A Melting Curve-Based Multiplex RT-qPCR Assay for Simultaneous Detection of Four Human Coronaviruses
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Results
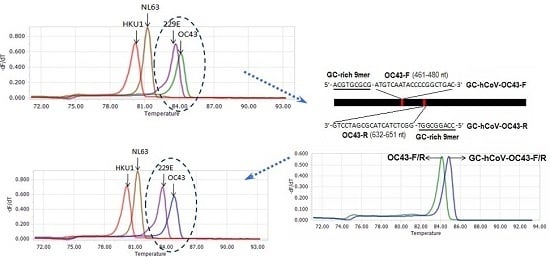
2.1. Selection of Primer Sets, and Modification of OC43 Primers
2.2. Specificity of the Melting Curve-Based Multiplex RT-qPCR
2.3. Sensitivity of the Melting Curve-Based Multiplex RT-qPCR
2.4. Evaluation and Confirmation of the Melting Curve-Based Multiplex RT-qPCR by Sequencing
3. Discussion
4. Materials and Methods
4.1. Virus Strains and Patient Samples
4.2. Primer Design
4.3. RT-qPCR and Melting Curve Analysis
4.4. Specificity and Sensitivity of the Melting Curve-Based Multiplex RT-qPCR
4.5. Evaluation of the Melting Curve-Based Multiplex RT-qPCR Using Clinical Samples
Supplementary Materials
Acknowledgments
Author Contributions
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Pyrc, K.; Jebbink, M.F.; Berkhout, B.; van der Hoek, L. Genome structure and transcriptional regulation of human coronavirus NL63. Virol. J. 2004, 1, 7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Su, S.; Wong, G.; Shi, W.; Liu, J.; Lai, A.C.; Zhou, J.; Liu, W.; Bi, Y.; Gao, G.F. Epidemiology, genetic recombination, and pathogenesis of coronaviruses. Trends Microbiol. 2016, 24, 490–502. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hamre, D.; Procknow, J.J. A new virus isolated from the human respiratory tract. Proc. Soc. Exp. Biol. Med. 1966, 121, 190–193. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- McIntosh, K.; Dees, J.H.; Becker, W.B.; Kapikian, A.Z.; Chanock, R.M. Recovery in tracheal organ cultures of novel viruses from patients with respiratory disease. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 1967, 57, 933–940. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Woo, P.C.; Lau, S.K.; Chu, C.M.; Chan, K.H.; Tsoi, H.W.; Huang, Y.; Wong, B.H.; Poon, R.W.; Cai, J.J.; Luk, W.K.; et al. Characterization and complete genome sequence of a novel coronavirus, coronavirus HKU1, from patients with pneumonia. J. Virol. 2005, 79, 884–895. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Van der Hoek, L.; Pyrc, K.; Jebbink, M.F.; Vermeulen-Oost, W.; Berkhout, R.J.; Wolthers, K.C.; Wertheim-van Dillen, P.M.; Kaandorp, J.; Spaargaren, J.; Berkhout, B. Identification of a new human coronavirus. Nat. Med. 2004, 10, 368–373. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Drosten, C.; Gunther, S.; Preiser, W.; van der Werf, S.; Brodt, H.R.; Becker, S.; Rabenau, H.; Panning, M.; Kolesnikova, L.; Fouchier, R.A.; et al. Identification of a novel coronavirus in patients with severe acute respiratory syndrome. N. Engl. J. Med. 2003, 348, 1967–1976. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ksiazek, T.G.; Erdman, D.; Goldsmith, C.S.; Zaki, S.R.; Peret, T.; Emery, S.; Tong, S.; Urbani, C.; Comer, J.A.; Lim, W.; et al. A novel coronavirus associated with severe acute respiratory syndrome. N. Engl. J. Med. 2003, 348, 1953–1966. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Raj, V.S.; Osterhaus, A.D.; Fouchier, R.A.; Haagmans, B.L. MERS: Emergence of a novel human coronavirus. Curr. Opin. Virol. 2014, 5, 58–62. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, Y.W.; Yuan, L.C.; Zhang, Y.M.; Zhang, X.P.; Zheng, M.H.; Kyaw, M.H. Burden of respiratory syncytial virus infections in China: Systematic review and meta-analysis. J. Glob. Health 2015, 5, 216–222. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lepiller, Q.; Barth, H.; Lefebvre, F.; Herbrecht, R.; Lutz, P.; Kessler, R.; Fafi-Kremer, S.; Stoll-Keller, F. High incidence but low burden of coronaviruses and preferential associations between respiratory viruses. J. Clin. Microbiol. 