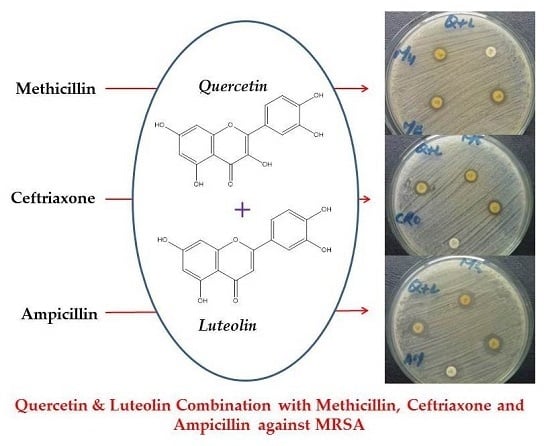
Effects of Luteolin and Quercetin in Combination with Some Conventional Antibiotics against Methicillin-Resistant Staphylococcus aureus
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Results and Discussion
3. Experimental Section
3.1. Materials
3.2. Bacterial Culturing and Antibacterial Assays
3.3. Minimum Inhibitory Concentration (MIC) Assay
3.4. Fractional Inhibitory Concentration (FIC) and FIC Index
3.5. Detection of Cytoplasmic Membrane Damage
3.6. Modified Ames’s Test
3.6.1. Treatment of Bacterial Cultures with Flavonoids, Antibiotics, and Flavonoids + Antibiotics
3.6.2. Statistical Analysis
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Morell, E.A.; Balkin, D.M. Methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus: A pervasive pathogen highlights the need for new antimicrobial development. Yale J. Biol. Med. 2010, 83, 223–233. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Taj, Y.; Abdullah, F.E.; Kazmi, S.U. Current pattern of antibiotic resistance in Staphylococcus aureus clinical isolates and the emergence of vancomycin resistance. J. Coll. Physicians Surg. Pak. 2010, 20, 728–732. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Hafiz, S.; Hafiz, A.N.; Ali, L.; Chughtai, A.S.; Memon, B.; Ahmed, A.; Hussain, S.; Sarwar, G.; Mughal, T.; Awan, A.; et al. Methicillin resistant Staphylococcus aureus: A multicentre study. J. Pak. Med. Assoc. 2002, 52, 312–314. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Lin, R.D.; Chin, Y.P.; Lee, M.H. Antimicrobial activity of antibiotics in combination with natural flavonoids against clinical extended-spectrum β-lactamase (ESBL)-producing Klebsiella pneumoniae. Phytother. Res. 2005, 19, 612–617. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Moon, S.H.; Lee, K.A.; Park, K.K.; Kim, K.T.; Park, Y.S.; Nah, S.Y.; Mendonca, A.F.; Paik, H.D. Antimicrobial effects of natural flavonoids and a novel flavonoid, 7-O-Butyl Naringenin, on growth of meat-borne Staphylococcus aureus strains. Korean J. Food Sci. Anim. Resour. 2011, 31, 413–419. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Darwish, R.M.; Ra’ed, J.; Zarga, M.H.A.; Nazer, I.K. Antibacterial effect of Jordanian propolis and isolated flavonoids against human pathogenic bacteria. Afr. J. Biotechnol. 2011, 9, 5966–5974. [Google Scholar]
- Su, Y.; Ma, L.; Wen, Y.; Wang, H.; Zhang, S. Studies of the in vitro antibacterial activities of several polyphenols against clinical isolates of methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus. Molecules 2014, 19, 12630–12639. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Idrees, F.; Jabeen, K.; Khan, M.S.; Zafar, A. Antimicrobial resistance profile of methicillin resistant staphylococcal aureus from skin and soft tissue isolates. J. Pak. Med. Assoc. 2009, 59, 266. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Liu, H.; Mou, Y.; Zhao, J.; Wang, J.; Zhou, L.; Wang, M.; Wang, D.; Han, J.; Yu, Z.; Yang, F. Flavonoids from Halostachys caspica and their antimicrobial and antioxidant activities. Molecules 2010, 15, 7933–7945. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xu, H.X.; Lee, S.F. Activity of plant flavonoids against antibiotic-resistant bacteria. Phytother. Res. 2001, 15, 39–43. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qiu, J.; Li, H.; Meng, H.; Hu, C.; Li, J.; Luo, M.; Dong, J.; Wang, X.; Wang, J.; Deng, Y.; et al. Impact of luteolin on the production of α-toxin by Staphylococcus aureus. Lett. Appl. Microbiol. 2011, 53, 238–243. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nadia, Z.; Rachid, M. Antioxidant and antibacterial activities of Thymus vulgaris L. Med. Aromat. Plant Res. J. 2013, 1, 5–11. [Google Scholar]
- Amin, M.U.; Khurram, M.; Khattak, B.; Khan, J. Antibiotic additive and synergistic action of rutin, morin and quercetin against methicillin resistant Staphylococcus aureus. BMC Complement. Altern. Med. 2015, 15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Stapleton, P.D.; Shah, S.; Anderson, J.C.; Hara, Y.; Hamilton-Miller, J.M.; Taylor, P.W. Modulation of β-lactam resistance in Staphylococcus aureus by catechins and gallates. Int. J. Antimicrob. Agents 2004, 23, 462–467. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shimamura, T.; Zhao, W.H.; Hu, Z.Q. Mechanism of action and potential for use of tea catechin as an anti-infective agent. Antiinfect. Agents Med. Chem. 2007, 6, 57–62. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stapleton, P.D.; Shah, S.; Hara, Y.; Taylor, P.W. Potentiation of catechin gallate-mediated sensitization of Staphylococcus aureus to oxacillin by nongalloylated catechins. Antimicrob. Agents Chemother. 