Probiotics Differently Affect Gut-Associated Lymphoid Tissue Indolamine-2,3-Dioxygenase mRNA and Cerebrospinal Fluid Neopterin Levels in Antiretroviral-Treated HIV-1 Infected Patients: A Pilot Study
Abstract
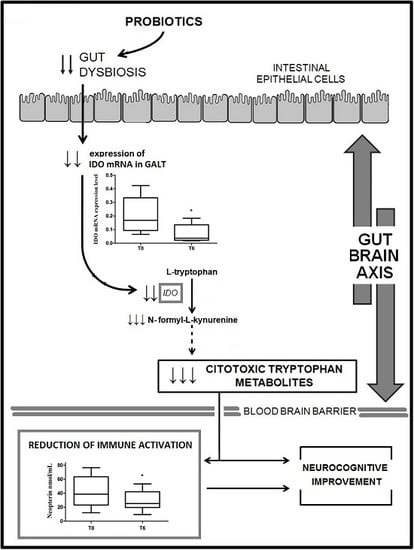
:1. Introduction
2. Results
2.1. Demographic and Clinical Characteristics of HIV-1-Positive Patients
2.2. IDO mRNA Expression
2.3. Neopterin Levels
3. Discussion
4. Materials and Methods
4.1. Patients
4.2. Samples
4.3. ELISA Assay
4.4. Real-Time PCR
4.5. Statistical Analysis
5. Conclusions
Acknowledgments
Author Contributions
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Routy, J.P.; Mehraj, V.; Vyboh, K.; Cao, W.; Kema, I.; Jenabian, M.A. Clinical relevance of kynurenine pathway in HIV/AIDS: An immune checkpoint at the crossroads of metabolism and inflammation. AIDS Rev. 2015, 17, 96–106. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Vyboh, K.; Jenabian, M.A.; Mehraj, V.; Routy, J.P. HIV and the gut microbiota, partners in crime: Breaking the vicious cycle to unearth new therapeutic targets. J. Immunol. Res. 2015, 2015, 614127. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Carabotti, M.; Scirocco, A.; Maselli, M.A.; Severi, C. The gut-brain axis: Interactions between enteric microbiota, central and enteric nervous systems. Ann. Gastroenterol. 2015, 28, 203–209. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Montiel-Castro, A.J.; González-Cervantes, R.M.; Bravo-Ruiseco, G.; Pacheco-López, G. The microbiota-gu-brain axis: Neurobehavioral correlates, health and sociality. Front. Integr. Neurosci. 2013, 7, 70. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Atarashi, K.; Tanoue, T.; Shima, T.; Imaoka, A.; Kuwahara, T.; Momose, Y.; Cheng, G.; Yamasaki, S.; Saito, T.; Ohba, Y.; et al. Induction of colonic regulatory T cells by indigenous Clostridium species. Science 2011, 331, 337–341. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Favre, D.; Mold, J.; Hunt, P.W.; Kanwar, B.; Loke, P.; Seu, L.; Barbour, J.D.; Lowe, M.M.; Jayawardene, A.; Aweeka, F.; et al. Tryptophan catabolism by indoleamine 2,3-dioxygenase 1 alters the balance of TH17 to regulatory T cells in HIV disease. Sci. Transl. Med. 2010, 2, 32–36. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Serrano-Villar, S.; Rojo, D.; Martínez-Martínez, M.; Deusch, S.; Vázquez-Castellanos, J.F.; Sainz, T.; Vera, M.; Moreno, S.; Estrada, V.; Gosalbes, M.J.; et al. HIV infection results in metabolic alterations in the gut microbiota different from those induced by other diseases. Sci. Rep. 2016, 6, 26192. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Boasso, A. Wounding the immune system with its own blade: HIV-induced tryptophan catabolism and pathogenesis. Curr. Med. Chem. 2011, 18, 2247–2256. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Boasso, A.; Shearer, G.M.; Chougnet, C. Immune dysregulation in human immunodeficiency virus infection: Know it, fix it, prevent it? J. Intern. Med. 2009, 265, 78–96. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Heyes, M.P.; Brew, B.J.; Martin, A.; Price, R.W.; Salazar, A.M.; Sidtis, J.J.; Yergey, J.A.; Mouradian, M.M.; Sadler, A.E.; Keilp, J.; et al. Quinolinic acid in cerebrospinal fluid and serum in HIV-1 infection: Relationship to clinical and neurological status. Ann. Neurol. 1991, 29, 202–209. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Heyes, M.P.; Ellis, R.J.; Ryan, L.; Childers, M.E.; Grant, I.; Wolfson, T.; Archibald, S.; Jernigan, T.L.; HNRC Group; HIV Neurobehavioral Research Center. Elevated cerebrospinal fluid quinolinic acid levels are associated with region-specific cerebral volume loss in HIV infection. Brain 2001, 124, 1033–1042. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Valle, M.; Price, R.W.; Nilsson, A.; Heyes, M.; Verotta, D. CSF quinolinic acid levels are determined by local HIV infection: Cross-sectional analysis and modelling of dynamics following antiretroviral therapy. Brain 2004, 127, 1047–1060. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- O’Mahony, S.M.; Clarke, G.; Borre, Y.E.; Dinan, T.G.; Cryan, J.F. Serotonin, tryptophan metabolism and the brain-gut-microbiome axis. Behav. Brain Res. 2015, 277, 32–48. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Boasso, A.; Herbeuval, J.P.; Hardy, A.W.; Anderson, S.A.; Dolan, M.J.; Fuchs, D.; Shearer, G.M. HIV inhibits CD4+ T-cell proliferation by inducing indoleamine 2,3-dioxygenase in plasmacytoid dendritic cells. Blood 2007, 109, 3351–3359. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Reeves, R.K.; Rajakumar, P.A.; Evans, T.I.; Connole, M.; Gillis, J.; Wong, F.E.; Kuzmichev, Y.V.; Carville, A.; Johnson, R.P. Gut inflammation and indoleamine deoxygenase inhibit IL-17 production and promote cytotoxic potential in NKp44+ mucosal NK cells during SIV infection. Blood 2011, 11, 3321–3330. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vujkovic-Cvijin, I.; Dunham, R.M.; Iwai, S.; Maher, M.C.; Albright, R.G.; Broadhurst, M.J.; Hernandez, R.D.; Lederman, M.M.; Huang, Y.; Somsouk, M.; et al. Dysbiosis of the gut microbiota is associated with HIV disease progression and tryptophan catabolism. Sci. Transl. Med. 2013, 5, 193ra91. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Griffin, D.E.; McArthur, J.C.; Cornblath, D.R. Neopterin and interferon-gamma in serum and cerebrospinal fluid of patients with HIV-associated neurologic disease. Neurology 1991, 41, 69–74. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sönnerborg, A.B.; von Stedingk, L.V.; Hansson, L.O.; Strannegård, O.O. Elevated neopterin and β2-microglobulin levels in blood and cerebrospinal fluid occur early in HIV-1 infection. AIDS 1989, 3, 277–283. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fuchs, D.; Chiodi, F.; Albert, J.; Asjö, B.; Hagberg, L.; Hausen, A.; Norkrans, G.; Reibnegger, G.; Werner, E.R.; Wachter, H. Neopterin concentrations in cerebrospinal fluid and serum of individuals infected with HIV-1. AIDS 1989, 3, 285–288. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Eden, A.; Price, R.W.; Spudich, S.; Fuchs, D.; Hagberg, L.; Gisslén, M. Immune activation of the central nervous system is still present after >4 years of effective HAART. J. Infect. Dis. 2007, 196, 1779–1783. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yilmaz, A.; Yiannoutsos, C.T.; Fuchs, D.; Price, R.W.; Crozier, K.; Hagberg, L.; Spudich, S.; Gisslén, M. Cerebrospinal fluid neopterin decay characteristics after initiation of antiretroviral therapy. J. Neuroinflamm. 2013, 10, 10–62. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hagberg, L.; Cinque, P.; Gisslen, M.; Brew, B.J.; Spudich, S.; Bestetti, A. Cerebrospinal fluid neopterin: An informative biomarker of central nervous system immune activation in HIV-1 infection. AIDS Res. Ther. 2010, 7, 15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Calcagno, A.; Atzori, C.; Romito, A.; Vai, D.; Audagnotto, S.; Stella, M.L.; Montrucchio, C.; Imperiale, D.; di Perri, G.; Bonora, S. Blood brain barrier impairment is associated with cerebrospinal fluid markers of neuronal damage in HIV-positive patients. J. Neurovirol. 2016, 22, 88–92. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Edén, A.; Marcotte, T.D.; Heaton, R.K.; Nilsson, S.; Zetterberg, H.; Fuchs, D.; Franklin, D.; Price, R.W.; Grant, I.; Letendre, S.L.; et al. Increased intrathecal immune activation in virally suppressed HIV-1 infected patients with neurocognitive impairment. PLoS ONE 2016, 11, e0157160. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Andersson, L.M.; Hagbwerg, L.; Fuchs, D.; Svennerholm, B.; Gisslen, M. Increased blood brain-barrier permeability in neuroasymptomatic HIV-1-infected individuals-correlation with cerebrospinal fluid HIV-1 RNA and neopterin levels. J. Neurovirol. 2001, 7, 542–547. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Schroecksnadel, K.; Sarcletti, M.; Winkler, C.; Mumelter, B.; Weiss, G.; Fuchs, D.; Kemmler, G.; Zangerle, R. Quality of life and immune activation in patients with HIV-infection. Brain Behav. Immun. 2008, 22, 881–889. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Huber, C.; Batchelor, J.R.; Fuchs, D.; Hausen, A.; Lang, A.; Niederwieser, D.; Reibnegger, G.; Swetly, P.; Troppmair, J.; Wachter, H. Immune response-associated production of neopterin. Release from macrophages primarily under control of interferon-γ. J. Exp. Med. 1984, 160, 310–316. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Borre, Y.E.; Moloney, R.D.; Clarke, G.; Dinan, T.G.; Cryan, J.F. The impact of microbiota on brain and behavior: Mechanisms & therapeutic potential. Adv. Exp. Med. Biol. 2014, 817, 373–403. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Cryan, J.F.; Dinan, T.G. Mind-altering microorganisms: The impact of the gut microbiota on brain and behaviour. Nat. Rev. Neurosci. 2012, 13, 701–712. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mayer, E.A. Gut feelings: The emerging biology of gut–brain communication. Nat. Rev. Neurosci. 2011, 12, 453–466. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Frazier, T.H.; DiBaise, J.K.; McClain, C.J. Gut microbiota, intestinal permeability, obesity-induced inflammation, and liver injury. J. Parenter. Enter. Nutr. 2011, 35, 14S–20S. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Camilleri, M.; Lasch, K.; Zhou, W. Irritable bowel syndrome: Methods, mechanisms, and pathophysiology. The confluence of increased permeability, inflammation, and pain in irritable bowel syndrome. Am. J. Physiol. Gastrointest. Liver Physiol. 2012, 303, G775–G785. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Matricon, J.; Meleine, M.; Gelot, A.; Piche, T.; Dapoigny, M.; Muller, E.; Ardid, D. Review article: Associations between immune activation, intestinal permeability and the irritable bowel syndrome. Aliment. Pharmacol. Ther. 2012, 36, 1009–1031. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Simrén, M.; Barbara, G.; Flint, H.J.; Spiegel, B.M.; Spiller, R.C.; Vanner, S.; Verdu, E.F.; Whorwell, P.J.; Zoetendal, E.G.; Rome Foundation Committee. Intestinal microbiota in functional bowel disorders: A Rome foundation report. Gut 2013, 62, 159–176. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Round, J.L.; Mazmanian, S.K. The gut microbiota shapes intestinal immune responses during health and disease. Nat. Rev. Immunol. 2009, 9, 313–323. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ringel, Y.; Maharshak, N. Intestinal microbiota and immune function in the pathogenesis of irritable bowel syndrome. Am. J. Physiol. Gastrointest. Liver Physiol. 2013, 305, G529–G541. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hughes, P.A.; Zola, H.; Penttila, I.A.; Blackshaw, L.A.; Andrews, J.M.; Krumbiegel, D. Immune activation in irritable bowel syndrome: Can neuroimmune interactions explain symptoms? Am. J. Gastroenterol. 2013, 108, 1066–1074. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Palego, L.; Betti, L.; Rossi, A.; Giannaccini, G. Tryptophan biochemistry: Structural, nutritional, metabolic, and medical aspects in humans. J. Amino Acids 2016, 2016, 8952520. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Murray, M.F. Insights into therapy: Tryptophan oxidation and HIV infection. Sci. Transl. Med. 2010, 2, 32ps23. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Alexaki, A.; Liu, Y.; Wigdahl, B. Cellular reservoirs of HIV-1 and their role in viral persistence. Curr. HIV Res. 2008, 6, 388–400. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Coleman, C.M.; Wu, L. HIV interactions with monocytes and dendritic cells: Viral latency and reservoirs. Retrovirology 2009, 6, 51. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Epelman, S.; Lavine, K.J.; Randolph, G.J. Origin and functions of tissue macrophages. Immunity 2014, 41, 21–35. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Distrutti, E.; O’Reilly, J.A.; McDonald, C.; Cipriani, S.; Renga, B.; Lynch, M.A.; Fiorucci, S. Modulation of intestinal microbiota by the probiotic VSL#3 resets brain gene expression and ameliorates the age-related deficit in LTP. PLoS ONE 2014, 9, e106503. [Google Scholar]
