DNA Double Strand Break Response and Limited Repair Capacity in Mouse Elongated Spermatids
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Results
2.1. Ku70 and 53BP1 Are Not Expressed in Elongated Spermatids

2.2. Incomplete Meiotic Recombination Repair in Late Spermatocytes Increases the Numbers of Background Foci during Spermatid Remodeling


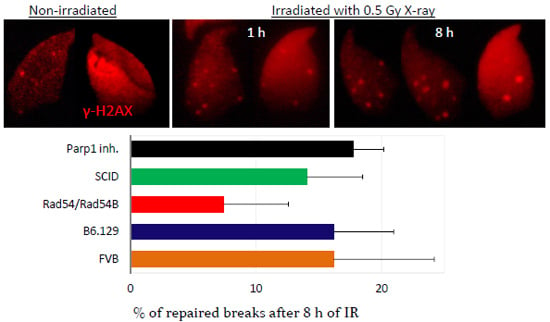
2.3. DNA Damage and Repair Responses to Irradiation-Induced DSBs in Elongated Spermatids


3. Discussion
4. Materials and Methods
4.1. Animals, Irradiation and Fixation
4.2. Immunohistochemistry
4.3. Immunofluorescence
4.4. Surface-Spread Preparations
4.5. The Kinetics of γ-H2AX Foci Loss after Irradiation
4.6. Statistical Analysis
5. Conclusions
Acknowledgments
Author Contributions
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Ahmed, E.A.; Sfeir, A.; Takai, H.; Scherthan, H. Ku70 and non-homologous end joining protect testicular cells from DNA damage. J. Cell Sci. 2013, 126, 3095–3104. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Baudat, F.; Imai, Y.; de Massy, B. Meiotic recombination in mammals: Localization and regulation. Nat. Rev. Genet. 2013, 14, 794–806. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ahmed, E.A.; Philippens, M.E.; Kal, H.B.; de Rooij, D.G.; de Boer, P. Genetic probing of homologous recombination and non-homologous end joining during meiotic prophase in irradiated mouse spermatocytes. Mutat. Res. 2010, 688, 12–18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Marchetti, F.; Wyrobek, A.J. DNA repair decline during mouse spermiogenesis results in the accumulation of heritable DNA damage. DNA Repair 2008, 7, 572–581. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ahmed, E.A.; de Boer, P.; Philippens, M.E.; Kal, H.B.; de Rooij, D.G. Parp1-XRCC1 and the repair of DNA double strand breaks in mouse round spermatids. Mutat. Res. 2010, 683, 84–90. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tusell, L.; Latre, L.; Ponsa, I.; Miro, R.; Egozcue, J.; Genesca, A. Capping of radiation-induced DNA breaks in mouse early embryos. J. Radiat. Res. 2004, 45, 415–422. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pacchierotti, F.; Ranaldi, R.; Derijck, A.A.; van der Heijden, G.W.; de Boer, P. In vivo repair of DNA damage induced by X-rays in the early stages of mouse fertilization, and the influence of maternal PARP1 ablation. Mutat. Res. 2011, 714, 44–52. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ahmed, E.A.; van der Vaart, A.; Barten, A.; Kal, H.B.; Chen, J.; Lou, Z.; Minter-Dykhouse, K.; Bartkova, J.; Bartek, J.; de Boer, P.; et al. Differences in DNA double strand breaks repair in male germ cell types: Lessons learned from a differential expression of Mdc1 and 53BP1. DNA Repair 2007, 6, 1243–1254. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chicheportiche, A.; Bernardino-Sgherri, J.; de Massy, B.; Dutrillaux, B. Characterization of Spo11-dependent and independent phospho-H2AX foci during meiotic prophase I in the male mouse. J. Cell Sci. 2007, 120, 1733–1742. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rube, C.E.; Zhang, S.; Miebach, N.; Fricke, A.; Rube, C. Protecting the heritable genome: DNA damage response mechanisms in spermatogonial stem cells. DNA Repair 2011, 10, 159–168. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cordelli, E.; Eleuteri, P.; Grollino, M.G.; Benassi, B.; Blandino, G.; Bartoleschi, C.; Pardini, M.C.; di Caprio, E.V.; Spano, M.; Pacchierotti, F.; et al. Direct and delayed X-ray-induced DNA damage in male mouse germ cells. Environ. Mol. Mutagenes. 2012, 53, 429–439. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Marcon, L.; Boissonneault, G. Transient DNA strand breaks during mouse and human spermiogenesis new insights in stage specificity and link to chromatin remodeling. Biol. Reprod. 2004, 70, 910–918. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Van Loon, A.A.; Sonneveld, E.; Hoogerbrugge, J.; van der Schans, G.P.; Grootegoed, J.A.; Lohman, P.H.; Baan, R.A. Induction and repair of DNA single-strand breaks and DNA base damage at different cellular stages of spermatogenesis of the hamster upon in vitro exposure to ionizing radiation. Mutat. Res. 1993, 294, 139–148. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Meyer-Ficca, M.L.; Scherthan, H.; Burkle, A.; Meyer, R.G. Poly(ADP-ribosyl)ation during chromatin remodeling steps in rat spermiogenesis. Chromosoma 2005, 114, 67–74. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Meyer-Ficca, M.L.; Lonchar, J.; Credidio, C.; Ihara, M.; Li, Y.; Wang, Z.Q.; Meyer, R.G. Disruption of poly(ADP-ribose) homeostasis affects spermiogenesis and sperm chromatin integrity in mice. Biol. Reprod. 2009, 81, 46–55. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ward, W.S. Regulating DNA supercoiling: Sperm points the way. Biol. Reprod. 2011, 84, 841–843. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Risley, M.S.; Einheber, S.; Bumcrot, D.A. Changes in DNA topology during spermatogenesis. Chromosoma 1986, 94, 217–227. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Laberge, R.M.; Boissonneault, G. On the nature and origin of DNA strand breaks in elongating spermatids. Biol. Reprod. 2005, 73, 289–296. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Leduc, F.; Maquennehan, V.; Nkoma, G.B.; Boissonneault, G. DNA damage response during chromatin remodeling in elongating spermatids of mice. Biol. Reprod. 2008, 78, 324–332. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Collins, A.R. The comet assay for DNA damage and repair: Principles, applications, and limitations. Mol. Biotechnol. 2004, 26, 249–261. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rogakou, E.P.; Pilch, D.R.; Orr, A.H.; Ivanova, V.S.; Bonner, W.M. DNA double-stranded breaks induce histone H2AX phosphorylation on serine 139. J. Biol. Chem. 1998, 273, 5858–5868. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kuo, L.J.; Yang, L.X. γ-H2AX—A novel biomarker for DNA double-strand breaks. In Vivo 2008, 22, 305–309. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Lobrich, M.; Shibata, A.; Beucher, A.; Fisher, A.; Ensminger, M.; Goodarzi, A.A.; Barton, O.; Jeggo, P.A. γH2AX foci analysis for monitoring DNA double-strand break repair: Strengths, limitations and optimization. Cell Cycle 2010, 9, 662–669. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pilch, D.R.; Sedelnikova, O.A.; Redon, C.; Celeste, A.; Nussenzweig, A.; Bonner, W.M. Characteristics of γ-H2AX foci at DNA double-strand breaks sites. Biochem. Cell Biol. 2003, 81, 123–129. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sedelnikova, O.A.; Rogakou, E.P.; Panyutin, I.G.; Bonner, W.M. Quantitative detection of (125)IdU-induced DNA double-strand breaks with γ-H2AX antibody. Radiat. Res. 2002, 158, 486–492. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fernandez-Capetillo, O.; Lee, A.; Nussenzweig, M.; Nussenzweig, A. H2AX: The histone guardian of the genome. DNA Repair 2004, 3, 959–967. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rothkamm, K.; Lobrich, M. Evidence for a lack of DNA double-strand break repair in human cells exposed to very low X-ray doses. Proc. Natl Acad. Sci. USA 2003, 100, 5057–5062. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Scherthan, H.; Hieber, L.; Braselmann, H.; Meineke, V.; Zitzelsberger, H. Accumulation of DSBs in γ-H2AX domains fuel chromosomal aberrations. Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 2008, 371, 694–697. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ward, W.S.; Zalensky, A.O. The unique, complex organization of the transcriptionally silent sperm chromatin. Crit. Rev. Eukaryot. Gene Expr. 1996, 6, 139–147. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Audebert, M.; Salles, B.; Calsou, P. Involvement of poly(ADP-ribose) polymerase-1 and XRCC1/DNA ligase III in an alternative route for DNA double-strand breaks rejoining. J. Biol. Chem. 2004, 279, 55117–55126. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Goedecke, W.; Eijpe, M.; Offenberg, H.H.; van Aalderen, M.; Heyting, C. Mre11 and Ku70 interact in somatic cells, but are differentially expressed in early meiosis. Nat. Genet. 