Neuroprotective Role of Liver Growth Factor “LGF” in an Experimental Model of Cerebellar Ataxia
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Results
2.1. LGF Ameliorates Motor Coordination in 3-AP-Lesioned Rats

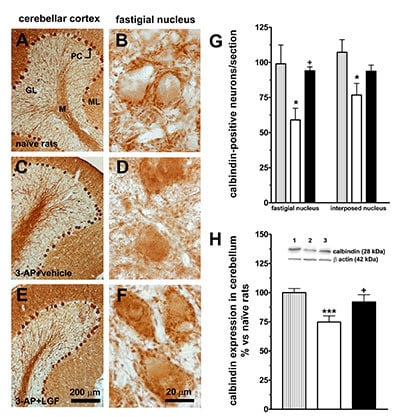
2.2. LGF Partially Prevents Neurotoxin-Induced Neuronal Loss in the Brainstem and Cerebellum of 3-AP-Lesioned Rats


2.3. LGF Regulates Bcl-2 and OX6 Protein Expression in the Brainstem and Cerebellum of 3-AP-Lesioned Rats


2.4. LGF Modulates the Extracellular Concentration of Glutamate and GABA in the Cerebellar Cortex of 3-AP-Lesioned Rats

3. Discussion
4. Experimental Section
4.1. LGF Purification
4.2. Ethics Statement
4.3. Experimental Model of Cerebellar Ataxia in Rats
4.4. Behavioral Testing
4.5. LGF Administration
4.6. Tissue Processing
4.7. Antibodies and Immunochemicals
4.8. Immunohistochemistry and Morphometric Analysis
4.9. Microdialysis Procedure
4.10. Amino Acids Determination
4.11. Western Blotting Protein Analysis
4.12. Data Analysis
5. Conclusions
Acknowledgments
Author Contributions
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Marmolino, D.; Manto, M. Past, present and future therapeutics for cerebellar ataxias. Curr. Neuropharmacol. 2010, 8, 41–61. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fernandez, A.M.; Carro, E.M.; Lopez-Lopez, C.; Torres-Aleman, I. Insulin-like growth factor I treatment for cerebellar ataxia: Addressing a common pathway in the pathological cascade? Brain Res. Brain Res. Rev. 2005, 50, 134–141. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Klockgether, T. Parkinsonism & related disorders. Ataxias. Parkinsonism Relat. Disord. 2007, 13, S391–S394. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, M.; Ma, W.; Zhao, L.; Fariss, R.N.; Wong, W.T. Adaptive Muller cell responses to microglial activation mediate neuroprotection and coordinate inflammation in the retina. J. Neuroinflamm. 2011, 8, 173. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Klockgether, T. Update on degenerative ataxias. Curr. Opin. Neurol. 2011, 24, 339–345. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Manto, M.; Marmolino, D. Cerebellar ataxias. Curr. Opin. Neurol. 2009, 22, 419–429. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fernandez, A.M.; de la Vega, A.G.; Torres-Aleman, I. Insulin-like growth factor I restores motor coordination in a rat model of cerebellar ataxia. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 1998, 95, 1253–1258. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tolbert, D.L.; Clark, B.R. GDNF and IGF-I trophic factors delay hereditary Purkinje cell degeneration and the progression of gait ataxia. Exp. Neurol. 2003, 183, 205–219. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vig, P.J.; Subramony, S.H.; D’Souza, D.R.; Wei, J.; Lopez, M.E. Intranasal administration of IGF-I improves behavior and Purkinje cell pathology in SCA1 mice. Brain Res. Bull. 2006, 69, 573–579. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fernandez, A.M.; Gonzalez de la Vega, A.G.; Planas, B.; Torres-Aleman, I. Neuroprotective actions of peripherally administered insulin-like growth factor I in the injured olivo-cerebellar pathway. Eur. J. Neurosci. 1999, 11, 2019–2030. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhong, J.; Deng, J.; Phan, J.; Dlouhy, S.; Wu, H.; Yao, W.; Ye, P.; D’Ercole, A.J.; Lee, W.H. Insulin-like growth factor-I protects granule neurons from apoptosis and improves ataxia in weaver mice. J. Neurosci. Res. 2005, 80, 481–490. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Diaz-Gil, J.J.; Escartin, P.; Garcia-Canero, R.; Trilla, C.; Veloso, J.J.; Sanchez, G.; Moreno-Caparros, A.; Enrique de Salamanca, C.; Lozano, R.; Gavilanes, J.G.; et al. Purification of a liver DNA-synthesis promoter from plasma of partially hepatectomized rats. Biochem. J. 1986, 235, 49–55. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Diaz-Gil, J.J.; Gavilanes, J.G.; Sanchez, G.; Garcia-Canero, R.; Garcia-Segura, J.M.; Santamaria, L.; Trilla, C.; Escartin, P. Identification of a liver growth factor as an albumin-bilirubin complex. Biochem. J. 1987, 243, 443–448. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Diaz-Gil, J.J.; Sanchez, G.; Trilla, C.; Escartin, P. Identification of biliprotein as a liver growth factor. Hepatology 1988, 8, 484–486. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Conde, M.V.; Gonzalez, M.C.; Quintana-Villamandos, B.; Abderrahim, F.; Briones, A.M.; Condezo-Hoyos, L.; Regadera, J.; Susin, C.; Gomez de Diego, J.J.; Delgado-Baeza, E.; et al. Liver growth factor treatment restores cell-extracellular matrix balance in resistance arteries and improves left ventricular hypertrophy in SHR. Am. J. Physiol. Heart Circ. Physiol. 2011, 301, H1153–H1165. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Diaz Gil, J.J.; Rua, C.; Machin, C.; Cereceda, R.M.; Garcia-Canero, R.; de Foronda, M.; Perez de Diego, J.; Trilla, C.; Escartin, P. Hepatic growth induced by injection of the liver growth factor into normal rats. Growth Regul. 1994, 4, 113–122. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Diaz-Gil, J.J.; Garcia-Monzon, C.; Rua, C.; Martin-Sanz, P.; Cereceda, R.M.; Miquilena-Colina, M.E.; Machin, C.; Fernandez-Martinez, A.; Garcia-Canero, R. Liver growth factor antifibrotic activity in vivo is associated with a decrease in activation of hepatic stellate cells. Histol. Histopathol. 2009, 24, 473–479. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Perez-Crespo, M.; Pericuesta, E.; Perez-Cerezales, S.; Arenas, M.I.; Lobo, M.V.; Diaz-Gil, J.J.; Gutierrez-Adan, A. Effect of liver growth factor on both testicular regeneration and recovery of spermatogenesis in busulfan-treated mice. Reprod. Biol. Endocrinol. 2011, 9, 21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Somoza, B.; Abderrahim, F.; Gonzalez, J.M.; Conde, M.V.; Arribas, S.M.; Starcher, B.; Regadera, J.; Fernandez-Alfonso, M.S.; Diaz-Gil, J.J.; Gonzalez, M.C. Short-term treatment of spontaneously hypertensive rats with liver growth factor reduces carotid artery fibrosis, improves vascular function, and lowers blood pressure. Cardiovasc. Res. 2006, 69, 764–771. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gonzalo-Gobernado, R.; Reimers, D.; Herranz, A.S.; Diaz-Gil, J.J.; Osuna, C.; Asensio, M.J.; Baena, S.; Rodriguez-Serrano, M.; Bazan, E. Mobilization of neural stem cells and generation of new neurons in 6-OHDA-lesioned rats by intracerebroventricular infusion of liver growth factor. J. Histochem. Cytochem. 2009, 57, 491–502. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Reimers, D.; Herranz, A.S.; Diaz-Gil, J.J.; Lobo, M.V.; Paino, C.L.; Alonso, R.; Asensio, M.J.; Gonzalo-Gobernado, R.; Bazan, E. Intrastriatal infusion of liver growth factor stimulates dopamine terminal sprouting and partially restores motor function in 6-hydroxydopamine-lesioned rats. J. Histochem. Cytochem. 2006, 54, 457–465. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Reimers, D.; Osuna, C.; Gonzalo-Gobernado, R.; Herranz, A.S.; Diaz-Gil, J.J.; Jimenez-Escrig, A.; Asensio, M.J.; Miranda, C.; Rodriguez-Serrano, M.; Bazan, E. Liver growth factor promotes the survival of grafted neural stem cells in a rat model of Parkinson’s disease. Curr. Stem Cell Res. Ther. 2012, 7, 15–25. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Aoki, H.; Sugihara, I. Morphology of single olivocerebellar axons in the denervation-reinnervation model produced by subtotal lesion of the rat inferior olive. Brain Res. 2012, 1449, 24–37. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ausim Azizi, S. ...And the olive said to the cerebellum: Organization and functional significance of the olivo-cerebellar system. Neuroscientist 2007, 13, 616–625. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Calatrava-Ferreras, L.; Gonzalo-Gobernado, R.; Herranz, A.S.; Reimers, D.; Montero Vega, T.; Jimenez-Escrig, A.; Richart Lopez, L.A.; Bazan, E. Effects of intravenous administration of human umbilical cord blood stem cells in 3-acetylpyridine-lesioned rats. Stem Cells Int. 2012, 2012, 135187. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gonzalo-Gobernado, R.; Calatrava-Ferreras, L.; Reimers, D.; Herranz, A.S.; Rodriguez-Serrano, M.; Miranda, C.; Jimenez-Escrig, A.; Diaz-Gil, J.J.; Bazan, E. Neuroprotective activity of peripherally administered liver growth factor in a rat model of Parkinson’s disease. PLoS One 2013, 8, e67771. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Frebel, K.; Wiese, S. Signalling molecules essential for neuronal survival and differentiation. Biochem. Soc. Trans. 