Antiangiogenesis, Loss of Cell Adhesion and Apoptosis Are Involved in the Antitumoral Activity of Proteases from V. cundinamarcensis (C. candamarcensis) in Murine Melanoma B16F1
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Results and Discussion
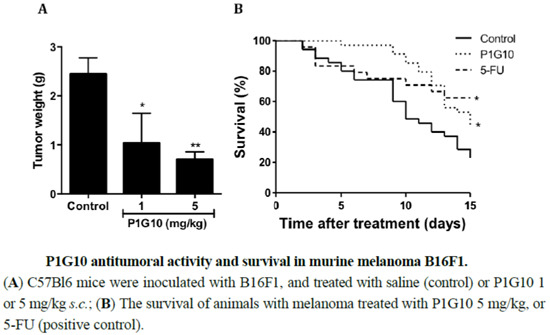
2.1. P1G10 Antitumoral Activity and Survival

2.2. Tumor Angiogenic and Anti-Inflammatory Parameters and P1G10 Content in Tumor Tissue


2.3. Cytotoxicity and Cell Apoptosis

| Types | Cell Lines | IC50 (µg/mL) |
|---|---|---|
| Tumoral | B16F1 | 12.7 |
| 4T1 | 9.1 | |
| Ehrlich | 6.9 | |
| Normal | CHO | 28.7 |
| CIPs | 16.6 | |
| BHK-21 | 19.0 |

2.4. Loss of Adhesion on Polystyrene Plates or Extracellular Matrix Components (ECM) by B16F1 Melanoma Cells

3. Experimental Section
3.1. Animals
3.2. Production of P1G10
3.3. Cell Culture
3.4. B16F1 Melanoma Model
3.5. Antitumor Activity
3.6. Survival
3.7. P1G10 Levels on Tumor
3.8. Tumor Hemoglobin Concentration and N-Acetyl-β-d-glucosaminidase activity (NAG)
3.9. Cytokines Quantification
3.10. Cytotoxicity Activity of P1G10
3.11. Flow Cytometer Analysis
3.12. Cell Adhesion Assays
4. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Acknowledgments
Author Contributions
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Keshet, E.; Ben-Sasson, S.A. Anticancer drug targets: Approaching angiogenesis. J. Clin. Investig. 1999, 104, 1497–1501. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Marneros, A.G. Tumor angiogenesis in melanoma. Hematol. Oncol. Clin. N. Am. 2009, 23, 431–446. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fiers, W. Tumor necrosis factor characterization at the molecular, cellular and in vivo level. FEBS Lett. 1991, 285, 199–212. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, Z.; Ramirez, N.E.; Yankeelov, T.E.; Li, Z.; Ford, L.E.; Qi, Y.; Pozzi, A.; Zutter, M.M. α2β1 Integrin expression in the tumor microenvironment enhances tumor angiogenesis in a tumor cell-specific manner. Blood 2008, 111, 1980–1988. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Teixeira, R.D.; Ribeiro, H.A.; Gomes, M.T.; Lopes, M.T.; Salas, C.E. The proteolytic activities in latex from carica candamarcensis. Plant Physiol. Biochem. 2008, 46, 956–961. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lemos, F.O.; Ferreira, L.A.; Cardoso, V.N.; Cassali, G.D.; Salas, C.E.; Lopes, M.T. Skin-healing activity and toxicological evaluation of a proteinase fraction from carica candamarcensis. Eur. J. Dermatol. 2011, 21, 722–730. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Gomes, F.S.; Spinola Cde, V.; Ribeiro, H.A.; Lopes, M.T.; Cassali, G.D.; Salas, C.E. Wound-healing activity of a proteolytic fraction from carica candamarcensis on experimentally induced burn. Burns 2010, 36, 277–283. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mello, V.J.; Gomes, M.T.; Lemos, F.O.; Delfino, J.L.; Andrade, S.P.; Lopes, M.T.; Salas, C.E. The gastric ulcer protective and healing role of cysteine proteinases from carica candamarcensis. Phytomedicine 2008, 15, 237–244. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bilheiro, R.P.; Braga, A.D.; Filho, M.L.; Carvalho-Tavares, J.; Agero, U.; Carvalho, M.G.; Sanchez, E.F.; Salas, C.E.; Lopes, M.T.P. The thrombolytic action of a proteolytic fraction (P1G10) from carica candamarcensis. Thromb. Res. 2013, 131, e175–e182. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lorkowski, G. Gastrointestinal absorption and biological activities of serine and cysteine proteases of animal and plant origin: Review on absorption of serine and cysteine proteases. Int. J. Physiol. Pathophysiol. Pharmacol. 2012, 4, 10–27. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Lemos, F.O.; Villalba, M.I.C.; Tagliati, C.A.; Cardoso, V.N.; Salas, C.E.; Lopes, M.T.P. Biodistribution, pharmacokinetic and toxicity of a Vasconcellea cundinamarcensis (Carica candamarcensis) proteinase fraction with pharmacological activity. Pharmacogn. Mag submitted for publication. 2015. [Google Scholar]
