Pharmacogenetics Informed Decision Making in Adolescent Psychiatric Treatment: A Clinical Case Report
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Results and Discussion
2.1. Clinical Case Report
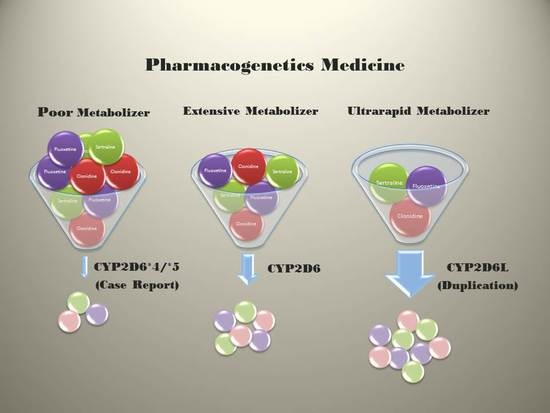
2.2. Pharmacogenetics
2.3. DNA-based Pharmacogenetic Results
| Substrate | Inhibitors | Inducers |
|---|---|---|
| Acetaminophen | Amiodarone | Dexamethasone |
| Amphetamine-Dextroamphetamine | Bupropion | Rifampin |
| Aripiprazole | Celecoxib | |
| Atomoxetine | Chlorpheniramine | |
| Clonidine | Chlorpromazine | |
| Codeine * | Citalopram | |
| Dextromethorphan | Clozapine | |
| Duloxetine | Cocaine | |
| Fluoxetine | Desipramine | |
| Fluvoxamine | Diphenhydramine | |
| Haloperidol | Duloxetine | |
| Iloperidone | Fluoxetine | |
| Methadone | Halofantrine | |
| Methamphetamine | Haloperidol | |
| Mirtazapine | Hydroxychloroquine | |
| Nefazodone | Imatinib | |
| Olanzapine | Imipramine | |
| Paroxetine | Levomepromazine | |
| Phenothiazines | Methadone | |
| Risperidone * | Metoclopramide | |
| Sertraline | Mibefradil | |
| Tricyclic antidepressants (TCAs) | Moclobemide | |
| Tramadol | Nelfinavir | |
| Venlafaxine * | Norfluoxetine | |
| Vortioxetine | Paroxetine | |
| Perphenazine | ||
| Quinidine | ||
| Ranitidine | ||
| Ritonavir | ||
| Sertraline | ||
| Terbinafine | ||
| Thioridazine | ||
| Tranylcypromine |
| Pharmacogenetic Target | Variant Functional Impact | Compounds Prescribed |
|---|---|---|
| CYP2D6 | Poor cytochrome p450 metabolism | Acetaminophen, Aripiprazole, Atomoxetine, Citalopram, Dextroamphetamine, Dextromethorphan, Fluoxetine, Fluvoxamine, Risperidone *, Sertraline |
| 5HT2C | Reduced affinity for serotonin | Fluoxetine, Fluvoamine, Sertraline |
| MTHFR | Reduced activity (low monoamine and catecholamine production) | Methyl/folate-related agents (vitamins) |
3. Experimental Section
4. Conclusions
Acknowledgments
Author Contributions
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Lee, J.W.; Aminkeng, F.; Bhavsar, A.P.; Shaw, K.; Carleton, B.C.; Hayden, M.R.; Ross, C.J. The emerging era of pharmacogenomics: Current successes, future potential, and challenges. Clin. Genet. 2014, 86, 21–28. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lynch, T.; Price, A. The effect of cytochrome p450 metabolism on drug response, interactions, and adverse effects. Am Fam Physician 2007, 76, 391–396. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Yang, X.; Zhang, B.; Molony, C.; Chudin, E.; Hao, K.; Zhu, J.; Gaedigk, A.; Suver, C.; Zhong, H.; Leeder, J.S.; et al. Systematic genetic and genomic analysis of cytochrome p450 enzyme activities in human liver. Genome Res. 2010, 20, 1020–1036. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Weng, L.; Zhang, L.; Peng, Y.; Huang, R.S. Pharmacogenetics and pharmacogenomics: A bridge to individualized cancer therapy. Pharmacogenomics 2013, 14, 315–324. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Toomula, N.; Hima Bindu, K.; Sathish Kumar, D.; Kumar, A. Pharmacogenomics—Personalized treatment of cancer, diabetes and cardiovascular diseases. J. Pharmacogenomics Pharmacoproteomics 2011, 2, 107. [Google Scholar]
- Hamilton, S.P. The promise of psychiatric pharmacogenomics. Biol. Psychiatry 2015, 77, 29–35. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zandi, P.P.; Judy, J.T. The promise and reality of pharmacogenetics in psychiatry. Psychiatr. Clin. N. Am. 2010, 33, 181–224. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Durham, D. Utilizing Pharmacogenetics in psychiarty: The time has come. Mol. Diagn. Ther. 2014, 18, 117–119. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- American Medical Association website resource. Available online: http://www.ama-assn.org/ama/pub/physician-resources/medical-science/genetics-molecular-medicine/current-topics/pharmacogenomics.page (accessed on 19 December 2014).
