Novel Electrocardiographic Patterns for the Prediction of Hypertensive Disorders of Pregnancy—From Pathophysiology to Practical Implications
Abstract
:1. Introduction
- (i)
- Pre-existing or chronic hypertension (hypertension that was present before pregnancy or that develops at <20th week gestation);
- (ii)
- Gestational hypertension (hypertension that develops for the first time at ≥20th week’ gestation; this definition is preferred over the older term of pregnancy-induced hypertension);
- (iii)
- Preeclampsia-eclampsia;
- (iv)
- Other hypertensive effects (including transient hypertensive effect, white-coat hypertensive effect and masked hypertensive effect).
2. Hemodynamic Changes in Pregnancy

3. Pregnancy-Induced ECG Changes

4. ECG Features of Increased Risk
| Study | [Ref.]/Year | Design | Sample Size (n) | ECG Features |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Isezuo and Ekele | [50]/2004 | Prospective | 60 | QT interval |
| Baumert et al. | [51]/2010 | Case-control | 64 | QT interval |
| Angeli et al. | [17]/2011 | Prospective | 221 | P-wave morphology |
| Raffaelli et al. | [52]/2014 | Case-control | 152 | QT interval, QT dispersion and P-wave duration |
4.1. QT Interval
4.2. Abnormal P-Wave Morphology


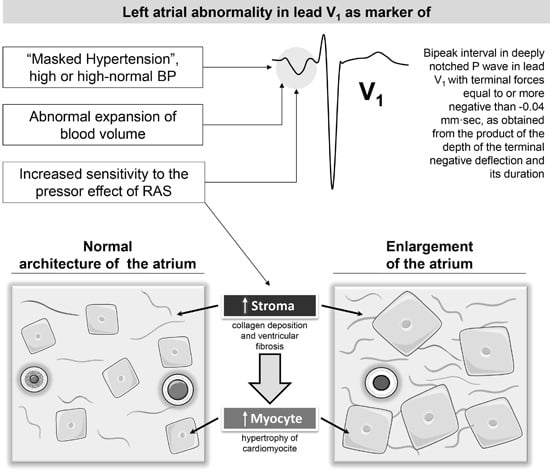
5. P-Wave Morphology and Risk of Hypertensive Disorders: Mechanisms
5.1. Hemodynamic Mechanisms

5.2. Molecular Mechanisms


6. Conclusions and Perspectives
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Berg, C.J.; Chang, J.; Callaghan, W.M.; Whitehead, S.J. Pregnancy-related mortality in the United States, 1991–1997. Obstet. Gynecol. 2003, 101, 289–296. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Chang, J.; Elam-Evans, L.D.; Berg, C.J.; Herndon, J.; Flowers, L.; Seed, K.A.; Syverson, C.J. Pregnancy-related mortality surveillance—United States, 1991–1999. MMWR Surveill. Summ. 2003, 52, 1–8. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- MacKay, A.P.; Berg, C.J.; Duran, C.; Chang, J.; Rosenberg, H. An assessment of pregnancy-related mortality in the United States. Paediatr. Perinat. Epidemiol. 2005, 19, 206–214. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- National High Blood Pressure Education Program. Report of the national high blood pressure education program working group on high blood pressure in pregnancy. Am. J. Obstet. Gynecol. 2000, 183, S1–S22. [Google Scholar]
- Magee, L.A.; Pels, A.; Helewa, M.; Rey, E.; von Dadelszen, P.; Hypertension Guideline Committee; Audibert, F.; Bujold, E.; Cote, A.M.; et al. Diagnosis, evaluation, and management of the hypertensive disorders of pregnancy: Executive summary. J. Obstet. Gynaecol. Can. 2014, 36, 416–438. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Audibert, F.; Benchimol, Y.; Benattar, C.; Champagne, C.; Frydman, R. Prediction of preeclampsia or intrauterine growth restriction by second trimester serum screening and uterine doppler velocimetry. Fetal Diagn. Ther. 2005, 20, 48–53. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Dugoff, L.; Hobbins, J.C.; Malone, F.D.; Porter, T.F.; Luthy, D.; Comstock, C.H.; Hankins, G.; Berkowitz, R.L.; Merkatz, I.; Craigo, S.D.; et al. First-trimester maternal serum papp-a and free-beta subunit human chorionic gonadotropin concentrations and nuchal translucency are associated with obstetric complications: A population-based screening study (the faster trial). Am. J. Obstet. Gynecol. 2004, 191, 1446–1451. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Halligan, A.; Bonnar, J.; Sheppard, B.; Darling, M.; Walshe, J. Haemostatic, fibrinolytic and endothelial variables in normal pregnancies and pre-eclampsia. Br. J. Obstet. Gynaecol. 1994, 101, 488–492. