J. Biol. Chem. 2013, 288, 25440–25449. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Martinez, S.C.; Tanabe, K.; Cras-Meneur, C.; Abumrad, N.A.; Bernal-Mizrachi, E.; Permutt, M.A. Inhibition of FOXO1 protects pancreatic islet beta-cells against fatty acid and endoplasmic reticulum stress-induced apoptosis. Diabetes 2008, 57, 846–859. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Miyazaki, S.; Minamida, R.; Furuyama, T.; Tashiro, F.; Yamato, E.; Inagaki, S.; Miyazaki, J. Analysis of FOXO1-regulated genes using FOXO1-deficient pancreatic beta cells. Genes Cell 2012, 17, 758–767. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, H.W.; Cheng, J.; Kovbasnjuk, O.; Donowitz, M.; Guggino, W.B. Insulin-like growth factor 1 (IGF-1) enhances the protein expression of CFTR. PLoS One 2013, 8, e59992. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yuen, K.; Frystyk, J.; Umpleby, M.; Fryklund, L.; Dunger, D. Changes in free rather than total insulin-like growth factor-I enhance insulin sensitivity and suppress endogenous peak growth hormone (GH) release following short-term low-dose GH administration in young healthy adults. J. Clin. Endocrinol. Metab. 2004, 89, 3956–3964. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Simpson, H.L.; Jackson, N.C.; Shojaee-Moradie, F.; Jones, R.H.; Russell-Jones, D.L.; Sonksen, P.H.; Dunger, D.B.; Umpleby, A.M. Insulin-like growth factor I has a direct effect on glucose and protein metabolism, but no effect on lipid metabolism in type I diabetes. J. Clin. Endocrinol. Metab. 2004, 89, 425–432. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bucuvalas, J.C.; Chernausek, S.D.; Alfaro, M.P.; Krug, S.H.; Ritschel, W.; Wilmot, R.W. Effect of insulin-like growth factor-I treatment in children with cystic fibrosis. J. Pediatr. Gastroenterol. Nutr. 2001, 33, 576–581. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Schnabel, D.; Grasemann, C.; Staab, D.; Wollmann, H.; Ratjen, F. A multicenter, randomized, double-blind, placebocontrolled trial to evaluate the metabolic and respiratory effects of growth hormone in children with cystic fibrosis. Pediatrics 2007, 119, e1230–e1238. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Thaker, V.; Haagensen, A.I.; Carter, B.; Fedorowicz, Z.; Houston, B.W. Recombinant growth hormone therapy for cystic fibrosis in children and young adults. Cochrane Database Syst. Rev. 2013, 6, CD008901. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Gruenert, D.C.; Basbaum, C.B.; Welsh, M.J.; Li, M.; Finkbeiner, W.E.; Nadel, J.A. Characterization of human tracheal epithelial cells transformed by an origin-defective simian virus 40. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 1988, 85, 5951–5955. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ehrhardt, C.; Collnot, E.M.; Baldes, C.; Becker, U.; Laue, M.; Kim, K.J.; Lehr, C.M. Towards an in vitro model of cystic fibrosis small airway epithelium: Characterisation of the human bronchial epithelial cell line CFBE41o-. Cell Tissue Res. 2006, 323, 405–415. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Street, M.E.; Miraki-Moud, F.; Sanderson, I.R.; Savage, M.O.; Giovannelli, G.; Bernasconi, S.; Camacho-Hübner, C. Interleukin-1β (IL1β) and IL6 modulate insulin-like growth factor-binding protein (IGFBP) secretion in colon cancer epithelial (Caco-2) cells. J. Endocrinol. 2003, 179, 405–415. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Perez, A.; Issler, A.C.; Cotton, C.U.; Kelley, T.J.; Verkman, A.S.; Davis, P.B. CFTR inhibition mimics the cystic fibrosis inflammatory profile. Am. J. Physiol. Lung Cell. Mol. Physiol. 2007, 292, L383–L395. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Muanprasat, C.; Sonawane, N.D.; Salinas, D.; Taddei, A.; Galietta, L.J.; Verkman, A.S. Discovery of glycine hydrazide pore-occluding CFTR inhibitors: Mechanism, structure-activity analysis, and in vivo efficacy. J. Gen. Physiol. 2004, 124, 125–137. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Van Doorninck, J.H.; French, P.J.; Verbeek, E.; Peters, R.H.; Morreau, H.; Bijman, J.; Scholte, B.J. A mouse model for the cystic fibrosis delta F508 mutation. EMBO J. 1995, 14, 4403–4411. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Nicklas, W.; Baneux, P.; Boot, R.; Decelle, T.; Deeny, A.A.; Fumanelli, M.; Illgen-Wilcke, B.; FELASA (Federation of European Laboratory Animal Science Associations Working Group on Health Monitoring of Rodent and Rabbit Colonies). Recommendations for the health monitoring of rodent and rabbit colonies in breeding and experimental units. Lab. Anim. 2002, 36, 20–42. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
© 2014 by the authors; licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Smerieri, A.; Montanini, L.; Maiuri, L.; Bernasconi, S.; Street, M.E. FOXO1 Content Is Reduced in Cystic Fibrosis and Increases with IGF-I Treatment. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2014, 15, 18000-18022. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms151018000
Smerieri A, Montanini L, Maiuri L, Bernasconi S, Street ME. FOXO1 Content Is Reduced in Cystic Fibrosis and Increases with IGF-I Treatment. International Journal of Molecular Sciences. 2014; 15(10):18000-18022. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms151018000
Chicago/Turabian StyleSmerieri, Arianna, Luisa Montanini, Luigi Maiuri, Sergio Bernasconi, and Maria E. Street. 2014. "FOXO1 Content Is Reduced in Cystic Fibrosis and Increases with IGF-I Treatment" International Journal of Molecular Sciences 15, no. 10: 18000-18022. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms151018000
APA StyleSmerieri, A., Montanini, L., Maiuri, L., Bernasconi, S., & Street, M. E. (2014). FOXO1 Content Is Reduced in Cystic Fibrosis and Increases with IGF-I Treatment. International Journal of Molecular Sciences, 15(10), 18000-18022. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms151018000