Distribution of ADAT-Dependent Codons in the Human Transcriptome
Abstract
:1. Introduction

2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Definitions
2.2. Human Transcriptome Retrieval
2.3. Identification of Stretches by the Halves-Gene Method
2.4. Identification of Stretches by the Running Windows Method


3. Results and Discussion
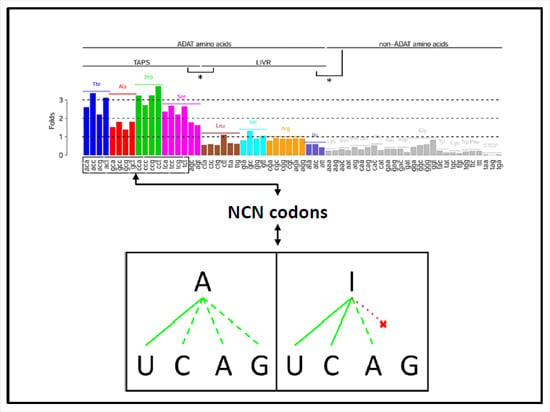
3.1. Identification of Human Proteins Highly Enriched in ADAT-aa
3.2. Stretches of A codons Are Composed Preferentially by Triplets Coding for TAPS
3.3. ADAT Stretches Are Composed Preferentially of D codons