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hershkovitz, R.; de Swiet, M.; Kingdom, J. Mid-trimester placentation assessment in high-risk pregnancies using maternal serum screening and uterine artery doppler. Hypertens. Pregnancy 2005, 24, 273–280. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kurdi, W.; Campbell, S.; Aquilina, J.; England, P.; Harrington, K. The role of color doppler imaging of the uterine arteries at 20 weeks’ gestation in stratifying antenatal care. Ultrasound Obstet. Gynecol. 1998, 12, 339–345. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Milne, F.; Redman, C.; Walker, J.; Baker, P.; Bradley, J.; Cooper, C.; de Swiet, M.; Fletcher, G.; Jokinen, M.; Murphy, D.; et al. The pre-eclampsia community guideline (precog): How to screen for and detect onset of pre-eclampsia in the community. BMJ 2005, 330, 576–580. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Salomon, O.; Seligsohn, U.; Steinberg, D.M.; Zalel, Y.; Lerner, A.; Rosenberg, N.; Pshithizki, M.; Oren, M.; Ravid, B.; Davidson, J.; et al. The common prothrombotic factors in nulliparous women do not compromise blood flow in the feto-maternal circulation and are not associated with preeclampsia or intrauterine growth restriction. Am. J. Obstet. Gynecol. 2004, 191, 2002–2009. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Steegers-Theunissen, R.P.; van Iersel, C.A.; Peer, P.G.; Nelen, W.L.; Steegers, E.A. Hyperhomocysteinemia, pregnancy complications, and the timing of investigation. Obstet. Gynecol. 2004, 104, 336–343. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yu, C.K.; Smith, G.C.; Papageorghiou, A.T.; Cacho, A.M.; Nicolaides, K.H. An integrated model for the prediction of preeclampsia using maternal factors and uterine artery doppler velocimetry in unselected low-risk women. Am. J. Obstet. Gynecol. 2005, 193, 429–436. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Duckitt, K.; Harrington, D. Risk factors for pre-eclampsia at antenatal booking: Systematic review of controlled studies. BMJ 2005, 330, 565. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Angeli, F.; Angeli, E.; Reboldi, G.; Verdecchia, P. Hypertensive disorders during pregnancy: Clinical applicability of risk prediction models. J. Hypertens. 2011, 29, 2320–2323. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Angeli, E.; Verdecchia, P.; Narducci, P.; Angeli, F. Additive value of standard ecg for the risk prediction of hypertensive disorders during pregnancy. Hypertens. Res. 2011, 34, 707–713. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Benedetto, C.; Valensise, H.; Marozio, L.; Giarola, M.; Massobrio, M.; Romanini, C. A two-stage screening test for pregnancy-induced hypertension and preeclampsia. Obstet. Gynecol. 1998, 92, 1005–1011. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Giguere, Y.; Charland, M.; Bujold, E.; Bernard, N.; Grenier, S.; Rousseau, F.; Lafond, J.; Legare, F.; Forest, J.C. Combining biochemical and ultrasonographic markers in predicting preeclampsia: A systematic review. Clin. Chem. 2010, 56, 361–375. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Poon, L.C.; Kametas, N.A.; Maiz, N.; Akolekar, R.; Nicolaides, K.H. First-trimester prediction of hypertensive disorders in pregnancy. Hypertension 2009, 53, 812–818. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Angeli, F.; Angeli, E.; Verdecchia, P. Electrocardiographic changes in hypertensive disorders of pregnancy. Hypertens. Res. 2014, 37, 973–975. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Haynes, R.B.; Kastner, M.; Wilczynski, N.L.; Hedges, T. Developing optimal search strategies for detecting clinically sound and relevant causation studies in embase. BMC Med. Inform. Decis. Mak. 2005, 5, 8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Haynes, R.B.; Wilczynski, N.; McKibbon, K.A.; Walker, C.J.; Sinclair, J.C. Developing optimal search strategies for detecting clinically sound studies in medline. J. Am. Med. Inform. Assoc. 1994, 1, 447–458. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chapman, A.B.; Abraham, W.T.; Zamudio, S.; Coffin, C.; Merouani, A.; Young, D.; Johnson, A.; Osorio, F.; Goldberg, C.; Moore, L.G.; et al. Temporal relationships between hormonal and hemodynamic changes in early human pregnancy. Kidney Int. 1998, 54, 2056–2063. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hunter, S.; Robson, S.C. Adaptation of the maternal heart in pregnancy. Br. Heart J. 1992, 68, 540–543. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Williams, D.J.; Vallance, P.J.; Neild, G.H.; Spencer, J.A.; Imms, F.J. Nitric oxide-mediated vasodilation in human pregnancy. Am. J. Physiol. 1997, 272, H748–H752. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Brown, M.A.; Gallery, E.D. Volume homeostasis in normal pregnancy and pre-eclampsia: Physiology and clinical implications. Baillieres Clin. Obstet. Gynaecol. 1994, 8, 287–310. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moran, P.; Lindheimer, M.D.; Davison, J.M. The renal response to preeclampsia. Semin. Nephrol. 2004, 24, 588–595. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Salas, S.P.; Marshall, G.; Gutierrez, B.L.; Rosso, P. Time course of maternal plasma volume and hormonal changes in women with preeclampsia or fetal growth restriction. Hypertension 2006, 47, 203–208. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Visser, W.; Wallenburg, H.C. Central hemodynamic observations in untreated preeclamptic patients. Hypertension 1991, 17, 1072–1077. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Huppertz, B. Placental origins of preeclampsia: Challenging the current hypothesis. Hypertension 2008, 51, 970–975. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Von Dadelszen, P.; Magee, L.A.; Roberts, J.M. Subclassification of preeclampsia. Hypertens. Pregnancy 2003, 22, 143–148. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Murphy, D.J.; Stirrat, G.M. Mortality and morbidity associated with early-onset preeclampsia. Hypertens. Pregnancy 2000, 19, 221–231. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ness, R.B.; Sibai, B.M. Shared and disparate components of the pathophysiologies of fetal growth restriction and preeclampsia. Am. J. Obstet. Gynecol. 2006, 195, 40–49. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sibai, B.; Dekker, G.; Kupferminc, M. Pre-eclampsia. Lancet 2005, 365, 785–799. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Crispi, F.; Dominguez, C.; Llurba, E.; Martin-Gallan, P.; Cabero, L.; Gratacos, E. Placental angiogenic growth factors and uterine artery doppler findings for characterization of different subsets in preeclampsia and in isolated intrauterine growth restriction. Am. J. Obstet. Gynecol. 2006, 195, 201–207. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Crispi, F.; Llurba, E.; Dominguez, C.; Martin-Gallan, P.; Cabero, L.; Gratacos, E. Predictive value of angiogenic factors and uterine artery doppler for early- vs. late-onset pre-eclampsia and intrauterine growth restriction. Ultrasound Obstet. Gynecol. 2008, 31, 303–309. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Novelli, G.P.; Valensise, H.; Vasapollo, B.; Larciprete, G.; Altomare, F.; di Pierro, G.; Casalino, B.; Galante, A.; Arduini, D. Left ventricular concentric geometry as a risk factor in gestational hypertension. Hypertension 2003, 41, 469–475. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Valensise, H.; Vasapollo, B.; Novelli, G.P.; Pasqualetti, P.; Galante, A.; Arduini, D. Maternal total vascular resistance and concentric geometry: A key to identify uncomplicated gestational hypertension. BJOG 2006, 113, 1044–1052. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vasapollo, B.; Novelli, G.P.; Valensise, H. Total vascular resistance and left ventricular morphology as screening tools for complications in pregnancy. Hypertension 2008, 51, 1020–1026. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Valensise, H.; Vasapollo, B.; Gagliardi, G.; Novelli, G.P. Early and late preeclampsia: Two different maternal hemodynamic states in the latent phase of the disease. Hypertension 2008, 52, 873–880. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Carruth, J.E.; Mivis, S.B.; Brogan, D.R.; Wenger, N.K. The electrocardiogram in normal pregnancy. Am. Heart J. 1981, 102, 1075–1078. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Akinwusi, P.O.; Oboro, V.O.; Adebayo, R.A.; Akintunde, A.A.; Adeniji, A.O.; Isawumi, I.A.; Balogun, M.O.; Ogungbamigbe, T.O. Cardiovascular and electrocardiographic changes in nigerians with a normal pregnancy. Cardiovasc. J. Afr. 2011, 22, 71–75. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Boyle, D.M.; Lloyd-Jones, R.L. The electrocardiographic st segment in pregnancy. J. Obstet. Gynaecol. Br. Commonw. 1966, 73, 986–987. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Grand, A.; Rigaud-Morel, N.; Drouin, B.; Boissel, J.; Burel, H. Electrocardiographic changes induced by pregnancy in healthy women. Arch. Mal. Coeur. Vaiss. 1983, 76, 77–86. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Gregorini, L.; Valentini, R.; lo Cicero, G.; Ferrari, A.; Mancia, G. Electrocardiographic and vectorcardiographic modifications during pregnancy and post partum. Boll. Soc. Ital. Cardiol. 1976, 21, 2049–2054. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Halphen, C.; Leguludec, D.; Valent, R.; Haiat, R. Electrocardiographic study of left ventricular performance in normal pregnancy. Arch. Mal. Coeur. Vaiss. 1984, 77, 212–217. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Illanes, A.; Droguett, A.; Fuentealba, A. Electrocardiographic studies on normal pregnancy. Rev. Med. Chil. 1953, 81, 152–159. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Wenger, N.K.; Hurst, J.W.; Strozier, V.N. Electrocardiographic changes in pregnancy. Am. J. Cardiol. 1964, 13, 774–778. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Isezuo, S.A.; Ekele, B.A. Eclampsia and abnormal qtc. West Afr. J. Med. 2004, 23, 123–127. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Baumert, M.; Seeck, A.; Faber, R.; Nalivaiko, E.; Voss, A. Longitudinal changes in QT interval variability and rate adaptation in pregnancies with normal and abnormal uterine perfusion. Hypertens. Res. 2010, 33, 555–560. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Raffaelli, R.; Prioli, M.A.; Parissone, F.; Prati, D.; Carli, M.; Bergamini, C.; Cacici, G.; Balestreri, D.; Vassanelli, C.; Franchi, M. Pre-eclampsia: Evidence of altered ventricular repolarization by standard ECG parameters and qt dispersion. Hypertens. Res. 2014, 37, 984–988. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Higham, P.D.; Campbell, R.W. Qt dispersion. Br. Heart J. 1994, 71, 508–510. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bazett, H. An analysis of the time-relations of electrocardiograms. Heart 1920, 7, 353–370. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Verdecchia, P.; Schillaci, G.; Borgioni, C.; Ciucci, A.; Gattobigio, R.; Zampi, I.; Porcellati, C. Prognostic value of a new electrocardiographic method for diagnosis of left ventricular hypertrophy in essential hypertension. J. Am. Coll. Cardiol. 1998, 31, 383–390. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Prineas, R.; Crow, R.; Blackburn, H. The Minnesota Code Manual of Electrocardiographic Findings: Standards and Procedures for Measurement and Classification; Springer: London, UK, 1982. [Google Scholar]