- Vujkovic-Cvijin, I.; Swainson, L.A.; Chu, S.N.; Ortiz, A.M.; Santee, C.A.; Petriello, A.; Dunham, R.M.; Fadrosh, D.W.; Lin, D.L.; Faruqi, A.A.; et al. Gut-resident lactobacillus abundance associates with IDO1 inhibition and Th17 dynamics in SIV-infected macaques. Cell Rep. 2015, 13, 1589–1597. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mardini, H.E.; Grigorian, A.Y. Probiotic mix VSL#3 is effective adjunctive therapy for mild to moderately active ulcerative colitis: A meta-analysis. Inflamm. Bowel. Dis. 2014, 20, 1562–1567. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Kumar, R.; Singh, J. The emerging therapy with probiotics in the management of inflammatory bowel disease: Current status. Int. J. Basic Clin. Pharmacol. 2013, 2, 360–367. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Scagnolari, C.; Monteleone, K.; Selvaggi, C.; Pierangeli, A.; D’Ettorre, G.; Mezzaroma, I.; Turriziani, O.; Gentile, M.; Vullo, V.; Antonelli, G. ISG15 expression correlates with HIV-1 viral load and with factors regulating T cell response. Immunobiology 2016, 221, 282–290. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]


| IDO mRNA T0 | IDO mRNA T6 | |
|---|---|---|
| Neopterin T0 | p = 0.004; r = 0.94 | NA |
| Neopterin T6 | NA | p = 0.54; r = −0.31 |
© 2016 by the authors; licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC-BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Scagnolari, C.; Corano Scheri, G.; Selvaggi, C.; Schietroma, I.; Najafi Fard, S.; Mastrangelo, A.; Giustini, N.; Serafino, S.; Pinacchio, C.; Pavone, P.; et al. Probiotics Differently Affect Gut-Associated Lymphoid Tissue Indolamine-2,3-Dioxygenase mRNA and Cerebrospinal Fluid Neopterin Levels in Antiretroviral-Treated HIV-1 Infected Patients: A Pilot Study. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2016, 17, 1639. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms17101639
Scagnolari C, Corano Scheri G, Selvaggi C, Schietroma I, Najafi Fard S, Mastrangelo A, Giustini N, Serafino S, Pinacchio C, Pavone P, et al. Probiotics Differently Affect Gut-Associated Lymphoid Tissue Indolamine-2,3-Dioxygenase mRNA and Cerebrospinal Fluid Neopterin Levels in Antiretroviral-Treated HIV-1 Infected Patients: A Pilot Study. International Journal of Molecular Sciences. 2016; 17(10):1639. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms17101639
Chicago/Turabian StyleScagnolari, Carolina, Giuseppe Corano Scheri, Carla Selvaggi, Ivan Schietroma, Saeid Najafi Fard, Andrea Mastrangelo, Noemi Giustini, Sara Serafino, Claudia Pinacchio, Paolo Pavone, and et al. 2016. "Probiotics Differently Affect Gut-Associated Lymphoid Tissue Indolamine-2,3-Dioxygenase mRNA and Cerebrospinal Fluid Neopterin Levels in Antiretroviral-Treated HIV-1 Infected Patients: A Pilot Study" International Journal of Molecular Sciences 17, no. 10: 1639. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms17101639
APA StyleScagnolari, C., Corano Scheri, G., Selvaggi, C., Schietroma, I., Najafi Fard, S., Mastrangelo, A., Giustini, N., Serafino, S., Pinacchio, C., Pavone, P., Fanello, G., Ceccarelli, G., Vullo, V., & D’Ettorre, G. (2016). Probiotics Differently Affect Gut-Associated Lymphoid Tissue Indolamine-2,3-Dioxygenase mRNA and Cerebrospinal Fluid Neopterin Levels in Antiretroviral-Treated HIV-1 Infected Patients: A Pilot Study. International Journal of Molecular Sciences, 17(10), 1639. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms17101639