- Gomes, M.T.; Bemquerer, M.P.; Lopes, M.T.; Richardson, M.; Junior, S.O.; Salas, C.E. The structure of CMS2MS2, a mitogenic protein isolated from carica candamarcensis. Biol. Chem. 2007, 388, 819–822. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gomes, M.T.; Mello, V.J.; Rodrigues, K.C.; Bemquerer, M.P.; Lopes, M.T.; Faca, V.M.; Salas, C.E. Isolation of two plant proteinases in latex from carica candamarcensis acting as mitogens for mammalian cells. Planta Med. 2005, 71, 244–248. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wald, M.; Olejar, T.; Pouckova, P.; Zadinova, M. Proteinases reduce metastatic dissemination and increase survival time in C57Bl6 mice with the lewis lung carcinoma. Life Sci. 1998, 63, PL237–PL243. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wald, M.; Olejar, T.; Sebkova, V.; Zadinova, M.; Boubelik, M.; Pouckova, P. Mixture of trypsin, chymotrypsin and papain reduces formation of metastases and extends survival time of C57Bl6 mice with syngeneic melanoma b16. Cancer Chemother. Pharmacol. 2001, 47, S16–S22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Beuth, J. Proteolytic enzyme therapy in evidence-based complementary oncology: Fact or fiction? Integr. Cancer Ther. 2008, 7, 311–316. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Beuth, J.; Ost, B.; Pakdaman, A.; Rethfeldt, E.; Bock, P.R.; Hanisch, J.; Schneider, B. Impact of complementary oral enzyme application on the postoperative treatment results of breast cancer patients—Results of an epidemiological multicentre retrolective cohort study. Cancer Chemother. Pharmacol. 2001, 47 (Suppl. 1), S45–S54. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Leipner, J.; Saller, R. Systemic enzyme therapy in oncology: Effect and mode of action. Drugs 2000, 59, 769–780. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Grabowska, E.; Eckert, K.; Fichtner, I.; Schulzeforster, K.; Maurer, H. Bromelain proteases suppress growth, invasion and lung metastasis of B16F10 mouse melanoma cells. Int. J. Oncol. 1997, 11, 243–248. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Baez, R.; Lopes, M.T.P.; Salas, C.E.; Hernandez, M. In vivo antitumoral activity of stem pineapple (Ananas comosus) bromelain. Planta Med. 2007, 73, 1377–1383. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Guimaraes-Ferreira, C.A.; Rodrigues, E.G.; Mortara, R.A.; Cabral, H.; Serrano, F.A.; Ribeiro-dos-Santos, R.; Travassos, L.R. Antitumor effects in vitro and in vivo and mechanisms of protection against melanoma B16F10-Nex2 cells by fastuosain, a cysteine proteinase from bromelia fastuosa. Neoplasia 2007, 9, 723–733. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Haq, M.; Shafii, A.; Zervos, E.E.; Rosemurgy, A.S. Addition of matrix metalloproteinase inhibition to conventional cytotoxic therapy reduces tumor implantation and prolongs survival in a murine model of human pancreatic cancer. Cancer Res. 2000, 60, 3207–3211. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Lavhale, M.S.; Kumar, S.; Mishra, S.H.; Sitasawad, S.L. A novel triterpenoid isolated from the root bark of Ailanthus excelsa Roxb (tree of heaven), AECHL-1 as a potential anti-cancer agent. PLoS ONE 2009, 4, e5365. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, F.; Awale, S.; Tezuka, Y.; Kadota, S. Cytotoxic constituents of propolis from myanmar and their structure-activity relationship. Biol. Pharm. Bull. 2009, 32, 2075–2078. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cabral, H.; Leopoldino Am Fau-Tajara, E.H.; Tajara Eh Fau-Greene, L.J.; Greene Lj Fau-Faca, V.M.; Faca Vm Fau-Mateus, R.P.; Mateus Rp Fau-Ceron, C.R.; Ceron Cr Fau-de Souza Judice, W.A.; de Souza Judice Wa Fau-Julianod, L.; Julianod L Fau-Bonilla-Rodriguez, G.O.; Bonilla-Rodriguez, G.O. Preliminary functional characterization, cloning and primary sequence of fastuosain, a cysteine peptidase isolated from fruits of Bromelia fastuosa. Protein Pept. Lett. 2006, 13, 83–89. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Harrach, T.; Eckert K Fau-Maurer, H.R.; Maurer Hr Fau-Machleidt, I.; Machleidt I Fau-Machleidt, W.; Machleidt W Fau-Nuck, R.; Nuck, R. Isolation and characterization of two forms of an acidic bromelain stem proteinase. J. Protein Chem. 1998, 17, 351–361. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Harrach, T.; Eckert K Fau-Schulze-Forster, K.; Schulze-Forster K Fau-Nuck, R.; Nuck R Fau-Grunow, D.; Grunow D Fau-Maurer, H.R.; Maurer, H.R. Isolation and partial characterization of basic proteinases from stem bromelain. J. Protein Chem. 1995, 14, 41–52. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gout, S.; Huot, J. Role of cancer microenvironment in metastasis: Focus on colon cancer. Cancer Microenviron. 2008, 1, 69–83. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Folkman, J. Angiogenesis. Annu. Rev. Med. 2006, 57, 1–18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Schafer, M.; Werner, S. Cancer as an overhealing wound: An old hypothesis revisited. Nat. Rev. Mol. Cell Biol. 2008, 9, 628–638. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Haddow, A. Molecular repair, wound healing, and carcinogenesis: Tumor production a possible overhealing? Adv. Cancer Res. 1972, 16, 181–234. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Stearns, M.E.; Garcia, F.U.; Fudge, K.; Rhim, J.; Wang, M. Role of interleukin 10 and transforming growth factor β1 in the angiogenesis and metastasis of human prostate primary tumor lines from orthotopic implants in severe combined immunodeficiency mice. Clin. Cancer Res. 1999, 5, 711–720. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Ramont, L.; Pasco, S.; Hornebeck, W.; Maquart, F.X.; Monboisse, J.C. Transforming growth factor-β1 inhibits tumor growth in a mouse melanoma model by down-regulating the plasminogen activation system. Exp. Cell Res. 2003, 291, 1–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Massague, J. Tgfbeta signalling in context. Nat. Rev. Mol. Cell Biol. 2012, 13, 616–630. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Desser, L.; Holomanova, D.; Zavadova, E.; Pavelka, K.; Mohr, T.; Herbacek, I. Oral therapy with proteolytic enzymes decreases excessive TGF-β levels in human blood. Cancer Chemother. Pharmacol. 2001, 47, S10–S15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Paczek, L.; Gaciong, Z.; Bartlomiejczyk, I.; Sebekova, K.; Birkenmeier, G.; Heidland, A. Protease administration decreases enhanced transforming growth factor-β 1 content in isolated glomeruli of diabetic rats. Drugs Exp. Clin. Res. 2001, 27, 141–149. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Balkwill, F.; Mantovani, A. Inflammation and cancer: Back to virchow? Lancet 2001, 357, 539–545. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Onken, J.E.; Greer, P.K.; Calingaert, B.; Hale, L.P. Bromelain treatment decreases secretion of pro-inflammatory cytokines and chemokines by colon biopsies in vitro. Clin. Immunol. 2008, 126, 345–352. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mantovani, A.; Muzio, M.; Garlanda, C.; Sozzani, S.; Allavena, P. Macrophage control of inflammation: Negative pathways of regulation of inflammatory cytokines. Novartis Found. Symp. 2001, 234, 120–131. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Grimshaw, M.J.; Wilson, J.L.; Balkwill, F.R. Endothelin-2 is a macrophage chemoattractant: Implications for macrophage distribution in tumors. Eur. J. Immunol. 2002, 32, 2393–2400. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bailey, P.J. Sponge implants as models. Methods Enzymol. 1988, 162, 327–334. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Engwerda, C.R.; Andrew, D.; Ladhams, A.; Mynott, T.L. Bromelain modulates T cell and B cell immune responses in vitro and in vivo. Cell Immunol. 2001, 210, 66–75. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- McGary, E.C.; Lev, D.C.; Bar-Eli, M. Cellular adhesion pathways and metastatic potential of human melanoma. Cancer Biol. Ther. 2002, 1, 459–465. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Otsuki, N.; Dang, N.H.; Kumagai, E.; Kondo, A.; Iwata, S.; Morimoto, C. Aqueous extract of Carica papaya leaves exhibits anti-tumor activity and immunomodulatory effects. J. Ethnopharmacol. 2010, 127, 760–767. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sarray, S.; Siret, C.; Lehmann, M.; Marrakchi, N.; Luis, J.; Ayeb, M.E.; André, F. Lebectin increases N-cadherin-mediated adhesion through PI3k/Akt pathway. Cancer Lett. 2009, 285, 174–181. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Koukoulis, G.K.; Patriarca, C.; Gould, V.E. Adhesion molecules and tumor metastasis. Hum. Pathol. 1998, 29, 889–892. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tucker, G.C. Integrins: Molecular targets in cancer therapy. Curr. Oncol. Rep. 2006, 8, 96–103. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nobumoto, A.; Nagahara, K.; Oomizu, S.; Katoh, S.; Nishi, N.; Takeshita, K.; Niki, T.; Tominaga, A.; Yamauchi, A.; Hirashima, M. Galectin-9 suppresses tumor metastasis by blocking adhesion to endothelium and extracellular matrices. Glycobiology 2008, 18, 735–744. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hale, L.P.; Greer, P.K.; Sempowski, G.D. Bromelain treatment alters leukocyte expression of cell surface molecules involved in cellular adhesion and activation. Clin. Immunol. 2002, 104, 183–190. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Maurer, H.R. Bromelain: Biochemistry, pharmacology and medical use. Cell. Mol. Life Sci. 2001, 58, 1234–1245. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hale, L.P.; Haynes, B.F. Bromelain treatment of human t cells removes CD44, CD45ra, E2/MIC2, CD6, CD7, CD8, and Leu 8/LAM1 surface molecules and markedly enhances CD2-mediated T cell activation. J. Immunol. 1992, 149, 3809–3816. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Novak, J.F.; Trnka, F. Proenzyme therapy of cancer. Anticancer Res. 2005, 25, 1157–1177. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Frisch, S.M.; Screaton, R.A. Anoikis mechanisms. Curr. Opin. Cell Biol. 2001, 13, 555–562. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Valentijn, A.J.; Zouq, N.; Gilmore, A.P. Anoikis. Biochem. Soc. Trans. 2004, 32, 421–425. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Moschos, S.J.; Drogowski, L.M.; Reppert, S.L.; Kirkwood, J.M. Integrins and cancer. Oncology (Williston Park) 2007, 21, 13–20. [Google Scholar]