- Tarazi, R.C.; Miller, A.; Frohlich, E.D.; Dustan, H.P. Electrocardiographic changes reflecting left atrial abnormality in hypertension. Circulation 1966, 34, 818–822. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Munuswamy, K.; Alpert, M.A.; Martin, R.H.; Whiting, R.B.; Mechlin, N.J. Sensitivity and specificity of commonly used electrocardiographic criteria for left atrial enlargement determined by m-mode echocardiography. Am. J. Cardiol. 1984, 53, 829–832. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lenfant, C. Working group report on high blood pressure in pregnancy. J. Clin. Hypertens. (Greenwich) 2001, 3, 75–88. [Google Scholar]
- Lindheimer, M.D.; Taler, S.J.; Cunningham, F.G. Hypertension in pregnancy. J. Am. Soc. Hypertens. 2008, 4, 68–78. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Frohlich, E.D.; Tarazi, R.C.; Dustan, H.P. Clinical-physiological correlations in the development of hypertensive heart disease. Circulation 1971, 44, 446–455. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Miller, J.T.; O'Rourke, R.A.; Crawford, M.H. Left atrial enlargement: An early sign of hypertensive heart disease. Am. Heart J. 1988, 116, 1048–1051. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bosio, P.M.; McKenna, P.J.; Conroy, R.; O’Herlihy, C. Maternal central hemodynamics in hypertensive disorders of pregnancy. Obstet. Gynecol. 1999, 94, 978–984. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dunn, F.G.; Chandraratna, P.; de Carvalho, J.G.; Basta, L.L.; Frohlich, E.D. Pathophysiologic assessment of hypertensive heart disease with echocardiography. Am. J. Cardiol. 1977, 39, 789–795. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pearson, A.C.; Gudipati, C.; Nagelhout, D.; Sear, J.; Cohen, J.D.; Labovitz, A.J. Echocardiographic evaluation of cardiac structure and function in elderly subjects with isolated systolic hypertension. J. Am. Coll. Cardiol. 1991, 17, 422–430. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vaziri, S.M.; Larson, M.G.; Lauer, M.S.; Benjamin, E.J.; Levy, D. Influence of blood pressure on left atrial size. The framingham heart study. Hypertension 1995, 25, 1155–1160. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lindheimer, M.D.; Katz, A.I. Sodium and diuretics in pregnancy. N. Engl. J. Med. 1973, 288, 891–894. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Myers, B.D.; Peterson, C.; Molina, C.; Tomlanovich, S.J.; Newton, L.D.; Nitkin, R.; Sandler, H.; Murad, F. Role of cardiac atria in the human renal response to changing plasma volume. Am. J. Physiol. 1988, 254, F562–F573. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Laragh, J.H.; Atlas, S.A. Atrial natriuretic hormone: A regulator of blood pressure and volume homeostasis. Kidney Int. Suppl. 1988, 25, S64–S71. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Lund, C.J.; Donovan, J.C. Blood volume during pregnancy. Significance of plasma and red cell volumes. Am. J. Obstet. Gynecol. 1967, 98, 394–403. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Bernstein, I.M.; Ziegler, W.; Badger, G.J. Plasma volume expansion in early pregnancy. Obstet. Gynecol. 2001, 97, 669–672. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nadel, A.S.; Ballermann, B.J.; Anderson, S.; Brenner, B.M. Interrelationships among atrial peptides, renin, and blood volume in pregnant rats. Am. J. Physiol. 