2013, 51, 3039–3046. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gaunt, E.R.; Hardie, A.; Claas, E.C.J.; Simmonds, P.; Templeton, K.E. Epidemiology and clinical presentations of the four human coronaviruses 229E, HKU1, NL63, and OC43 detected over 3 years using a novel multiplex real-time PCR method. J. Clin. Microbiol. 2010, 48, 2940–2947. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Matoba, Y.; Abiko, C.; Ikeda, T.; Aoki, Y.; Suzuki, Y.; Yahagi, K.; Matsuzaki, Y.; Itagaki, T.; Katsushima, F.; Katsushima, Y.; et al. Detection of the human coronavirus 229E, HKU1, NL63, and OC43 between 2010 and 2013 in Yamagata, Japan. Jpn. J. Infect. Dis. 2015, 68, 138–141. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wevers, B.A.; van der Hoek, L. Recently discovered human coronaviruses. Clin. Lab. Med. 2009, 29, 715–724. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pene, F.; Merlat, A.; Vabret, A.; Rozenberg, F.; Buzyn, A.; Dreyfus, F.; Cariou, A.; Freymuth, F.; Lebon, P. Coronavirus 229E-related pneumonia in immunocompromised patients. Clin. Infect. Dis. 2003, 37, 929–932. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Oosterhof, L.; Christensen, C.B.; Sengelov, H. Fatal lower respiratory tract disease with human corona virus NL63 in an adult haematopoietic cell transplant recipient. Bone Marrow Transplant. 2010, 45, 1115–1116. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Geller, C.; Varbanov, M.; Duval, R.E. Human coronaviruses: Insights into environmental resistance and its influence on the development of new antiseptic strategies. Viruses 2012, 4, 3044–3068. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lehmann, C.; Wolf, H.; Xu, J.; Zhao, Q.; Shao, Y.; Motz, M.; Lindner, P. A line immunoassay utilizing recombinant nucleocapsid proteins for detection of antibodies to human coronaviruses. Diagn. Microbiol. Infect. Dis. 2008, 61, 40–48. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- McIntosh, K.; McQuillin, J.; Reed, S.E.; Gardner, P.S. Diagnosis of human coronavirus infection by immunofluorescence: Method and application to respiratory disease in hospitalized children. J. Med. Virol. 1978, 2, 341–346. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Meyer, B.; Drosten, C.; Muller, M.A. Serological assays for emerging coronaviruses: Challenges and pitfalls. Virus Res. 2014, 194, 175–183. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rovida, F.; Percivalle, E.; Zavattoni, M.; Torsellini, M.; Sarasini, A.; Campanini, G.; Paolucci, S.; Baldanti, F.; Revello, M.G.; Gerna, G. Monoclonal antibodies versus reverse transcription-PCR for detection of respiratory viruses in a patient population with respiratory tract infections admitted to hospital. J. Med. Virol. 2005, 75, 336–347. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chan, K.H.; Chan, J.F.; Tse, H.; Chen, H.; Lau, C.C.; Cai, J.P.; Tsang, A.K.; Xiao, X.; To, K.K.; Lau, S.K.; et al. Cross-reactive antibodies in convalescent SARS patients’ sera against the emerging novel human coronavirus EMC (2012) by both immunofluorescent and neutralizing antibody tests. J. Infect. 2013, 67, 130–140. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chan, K.H.; Cheng, V.C.; Woo, P.C.; Lau, S.K.; Poon, L.L.; Guan, Y.; Seto, W.H.; Yuen, K.Y.; Peiris, J.S. Serological responses in patients with severe acute respiratory syndrome coronavirus infection and cross-reactivity with human coronaviruses 229E, OC43, and NL63. Clin. Diagn. Lab. Immunol. 2005, 12, 1317–1321. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Van Elden, L.J.; van Kraaij, M.G.; Nijhuis, M.; Hendriksen, K.A.; Dekker, A.W.; Rozenberg-Arska, M.; van Loon, A.M. Polymerase chain reaction is more sensitive than viral culture and antigen testing for the detection of respiratory viruses in adults with hematological cancer and pneumonia. Clin. Infect. Dis. 2002, 34, 177–183. