Exploring Neighborhoods in the Metagenome Universe
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Results and Discussion
2.1. Neighborhood Accuracy
2.1.1. HMP Collection

2.1.2. Metagenome Universe Collection

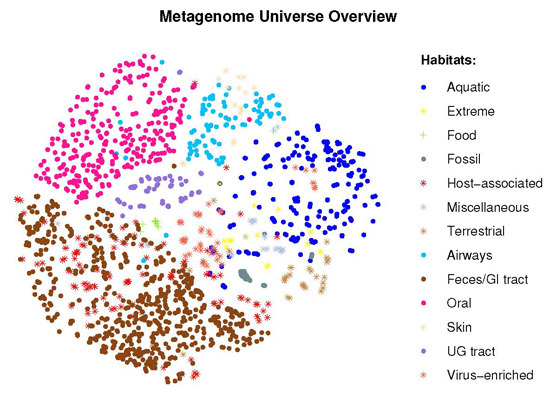
2.2. Visual Exploration of the Metagenome Universe

3. Materials and Methods
3.1. Metagenome Dataset Collections
3.1.1. HMP Collection
3.1.2. Metagenome Universe
3.2. Profiling Methods
3.2.1. Pfam Protein Domain Annotation
3.2.2. Taxonomic Profiling
3.2.3. Mixture-of-Pathways
3.2.4. Protein Alignment Using a DNA Aligner (PAUDA) Annotation
3.3. Nearest Neighbor Analysis





