Synergistic Anticancer Effect of Tocotrienol Combined with Chemotherapeutic Agents or Dietary Components: A Review
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Synergistic Anticancer Actions of T3 and Chemotherapeutic Drugs
2.1. Statins
2.2. Gefitinib and Erlotinib
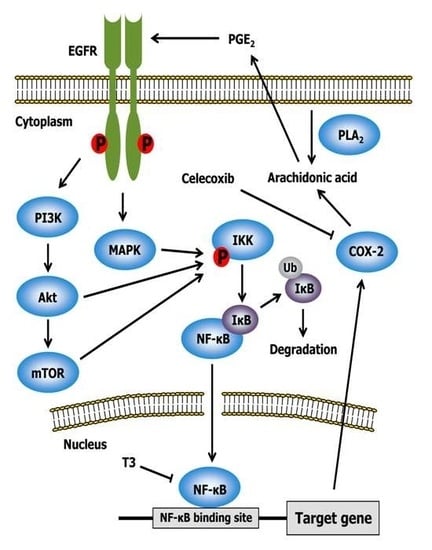
2.3. Celecoxib
2.4. Other Drugs
3. Synergistic Anti-Proliferative Effects of T3 and Dietary Components
3.1. Epigallocatechin Gallate (EGCG) and Resveratrol
3.2. Sesamin
3.3. Ferulic Acid
4. Conclusions
Acknowledgments
Author Contributions
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Mustacich, D.J.; Bruno, R.S.; Traber, M.G. Vitamin E. Vitam. Horm. 2007, 76, 1–21. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Packer, L.; Weber, S.U.; Rimbach, G. Molecular aspects of α-tocotrienol antioxidant action and cell signalling. J. Nutr. 2001, 131, 369S–373S. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Pennock, J.F.; Hemming, F.W.; Kerr, J.D. A reassessment of tocopherol chemistry. Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 1964, 17, 542–548. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qureshi, A.A.; Burger, W.C.; Peterson, D.M.; Elson, C.E. The structure of an inhibitor of cholesterol biosynthesis isolated from barley. J. Biol. Chem. 1986, 261, 10544–10550. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Sundram, K.; Khor, H.T.; Ong, A.S.; Pathmanathan, R. Effect of dietary palm oils on mammary carcinogenesis in female rats induced by 7,12-dimethylbenz(a)anthracene. Cancer Res. 1989, 49, 1447–1451. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Nesaretnam, K.; Guthrie, N.; Chambers, A.F.; Carroll, K.K. Effect of tocotrienols on the growth of a human breast cancer cell line in culture. Lipids 1995, 30, 1139–1143. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Serbinova, E.; Kagan, V.; Han, D.; Packer, L. Free radical recycling and intramembrane mobility in the antioxidant properties of α-tocopherol and α-tocotrienol. Free Radic. Biol. Med. 1991, 10, 263–275. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wan Nazaimoon, W.M.; Khalid, B.A. Tocotrienols-rich diet decreases advanced glycosylation end-products in non-diabetic rats and improves glycemic control in streptozotocin-induced diabetic rats. Malays. J. Pathol. 2002, 24, 77–82. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Wu, S.J.; Liu, P.L.; Ng, L.T. Tocotrienol-rich fraction of palm oil exhibits anti-inflammatory property by suppressing the expression of inflammatory mediators in human monocytic cells. Mol. Nutr. Food Res. 2008, 52, 921–929. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ren, Z.; Pae, M.; Dao, M.C.; Smith, D.; Meydani, S.N.; Wu, D. Dietary supplementation with tocotrienols enhances immune function in C57BL/6 mice. J. Nutr. 2010, 140, 1335–1341. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vasanthi, H.R.; Parameswari, R.P.; Das, D.K. Multifaceted role of tocotrienols in cardioprotection supports their structure: Function relation. Genes Nutr. 2012, 7, 19–28. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Norazlina, M.; Lee, P.L.; Lukman, H.I.; Nazrun, A.S.; Ima-Nirwana, S. Effects of vitamin E supplementation on bone metabolism in nicotine-treated rats. Singap. Med. J. 2007, 48, 195–199. [Google Scholar]
- Khanna, S.; Roy, S.; Slivka, A.; Craft, T.K.S.; Chaki, S.; Rink, C.; Notestine, M.A.; DeVries, A.C.; Parinandi, N.L.; Sen, C.K. Neuroprotective properties of the natural vitamin E α-tocotrienol. Stroke 2005, 36, 2258–2264. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ong, F.B.; Wan Ngah, W.Z.; Shamaan, N.A.; Md Top, A.G.; Marzuki, A.; Khalid, A.K. Glutathione S-transferase and γ-glutamyl transpeptidase activities in cultured rat hepatocytes treated with tocotrienol and tocopherol. Comp. Biochem. Physiol. C 1993, 106, 237–240. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gupta, A.; Chopra, K. Effect of tocotrienols on iron-induced renal dysfunction and oxidative stress in rats. Drug Chem. Toxicol. 2009, 32, 319–325. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Suzuki, Y.J.; Tsuchiya, M.; Wassall, S.R.; Choo, Y.M.; Govil, G.; Kagan, V.E.; Packer, L. Structural and dynamic membrane properties of α-tocopherol and α-tocotrienol: Implication to the molecular mechanism of their antioxidant potency. Biochemistry 1993, 32, 10692–10699. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Traber, M.G. Vitamin E regulatory mechanisms. Annu. Rev. Nutr. 2007, 27, 347–362. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hosomi, A.; Arita, M.; Sato, Y.; Kiyose, C.; Ueda, T.; Igarashi, O.; Arai, H.; Inoue, K. Affinity for α-tocopherol transfer protein as a determinant of the biological activities of vitamin E analogs. FEBS Lett. 1997, 409, 105–108. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- O’Byrne, D.; Grundy, S.; Packer, L.; Devaraj, S.; Baldenius, K.; Hoppe, P.P.; Kraemer, K.; Jialal, I.; Traber, M.G. Studies of LDL oxidation following α-, γ-, or δ-tocotrienyl acetate supplementation of hypercholesterolemic humans. Free Radic. Biol. Med. 2000, 29, 834–845. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shibata, A.; Nakagawa, K.; Sookwong, P.; Tsuduki, T.; Asai, A.; Miyazawa, T. α-Tocopherol attenuates the cytotoxic effect of δ-tocotrienol in human colorectal adenocarcinoma cells. Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 2010, 397, 214–219. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ikeda, S.; Tohyama, T.; Yoshimura, H.; Hamamura, K.; Abe, K.; Yamashita, K. Dietary α-tocopherol decreases α-tocotrienol but not γ-tocotrienol concentration in rats. J. Nutr. 2003, 133, 428–434. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Mo, H.; Elson, C.E. Studies of the isoprenoid-mediated inhibition of mevalonate synthesis applied to cancer chemotherapy and chemoprevention. Exp. Biol. Med. 2004, 229, 567–585. [Google Scholar]
- Bachawal, S.V.; Wali, V.B.; Sylvester, P.W. Enhanced antiproliferative and apoptotic response to combined treatment of γ-tocotrienol with erlotinib or gefitinib in mammary tumor cells. BMC Cancer 2010. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shirode, A.B.; Sylvester, P.W. Synergistic anticancer effects of combined γ-tocotrienol and celecoxib treatment are associated with suppression in Akt and NFκB signaling. Biomed. Pharmacother. 2010, 64, 327–332. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ayoub, N.M.; Bachawal, S.V.; Sylvester, P.W. γ-Tocotrienol inhibits HGF-dependent mitogenesis and Met activation in highly malignant mammary tumour cells. Cell Prolif. 2011, 44, 516–526. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Malaviya, A.; Sylvester, P.W. Mechanisms mediating the effects of γ-tocotrienol when used in combination with PPARγ agonists or antagonists on MCF-7 and MDA-MB-231 breast cancer cells. Int. J. Breast Cancer 2013, 2013, 101705. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tiwari, R.V.; Parajuli, P.; Sylvester, P.W. Synergistic anticancer effects of combined γ-tocotrienol and oridonin treatment is associated with the induction of autophagy. Mol. Cell. Biochem. 2015, 408, 123–137. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yamashita, S.; Baba, K.; Makio, A.; Kumazoe, M.; Huang, Y.; Lin, I.C.; Bae, J.; Murata, M.; Yamada, S.; Tachibana, H. γ-Tocotrienol upregulates aryl hydrocarbon receptor expression and enhances the anticancer effect of baicalein. Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 2016, 473, 801–807. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hsieh, T.C.; Wu, J.M. Suppression of cell proliferation and gene expression by combinatorial synergy of EGCG, resveratrol and γ-tocotrienol in estrogen receptor-positive MCF-7 breast cancer cells. Int. J. Oncol. 2008, 33, 851–859. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Akl, M.R.; Ayoub, N.M.; Sylvester, P.W. Mechanisms mediating the synergistic anticancer effects of combined γ-tocotrienol and sesamin treatment. Planta Med. 2012, 78, 1731–1739. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Eitsuka, T.; Tatewaki, N.; Nishida, H.; Kurata, T.; Nakagawa, K.; Miyazawa, T. Synergistic inhibition of cancer cell proliferation with a combination of δ-tocotrienol and ferulic acid. Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 2014, 453, 606–611. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Goldstein, J.L.; Brown, M.S. Regulation of the mevalonate pathway. Nature 1990, 343, 425–430. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, F.L.; Casey, P.J. Protein prenylation: Molecular mechanisms and functional consequences. Annu. Rev. Biochem. 1996, 65, 241–269. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dricu, A.; Carlberg, M.; Wang, M.; Larsson, O. Inhibition of N-linked glycosylation using tunicamycin causes cell death in malignant cells: Role of down-regulation of the insulin-like growth factor 1 receptor in induction of apoptosis. Cancer Res. 1997, 57, 543–548. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Demierre, M.F.; Higgins, P.D.; Gruber, S.B.; Hawk, E.; Lippman, S.M. Statins and cancer prevention. Nat. Rev. Cancer 2005, 5, 930–942. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Parker, R.A.; Pearce, B.C.; Clark, R.W.; Gordon, D.A.; Wright, J.J. Tocotrienols regulate cholesterol production in mammalian cells by post-transcriptional suppression of 3-hydroxy-3-methylglutaryl-coenzyme A reductase. J. Biol. Chem. 1993, 268, 11230–11238. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Song, B.L.; DeBose-Boyd, R.A. Insig-dependent ubiquitination and degradation of 3-hydroxy-3-methylglutaryl coenzyme a reductase stimulated by δ- and γ-tocotrienols. J. Biol. Chem. 2006, 281, 25054–25061. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hussein, D.; Mo, H. d-δ-Tocotrienol-mediated suppression of the proliferation of human PANC-1, MIA PaCa-2, and BxPC-3 pancreatic carcinoma cells. Pancreas 2009, 38, e124–e136. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- McAnally, J.A.; Gupta, J.; Sodhani, S.; Bravo, L.; Mo, H. Tocotrienols potentiate lovastatin-mediated growth suppression in vitro and in vivo. Exp. Biol. Med. 2007, 232, 523–531. [Google Scholar]
- Wali, V.B.; Sylvester, P.W. Synergistic antiproliferative effects of γ-tocotrienol and statin treatment on mammary tumor cells. Lipids 2007, 42, 1113–1123. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yang, Z.; Xiao, H.; Jin, H.; Koo, P.T.; Tsang, D.J.; Yang, C.S. Synergistic actions of atorvastatin with γ-tocotrienol and celecoxib against human colon cancer HT29 and HCT116 cells. Int. J. Cancer 2010, 126, 852–863. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fernandes, N.V.; Guntipalli, P.K.; Mo, H. d-δ-Tocotrienol-mediated cell cycle arrest and apoptosis in human melanoma cells. Anticancer Res. 2010, 30, 4937–4944. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Yuan, Y.; Li, X.F.; Chen, J.Q.; Dong, C.X.; Weng, S.S.; Huang, J.J. Critical appraisal of the role of gefitinib in the management of locally advanced or metastatic non-small cell lung cancer. OncoTargets Ther. 2014, 7, 841–852. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ciardiello, F.; Tortora, G. EGFR antagonists in cancer treatment. N. Engl. J. Med. 2008, 358, 1160–1174. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hynes, N.E.; Lane, H.A. ERBB receptors and cancer: The complexity of targeted inhibitors. Nat. Rev. Cancer 2005, 5, 341–354. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Laurent-Puig, P.; Lievre, A.; Blons, H. Mutations and response to epidermal growth factor receptor inhibitors. Clin. Cancer Res. 2009, 15, 1133–1139. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Olayioye, M.A.; Neve, R.M.; Lane, H.A.; Hynes, N.E. The ErbB signaling network: Receptor heterodimerization in development and cancer. EMBO J. 2000, 19, 3159–3167. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Samant, G.V.; Sylvester, P.W. γ-Tocotrienol inhibits ErbB3-dependent PI3K/Akt mitogenic signalling in neoplastic mammary epithelial cells. Cell Prolif. 2006, 39, 563–574. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shin-Kang, S.; Ramsauer, V.P.; Lightner, J.; Chakraborty, K.; Stone, W.; Campbell, S.; Reddy, S.A.; Krishnan, K. Tocotrienols inhibit AKT and ERK activation and suppress pancreatic cancer cell proliferation by suppressing the ErbB2 pathway. Free Radic. Biol. Med. 2011, 51, 1164–1174. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pierpaoli, E.; Viola, V.; Barucca, A.; Orlando, F.; Galli, F.; Provinciali, M. Effect of annatto-tocotrienols supplementation on the development of mammary tumors in HER-2/neu transgenic mice. Carcinogenesis 2013, 34, 1352–1360. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Alawin, O.A.; Ahmed, R.A.; Ibrahim, B.A.; Briski, K.P.; Sylvester, P.W. Antiproliferative effects of γ-tocotrienol are associated with lipid raft disruption in HER2-positive human breast cancer cells. J. Nutr. Biochem. 2016, 27, 266–277. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bachawal, S.V.; Wali, V.B.; Sylvester, P.W. Combined γ-tocotrienol and erlotinib/gefitinib treatment suppresses Stat and Akt signaling in murine mammary tumor cells. Anticancer Res. 2010, 30, 429–437. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Thun, M.J.; Henley, S.J.; Patrono, C. Nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs as anticancer agents: Mechanistic, pharmacologic, and clinical issues. J. Natl. Cancer Inst. 2002, 94, 252–266. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Brown, J.R.; DuBois, R.N. Cyclooxygenase as a target in lung cancer. Clin. Cancer Res. 2004, 10, 4266s–4269s. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pai, R.; Soreghan, B.; Szabo, I.L.; Pavelka, M.; Baatar, D.; Tarnawski, A.S. Prostaglandin E2 transactivates EGF receptor: A novel mechanism for promoting colon cancer growth and gastrointestinal hypertrophy. Nat. Med. 2002, 8, 289–293. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shostak, K.; Chariot, A. EGFR and NF-κB: Partners in cancer. Trends Mol. Med. 2015, 21, 385–393. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ozes, O.N.; Mayo, L.D.; Gustin, J.A.; Pfeffer, S.R.; Pfeffer, L.M.; Donner, D.B. NF-κB activation by tumour necrosis factor requires the Akt serine-threonine kinase. Nature 1999, 401, 82–85. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gupta, S.C.; Sundaram, C.; Reuter, S.; Aggarwal, B.B. Inhibiting NF-κB activation by small molecules as a therapeutic strategy. Biochim. Biophys. Acta 2010, 1799, 775–787. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shishodia, S.; Koul, D.; Aggarwal, B.B. Cyclooxygenase (COX)-2 inhibitor celecoxib abrogates TNF-induced NF-κB activation through inhibition of activation of IκB α kinase and Akt in human non-small cell lung carcinoma: Correlation with suppression of COX-2 synthesis. J. Immunol. 2004, 173, 2011–2022. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shah, S.J.; Sylvester, P.W. Γ-tocotrienol inhibits neoplastic mammary epithelial cell proliferation by decreasing Akt and nuclear factor κB activity. Exp. Biol. Med. 2005, 230, 235–241. [Google Scholar]
- Ahn, K.S.; Sethi, G.; Krishnan, K.; Aggarwal, B.B. Γ-tocotrienol inhibits nuclear factor-κB signaling pathway through inhibition of receptor-interacting protein and TAK1 leading to suppression of antiapoptotic gene products and potentiation of apoptosis. J. Biol. Chem. 2007, 282, 809–820. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yap, W.N.; Chang, P.N.; Han, H.Y.; Lee, D.T.; Ling, M.T.; Wong, Y.C.; Yap, Y.L. Γ-tocotrienol suppresses prostate cancer cell proliferation and invasion through multiple-signalling pathways. Br. J. Cancer 2008, 99, 1832–1841. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xu, W.L.; Liu, J.R.; Liu, H.K.; Qi, G.Y.; Sun, X.R.; Sun, W.G.; Chen, B.Q. Inhibition of proliferation and induction of apoptosis by γ-tocotrienol in human colon carcinoma HT-29 cells. Nutrition 2009, 25, 555–566. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chang, P.N.; Yap, W.N.; Lee, D.T.; Ling, M.T.; Wong, Y.C.; Yap, Y.L. Evidence of γ-tocotrienol as an apoptosis-inducing, invasion-suppressing, and chemotherapy drug-sensitizing agent in human melanoma cells. Nutr. Cancer 2009, 61, 357–366. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yap, W.N.; Zaiden, N.; Tan, Y.L.; Ngoh, C.P.; Zhang, X.W.; Wong, Y.C.; Ling, M.T.; Yap, Y.L. Id1, inhibitor of differentiation, is a key protein mediating anti-tumor responses of γ-tocotrienol in breast cancer cells. Cancer Lett. 2010, 291, 187–199. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kunnumakkara, A.B.; Sung, B.; Ravindran, J.; Diagaradjane, P.; Deorukhkar, A.; Dey, S.; Koca, C.; Yadav, V.R.; Tong, Z.; Gelovani, J.G.; et al. Γ-tocotrienol inhibits pancreatic tumors and sensitizes them to gemcitabine treatment by modulating the inflammatory microenvironment. Cancer Res. 2010, 70, 8695–8705. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ji, X.; Wang, Z.; Geamanu, A.; Sarkar, F.H.; Gupta, S.V. Inhibition of cell growth and induction of apoptosis in non-small cell lung cancer cells by δ-tocotrienol is associated with notch-1 down-regulation. J. Cell. Biochem. 2011, 112, 2773–2783. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Manu, K.A.; Shanmugam, M.K.; Ramachandran, L.; Li, F.; Fong, C.W.; Kumar, A.P.; Tan, P.; Sethi, G. First evidence that γ-tocotrienol inhibits the growth of human gastric cancer and chemosensitizes it to capecitabine in a xenograft mouse model through the modulation of NF-κB pathway. Clin. Cancer Res. 2012, 18, 2220–2229. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kani, K.; Momota, Y.; Harada, M.; Yamamura, Y.; Aota, K.; Yamanoi, T.; Takano, H.; Motegi, K.; Azuma, M. γ-Tocotrienol enhances the chemosensitivity of human oral cancer cells to docetaxel through the downregulation of the expression of NF-κB-regulated anti-apoptotic gene products. Int. J. Oncol. 2013, 42, 75–82. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Wang, Y.; Park, N.Y.; Jang, Y.; Ma, A.; Jiang, Q. Vitamin E γ-tocotrienol inhibits cytokine-stimulated NF-κB activation by induction of anti-inflammatory A20 via stress adaptive response due to modulation of sphingolipids. J. Immunol. 2015, 195, 126–133. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shirode, A.B.; Sylvester, P.W. Mechanisms mediating the synergistic anticancer effects of combined γ-tocotrienol and celecoxib treatment. J. Bioanal. Biomed. 