- Reynolds, G.P.; Zhang, Z.J.; Zhang, X.B. Association of antipsychitic drug-induced weight gain with a 5-HT2C receptor gene polymorphism. Lancet 2002, 359, 2086–2087. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mulder, H.; Franke, B.; van der-Beek vander, A.A.; Arends, J.; Wilmink, F.W.; Scheffer, H.; Egberts, A.C. The association between HTR2C gene polymorphisms and the metabolic syndrome in patients with schizophrenia. J. Clin. Psychopharmacol. 2007, 27, 338–343. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Reynolds, G.P. Pharmacogenetic aspects of antipsychotic drug-induced weight gain—A critical review. Clin. Psychopharmacol. Neurosci. 2012, 10, 71–77. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Altar, C.A.; Hornberger, J.; Shewade, A.; Cruz, V.; Garrison, J.; Mrazek, D. Clinical validity of cytochrome P450 metabolism and serotonin gene variants in psychiatric pharmacotherapy. Int. Rev. Psychiatry 2013, 25, 509–533. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Reynolds, G.P.; Hill, M.J.; Kirk, S.L. The 5HT2C receptor and antipsychotic induced weight grain–mechanisms and genetics. J. Psychopharmacol. 2006, 20, 15–18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Serretti, A.; Kato, M.; de Ronchi, D.; Kinoshita, T. Meta-analysis of serotonin transporter gene promoter polymorphism (5-HTTLPR) association with selective serotonin reuptake inhibitor efficacy in depressed patients. Mol. Psychiatry 2007, 12, 247–257. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Cohen, B.M.; Carlezon, W.A., Jr. Can’t get enough of that dopamine. Am. J. Psychiatry 2007, 164, 543–546. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sim, S.C.; Kacevska, M.; Ingelman-Sundberg, M. Pharmacogenomics of drug-metabolizing enzymes: A recent update on clinical implications and endogenous effects. Pharmacogenomics J. 2013, 13, 1–11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lachman, H.M.; Papolos, D.F.; Saito, T.; Yu, Y.M.; Szumlanski, C.L.; Weinshilboum, R.M. Human catechol-O-methyltransferase pharmacogenetics: Description of a functional polymorphism and its potential application to neuropsychiatric disorders. Pharmacogenetics 1996, 6, 243–250. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Heisler, L.K; Zhou, L.; Bajwa, P.; Hsu, J.; Tecott, L.H. Serotonin 5HT2C receptors regulate anxiety-like behavior. Genes Brain Behav. 2007, 6, 491–496. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Alex, K.D.; Yavanian, G.J.; McFarlane, H.G.; Pluto, C.P.; Pehak, E.A. Modulation of dopamine release by striatal 5-HT2C receptors. Synapse 2007, 55, 242–251. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stahl, S.M. L-methylfolate: A vitamin for your monoamines. J. Clin. Psychiatry 2008, 69, 1352–1353. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gilbody, S.; Lewis, S.; Lightfoot, T. Methylenetetrahydrofolate reductase (MTHFR) genetic polymorphisms and psychiatric disorders: A huge review. Am. J. Epidemiol. 2007, 165, 1–13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wu, Y.L.; Ding, X.X.; Sun, Y.H.; Chen, J.; Zhao, X.; Jiang, Y.H.; Lv, X.L.; Wu, Z.Q. Association between MTHFR C677T polymorphism and depression: An updated meta-analysis of 26 studies. Prog. Neuropsychopharmacol. Biol. Psychiatry 2013, 46, 78–85. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ginsberg, L.D.; Oubre, A.Y.; Daoud, Y.A. L-methylfolate plus SSRI or SNRI from treatment initiation compared to SSRI or SNRI monotherapy in a major depressive episode. Innov. Clin. Neurosci. 