4. Conclusions

Supplementary Materials
Acknowledgments
Author Contributions
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Crick, F.H. On protein synthesis. Symp. Soc. Exp. Biol. 1958, 12, 138–163. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Demeshkina, N.; Jenner, L.; Westhof, E.; Yusupov, M.; Yusupova, G. New structural insights into the decoding mechanism: Translation infidelity via a G.U pair with Watson-Crick geometry. FEBS Lett. 2013, 587, 1848–1857. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Novoa, E.M.; Pavon-Eternod, M.; Pan, T.; Ribas de Pouplana, L. A role for tRNA modifications in genome structure and codon usage. Cell 2012, 149, 202–213. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Auxilien, S.; Crain, P.F.; Trewyn, R.W.; Grosjean, H. Mechanism, specificity and general properties of the yeast enzyme catalysing the formation of inosine 34 in the anticodon of transfer RNA. J. Mol. Biol. 1996, 262, 437–458. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gerber, A.P.; Keller, W. An adenosine deaminase that generates inosine at the wobble position of tRNAs. Science 1999, 286, 1146–1149. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Marck, C.; Grosjean, H. tRNomics: Analysis of tRNA genes from 50 genomes of Eukarya, Archaea, and Bacteria reveals anticodon-sparing strategies and domain-specific features. RNA 2002, 8, 1189–1232. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Crick, F.H. Codon—Anticodon pairing: The wobble hypothesis. J. Mol. Biol. 1966, 19, 548–555. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rubio, M.A.; Pastar, I.; Gaston, K.W.; Ragone, F.L.; Janzen, C.J.; Cross, G.A.; Papavasiliou, F.N.; Alfonzo, J.D. An adenosine-to-inosine tRNA-editing enzyme that can perform C-to-U deamination of DNA. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2007, 104, 7821–7826. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Spears, J.L.; Rubio, M.A.; Gaston, K.W.; Wywial, E.; Strikoudis, A.; Bujnicki, J.M.; Papavasiliou, F.N.; Alfonzo, J.D. A single zinc ion is sufficient for an active Trypanosoma brucei tRNA editing deaminase. J. Biol. Chem. 2011, 286, 20366–20374. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhou, W.; Karcher, D.; Bock, R. Identification of enzymes for adenosine-to-inosine editing and discovery of cytidine-to-uridine editing in nucleus-encoded transfer RNAs of Arabidopsis. Plant Physiol. 2014, 166, 1985–1997. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Torres, A.; Piñeyro, D.; Rodríguez-Escribà, M.; Camacho, N.; Reina, O.; Saint-Leger, A.; Filonava, L.; Batlle, E.; de Pouplana, L.R. Inosine modifications in human tRNAs are incorporated at the precursor tRNA level. Nucleic Acids Res. 2015, 43. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Novoa, E.M.; Ribas de Pouplana, L. Speeding with control: Codon usage, tRNAs and ribosomes. Trends Genet. 2012, 28, 574–581. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yona, A.H.; Bloom-Ackermann, Z.; Frumkin, I.; Hanson-Smith, V.; Charpak-Amikam, Y.; Feng, Q.; Boeke, J.D.; Dahan, O.; Pilpel, Y. tRNA genes rapidly change in evolution to meet novel translational demands. Elife 2013, 2, e01339. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bauer, F.; Hermand, D. A coordinated codon-dependent regulation of translation by Elongator. Cell Cycle 2012, 11, 4524–4529. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bauer, F.; Matsuyama, A.; Candiracci, J.; Dieu, M.; Scheliga, J.; Wolf, D.A.; Yoshida, M.; Hermand, D. Translational control of cell division by Elongator. Cell Rep. 2012, 1, 424–433. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fernandez-Vazquez, J.; Vargas-Perez, I.; Sanso, M.; Buhne, K.; Carmona, M.; Paulo, E.; Hermand, D.; Rodríguez-Gabriel, M.; Ayté, J.; Leidel, S.; et al. Modification of tRNA(Lys) UUU by elongator is essential for efficient translation of stress mRNAs. PLoS Genet. 2013, 9, e1003647. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Huang, B.; Johansson, M.J.; Bystrom, A.S. An early step in wobble uridine tRNA modification requires the Elongator complex. RNA 2005, 11, 424–436. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- CCDS Database. Available online: http://ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/CCDS/ (accessed on 13 July 2015).
- Muggeo, V.M.R. Segmented: An R package to fit regression models with broken-line relationships. R News, 2008; 8, 20–25. [Google Scholar]
- Librado, P.; Rozas, J. DnaSP v5: A software for comprehensive analysis of DNA polymorphism data. Bioinformatics 2009, 25, 1451–1452. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- McDonald, J.H. Detecting non-neutral heterogeneity across a region of DNA sequence in the ratio of polymorphism to divergence. Mol. Biol. Evol. 1996, 13, 253–260. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hutter, S.; Vilella, A.J.; Rozas, J. Genome-wide DNA polymorphism analyses using VariScan. BMC Bioinform. 2006, 7, 409. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sander, C.; Schneider, R. Database of homology-derived protein structures and the structural meaning of sequence alignment. Proteins 1991, 9, 56–68. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Genomic tRNA Database. Available online: http://gtrnadb.ucsc.edu (accessed on 13 July 2015).
- Alkatib, S.; Scharff, L.B.; Rogalski, M.; Fleischmann, T.T.; Matthes, A.; Seeger, S.; Schöttler, M.A.; Ruf, S.; Bock, R. The contributions of wobbling and superwobbling to the reading of the genetic code. PLoS Genet. 2012, 8, e1003076. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Haumont, E.; Fournier, M.; de Henau, S.; Grosjean, H. Enzymatic conversion of adenosine to inosine in the wobble position of yeast tRNAAsp: The dependence on the anticodon sequence. Nucleic Acids Res. 1984, 12, 2705–2715. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Leonard, G.A.; Booth, E.D.; Hunter, W.N.; Brown, T. The conformational variability of an adenosine inosine base-pair in a synthetic DNA dodecamer. Nucleic Acids Res. 1992, 20, 4753–4759. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Torres, A.G.; Pineyro, D.; Filonava, L.; Stracker, T.H.; Batlle, E.; Ribas de Pouplana, L. A-to-I editing on tRNAs: Biochemical, biological and evolutionary implications. FEBS Lett. 2014, 588, 4279–4286. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pavlov, M.Y.; Watts, R.E.; Tan, Z.; Cornish, V.W.; Ehrenberg, M.; Forster, A.C. Slow peptide bond formation by proline and other N-alkylamino acids in translation. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2009, 106, 50–54. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Guimaraes, J.C.; Rocha, M.; Arkin, A.P. Transcript level and sequence determinants of protein abundance and noise in Escherichia coli. Nucleic Acids Res. 2014, 42, 4791–4719. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ude, S.; Lassak, J.; Starosta, A.L.; Kraxenberger, T.; Wilson, D.N.; Jung, K. Translation elongation factor EF-P alleviates ribosome stalling at polyproline stretches. Science 2013, 339, 82–85. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Doerfel, L.K.; Wohlgemuth, I.; Kothe, C.; Peske, F.; Urlaub, H.; Rodnina, M.V. EF-P is essential for rapid synthesis of proteins containing consecutive proline residues. Science 2013, 339, 85–88. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
© 2015 by the authors; licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Rafels-Ybern, À.; Stephan-Otto Attolini, C.; De Pouplana, L.R. Distribution of ADAT-Dependent Codons in the Human Transcriptome. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2015, 16, 17303-17314. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms160817303
Rafels-Ybern À, Stephan-Otto Attolini C, De Pouplana LR. Distribution of ADAT-Dependent Codons in the Human Transcriptome. International Journal of Molecular Sciences. 2015; 16(8):17303-17314. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms160817303
Chicago/Turabian StyleRafels-Ybern, Àlbert, Camille Stephan-Otto Attolini, and Lluís Ribas De Pouplana. 2015. "Distribution of ADAT-Dependent Codons in the Human Transcriptome" International Journal of Molecular Sciences 16, no. 8: 17303-17314. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms160817303
APA StyleRafels-Ybern, À., Stephan-Otto Attolini, C., & De Pouplana, L. R. (2015). Distribution of ADAT-Dependent Codons in the Human Transcriptome. International Journal of Molecular Sciences, 16(8), 17303-17314. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms160817303