2011, 3, 1–7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bottaro, D.P.; Rubin, J.S.; Faletto, D.L.; Chan, A.M.; Kmiecik, T.E.; Vande Woude, G.F.; Aaronson, S.A. Identification of the hepatocyte growth factor receptor as the c-Met proto-oncogene product. Science 1991, 251, 802–804. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Eder, J.P.; Vande Woude, G.F.; Boerner, S.A.; LoRusso, P.M. Novel therapeutic inhibitors of the c-Met signaling pathway in cancer. Clin. Cancer Res. 2009, 15, 2207–2214. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Guo, A.; Villén, J.; Kornhauser, J.; Lee, K.A.; Stokes, M.P.; Rikova, K.; Possemato, A.; Nardone, J.; Innocenti, G.; Wetzel, R.; et al. Signaling networks assembled by oncogenic EGFR and c-Met. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2008, 105, 692–697. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ayoub, N.M.; Akl, M.R.; Sylvester, P.W. Combined γ-tocotrienol and Met inhibitor treatment suppresses mammary cancer cell proliferation, epithelial-to-mesenchymal transition and migration. Cell Prolif. 2013, 46, 538–553. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mangelsdorf, D.J.; Evans, R.M. The RXR heterodimers and orphan receptors. Cell 1995, 83, 841–850. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Koeffler, H.P. Peroxisome proliferator-activated receptor γ and cancers. Clin. Cancer Res. 2003, 9, 1–9. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Ricote, M.; Li, A.C.; Willson, T.M.; Kelly, C.J.; Glass, C.K. The peroxisome proliferator-activated receptor-γ is a negative regulator of macrophage activation. Nature 1998, 391, 79–82. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Campbell, S.E.; Rudder, B.; Phillips, R.B.; Whaley, S.G.; Stimmel, J.B.; Leesnitzer, L.M.; Lightner, J.; Dessus-Babus, S.; Duffourc, M.; Stone, W.L.; et al. γ-Tocotrienol induces growth arrest through a novel pathway with TGFβ2 in prostate cancer. Free Radic. Biol. Med. 2011, 50, 1344–1354. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Malaviya, A.; Sylvester, P.W. Synergistic antiproliferative effects of combined γ-tocotrienol and PPARγ antagonist treatment are mediated through PPAR γ-independent mechanisms in breast cancer cells. PPAR Res. 2014, 2014, 439146. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rabinowitz, J.D.; White, E. Autophagy and metabolism. Science 2010, 330, 1344–1348. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lin, L.; Baehrecke, E.H. Autophagy, cell death, and cancer. Mol. Cell. Oncol. 2015, 2, e985913. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Su, Z.; Yang, Z.; Xu, Y.; Chen, Y.; Yu, Q. Apoptosis, autophagy, necroptosis, and cancer metastasis. Mol. Cancer 2015, 14, 48. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jiang, Q.; Rao, X.; Kim, C.Y.; Freiser, H.; Zhang, Q.; Jiang, Z.; Li, G. γ-Tocotrienol induces apoptosis and autophagy in prostate cancer cells by increasing intracellular dihydrosphingosine and dihydroceramide. Int. J. Cancer 2012, 130, 685–693. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tiwari, R.V.; Parajuli, P.; Sylvester, P.W. γ-Tocotrienol-induced autophagy in malignant mammary cancer cells. Exp. Biol. Med. 2014, 239, 33–44. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cui, Q.; Tashiro, S.; Onodera, S.; Minami, M.; Ikejima, T. Autophagy preceded apoptosis in oridonin-treated human breast cancer MCF-7 cells. Biol. Pharm. Bull. 2007, 30, 859–864. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Safe, S.; Lee, S.O.; Jin, U.H. Role of the aryl hydrocarbon receptor in carcinogenesis and potential as a drug target. Toxicol. Sci. 2013, 135, 1–16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pang, P.H.; Lin, Y.H.; Lee, Y.H.; Hou, H.H.; Hsu, S.P.; Juan, S.H. Molecular mechanisms of p21 and p27 induction by 3-methylcholanthrene, an aryl-hydrocarbon receptor agonist, involved in antiproliferation of human umbilical vascular endothelial cells. J. Cell. Physiol. 2008, 215, 161–171. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Matikainen, T.; Perez, G.I.; Jurisicova, A.; Pru, J.K.; Schlezinger, J.J.; Ryu, H.Y.; Laine, J.; Sakai, T.; Korsmeyer, S.J.; Casper, R.F.; et al. Aromatic hydrocarbon receptor-driven Bax gene expression is required for premature ovarian failure caused by biohazardous environmental chemicals. Nat. Genet. 2001, 28, 355–360. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Contador-Troca, M.; Alvarez-Barrientos, A.; Barrasa, E.; Rico-Leo, E.M.; Catalina-Fernández, I.; Menacho-Márquez, M.; Bustelo, X.R.; García-Borrón, J.C.; Gómez-Durán, A.; Sáenz-Santamaría, J.; et al. The dioxin receptor has tumor suppressor activity in melanoma growth and metastasis. Carcinogenesis 2013, 34, 2683–2693. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cheng, Y.H.; Li, L.A.; Lin, P.; Cheng, L.C.; Hung, C.H.; Chang, N.W.; Lin, C. Baicalein induces G1 arrest in oral cancer cells by enhancing the degradation of cyclin D1 and activating AhR to decrease Rb phosphorylation. Toxicol. Appl. Pharmacol. 2012, 263, 360–367. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Manach, C.; Scalbert, A.; Morand, C.; Remesy, C.; Jimenez, L. Polyphenols: Food sources and bioavailability. Am. J. Clin. Nutr. 2004, 79, 727–747. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Burns, J.; Yokota, T.; Ashihara, H.; Lean, M.E.; Crozier, A. Plant foods and herbal sources of resveratrol. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2002, 50, 3337–3340. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Singh, B.N.; Shankar, S.; Srivastava, R.K. Green tea catechin, epigallocatechin-3-gallate (EGCG): Mechanisms, perspectives and clinical applications. Biochem. Pharmacol. 2011, 82, 1807–1821. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Singh, C.K.; Ndiaye, M.A.; Ahmad, N. Resveratrol and cancer: Challenges for clinical translation. Biochim. Biophys. Acta 2015, 1852, 1178–1185. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shimizu, M.; Shirakami, Y.; Moriwaki, H. Targeting receptor tyrosine kinases for chemoprevention by green tea catechin, EGCG. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2008, 9, 1034–1049. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Provinciali, M.; Re, F.; Donnini, A.; Orlando, F.; Bartozzi, B.; di Stasio, G.; Smorlesi, A. Effect of resveratrol on the development of spontaneous mammary tumors in HER-2/neu transgenic mice. Int. J. Cancer 2005, 115, 36–45. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cho, I.J.; Ahn, J.Y.; Kim, S.; Choi, M.S.; Ha, T.Y. Resveratrol attenuates the expression of HMG-CoA reductase mRNA in hamsters. Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 2008, 367, 190–194. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wong, D.H.; Villanueva, J.A.; Cress, A.B.; Sokalska, A.; Ortega, I.; Duleba, A.J. Resveratrol inhibits the mevalonate pathway and potentiates the antiproliferative effects of simvastatin in rat theca-interstitial cells. Fertil. Steril. 2011, 96, 1252–1258. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dinkova-Kostova, A.T.; Talalay, P. NAD(P)H:quinone acceptor oxidoreductase 1 (NQO1), a multifunctional antioxidant enzyme and exceptionally versatile cytoprotector. Arch. Biochem. Biophys. 2010, 501, 116–123. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kensler, T.W.; Wakabayashi, N. Nrf2: Friend or foe for chemoprevention? Carcinogenesis 2010, 31, 90–99. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sriram, N.; Kalayarasan, S.; Sudhandiran, G. Epigallocatechin-3-gallate augments antioxidant activities and inhibits inflammation during bleomycin-induced experimental pulmonary fibrosis through Nrf2-Keap1 signaling. Pulm. Pharmacol. Ther. 2009, 22, 221–236. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hsieh, T.C.; Lu, X.; Wang, Z.; Wu, J.M. Induction of quinone reductase NQO1 by resveratrol in human K562 cells involves the antioxidant response element ARE and is accompanied by nuclear translocation of transcription factor Nrf2. Med. Chem. 2006, 2, 275–285. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Hsieh, T.C.; Elangovan, S.; Wu, J.M. Differential suppression of proliferation in MCF-7 and MDA-MB-231 breast cancer cells exposed to α-, γ- and delta-tocotrienols is accompanied by altered expression of oxidative stress modulatory enzymes. Anticancer Res. 2010, 30, 4169–4176. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Cao, J.; Chen, J.; Xie, L.; Wang, J.; Feng, C.; Song, J. Protective properties of sesamin against fluoride-induced oxidative stress and apoptosis in kidney of carp (Cyprinus carpio) via JNK signaling pathway. Aquat. Toxicol. 2015, 167, 180–190. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shimizu, S.; Akimoto, K.; Shinmen, Y.; Kawashima, H.; Sugano, M.; Yamada, H. Sesamin is a potent and specific inhibitor of δ5 desaturase in polyunsaturated fatty acid biosynthesis. Lipids 1991, 26, 512–516. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hirose, N.; Inoue, T.; Nishihara, K.; Sugano, M.; Akimoto, K.; Shimizu, S.; Yamada, H. Inhibition of cholesterol absorption and synthesis in rats by sesamin. J. Lipid Res. 1991, 32, 629–638. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Nakano, D.; Itoh, C.; Ishii, F.; Kawanishi, H.; Takaoka, M.; Kiso, Y.; Tsuruoka, N.; Tanaka, T.; Matsumura, Y. Effects of sesamin on aortic oxidative stress and endothelial dysfunction in deoxycorticosterone acetate-salt hypertensive rats. Biol. Pharm. Bull. 2003, 26, 1701–1705. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fujikawa, T.; Kanada, N.; Shimada, A.; Ogata, M.; Suzuki, I.; Hayashi, I.; Nakashima, K. Effect of sesamin in Acanthopanax senticosus HARMS on behavioral dysfunction in rotenone-induced parkinsonian rats. Biol. Pharm. Bull. 2005, 28, 169–172. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yokota, T.; Matsuzaki, Y.; Koyama, M.; Hitomi, T.; Kawanaka, M.; Enoki-Konishi, M.; Okuyama, Y.; Takayasu, J.; Nishino, H.; Nishikawa, A.; et al. Sesamin, a lignan of sesame, down-regulates cyclin D1 protein expression in human tumor cells. Cancer Sci. 2007, 98, 1447–1453. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Monteiro, E.M.; Chibli, L.A.; Yamamoto, C.H.; Pereira, M.C.; Vilela, F.M.; Rodarte, M.P.; Pinto, M.A.; do Amaral Mda, P.; Silverio, M.S.; Araujo, A.L.; et al. Antinociceptive and anti-inflammatory activities of the sesame oil and sesamin. Nutrients 2014, 6, 1931–1944. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- You, C.S.; Sontag, T.J.; Swanson, J.E.; Parker, R.S. Long-chain carboxychromanols are the major metabolites of tocopherols and tocotrienols in A549 lung epithelial cells but not HepG2 cells. J. Nutr. 2005, 135, 227–232. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Ikeda, S.; Toyoshima, K.; Yamashita, K. Dietary sesame seeds elevate α- and γ-tocotrienol concentrations in skin and adipose tissue of rats fed the tocotrienol-rich fraction extracted from palm oil. J. Nutr. 2001, 131, 2892–2897. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Sontag, T.J.; Parker, R.S. Cytochrome P450 ω-hydroxylase pathway of tocopherol catabolism. Novel mechanism of regulation of vitamin E status. J. Biol. Chem. 2002, 277, 25290–25296. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Parker, R.S.; Sontag, T.J.; Swanson, J.E. Cytochrome P4503A-dependent metabolism of tocopherols and inhibition by sesamin. Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 2000, 277, 531–534. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Birringer, M.; Pfluger, P.; Kluth, D.; Landes, N.; Brigelius-Flohé, R. Identities and differences in the metabolism of tocotrienols and tocopherols in HepG2 cells. J. Nutr. 2002, 132, 3113–3118. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Freiser, H.; Jiang, Q. Γ-tocotrienol and γ-tocopherol are primarily metabolized to conjugated 2-(β-carboxyethyl)-6-hydroxy-2,7,8-trimethylchroman and sulfated long-chain carboxychromanols in rats. J. Nutr. 2009, 139, 884–889. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Abe, C.; Uchida, T.; Ohta, M.; Ichikawa, T.; Yamashita, K.; Ikeda, S. Cytochrome P450-dependent metabolism of vitamin E isoforms is a critical determinant of their tissue concentrations in rats. Lipids 2007, 42, 637–645. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Akl, M.R.; Ayoub, N.M.; Abuasal, B.S.; Kaddoumi, A.; Sylvester, P.W. Sesamin synergistically potentiates the anticancer effects of γ-tocotrienol in mammary cancer cell lines. Fitoterapia 2013, 84, 347–359. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Henderson, A.J.; Ollila, C.A.; Kumar, A.; Borresen, E.C.; Raina, K.; Agarwal, R.; Ryan, E.P. Chemopreventive properties of dietary rice bran: Current status and future prospects. Adv. Nutr. 2012, 3, 643–653. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tantamango, Y.M.; Knutsen, S.F.; Beeson, W.L.; Fraser, G.; Sabate, J. Foods and food groups associated with the incidence of colorectal polyps: The Adventist Health Study. Nutr. Cancer 2011, 63, 565–572. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Miyazawa, T.; Shibata, A.; Sookwong, P.; Kawakami, Y.; Eitsuka, T.; Asai, A.; Oikawa, S.; Nakagawa, K. Antiangiogenic and anticancer potential of unsaturated vitamin E (tocotrienol): A review. J. Nutr. Biochem. 2009, 20, 79–86. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Eitsuka, T.; Nakagawa, K.; Miyazawa, T. Down-regulation of telomerase activity in DLD-1 human colorectal adenocarcinoma cells by tocotrienol. Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 2006, 348, 170–175. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kawabata, K.; Yamamoto, T.; Hara, A.; Shimizu, M.; Yamada, Y.; Matsunaga, K.; Tanaka, T.; Mori, H. Modifying effects of ferulic acid on azoxymethane-induced colon carcinogenesis in F344 rats. Cancer Lett. 2000, 157, 15–21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ohnishi, M.; Matuo, T.; Tsuno, T.; Hosoda, A.; Nomura, E.; Taniguchi, H.; Sasaki, H.; Morishita, H. Antioxidant activity and hypoglycemic effect of ferulic acid in STZ-induced diabetic mice and KK-Ay mice. Biofactors 2004, 21, 315–319. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xu, X.; Xiao, H.; Zhao, J.; Zhao, T. Cardioprotective effect of sodium ferulate in diabetic rats. Int. J. Med. Sci. 2012, 9, 291–300. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yan, J.J.; Cho, J.Y.; Kim, H.S.; Kim, K.L.; Jung, J.S.; Huh, S.O.; Suh, H.W.; Kim, Y.H.; Song, D.K. Protection against beta-amyloid peptide toxicity in vivo with long-term administration of ferulic acid. Br. J. Pharmacol. 2001, 133, 89–96. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhao, Z.; Egashira, Y.; Sanada, H. Ferulic acid sugar esters are recovered in rat plasma and urine mainly as the sulfoglucuronide of ferulic acid. J. Nutr. 2003, 133, 1355–1361. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Eitsuka, T.; Tatewaki, N.; Nishida, H.; Nakagawa, K.; Miyazawa, T. A combination of δ-tocotrienol and ferulic acid synergistically inhibits telomerase activity in DLD-1 human colorectal adenocarcinoma cells. J. Nutr. Sci. Vitaminol. 2016, 62, 281–287. [Google Scholar]
- Sookwong, P.; Nakagawa, K.; Yamaguchi, Y.; Miyazawa, T.; Kato, S.; Kimura, F.; Miyazawa, T. Tocotrienol distribution in foods: Estimation of daily tocotrienol intake of Japanese population. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2010, 58, 3350–3355. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hiura, Y.; Tachibana, H.; Arakawa, R.; Aoyama, N.; Okabe, M.; Sakai, M.; Yamada, K. Specific accumulation of γ- and δ-tocotrienols in tumor and their antitumor effect in vivo. Nutr. Biochem. 2009, 20, 607–613. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yap, S.P.; Yuen, K.H.; Wong, J.W. Pharmacokinetics and bioavailability of α-, γ- and δ-tocotrienols under different food status. J. Pharm. Pharmacol. 2001, 53, 67–71. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nesaretnam, K.; Selvaduray, K.R.; Abdul Razak, G.; Veerasenan, S.D.; Gomez, P.A. Effectiveness of tocotrienol-rich fraction combined with tamoxifen in the management of women with early breast cancer: A pilot clinical trial. Breast Cancer Res. 2010, 12, R81. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rice, S.; Whitehead, S.A. Phytoestrogens oestrogen synthesis and breast cancer. J. Steroid Biochem. Mol. Biol. 2008, 108, 186–195. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lindberg, K.; Helguero, L.A.; Omoto, Y.; Gustafsson, J.Å.; Haldosén, L.A. Estrogen receptor β represses Akt signaling in breast cancer cells via downregulation of HER2/HER3 and upregulation of PTEN: Implications for tamoxifen sensitivity. Breast Cancer Res. 2011, 13, R43. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Comitato, R.; Nesaretnam, K.; Leoni, G.; Ambra, R.; Canali, R.; Bolli, A.; Marino, M.; Virgili, F. A novel mechanism of natural vitamin E tocotrienol activity: Involvement of ERβ signal transduction. Am. J. Physiol. Endocrinol. Metab. 2009, 297, E427–E437. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Comitato, R.; Leoni, G.; Canali, R.; Ambra, R.; Nesaretnam, K.; Virgili, F. Tocotrienols activity in MCF-7 breast cancer cells: Involvement of ERβ signal transduction. Mol. Nutr. Food Res. 2010, 54, 669–678. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]





© 2016 by the authors; licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC-BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Eitsuka, T.; Tatewaki, N.; Nishida, H.; Nakagawa, K.; Miyazawa, T. Synergistic Anticancer Effect of Tocotrienol Combined with Chemotherapeutic Agents or Dietary Components: A Review. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2016, 17, 1605. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms17101605
Eitsuka T, Tatewaki N, Nishida H, Nakagawa K, Miyazawa T. Synergistic Anticancer Effect of Tocotrienol Combined with Chemotherapeutic Agents or Dietary Components: A Review. International Journal of Molecular Sciences. 2016; 17(10):1605. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms17101605
Chicago/Turabian StyleEitsuka, Takahiro, Naoto Tatewaki, Hiroshi Nishida, Kiyotaka Nakagawa, and Teruo Miyazawa. 2016. "Synergistic Anticancer Effect of Tocotrienol Combined with Chemotherapeutic Agents or Dietary Components: A Review" International Journal of Molecular Sciences 17, no. 10: 1605. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms17101605
APA StyleEitsuka, T., Tatewaki, N., Nishida, H., Nakagawa, K., & Miyazawa, T. (2016). Synergistic Anticancer Effect of Tocotrienol Combined with Chemotherapeutic Agents or Dietary Components: A Review. International Journal of Molecular Sciences, 17(10), 1605. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms17101605