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, W.; Ren, P.; Sheng, J.; Mardy, S.; Yan, H.; Zhang, J.; Hou, L.; Vabret, A.; Buchy, P.; Freymuth, F.; et al. Simultaneous detection of respiratory viruses in children with acute respiratory infection using two different multiplex reverse transcription-PCR assays. J. Virol. Methods 2009, 162, 40–45. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Choudhary, M.L.; Anand, S.P.; Heydari, M.; Rane, G.; Potdar, V.A.; Chadha, M.S.; Mishra, A.C. Development of a multiplex one step RT-PCR that detects eighteen respiratory viruses in clinical specimens and comparison with real time RT-PCR. J. Virol. Methods 2013, 189, 15–19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Malhotra, B.; Swamy, M.A.; Reddy, P.V.; Kumar, N.; Tiwari, J.K. Evaluation of custom multiplex real-Time RT-PCR in comparison to fast—Track diagnostics respiratory 21 pathogens kit for detection of multiple respiratory viruses. Virol. J. 2016, 13, 91. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cho, C.H.; Lee, C.K.; Nam, M.H.; Yoon, S.Y.; Lim, C.S.; Cho, Y.; Kim, Y.K. Evaluation of the AdvanSure real-time RT-PCR compared with culture and Seeplex RV15 for simultaneous detection of respiratory viruses. Diagn. Microbiol. Infecti. Dis. 2014, 79, 14–18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jansen, R.R.; Schinkel, J.; Koekkoek, S.; Pajkrt, D.; Beld, M.; de Jong, M.D.; Molenkamp, R. Development and evaluation of a four-tube real time multiplex PCR assay covering fourteen respiratory viruses, and comparison to its corresponding single target counterparts. J. Clin. Virol. Off. Publ. Pan Am. Soc. Clin. Virol. 2011, 51, 179–185. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jung, Y.J.; Kwon, H.J.; Huh, H.J.; Ki, C.S.; Lee, N.Y.; Kim, J.W. Comparison of the AdvanSure™ real-time RT-PCR and Seeplex® RV12 ACE assay for the detection of respiratory viruses. J. Virol. Methods 2015, 224, 42–46. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jevsnik, M.; Steyer, A.; Zrim, T.; Pokorn, M.; Mrvic, T.; Grosek, S.; Strle, F.; Lusa, L.; Petrovec, M. Detection of human coronaviruses in simultaneously collected stool samples and nasopharyngeal swabs from hospitalized children with acute gastroenteritis. Virol. J. 2013, 10, 46. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Van Elden, L.J.; van Loon, A.M.; van Alphen, F.; Hendriksen, K.A.; Hoepelman, A.I.; van Kraaij, M.G.; Oosterheert, J.J.; Schipper, P.; Schuurman, R.; Nijhuis, M. Frequent detection of human coronaviruses in clinical specimens from patients with respiratory tract infection by use of a novel real-time reverse-transcriptase polymerase chain reaction. J. Infect. Dis. 2004, 189, 652–657. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Souza, T.B.; Lozer, D.M.; Kitagawa, S.M.; Spano, L.C.; Silva, N.P.; Scaletsky, I.C. Real-time multiplex PCR assay and melting curve analysis for identifying diarrheagenic Escherichia coli. J. Clin. Microbiol. 2013, 51, 1031–1033. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kim, J.U.; Cha, C.H.; An, H.K. Multiplex real-time PCR assay and melting curve analysis for identifying mycobacterium tuberculosis complex and nontuberculous mycobacteria. J. Clin. Microbiol. 2012, 50, 483–487. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, C.; Niu, P.; Hong, Y.; Wang, J.; Zhang, J.; Ma, X. A probe-free four-tube real-time PCR assay for simultaneous detection of twelve enteric viruses and bacteria. J. Microbiol. Methods 2015, 118, 93–98. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Monis, P.T.; Giglio, S.; Saint, C.P. Comparison of SYTO9 and SYBR Green I for real-time polymerase chain reaction and investigation of the effect of dye concentration on amplification and DNA melting curve analysis. Anal. Biochem. 2005, 340, 24–34. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, J.; Mu, Y.; Dong, W.; Yao, F.; Wang, L.; Yan, H.; Lan, K.; Zhang, C. Genetic variation of human respiratory syncytial virus among children with fever and respiratory symptoms in Shanghai, China, from 2009 to 2012. Infect. Genet. Evol. 2014, 27, 131–136. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dong, W.; Chen, Q.; Hu, Y.; He, D.; Liu, J.; Yan, H.; Lan, K.; Zhang, C. Epidemiological and clinical characteristics of respiratory viral infections in children in Shanghai, China. Arch. Virol. 2016, 161, 1907–1913. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kibbe, W.A. OligoCalc: An online oligonucleotide properties calculator. Nucleic Acids Res. 2007, 35, W43–W46. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]



| Coronavirus | Primer Set | Primer Name | Sequence (5′-3′) | Amplicon Size (bps) | Theoretical Tm (°C) | Actual Tm (°C) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| HCoV-229E | set1 | 229E-F | TGAAGATGCTTGTACTGTGGCT | 513 | 84.16 | 83.39 |
| 229E-R | CTGTCATGTTGCTCATGGGG | |||||
| set2 | 229E-F2 | AGATGCTTGTACTGTGGCTTCT | 506 | 84.15 | 83.48 | |
| 229E-R2 | CATGTTGCTCATGGGGGAGC | |||||
| set3 | 229E-F3 | TGCTTGTACTGTGGCTTCTTTG | 505 | 84.11 | 83.52 | |
| 229E-R3 | GTCATGTTGCTCATGGGGGAG | |||||
| HCoV-OC43 | set1 | OC43-F | ATGTCAATACCCCGGCTGAC | 191 | 84.97 | 83.96 |
| OC43-R | GGCTCTACTACGCGATCCTG | |||||
| set2 | OC43-F2 | CTATCTGGGAACAGGACCGC | 122 | 82.46 | 83.24 | |
| OC43-R2 | TTGGGTCCCGATCGACAATG | |||||
| set3 | OC43-F3 | ATTGTCGATCGGGACCCAAG | 132 | 82.58 | 82.32 | |
| OC43-R3 | TGTGCGCGAAGTAGATCTGG | |||||
| HCoV-NL63 | set1 | NL63-F | GATAACCAGTCGAAGTCACCTAGTTC | 255 | 81.84 | 81.10 |
| NL63-R | ATTAGGAATCAATTCAGCAAGCTGTG | |||||
| HCoV-HKU1 | set1 | HKU1-F | AGGCTCAGGAAGGTCTGCTT | 261 | 81.44 | 80.00 |
| HKU1-R | TTAGGAGTTCGCTTTTGGCGA | |||||
| set2 | HKU1-F2 | AGAGGCAGAAAAACCCAACCTA | 374 | 83.04 | 83.05 | |
| HKU1-R2 | TCCCTTGACGAAACATCGGA | |||||
| set3 | HKU1-F3 | AGGCAGAAAAACCCAACCTAA | 371 | 83.00 | 82.75 | |
| HKU1-R3 | CCCTTGACGAAACATCGGAG |
© 2016 by the authors; licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC-BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Wan, Z.; Zhang, Y.; He, Z.; Liu, J.; Lan, K.; Hu, Y.; Zhang, C. A Melting Curve-Based Multiplex RT-qPCR Assay for Simultaneous Detection of Four Human Coronaviruses. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2016, 17, 1880. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms17111880
Wan Z, Zhang Y, He Z, Liu J, Lan K, Hu Y, Zhang C. A Melting Curve-Based Multiplex RT-qPCR Assay for Simultaneous Detection of Four Human Coronaviruses. International Journal of Molecular Sciences. 2016; 17(11):1880. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms17111880
Chicago/Turabian StyleWan, Zhenzhou, Ya’nan Zhang, Zhixiang He, Jia Liu, Ke Lan, Yihong Hu, and Chiyu Zhang. 2016. "A Melting Curve-Based Multiplex RT-qPCR Assay for Simultaneous Detection of Four Human Coronaviruses" International Journal of Molecular Sciences 17, no. 11: 1880. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms17111880
APA StyleWan, Z., Zhang, Y., He, Z., Liu, J., Lan, K., Hu, Y., & Zhang, C. (2016). A Melting Curve-Based Multiplex RT-qPCR Assay for Simultaneous Detection of Four Human Coronaviruses. International Journal of Molecular Sciences, 17(11), 1880. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms17111880