2006, 34, 1287–1290. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lossi, L.; Gambino, G.; Ferrini, F.; Alasia, S.; Merighi, A. Posttranslational regulation of BCL2 levels in cerebellar granule cells: A mechanism of neuronal survival. Dev. Neurobiol. 2009, 69, 855–870. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sillitoe, R.V.; Joyner, A.L. Morphology, molecular codes, and circuitry produce the three-dimensional complexity of the cerebellum. Annu. Rev. Cell Dev. Biol. 2007, 23, 549–577. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cicchetti, F.; Brownell, A.L.; Williams, K.; Chen, Y.I.; Livni, E.; Isacson, O. Neuroinflammation of the nigrostriatal pathway during progressive 6-OHDA dopamine degeneration in rats monitored by immunohistochemistry and PET imaging. Eur. J. Neurosci. 2002, 15, 991–998. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Reimers, D.; Gonzalo-Gobernado, R.; Herranz, A.S.; Osuna, C.; Asensio, M.J.; Baena, S.; Rodriguez, M.; Bazan, E. Driving neural stem cells towards a desired phenotype. Curr. Stem Cell Res. Ther. 2008, 3, 247–253. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Diaz-Gil, J.J.; Munoz, J.; Albillos, A.; Rua, C.; Machin, C.; Garcia-Canero, R.; Cereceda, R.M.; Guijarro, M.C.; Trilla, C.; Escartin, P. Improvement in liver fibrosis, functionality and hemodynamics in CCI4-cirrhotic rats after injection of the Liver Growth Factor. J. Hepatol. 1999, 30, 1065–1072. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fernandez, A.M.; Garcia-Estrada, J.; Garcia-Segura, L.M.; Torres-Aleman, I. Insulin-like growth factor I modulates c-Fos induction and astrocytosis in response to neurotoxic insult. Neuroscience 1997, 76, 117–122. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shi, J.; Ma, Y.; Zheng, M.; Ruan, Z.; Liu, J.; Tian, S.; Zhang, D.; He, X.; Li, G. Effect of sub-acute exposure to acrylamide on GABAergic neurons and astrocytes in weaning rat cerebellum. Toxicol. Ind. Health 2012, 28, 10–20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mittelbronn, M.; Schittenhelm, J.; Bakos, G.; de Vos, R.A.; Wehrmann, M.; Meyermann, R.; Burk, K. CD8(+)/perforin/granzyme B(+) effector cells infiltrating cerebellum and inferior olives in gluten ataxia. Neuropathology 2010, 30, 92–96. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Buffo, A.; Rolando, C.; Ceruti, S. Astrocytes in the damaged brain: Molecular and cellular insights into their reactive response and healing potential. Biochem. Pharmacol. 2010, 79, 77–89. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chvatal, A.; Anderova, M.; Neprasova, H.; Prajerova, I.; Benesova, J.; Butenko, O.; Verkhratsky, A. Pathological potential of astroglia. Physiol. Res. 2008, 57, S101–110. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Zhang, D.; Hu, X.; Qian, L.; O’Callaghan, J.P.; Hong, J.S. Astrogliosis in CNS pathologies: Is there a role for microglia? Mol. Neurobiol. 2010, 41, 232–41. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Colin, F.; Manil, J.; Desclin, J.C. The olivocerebellar system. I. Delayed and slow inhibitory effects: An overlooked salient feature of cerebellar climbing fibers. Brain Res. 1980, 187, 3–27. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cerminara, N.L.; Rawson, J.A. Evidence that climbing fibers control an intrinsic spike generator in cerebellar Purkinje cells. J. Neurosci. 2004, 24, 4510–4517. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kaffashian, M.; Shabani, M.; Goudarzi, I.; Behzadi, G.; Zali, A.; Janahmadi, M. Profound alterations in the intrinsic excitability of cerebellar Purkinje neurons following neurotoxin 3-acetylpyridine (3-AP)-induced ataxia in rat: New insights into the role of small conductance K+ channels. Physiol. Res. 2011, 60, 355–365. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Janahmadi, M.; Goudarzi, I.; Kaffashian, M.R.; Behzadi, G.; Fathollahi, Y.; Hajizadeh, S. Co-treatment with riluzole, a neuroprotective drug, ameliorates the 3-acetylpyridine-induced neurotoxicity in cerebellar Purkinje neurones of rats: behavioural and electrophysiological evidence. Neurotoxicology 2009, 30, 393–402. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lerma, J.; Herreras, O.; Herranz, A.S.; Munoz, D.; del Rio, R.M. In vivo effects of nipecotic acid on levels of extracellular GABA and taurine, and hippocampal excitability. Neuropharmacology 1984, 23, 595–598. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lerma, J.; Herranz, A.S.; Herreras, O.; Abraira, V.; Martin del Rio, R. In vivo determination of extracellular concentration of amino acids in the rat hippocampus. A method based on brain dialysis and computerized analysis. Brain Res. 1986, 384, 145–155. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Blaylock, R.L. Immunology primer for neurosurgeons and neurologists part 2: Innate brain immunity. Surg. Neurol. Int. 2013, 4, 118. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Danbolt, N.C. Glutamate uptake. Prog. Neurobiol. 2001, 65, 1–105. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Beart, P.M.; O’Shea, R.D. Transporters for L-glutamate: An update on their molecular pharmacology and pathological involvement. Br. J. Pharmacol. 2007, 150, 5–17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Walter, J.T.; Alvina, K.; Womack, M.D.; Chevez, C.; Khodakhah, K. Decreases in the precision of Purkinje cell pacemaking cause cerebellar dysfunction and ataxia. Nat. Neurosci. 2006, 9, 389–397. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chiu, C.S.; Brickley, S.; Jensen, K.; Southwell, A.; McKinney, S.; Cull-Candy, S.; Mody, I.; Lester, H.A. GABA transporter deficiency causes tremor, ataxia, nervousness, and increased GABA-induced tonic conductance in cerebellum. J. Neurosci. 2005, 25, 3234–3245. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhou, Y.; Danbolt, N.C. GABA and Glutamate Transporters in Brain. Front. Endocrinol. (Lausanne) 2013, 4, 165. [Google Scholar]
- Richerson, G.B.; Wu, Y. Dynamic equilibrium of neurotransmitter transporters: Not just for reuptake anymore. J. Neurophysiol. 2003, 90, 1363–1374. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Richerson, G.B.; Wu, Y. Role of the GABA transporter in epilepsy. Adv. Exp. Med. Biol. 2004, 548, 76–91. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Singh, J.; Bowers, L.D. Quantitative fractionation of serum bilirubin species by reversed-phase high-performance liquid chromatography. J. Chromatogr. 1986, 380, 321–330. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Paxinos, G.; Watson, C. The Rat Brain in Stereotaxic Coordinates; Academic Press, Inc.: San Diego, CA, USA, 1997. [Google Scholar]
- Carlsson, A.; Lindqvist, M. Effect of ethanol on the hydroxylation of tyrosine and tryptophan in rat brain in vivo. J. Pharm. Pharmacol. 1973, 25, 437–440. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
© 2014 by the authors; licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Calatrava-Ferreras, L.; Gonzalo-Gobernado, R.; Reimers, D.; Herranz, A.S.; Jiménez-Escrig, A.; Díaz-Gil, J.J.; Casarejos, M.J.; Montero-Vega, M.T.; Bazán, E. Neuroprotective Role of Liver Growth Factor “LGF” in an Experimental Model of Cerebellar Ataxia. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2014, 15, 19056-19073. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms151019056
Calatrava-Ferreras L, Gonzalo-Gobernado R, Reimers D, Herranz AS, Jiménez-Escrig A, Díaz-Gil JJ, Casarejos MJ, Montero-Vega MT, Bazán E. Neuroprotective Role of Liver Growth Factor “LGF” in an Experimental Model of Cerebellar Ataxia. International Journal of Molecular Sciences. 2014; 15(10):19056-19073. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms151019056
Chicago/Turabian StyleCalatrava-Ferreras, Lucía, Rafael Gonzalo-Gobernado, Diana Reimers, Antonio S. Herranz, Adriano Jiménez-Escrig, Juan José Díaz-Gil, María José Casarejos, María Teresa Montero-Vega, and Eulalia Bazán. 2014. "Neuroprotective Role of Liver Growth Factor “LGF” in an Experimental Model of Cerebellar Ataxia" International Journal of Molecular Sciences 15, no. 10: 19056-19073. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms151019056
APA StyleCalatrava-Ferreras, L., Gonzalo-Gobernado, R., Reimers, D., Herranz, A. S., Jiménez-Escrig, A., Díaz-Gil, J. J., Casarejos, M. J., Montero-Vega, M. T., & Bazán, E. (2014). Neuroprotective Role of Liver Growth Factor “LGF” in an Experimental Model of Cerebellar Ataxia. International Journal of Molecular Sciences, 15(10), 19056-19073. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms151019056