1999, 23, 194–198. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Noda, A.; Hirai, Y.; Hamasaki, K.; Mitani, H.; Nakamura, N.; Kodama, Y. Unrepairable DNA double-strand breaks that are generated by ionising radiation determine the fate of normal human cells. J. Cell Sci. 2012, 125, 5280–5287. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Iwabuchi, K.; Basu, B.P.; Kysela, B.; Kurihara, T.; Shibata, M.; Guan, D.; Cao, Y.; Hamada, T.; Imamura, K.; Jeggo, P.A.; et al. Potential role for 53BP1 in DNA end-joining repair through direct interaction with DNA. J. Biol. Chem. 2003, 278, 36487–36495. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Panier, S.; Boulton, S.J. Double-strand break repair: 53BP1 comes into focus. Nat. Rev. Mol. Cell Biol. 2014, 15, 7–18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hamer, G.; Roepers-Gajadien, H.L.; van Duyn-Goedhart, A.; Gademan, I.S.; Kal, H.B.; van Buul, P.P.; Ashley, T.; de Rooij, D.G. Function of DNA-protein kinase catalytic subunit during the early meiotic prophase without Ku70 and Ku86. Biol. Reprod. 2003, 68, 717–721. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mansour, W.Y.; Borgmann, K.; Petersen, C.; Dikomey, E.; Dahm-Daphi, J. The absence of Ku but not defects in classical non-homologous end-joining is required to trigger PARP1-dependent end-joining. DNA Repair 2013, 12, 1134–1142. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Maymon, B.B.; Cohen-Armon, M.; Yavetz, H.; Yogev, L.; Lifschitz-Mercer, B.; Kleiman, S.E.; Botchan, A.; Hauser, R.; Paz, G. Role of poly(ADP-ribosyl)ation during human spermatogenesis. Fertil. Steril. 2006, 86, 1402–1407. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Manova, V.; Singh, S.K.; Iliakis, G. Processing of DNA double strand breaks by alternative non-homologous end-joining in hyperacetylated chromatin. Genome Integr. 2012, 3, 4. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Balhorn, R. A model for the structure of chromatin in mammalian sperm. J. Cell. Biol. 1982, 93, 298–305. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rathke, C.; Baarends, W.M.; Awe, S.; Renkawitz-Pohl, R. Chromatin dynamics during spermiogenesis. BBA Gene Regul. Mech. 2014, 1839, 155–168. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Van Loon, A.A.; den Boer, P.J.; van der Schans, G.P.; Mackenbach, P.; Grootegoed, J.A.; Baan, R.A.; Lohman, P.H. Immunochemical detection of DNA damage induction and repair at different cellular stages of spermatogenesis of the hamster after in vitro or in vivo exposure to ionizing radiation. Exp. Cell Res. 1991, 193, 303–309. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cordelli, E.; Fresegna, A.M.; Leter, G.; Eleuteri, P.; Spano, M.; Villani, P. Evaluation of DNA damage in different stages of mouse spermatogenesis after testicular X irradiation. Radiat. Res. 2003, 160, 443–451. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Haines, G.; Marples, B.; Daniel, P.; Morris, I. DNA damage in human and mouse spermatozoa after in vitro-irradiation assessed by the comet assay. Adv. Exp. Med. Biol. 1998, 444, 79–91. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Haines, G.A.; Hendry, J.H.; Daniel, C.P.; Morris, I.D. Increased levels of comet-detected spermatozoa DNA damage following in vivo isotopic- or X-irradiation of spermatogonia. Mutat. Res. 2001, 495, 21–32. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hales, B.F.; Aguilar-Mahecha, A.; Robaire, B. The stress response in gametes and embryos after paternal chemical exposures. Toxicol. Appl. Pharmacol. 2005, 207, 514–520. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bellver, J.; Meseguer, M.; Muriel, L.; Garcia-Herrero, S.; Barreto, M.A.; Garda, A.L.; Remohi, J.; Pellicer, A.; Garrido, N. Y chromosome microdeletions, sperm DNA fragmentation and sperm oxidative stress as causes of recurrent spontaneous abortion of unknown etiology. Hum. Reprod. 2010, 25, 1713–1721. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Venkatesh, S.; Kumar, R.; Deka, D.; Deecaraman, M.; Dada, R. Analysis of sperm nuclear protein gene polymorphisms and DNA integrity in infertile men. Syst. Biol. Reprod. Med. 2011, 57, 124–132. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Watanabe, S.; Tanaka, A.; Fujii, S.; Mizunuma, H.; Fukui, A.; Fukuhara, R.; Nakamura, R.; Yamada, K.; Tanaka, I.; Awata, S.; et al. An investigation of the potential effect of vacuoles in human sperm on DNA damage using a chromosome assay and the TUNEL assay. Hum. Reprod. 2011, 26, 978–986. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Brahem, S.; Mehdi, M.; Elghezal, H.; Saad, A. Analysis of sperm aneuploidies and DNA fragmentation in patients with globozoospermia or with abnormal acrosomes. Urology 2011, 77, 1343–1348. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mahadevaiah, S.K.; Turner, J.M.; Baudat, F.; Rogakou, E.P.; de Boer, P.; Blanco-Rodriguez, J.; Jasin, M.; Keeney, S.; Bonner, W.M.; Burgoyne, P.S. Recombinational DNA double-strand breaks in mice precede synapsis. Nat. Genet. 2001, 27, 271–276. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wesoly, J.; Agarwal, S.; Sigurdsson, S.; Bussen, W.; van Komen, S.; Qin, J.; van Steeg, H.; van Benthem, J.; Wassenaar, E.; Baarends, W.M.; et al. Differential contributions of mammalian Rad54 paralogs to recombination, DNA damage repair, and meiosis. Mol. Cell. Biol. 2006, 26, 976–989. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- De Rooij, D.G.; de Boer, P. Specific arrests of spermatogenesis in genetically modified and mutant mice. Cytogenet. Genome Res. 2003, 103, 267–276. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Villani, P.; Fresegna, A.M.; Ranaldi, R.; Eleuteri, P.; Paris, L.; Pacchierotti, F.; Cordelli, E. X-ray induced DNA damage and repair in germ cells of PARP1−/− male mice. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2013, 14, 18078–18092. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Derijck, A.; van der Heijden, G.; Giele, M.; Philippens, M.; de Boer, P. DNA double-strand break repair in parental chromatin of mouse zygotes, the first cell cycle as an origin of de novo mutation. Hum. Mol. Genet. 2008, 17, 1922–1937. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, G.; Huang, X.; Li, Y.; Guo, K.; Ning, P.; Zhang, Y. PARP-1 inhibitor, DPQ, attenuates LPS-induced acute lung injury through inhibiting NF-κB-mediated inflammatory response. PLoS ONE 2013, 8, e79757. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Peters, A.H.; Plug, A.W.; van Vugt, M.J.; de Boer, P. A drying-down technique for the spreading of mammalian meiocytes from the male and female germline. Chromosome Res. 1997, 5, 66–68. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
© 2015 by the authors; licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons by Attribution (CC-BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Ahmed, E.A.; Scherthan, H.; De Rooij, D.G. DNA Double Strand Break Response and Limited Repair Capacity in Mouse Elongated Spermatids. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2015, 16, 29923-29935. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms161226214
Ahmed EA, Scherthan H, De Rooij DG. DNA Double Strand Break Response and Limited Repair Capacity in Mouse Elongated Spermatids. International Journal of Molecular Sciences. 2015; 16(12):29923-29935. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms161226214
Chicago/Turabian StyleAhmed, Emad A., Harry Scherthan, and Dirk G. De Rooij. 2015. "DNA Double Strand Break Response and Limited Repair Capacity in Mouse Elongated Spermatids" International Journal of Molecular Sciences 16, no. 12: 29923-29935. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms161226214
APA StyleAhmed, E. A., Scherthan, H., & De Rooij, D. G. (2015). DNA Double Strand Break Response and Limited Repair Capacity in Mouse Elongated Spermatids. International Journal of Molecular Sciences, 16(12), 29923-29935. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms161226214