Dietary Compound Kaempferol Inhibits Airway Thickening Induced by Allergic Reaction in a Bovine Serum Albumin-Induced Model of Asthma
Abstract
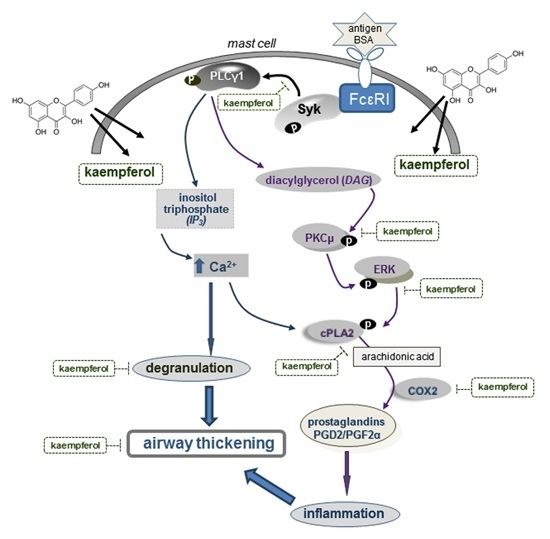
:1. Introduction

2. Results
2.1. Effects of Kaempferol on Leukocyte Distribution and β–Hexosaminidase Release
2.2. Inhibitory Effects of Kaempferol on Prostaglandin Release and Cyclooxygenase 2 (COX2) Induction




2.3. Inhibition of Airway Thickening by Kaempferol
2.4. Inhibition of Cytosolic Phospholipase A2 (cPLA2) Activation by Kaempferol


2.5. Blockade of Syk-ERK (Extracellular Signal-Regulated Kinase) Signaling by Kaempferol


3. Discussion
4. Materials and Methods
4.1. Materials
4.2. Cell Culture and Kaempferol Treatment
4.3. Murine Animal Model
4.4. β-Hexosaminidase Analysis
4.5. Western Blot Analysis
4.6. Immunohistochemical Analysis
4.7. Enzyme-Linked Immunosorbent Assay (ELISA)
4.8. Statistical Analysis

5. Conclusions
Acknowledgments
Author Contributions
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Platts-Mills, T.A.; Woodfolk, J.A. Allergens and their role in the allergic immune response. Immunol. Rev. 2011, 242, 51–68. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Broide, D.H. Allergic rhinitis: Pathophysiology. Allergy Asthma Proc. 2010, 31, 370–374. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Galli, E.; Cicconi, R.; Rossi, P.; Casati, A.; Brunetti, E.; Mancino, G. Atopic dermatitis: Molecular mechanisms, clinical aspects and new therapeutical approaches. Curr. Mol. Med. 2003, 3, 127–138. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Galli, S.J.; Tsai, M. IgE and mast cells in allergic disease. Nat. Med. 2012, 18, 693–704. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cromheecke, J.L.; Nguyen, K.T.; Huston, D.P. Emerging role of human basophil biology in health and disease. Curr. Allergy Asthma Rep. 2014, 14, 408. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Amin, K. The role of mast cells in allergic inflammation. Respir. Med. 2012, 106, 9–14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yokoi, H.; Choi, O.H.; Hubbard, W.; Lee, H.S.; Canning, B.J.; Lee, H.H.; Ryu, S.D.; von Gunten, S.; Bickel, C.A.; Hudson, S.A.; et al. Inhibition of FcεRI-dependent mediator release and calcium flux from human mast cells by sialic acid-binding immunoglobulin-like lectin 8 engagement. J. Allergy Clin. Immunol. 2008, 121, 499–505. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Reddy, S.T.; Wadleigh, D.J.; Herschman, H.R. Transcriptional regulation of the cyclooxygenase-2 gene in activated mast cells. J. Biol. Chem. 2000, 275, 3107–3113. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Oh, Y.C.; Kang, O.H.; Choi, J.G.; Lee, Y.S.; Brice, O.O.; Jung, H.J.; Hong, S.H.; Lee, Y.M.; Shin, D.W.; Kim, Y.S.; et al. Anti-allergic activity of a platycodon root ethanol extract. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2010, 11, 2746–2758. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kudo, M.; Melton, A.C.; Chen, C.; Engler, M.B.; Huang, K.E.; Ren, X.; Wang, Y.; Bernstein, X.; Li, J.T.; Atabai, K.; et al. IL-17A produced by αβ T cells drives airway hyper-responsiveness in mice and enhances mouse and human airway smooth muscle contraction. Nat. Med. 2012, 18, 547–554. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fujitani, Y.; Kanaoka, Y.; Aritake, K.; Uodome, N.; Okazaki-Hatake, K.; Urade, Y. Pronounced eosinophilic lung inflammation and Th2 cytokine release in human lipocalin-type prostaglandin D synthase transgenic mice. J. Immunol. 2002, 168, 443–449. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Luster, A.D.; Tager, A.M. T-cell trafficking in asthma: Lipid mediators grease the way. Nat. Rev. Immunol. 2004, 4, 711–724. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chung, W.C.; Ryu, S.H.; Sun, H.; Zeldin, D.C.; Koo, J.S. CREB mediates prostaglandin F2α-induced MUC5AC overexpression. J. Immunol. 2009, 182, 2349–2356. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Park, J.Y.; Pillinger, M.H.; Abramson, S.B. Prostaglandin E2 synthesis and secretion: The role of PGE2 synthases. Clin. Immunol. 2006, 119, 229–240. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lee, I.T.; Yang, C.M. Inflammatory signalings involved in airway and pulmonary diseases. Mediat. Inflamm. 2013, 2013. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sapirstein, A.; Bonventre, J.V. Specific physiological roles of cytosolic phospholipase A2 as defined by gene knockouts. Biochim. Biophys. Acta 2000, 1488, 139–148. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Daham, K.; Song, W.L.; Lawson, J.A.; Kupczyk, M.; Gülich, A.; Dahlén, S.E.; FitzGerald, G.A.; Dahlén, B. Effects of celecoxib on major prostaglandins in asthma. Clin. Exp. Allergy 2011, 41, 36–45. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pang, L. COX-2 expression in asthmatic airways: The story so far. Thorax 2001, 56, 335–336. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Stumm, C.L.; Wettlaufer, S.H.; Jancar, S.; Peters-Golden, M. Airway remodeling in murine asthma correlates with a defect in PGE2 synthesis by lung fibroblasts. Am. J. Physiol. Lung Cell. Mol. Physiol. 2011, 301, L636–L644. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Card, J.W.; Voltz, J.W.; Carey, M.A.; Bradbury, J.A.; Degraff, L.M.; Lih, F.B.; Bonner, J.C.; Morgan, D.L.; Flake, G.P.; Zeldin, D.C. Cyclooxygenase-2 deficiency exacerbates bleomycin-induced lung dysfunction but not fibrosis. Am. J. Respir. Cell Mol. Biol. 2007, 37, 300–308. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lovgren, A.K.; Jania, L.A.; Hartney, J.M.; Parsons, K.K.; Audoly, L.P.; Fitzgerald, G.A.; Tilley, S.L.; Koller, B.H. COX-2-derived prostacyclin protects against bleomycin-induced pulmonary fibrosis. Am. J. Physiol. Lung Cell. Mol. Physiol. 2006, 291, L144–L156. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dempsey, E.C.; Cool, C.D.; Littler, C.M. Lung disease and PKCs. Pharmacol. Res. 2007, 55, 545–559. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gerthoffer, W.T.; Singer, C.A. MAPK regulation of gene expression in airway smooth muscle. Respir. Physiol. Neurobiol. 2003, 137, 237–250. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, T.; Han, C.; Shelhamer, J.H. Involvement of p38 and p42/44 MAP kinases and protein kinase C in the interferon-γ and interleukin-1α-induced phosphorylation of 85-kDa cytosolic phospholipase A2 in primary human bronchial epithelial cells. Cytokine 2004, 25, 11–20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tourkina, E.; Gooz, P.; Pannu, J.; Bonner, M.; Scholz, D.; Hacker, S.; Silver, R.M.; Trojanowska, M.; Hoffman, S. Opposing effects of protein kinase Calpha and protein kinase Cepsilon on collagen expression by human lung fibroblasts are mediated via MEK/ERK and caveolin-1 signaling. J. Biol. Chem. 2005, 280, 13879–13887. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Laporte, J.D.; Moore, P.E.; Abraham, J.H.; Maksym, G.N.; Fabry, B.; Panettieri, R.A., Jr.; Shore, S.A. Role of ERK MAP kinases in responses of cultured human airway smooth muscle cells to IL-1β. Am. J. Physiol. Lung Cell. Mol. Physiol. 1999, 277, L943–L951. [Google Scholar]