1988, 254, R793–R800. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Schrier, R.W. Pathogenesis of sodium and water retention in high-output and low-output cardiac failure, nephrotic syndrome, cirrhosis, and pregnancy. N. Engl. J. Med. 1988, 319, 1127–1134. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bond, A.L.; August, P.; Druzin, M.L.; Atlas, S.A.; Sealey, J.E.; Laragh, J.H. Atrial natriuretic factor in normal and hypertensive pregnancy. Am. J. Obstet. Gynecol. 1989, 160, 1112–1116. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mikkelsen, A.L.; Schutten, G.; Asping, U.; Schutten, H.J. Plasma concentration of atrial natriuretic peptide in normal pregnant women and in pregnant women with preeclampsia. Gynecol. Obstet. Investig. 1991, 31, 192–195. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sumioki, H.; Shimokawa, H.; Miyamoto, S.; Uezono, K.; Utsunomiya, T.; Nakano, H. Circadian variations of plasma atrial natriuretic peptide in four types of hypertensive disorder during pregnancy. Br. J. Obstet. Gynaecol. 1989, 96, 922–927. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gerdts, E.; Oikarinen, L.; Palmieri, V.; Otterstad, J.E.; Wachtell, K.; Boman, K.; Dahlof, B.; Devereux, R.B.; Losartan Intervention For Endpoint Reduction in Hypertension (LIFE) Study. Correlates of left atrial size in hypertensive patients with left ventricular hypertrophy: The losartan intervention for endpoint reduction in hypertension (life) study. Hypertension 2002, 39, 739–743. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ingec, M.; Yilmaz, M.; Gundogdu, F. Left atrial mechanical functions in pre-eclampsia. J. Obstet. Gynaecol. Res. 2005, 31, 535–539. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Borghi, C.; Esposti, D.D.; Immordino, V.; Cassani, A.; Boschi, S.; Bovicelli, L.; Ambrosioni, E. Relationship of systemic hemodynamics, left ventricular structure and function, and plasma natriuretic peptide concentrations during pregnancy complicated by preeclampsia. Am. J. Obstet. Gynecol. 2000, 183, 140–147. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vazquez Blanco, M.; Grosso, O.; Bellido, C.A.; Iavicoli, O.R.; Berensztein, C.S.; Ruda Vega, H.; Lerman, J. Dimensions of the left ventricle, atrium, and aortic root in pregnancy-induced hypertension. Am. J. Hypertens. 2001, 14, 390–392. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Pritchett, A.M.; Mahoney, D.W.; Jacobsen, S.J.; Rodeheffer, R.J.; Karon, B.L.; Redfield, M.M. Diastolic dysfunction and left atrial volume: A population-based study. J. Am. Coll. Cardiol. 2005, 45, 87–92. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Valensise, H.; Novelli, G.P.; Vasapollo, B.; Borzi, M.; Arduini, D.; Galante, A.; Romanini, C. Maternal cardiac systolic and diastolic function: Relationship with uteroplacental resistances. A doppler and echocardiographic longitudinal study. Ultrasound Obstet. Gynecol. 2000, 15, 487–497. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Brown, M.A.; Gallery, E.D.; Ross, M.R.; Esber, R.P. Sodium excretion in normal and hypertensive pregnancy: A prospective study. Am. J. Obstet. Gynecol. 1988, 159, 297–307. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hsueh, W.A.; Luetscher, J.A.; Carlson, E.J.; Grislis, G.; Fraze, E.; McHargue, A. Changes in active and inactive renin throughout pregnancy. J. Clin. Endocrinol. Metab. 1982, 54, 1010–1016. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Merrill, D.C.; Karoly, M.; Chen, K.; Ferrario, C.M.; Brosnihan, K.B. Angiotensin-(1–7) in normal and preeclamptic pregnancy. Endocrine 2002, 18, 239–245. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Assali, N.S.; Westersten, A. Regional flow-pressure relationship in response to angiotensin in the intact dog and sheep. Circ. Res. 1961, 9, 189–193. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gant, N.F.; Worley, R.J.; Everett, R.B.; MacDonald, P.C. Control of vascular responsiveness during human pregnancy. Kidney Int. 1980, 18, 253–258. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- AbdAlla, S.; Lother, H.; el Massiery, A.; Quitterer, U. Increased AT1 receptor heterodimers in preeclampsia mediate enhanced angiotensin II responsiveness. Nat. Med. 2001, 7, 1003–1009. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Acar, K.; Beyazit, Y.; Sucak, A.; Haznedaroglu, I.C.; Aksu, S.; Tuncer, S.; Ozturkkan, D.; Danisman, N.; Purnak, T.; Misirlioglu, M.; et al. Alterations in the “local umbilical cord blood renin-angiotensin system” during pre-eclampsia. Acta Obstet. Gynecol. Scand. 2007, 86, 1193–1199. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Benedetto, C.; Marozio, L.; Ciccone, G.; Chieppa, G.; Quaglia, M.; Matullo, G.; Bertola, L.; Guarrera, S.; Carturan, S.; Stratta, P. Synergistic effect of renin-angiotensin system and nitric oxide synthase genes polymorphisms in pre-eclampsia. Acta Obstet. Gynecol. Scand. 2007, 86, 678–682. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Brown, M.A.; Reiter, L.; Rodger, A.; Whitworth, J.A. Impaired renin stimulation in pre-eclampsia. Clin. Sci. (Lond.) 1994, 86, 575–581. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Brown, M.A.; Wang, J.; Whitworth, J.A. The renin-angiotensin-aldosterone system in pre-eclampsia. Clin. Exp. Hypertens. 1997, 19, 713–726. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Herse, F.; Dechend, R.; Harsem, N.K.; Wallukat, G.; Janke, J.; Qadri, F.; Hering, L.; Muller, D.N.; Luft, F.C.; Staff, A.C. Dysregulation of the circulating and tissue-based renin-angiotensin system in preeclampsia. Hypertension 2007, 49, 604–611. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mistry, H.D.; Kurlak, L.O.; Broughton Pipkin, F. The placental renin-angiotensin system and oxidative stress in pre-eclampsia. Placenta 2013, 34, 182–186. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pedersen, E.B.; Rasmussen, A.B.; Johannesen, P.; Kornerup, H.J.; Kristensen, S.; Lauritsen, J.G.; Wohlert, M. The renin-aldosterone system in pre-eclampsia, essential and transient hypertension during pregnancy, and normotensive pregnant and non-pregnant control subjects. Acta Endocrinol. (Cph.) 1982, 101, 273–280. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Raty, R.; Koskinen, P.; Alanen, A.; Irjala, K.; Matinlauri, I.; Ekblad, U. Prediction of pre-eclampsia with maternal mid-trimester total renin, inhibin A, AFP and free β-hCG levels. Prenat. Diagn. 1999, 19, 122–127. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Verdonk, K.; Visser, W.; van den Meiracker, A.H.; Danser, A.H. The renin-angiotensin-aldosterone system in pre-eclampsia: The delicate balance between good and bad. Clin. Sci. (Lond.) 2014, 126, 537–544. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mazzolai, L.; Nussberger, J.; Aubert, J.F.; Brunner, D.B.; Gabbiani, G.; Brunner, H.R.; Pedrazzini, T. Blood pressure-independent cardiac hypertrophy induced by locally activated renin-angiotensin system. Hypertension 1998, 31, 1324–1330. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hein, L.; Stevens, M.E.; Barsh, G.S.; Pratt, R.E.; Kobilka, B.K.; Dzau, V.J. Overexpression of angiotensin at1 receptor transgene in the mouse myocardium produces a lethal phenotype associated with myocyte hyperplasia and heart block. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 1997, 94, 6391–6396. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Briceno-Perez, C.; Briceno-Sanabria, L.; Vigil-de Gracia, P. Prediction and prevention of preeclampsia. Hypertens. Pregnancy 2009, 28, 138–155. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cnossen, J.S.; ter Riet, G.; Mol, B.W.; van der Post, J.A.; Leeflang, M.M.; Meads, C.A.; Hyde, C.; Khan, K.S. Are tests for predicting pre-eclampsia good enough to make screening viable? A review of reviews and critical appraisal. Acta Obstet. Gynecol. Scand. 2009, 88, 758–765. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Conde-Agudelo, A.; Villar, J.; Lindheimer, M. World health organization systematic review of screening tests for preeclampsia. Obstet. Gynecol. 2004, 104, 1367–1391. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Meads, C.A.; Cnossen, J.S.; Meher, S.; Juarez-Garcia, A.; ter Riet, G.; Duley, L.; Roberts, T.E.; Mol, B.W.; van der Post, J.A.; Leeflang, M.M.; et al. Methods of prediction and prevention of pre-eclampsia: Systematic reviews of accuracy and effectiveness literature with economic modelling. Health Technol. Assess. 2008, 12, 1–270. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Powers, R.W.; Catov, J.M.; Bodnar, L.M.; Gallaher, M.J.; Lain, K.Y.; Roberts, J.M. Evidence of endothelial dysfunction in preeclampsia and risk of adverse pregnancy outcome. Reprod. Sci. 2008, 15, 374–381. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Redman, C.W.; Sacks, G.P.; Sargent, I.L. Preeclampsia: An excessive maternal inflammatory response to pregnancy. Am. J. Obstet. Gynecol. 1999, 180, 499–506. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Roberts, J.M. Endothelial dysfunction in preeclampsia. Semin. Reprod. Endocrinol. 1998, 16, 5–15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ridker, P.M.; Hennekens, C.H.; Buring, J.E.; Rifai, N. C-reactive protein and other markers of inflammation in the prediction of cardiovascular disease in women. N. Engl. J. Med. 2000, 342, 836–843. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wolf, M.; Kettyle, E.; Sandler, L.; Ecker, J.L.; Roberts, J.; Thadhani, R. Obesity and preeclampsia: The potential role of inflammation. Obstet. Gynecol. 2001, 98, 757–762. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
© 2015 by the authors; licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Angeli, F.; Angeli, E.; Verdecchia, P. Novel Electrocardiographic Patterns for the Prediction of Hypertensive Disorders of Pregnancy—From Pathophysiology to Practical Implications. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2015, 16, 18454-18473. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms160818454
Angeli F, Angeli E, Verdecchia P. Novel Electrocardiographic Patterns for the Prediction of Hypertensive Disorders of Pregnancy—From Pathophysiology to Practical Implications. International Journal of Molecular Sciences. 2015; 16(8):18454-18473. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms160818454
Chicago/Turabian StyleAngeli, Fabio, Enrica Angeli, and Paolo Verdecchia. 2015. "Novel Electrocardiographic Patterns for the Prediction of Hypertensive Disorders of Pregnancy—From Pathophysiology to Practical Implications" International Journal of Molecular Sciences 16, no. 8: 18454-18473. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms160818454
APA StyleAngeli, F., Angeli, E., & Verdecchia, P. (2015). Novel Electrocardiographic Patterns for the Prediction of Hypertensive Disorders of Pregnancy—From Pathophysiology to Practical Implications. International Journal of Molecular Sciences, 16(8), 18454-18473. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms160818454