2011, 8, 19–28. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Papkostas, G.I.; Shelton, R.C.; Zajecka, J.M.; Etemad, B.; Rickels, K.; Clain, A.; Baer, L.; Dalton, E.D.; Sacco, G.R.; Shoenfeld, D.; et al. l-methylfolate as adjunctive therapy for SSRI-resistant major depression: Results of two randomized, double-blind, parallel-sequential trials. Am. J. Psychiatry 2012, 169, 1267–1274. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Frosst, P.; Blom, H.J.; Milos, R.; Goyette, P.; Sheppard, C.A.; Matthews, R.G.; Boers, G.J.; den Heijer, M.; Kluijtmans, L.A.; van den Heuvel, L.P.; et al. A candidate genetic risk factor for vascular disease: A common mutation in methylenetetrahydrofolate reductase. Nat. Genet. 1995, 10, 111–113. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yoshimizu, T.; Pan, J.Q.; Mungenast, A.E.; Madison, J.M.; Su, S.; Ketterman, J.; Ongur, D.; McPhie, D.; Cohen, B.; Perlis, R.; et al. Functional implications of a psychiatric risk variant within CACNA1C in induced human neurons. Mol. Psychiatry. 2014. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yao, H.T.; Chang, Y.W.; Lan, S.J.; Chen, C.T.; Hsu, J.T.; Yeh, T.K. The inhibitory effect of polyunsaturated fatty acids on human CYP enzymes. Life Sci. 2006, 79, 2432–2440. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gough, A.C.; Miles, J.S.; Spurr, N.K.; Moss, J.E.; Gaedigk, A.; Eichelbaum, M.; Wolf, C.R. Identification of the primary gene defect at the cytochrome p450 CYP2D locus. Nature 1990, 347, 773–776. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nichols, A.I.; Focht, K.; Jiang, Q.; Preskorn, S.H.; Kane, C.P. Pharmacokinetics of venlafaxine extended release 75 mg and desvenlafaxine 50 mg in healthy CYP2D6 extensive and poor metabolizers: A randomized, open-label, two-period, parallel-group, crossover study. Clin. Drug Investig. 2011, 48, 155–167. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, S.F. Polymorphism of human cytochrome P450 2D6 and its clinical significance: Part I. Clin. Pharmacokinet. 2009, 48, 689–723. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Grasmader, K.; Verwohlt, P.L.; Rietschel, M.; Dragicevic, A.; Muller, M.; Hiemke, C.; Freymann, N.; Zobel, A.; Maier, W.; Rao, M.L. Impact of polymorphism of human cytochrome-450 isoenzymes 2C9, 2C19, and 2D6 on plasma concentrations and clinical effects of antidepressants in a naturalistic clinical setting. Eur. J. Clin. Pharmacol. 2004, 60, 329–336. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Zhou, S.F. Polymorphism of human cytochrome P450 2D6 and its clinical significance: Part II. Clin. Pharmacokinet. 2009, 48, 761–804. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Samer, C.F.; Lorenzini, K.I.; Rollason, V.; Daali, Y.; Desmeules, J.A. Applications of CYP450 testing in the clinical setting. Mol. Diagn. Ther. 2013, 17, 165–184. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Haertter, S. Recent examples on the clinical relevance of the CYP2D6 polymorphism and endogenous functionality of CYP2D6. Drug Metab. Drug Interact. 2013, 28, 209–216. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- De Leon, J.; Susce, M.T.; Pan, R.M.; Fairchild, M.; Koch, W.H.; Wedlund, P.J. The CYP2D6 poor metabolizer phenotype may be associated with risperidone adverse drug reactions and discontinuation. J. Clin. Psychiatry 2005, 66, 15–27. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wantanabe, J.; Suzuki, Y.; Fukui, N.; Sugai, T.; Ono, S.; Inoue, Y.; Someya, T. Dose-dependent effect of the CYP2D6 genotype on the steady-state fluvoxamine concentration. Ther. Drug Monit. 2008, 30, 705–708. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Whyte, E.M.; Romkes, M.; Mulsant, B.H.; Kirshne, M.A.; Begley, A.E.; Reynolds, C.F., III; Pollock, B.G. CYP2D6 genotype and venlafaxine-XR concentrations in depressed elderly. Int. J. Geriatr. Psychiatry 2006, 21, 542–549. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lobello, K.W.; Preskorn, S.H.; Guico-Pabia, C.J.; Jiang, Q.; Paul, J.; Nichols, A.L.; Patroneva, A.; Ninan, P.T. Cytochrome P450 2D6 predicts antidepressant efficacy of venlafaxine: A secondary analysis of 4 studies in major depressive disorder. J. Clin. Psychiatry 2010, 71, 1482–1487. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Van der Weide, J.; van Baalen-Benedek, E.H.; Kootstra-Ros, J.E. Matabloic ratios of psychotropics as indications of cytochrome P450 2D6/2C19 genotype. Ther. Drug Monit. 2005, 27, 478–483. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sauer, J.M.; Ring, B.J.; Witcher, J.W. Clinical pharmacokinetics of atomoxetine. Clin. Pharmacokinet. 2005, 44, 571–590. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wu, A.H. Drug metabolizing enzyme activities versus genetic variances for drug of clinical pharmacogenomics relevance. Clin. Proteomics 2011, 8, 12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Desmarais, J.R.; Looper, K.J. Interactions between tamoxifen and antidepressants via cytochrome P450 2D6. J. Clin. Psychiatry 2009, 70, 1688–1697. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Anzenbacher, P.; Anzenbacherova, E. Cytochromes P450 and metabolism of xenobiotics. Cell Mol. Life Sci. 2001, 58, 737–747. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mannheimer, B.; von Bahr, C.; Pettersson, H.; Eliasson, E. Impact of multiple inhibitors or substrates of cytochrome P450 on plasma risperidone levels in patients on polypharmacy. Ther. Drug Monit. 2008, 30, 565–569. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jeppesen, U.; Gram, L.F.; Vistisen, K.; Loft, S.; Poulsen, H.E.; Brosen, K. Dose-dependent inhibition of CYP1A2, CYP2C19 and CYP2D6 by citalopram, fluoxetine, fluvoxamine and paroxetine. Eur. J. Clin. Pharmacol. 1996, 51, 73–78. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- DeLeon, J.; Armstrong, S.C.; Cozza, K.L. The dosing of atypical antipsychotics. Psychosomatics 2005, 46, 262–273. [Google Scholar]
- DeLeon, J. Psychopharmacology: Atypical antipsychotic dosing: The effect of co-medication with anticonvulsants. Psychiatr. Serv. 2004, 55, 125–128. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sistonen, J.; Sajantila, A.; Lao, O.; Corander, J.; Barbujani, G.; Fuselli, S. CYP2D6 worldwide genetic variation shows high frequency of altered activity variants and no continental structure. Pharmacogenet. Genomics 2007, 17, 93–101. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Gaedigk, A.; Gotschall, R.R.; Forbes, N.S.; Simon, S.D.; Kearns, G.L.; Leeder, J.S. Optimization of cytochrome P4502D6 (CYP2D6) phenotype assignment using a genotyping algorithm based on allele frequency data. Pharmacogenetics 1999, 9, 669–682. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Swen, J.J.; Nijenhuis, M.; de Boer, A.; Grandia, L.; Maitland-van der Zee, A.H.; Mulder, H.; Rongen, G.A.; van Schaik, R.H.; Schalekamp, T.; Touw, D.J.; et al. Pharmacogenetics: From bench to byte—An update of guidelines. Clin. Pharmacol. Ther. 2011, 89, 662–673. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pratt, V.M.; Zehnbauer, B.; Wilson, J.A.; Baak, R.; Babic, N.; Bettinotti, M.; Buller, A.; Butz, K.; Campbell, M.; Civalier, C.; et al. Characterization of 107 genomic DNA reference materials for CYP2D6, CYP2C19, CYP2C9, VKORC1, and UGT1A1: A GeT-RM and Association for Molecular Pathology collaborative project. J. Mol. Diagn. 2010, 12, 835–846. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Huezo-Diaz, P.L.; Perroud, N.; Spencer, E.P.; Smith, R.; Sim, S.; Virding, S.; Uher, R.; Gunasinghe, C.; Gray, J.; Campbell, D.; Hauser, J.; et al. CYP2C19 genotype predicts steady state escitalopram concentration in GENDEP. J. Psychopharmacol. 2012, 26, 398–407. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Genomind Literature Review, Version 3.0. Available online: http://www.geneceptassay.com/Content/LitReview/GNOMD_Lit_Review_LATEST.pdf (accessed 9 December 2014).
- Genomind Assay Report (Sample). Available online: https://www.genomind.com/wp-content/uploads/2014/09/Sample-10-Gene-Report-Jul-2014-Lit-Sum-V-3.01.pdf (accessed 10 December 2014).
- Zawertailo, L.A.; Kaplan, H.L.; Busto, U.E.; Tyndale, R.F.; Sellers, E.M. Psychotropic effects of dextromethorphan are altered by the CYP2D6 polymorphism: A pilot study. J. Clin. Psychopharmacol. 1998, 18, 332–337. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Manap, R.A.; Wright, C.E.; Gregory, A.; Rostami-Hodjegan, A.; Meller, S.T.; Kelm, G.R.; Lennard, M.S.; Tucker, G.T.; Morice, A.H. The antitussive effect of dextromethorphan in relation to CYP2D6 activity. Br. J. Clin. Pharmacol. 1999, 48, 382–387. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hamelin, B.A.; Bouayad, A.; Methot, J.; Jobin, J.; Desgagnes, P.; Poirier, P.; Allaire, J.; Dumesnil, J.; Turgeon, J. Significant interaction between the nonprescription antihistamine diphenhydramine and the CYP2D6 substrate metoprolol in healthy men with high or low CYP2D6 activity. Clin. Pharmaco. Ther. 2000, 67, 466–477. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
© 2015 by the authors; licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Smith, T.; Sharp, S.; Manzardo, A.M.; Butler, M.G. Pharmacogenetics Informed Decision Making in Adolescent Psychiatric Treatment: A Clinical Case Report. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2015, 16, 4416-4428. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms16034416
Smith T, Sharp S, Manzardo AM, Butler MG. Pharmacogenetics Informed Decision Making in Adolescent Psychiatric Treatment: A Clinical Case Report. International Journal of Molecular Sciences. 2015; 16(3):4416-4428. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms16034416
Chicago/Turabian StyleSmith, Teri, Susan Sharp, Ann M. Manzardo, and Merlin G. Butler. 2015. "Pharmacogenetics Informed Decision Making in Adolescent Psychiatric Treatment: A Clinical Case Report" International Journal of Molecular Sciences 16, no. 3: 4416-4428. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms16034416
APA StyleSmith, T., Sharp, S., Manzardo, A. M., & Butler, M. G. (2015). Pharmacogenetics Informed Decision Making in Adolescent Psychiatric Treatment: A Clinical Case Report. International Journal of Molecular Sciences, 16(3), 4416-4428. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms16034416