- Lin, C.C.; Lee, I.T.; Yang, Y.L.; Lee, C.W.; Kou, Y.R.; Yang, C.M. Induction of COX-2/PGE2/IL-6 is crucial for cigarette smoke extract-induced airway inflammation: Role of TLR4-dependent NADPH oxidase activation. Free Radic. Biol. Med. 2010, 48, 240–254. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- García-Mediavilla, V.; Crespo, I.; Collado, P.S.; Esteller, A.; Sánchez-Campos, S.; Tuñón, M.J.; González-Gallego, J. The anti-inflammatory flavones quercetin and kaempferol cause inhibition of inducible nitric oxide synthase, cyclooxygenase-2 and reactive C-protein, and down-regulation of the nuclear factor κB pathway in Chang Liver cells. Eur. J. Pharmacol. 2007, 557, 221–229. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hämäläinen, M.; Nieminen, R.; Vuorela, P.; Heinonen, M.; Moilanen, E. Anti-inflammatory effects of flavonoids: Genistein, kaempferol, quercetin, and daidzein inhibit STAT-1 and NF-κB activations, whereas flavone, isorhamnetin, naringenin, and pelargonidin inhibit only NF-κB activation along with their inhibitory effect on iNOS expression and NO production in activated macrophages. Mediat. Inflamm. 2007, 2007. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, J.M.; Lee, E.K.; Kim, D.H.; Yu, B.P.; Chung, H.Y. Kaempferol modulates pro-inflammatory NF-κB activation by suppressing advanced glycation end products-induced NADPH oxidase. Age 2010, 32, 197–208. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gong, J.H.; Cho, I.H.; Shin, D.; Han, S.Y.; Park, S.H.; Kang, Y.H. Inhibition of airway epithelial-to-mesenchymal transition and fibrosis by kaempferol in endotoxin-induced epithelial cells and ovalbumin-sensitized mice. Lab. Investig. 2014, 94, 297–308. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gong, J.H.; Shin, D.; Han, S.Y.; Park, S.H.; Kang, M.K.; Kim, J.L.; Kang, Y.H. Blockade of airway inflammation by kaempferol via disturbing Tyk-STAT signaling in airway epithelial cells and in asthmatic mice. Evid. Based Complement. Altern. Med. 2013, 2013. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fahy, J.V.; Corry, D.B.; Boushey, H.A. Airway inflammation and remodeling in asthma. Curr. Opin. Pulm. Med. 2000, 6, 15–20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sanderson, M.P.; Wex, E.; Kono, T.; Uto, K.; Schnapp, A. Syk and Lyn mediate distinct Syk phosphorylation events in FcɛRI-signal transduction: Implications for regulation of IgE-mediated degranulation. Mol. Immunol. 2010, 48, 171–178. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Oh, H.A.; Han, N.R.; Kim, M.J.; Kim, H.M.; Jeong, H.J. Evaluation of the effect of kaempferol in a murine allergic rhinitis model. Eur. J. Pharmacol. 2013, 718, 48–56. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gong, J.H.; Shin, D.; Han, S.Y.; Kim, J.L.; Kang, Y.H. Kaempferol suppresses eosinophil infiltration and airway inflammation in airway epithelial cells and in mice with allergic asthma. J. Nutr. 2012, 142, 47–56. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lee, E.J.; Ji, G.E.; Sung, M.K. Quercetin and kaempferol suppress immunoglobulin E-mediated allergic inflammation in RBL-2H3 and Caco-2 cells. Inflamm. Res. 2010, 59, 847–854. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chung, M.J.; Pandey, R.P.; Choi, J.W.; Sohng, J.K.; Choi, D.J.; Park, Y.I. Inhibitory effects of kaempferol-3-O-rhamnoside on ovalbumin-induced lung inflammation in a mouse model of allergic asthma. Int. Immunopharmacol. 2015, 25, 302–310. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Noble, P.B.; Pascoe, C.D.; Lan, B.; Ito, S.; Kistemaker, L.E.; Tatler, A.L.; Pera, T.; Brook, B.S.; Gosens, R.; West, A.R. Airway smooth muscle in asthma: Linking contraction and mechanotransduction to disease pathogenesis and remodelling. Pulm. Pharmacol. Ther. 2014, 29, 96–107. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Brightling, C.E.; Bradding, P.; Symon, F.A.; Holgate, S.T.; Wardlaw, A.J.; Pavord, I.D. Mast-cell infiltration of airway smooth muscle in asthma. N. Engl. J. Med. 2002, 346, 1699–1705. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Amin, K.; Janson, C.; Boman, G.; Venge, P. The extracellular deposition of mast cell products is increased in hypertrophic airways smooth muscles in allergic asthma but not in nonallergic asthma. Allergy 2005, 60, 1241–1247. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Black, J.L.; Panettieri, R.A., Jr.; Banerjee, A.; Berger, P. Airway smooth muscle in asthma: Just a target for bronchodilation? Clin. Chest Med. 2012, 33, 543–558. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chambers, L.S.; Black, J.L.; Ge, Q.; Carlin, S.M.; Au, W.W.; Poniris, M.; Thompson, J.; Johnson, P.R.; Burgess, J.K. PAR-2 activation, PGE2, and COX-2 in human asthmatic and nonasthmatic airway smooth muscle cells. Am. J. Physiol. Lung Cell. Mol. Physiol. 2003, 285, L619–L627. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hewson, C.A.; Patel, S.; Calzetta, L.; Campwala, H.; Havard, S.; Luscombe, E.; Clarke, P.A.; Peachell, P.T.; Matera, M.G.; Cazzola, M.; et al. Preclinical evaluation of an inhibitor of cytosolic phospholipase A2α for the treatment of asthma. J. Pharmacol. Exp. Ther. 2012, 340, 656–665. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lee, Y.S.; Hur, S.; Kim, T.Y. Homoisoflavanone prevents mast cell activation and allergic responses by inhibition of Syk signaling pathway. Allergy 2014, 69, 453–462. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ramis, I.; Otal, R.; Carreño, C.; Domènech, A.; Eichhorn, P.; Orellana, A.; Maldonado, M.; de Alba, J.; Prats, N.; Fernández, J.C.; et al. A novel inhaled Syk inhibitor blocks mast cell degranulation and early asthmatic response. Pharmacol. Res. 2015, 99, 116–124. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Moy, L.Y.; Jia, Y.; Caniga, M.; Lieber, G.; Gil, M.; Fernandez, X.; Sirkowski, E.; Miller, R.; Alexander, J.P.; Lee, H.H.; et al. Inhibition of spleen tyrosine kinase attenuates allergen-mediated airway constriction. Am. J. Respir. Cell Mol. Biol. 2013, 49, 1085–1092. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
© 2015 by the authors; licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons by Attribution (CC-BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Shin, D.; Park, S.-H.; Choi, Y.-J.; Kim, Y.-H.; Antika, L.D.; Habibah, N.U.; Kang, M.-K.; Kang, Y.-H. Dietary Compound Kaempferol Inhibits Airway Thickening Induced by Allergic Reaction in a Bovine Serum Albumin-Induced Model of Asthma. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2015, 16, 29980-29995. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms161226218
Shin D, Park S-H, Choi Y-J, Kim Y-H, Antika LD, Habibah NU, Kang M-K, Kang Y-H. Dietary Compound Kaempferol Inhibits Airway Thickening Induced by Allergic Reaction in a Bovine Serum Albumin-Induced Model of Asthma. International Journal of Molecular Sciences. 2015; 16(12):29980-29995. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms161226218
Chicago/Turabian StyleShin, Daekeun, Sin-Hye Park, Yean-Jung Choi, Yun-Ho Kim, Lucia Dwi Antika, Nurina Umy Habibah, Min-Kyung Kang, and Young-Hee Kang. 2015. "Dietary Compound Kaempferol Inhibits Airway Thickening Induced by Allergic Reaction in a Bovine Serum Albumin-Induced Model of Asthma" International Journal of Molecular Sciences 16, no. 12: 29980-29995. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms161226218
APA StyleShin, D., Park, S. -H., Choi, Y. -J., Kim, Y. -H., Antika, L. D., Habibah, N. U., Kang, M. -K., & Kang, Y. -H. (2015). Dietary Compound Kaempferol Inhibits Airway Thickening Induced by Allergic Reaction in a Bovine Serum Albumin-Induced Model of Asthma. International Journal of Molecular Sciences, 16(12), 29980-29995. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms161226218