- Chobotova, K.; Vernallis, A.B.; Majid, F.A.A. Bromelain’s activity and potential as an anti-cancer agent: Current evidence and perspectives. Cancer Lett. 2010, 290, 148–156. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zuberek, K.; Ling, V.; Wu, P.; Ma, H.L.; Leonard, J.P.; Collins, M.; Dunussi-Joannopoulos, K. Comparable in vivo efficacy of CD28/B7, ICOS/GL50, and ICOS/GL50B costimulatory pathways in murine tumor models: IFN γ-dependent enhancement of CTL priming, effector functions, and tumor specific memory CTL. Cell. Immunol. 2003, 225, 53–63. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Plunkett, M.L.; Hailey, J.A. An in vivo quantitative angiogenesis model using tumor cells entrapped in alginate. Lab. Investig. 1990, 62, 510–517. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Heo, D.S.; Park, J.G.; Hata, K.; Day, R.; Herberman, R.B.; Whiteside, T.L. Evaluation of tetrazolium-based semiautomatic colorimetric assay for measurement of human antitumor cytotoxicity. Cancer Res. 1990, 50, 3681–3690. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Nicoletti, I.; Migliorati, G.; Pagliacci, M.C.; Grignani, F.; Riccardi, C. A rapid and simple method for measuring thymocyte apoptosis by propidium iodide staining and flow-cytometry. J. Immunol. Methods 1991, 139, 271–279. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
© 2015 by the authors; licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Dittz, D.; Figueiredo, C.; Lemos, F.O.; Viana, C.T.R.; Andrade, S.P.; Souza-Fagundes, E.M.; Fujiwara, R.T.; Salas, C.E.; Lopes, M.T.P. Antiangiogenesis, Loss of Cell Adhesion and Apoptosis Are Involved in the Antitumoral Activity of Proteases from V. cundinamarcensis (C. candamarcensis) in Murine Melanoma B16F1. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2015, 16, 7027-7044. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms16047027
Dittz D, Figueiredo C, Lemos FO, Viana CTR, Andrade SP, Souza-Fagundes EM, Fujiwara RT, Salas CE, Lopes MTP. Antiangiogenesis, Loss of Cell Adhesion and Apoptosis Are Involved in the Antitumoral Activity of Proteases from V. cundinamarcensis (C. candamarcensis) in Murine Melanoma B16F1. International Journal of Molecular Sciences. 2015; 16(4):7027-7044. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms16047027
Chicago/Turabian StyleDittz, Dalton, Cinthia Figueiredo, Fernanda O. Lemos, Celso T. R. Viana, Silvia P. Andrade, Elaine M. Souza-Fagundes, Ricardo T. Fujiwara, Carlos E. Salas, and Miriam T. P. Lopes. 2015. "Antiangiogenesis, Loss of Cell Adhesion and Apoptosis Are Involved in the Antitumoral Activity of Proteases from V. cundinamarcensis (C. candamarcensis) in Murine Melanoma B16F1" International Journal of Molecular Sciences 16, no. 4: 7027-7044. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms16047027
APA StyleDittz, D., Figueiredo, C., Lemos, F. O., Viana, C. T. R., Andrade, S. P., Souza-Fagundes, E. M., Fujiwara, R. T., Salas, C. E., & Lopes, M. T. P. (2015). Antiangiogenesis, Loss of Cell Adhesion and Apoptosis Are Involved in the Antitumoral Activity of Proteases from V. cundinamarcensis (C. candamarcensis) in Murine Melanoma B16F1. International Journal of Molecular Sciences, 16(4), 7027-7044. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms16047027