3.4. Dimensionality Reduction
4. Conclusions
Supplementary Files
Supplementary File 1Acknowledgments
Author Contributions
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Delmont, T.O.; Malandain, C.; Prestat, E.; Larose, C.; Monier, J.M.; Simonet, P.; Vogel, T.M. Metagenomic mining for microbiologists. ISME J. 2011, 5, 1837–1843. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Teeling, H.; Glöckner, F.O. Current opportunities and challenges in microbial metagenome analysis—A bioinformatic perspective. Brief. Bioinform. 2012, 13, 728–742. [Google Scholar]
- Knights, D.; Kuczynski, J.; Charlson, E.S.; Zaneveld, J.; Mozer, M.C.; Collman, R.G.; Bushman, F.D.; Knight, R.; Kelley, S.T. Bayesian community-wide culture-independent microbial source tracking. Nat. Methods 2011, 8, 761–763. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Maillet, N.; Lemaitre, C.; Chikhi, R.; Lavenier, D.; Peterlongo, P. Compareads: Comparing huge metagenomic experiments. BMC Bioinform. 2012, 13, S10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Li, W. Analysis and comparison of very large metagenomes with fast clustering and functional annotation. BMC Bioinform. 2009, 10, 359. [Google Scholar]
- Mitra, S.; Klar, B.; Huson, D.H. Visual and statistical comparison of metagenomes. Bioinformatics 2009, 25, 1849–1855. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mitra, S.; Rupek, P.; Richter, D.C.; Urich, T.; Gilbert, J.A.; Meyer, F.; Wilke, A.; Huson, D.H. Functional analysis of metagenomes and metatranscriptomes using SEED and KEGG. BMC Bioinform. 2011, 12, S21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lingner, T.; Aßhauer, K.P.; Schreiber, F.; Meinicke, P. CoMet—A web server for comparative functional profiling of metagenomes. Nucleic Acids Res. 2011, 39, W518–W523. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Klingenberg, H.; Aßhauer, K.P.; Lingner, T.; Meinicke, P. Protein signature-based estimation of metagenomic abundances including all domains of life and viruses. Bioinformatics 2013, 29, 973–980. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sanli, K.; Karlsson, F.H.; Nookaew, I.; Nielsen, J. FANTOM: Functional and taxonomic analysis of metagenomes. BMC Bioinform. 2013, 14, 38. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Su, X.; Xu, J.; Ning, K. Meta-Storms: Efficient search for similar microbial communities based on a novel indexing scheme and similarity score for metagenomic data. Bioinformatics 2012, 28, 2493–2501. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Meinicke, P.; Klanke, S.; Memisevic, R.; Ritter, H. Principal surfaces from unsupervised kernel regression. IEEE Trans. Pattern Anal. Mach. Intell. 2005, 27, 1379–1391. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Group, T.N.H.W.; Peterson, J.; Garges, S.; Giovanni, M.; McInnes, P.; Wang, L.; Schloss, J.A.; Bonazzi, V.; McEwen, J.E.; Wetterstrand, K.A.; et al. The NIH human microbiome project. Genome Res. 2009, 19, 2317–2323. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Segata, N.; Waldron, L.; Ballarini, A.; Narasimhan, V.; Jousson, O.; Huttenhower, C. Metagenomic microbial community profiling using unique clade-specific marker genes. Nat. Methods 2012, 9, 811–814. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Abubucker, S.; Segata, N.; Goll, J.; Schubert, A.M.; Izard, J.; Cantarel, B.L.; Rodriguez-Mueller, B.; Zucker, J.; Thiagarajan, M.; Henrissat, B.; et al. Metabolic reconstruction for Metagenomic data and its application to the human microbiome. PLoS Comput. Biol. 2012, 8, e1002358. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Meyer, F.; Paarmann, D.; D’Souza, M.; Olson, R.; Glass, E.M.; Kubal, M.; Paczian, T.; Rodriguez, A.; Stevens, R.; Wilke, A.; et al. The metagenomics RAST server—A public resource for the automatic phylogenetic and functional analysis of metagenomes. BMC Bioinform. 2008, 9, 386. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Brooksbank, C.; Bergman, M.T.; Apweiler, R.; Birney, E.; Thornton, J. The European Bioinformatics Institute’s data resources 2014. Nucleic Acids Res. 2014, 42, 18–25. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Meinicke, P.; Aßhauer, K.P.; Lingner, T. Mixture models for analysis of the taxonomic composition of metagenomes. Bioinformatics 2011, 27, 1618–1624. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hammesfahr, B.; Odronitz, F.; Hellkamp, M.; Kollmar, M. diArk 2.0 provides detailed analyses of the ever increasing eukaryotic genome sequencing data. BMC Res. Notes 2011, 4, 338. [Google Scholar]
- Aßhauer, K.P.; Meinicke, P. On the estimation of metabolic profiles in metagenomics. In German Conference on Bioinformatics 2013; Beißbarth, T., Kollmar, M., Leha, A., Morgenstern, B., Schultz, A.K., Waack, S., Wingender, E., Eds.; OpenAccess Series in Informatics (OASIcs); Schloss Dagstuhl–Leibniz-Zentrum fuer Informatik: Dagstuhl, Germany, 2013; Volume 34, pp. 1–13. [Google Scholar]
- Huson, D.H.; Xie, C. A poor man’s BLASTX–high-throughput metagenomic protein database search using PAUDA. Bioinformatics 2014, 30, 38–39. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bray, J.R.; Curtis, J.T. An ordination of the upland forest communities of southern Wisconsin. Ecol. Monogr. 1957, 27, 325–349. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ripley, B.D.; Hjort, N.L. Pattern Recognition and Neural Networks, 1st ed.; Cambridge University Press: New York, NY, USA, 1995. [Google Scholar]
- Sammon, J.W. A nonlinear mapping for data structure analysis. IEEE Trans. Comput. 1969, 18, 401–409. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hubert, M.; Engelen, S. Robust PCA and classification in biosciences. Bioinformatics 2004, 20, 1728–1736. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Diaconis, P.; Goel, S.; Holmes, S. Horseshoes in multidimensional scaling and local kernel methods. Ann. Appl. Stat. 2008, 2, 777–807. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Z.; Hsiao, W.; Cantarel, B.L.; Drabek, E.F.; Fraser-Liggett, C. Sparse distance-based learning for simultaneous multiclass classification and feature selection of metagenomic data. Bioinformatics 2011, 27, 3242–3249. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yilmaz, P.; Kottmann, R.; Field, D.; Knight, R.; Cole, J.R.; Amaral-Zettler, L.; Gilbert, J.A.; Karsch-Mizrachi, I.; Johnston, A.; Cochrane, G.; et al. Minimum information about a marker gene sequence (MIMARKS) and minimum information about any (x) sequence (MIxS) specifications. Nat. Biotechnol. 2011, 29, 415–420. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Human Microbiome Project DACC - HMPDACC Data Browser. Available online: http://www.hmpdacc.org/resources/data_browser.php (accessed on 6 February 2013).
- Human Microbiome Project DACC - HMP Project Catalog - View Dataset. Available online: http://www.hmpdacc.org/catalog/grid.php?dataset=metagenomic (accessed on 8 July 2014).
- Human Microbiome Project DACC - HMSMCP. Available online: http://hmpdacc.org/HMSMCP (accessed on 11 February 2013).
- Human Microbiome Project DACC - HMGS. Available online: http://hmpdacc.org/HMGS (accessed on 7 February 2013).
- Human Microbiome Project DACC - HMMRC. Available online: http://www.hmpdacc.org/HMMRC (accessed on 5 April 2013).
- MG-RAST -Home. Available online: http://metagenomics.anl.gov/ (accessed on 6 November 2012).
- EBI Metagenomics: Archiving, Analysis and Integration of Metagenomics Data <EBI metagenomics <EMBL-EBI. Available online: https://www.ebi.ac.uk/metagenomics/ (accessed on 24 January 2014).
- Gene Ontology Consortium — Gene Ontology Consortium. Available online: http://www.geneontology.org/external2go/pfam2go (accessed on 4 October 2013).
- Index von ftp://ftp.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/genomes/Bacteria/. Available online: ftp://ftp.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/genomes/Bacteria/ (accessed on 5 November 2013).
- Index von ftp://ftp.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/genomes/Viruses/. Available online: ftp://ftp.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/genomes/Viruses/ (accessed on 5 November 2013).
- Matlab Toolbox for Dimensionality Reduction. Available online: http://homepage.tudelft.nl/19j49/Matlab_Toolbox_for_Dimensionality_Reduction.html (accessed on 30 September 2011).
- Stefan Klanke: UKR Toolbox. Available online: http://www.sklanke.de/ukrtoolbox.zip (accessed on 27 March 2014).
- CoMet-Universe: Home. Available online: http://comet2.gobics.de (accessed on 31 March 2014).
© 2014 by the authors; licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/3.0/).
Share and Cite
Aßhauer, K.P.; Klingenberg, H.; Lingner, T.; Meinicke, P. Exploring Neighborhoods in the Metagenome Universe. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2014, 15, 12364-12378. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms150712364
Aßhauer KP, Klingenberg H, Lingner T, Meinicke P. Exploring Neighborhoods in the Metagenome Universe. International Journal of Molecular Sciences. 2014; 15(7):12364-12378. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms150712364
Chicago/Turabian StyleAßhauer, Kathrin P., Heiner Klingenberg, Thomas Lingner, and Peter Meinicke. 2014. "Exploring Neighborhoods in the Metagenome Universe" International Journal of Molecular Sciences 15, no. 7: 12364-12378. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms150712364
APA StyleAßhauer, K. P., Klingenberg, H., Lingner, T., & Meinicke, P. (2014). Exploring Neighborhoods in the Metagenome Universe. International Journal of Molecular Sciences, 15(7), 12364-12378. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms150712364