2006, 50, 752–755. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Eumkeb, G.; Siriwong, S.; Thumanu, K. Synergistic activity of luteolin and amoxicillin combination against amoxicillin-resistant Escherichia coli and mode of action. J. Photochem. Photobiol. B 2012, 117, 247–253. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Caturla, N.; Vera-Samper, E.; Villalaín, J.; Mateo, C.R.; Micol, V. The relationship between the antioxidant and the antibacterial properties of galloylated catechins and the structure of phospholipid model membranes. Free Radic. Biol. Med. 2003, 34, 648–662. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, S.Y.; Sun, Z.L.; Liu, T.; Gibbons, S.; Zhang, W.J.; Qing, M. Flavonoids from Sophora moorcroftiana and their synergistic antibacterial effects on MRSA. Phytother. Res. 2014, 28, 1071–1076. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Novy, P.; Urban, J.; Leuner, O.; Vadlejch, J.; Kokoska, L. In vitro synergistic effects of baicalin with oxytetracycline and tetracycline against Staphylococcus aureus. J. Antimicrob. Chemother. 2011, 108. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Campos, F.M.; Couto, J.A.; Figueiredo, A.R.; Tóth, I.V.; Rangel, A.O.; Hogg, T.A. Cell membrane damage induced by phenolic acids on wine lactic acid bacteria. Int. J. Food Microbiol. 2009, 135, 144–151. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cushnie, T.T.; Lamb, A.J. Antimicrobial activity of flavonoids. Int. J. Antimicrob. Agents 2005, 26, 343–356. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Meghashri, S.; Gopal, S. Dihydroxy flavone-induced cytoplasmic membrane damage in Staphylococcus aureus. Int. J. Phytomed. 2012, 4, 150. [Google Scholar]
- Kobayashi, N.; Wu, H.; Kojima, K.; Taniguchi, K.; Urasawa, S.; Uehara, N.; Omizu, Y.; Kishi, Y.; Yagihashi, A.; Kurokawa, I. Detection of mecA, femA, and femB genes in clinical strains of staphylococci using polymerase chain reaction. Epidemiol. Infect. 1994, 113, 259–266. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Alam, M.M.; Uddin, M.S.; Kobayashi, N.; Ahmed, M.U. Detection of methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus (MRSA) from animal and human origin in Bangladesh by polymerase chain reaction. Bangladesh J. Vet. Med. 2013, 9, 161–166. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Goffin, C.; Ghuysen, J.M. Multimodular penicillin-binding proteins: An enigmatic family of orthologs and paralogs. Microbiol. Mol. Biol. Rev. 1998, 62, 1079–1093. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Murakami, K.; Fujimura, T.; Doi, M. Nucleotide sequence of the structural gene for the penicillin-binding protein 2 of Staphylococcus aureus and the presence of a homologous gene in other staphylococci. FEMS Microbiol. Lett. 1994, 117, 131–136. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pinho, M.G.; de Lencastre, H.; Tomasz, A. An acquired and a native penicillin-binding protein cooperate in building the cell wall of drug-resistant staphylococci. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2001, 98, 10886–10891. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sato, Y.; Shibata, H.; Arai, T.; Yamamoto, A.; Okimura, Y.; Arakaki, N.; Higuti, T. Variation in synergistic activity by flavone and its related compounds on the increased susceptibility of various strains of methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus to β-lactam antibiotics. Int. J. Antimicrob. Agents 2004, 24, 226–233. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Giesbrecht, P.; Kersten, T.; Maidhof, H.; Wecke, J. Staphylococcal cell wall: Morphogenesis and fatal variations in the presence of penicillin. Microbiol. Mol. Biol. Rev. 1998, 62, 1371–1414. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Kosmidis, C.; Schindler, B.D.; Jacinto, P.L.; Patel, D.; Bains, K.; Seo, S.M.; Kaatz, G.W. Expression of multidrug resistance efflux pump genes in clinical and environmental isolates of Staphylococcus aureus. Int. J. Antimicrob. Agents 2012, 40, 204–209. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Truong-Bolduc, Q.C.; Hooper, D.C. The transcriptional regulators NorG and MgrA modulate resistance to both quinolones and β-lactams in Staphylococcus aureus. J. Bacterial. 2007, 189, 2996–3005. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- DeMarco, C.E.; Cushing, L.A.; Frempong-Manso, E.; Seo, S.M.; Jaravaza, T.A.; Kaatz, G.W. Efflux-related resistance to norfloxacin, dyes, and biocides in bloodstream isolates of Staphylococcus aureus. Antimicrob. Agents Chemother. 2007, 51, 3235–3239. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gibbons, S.; Moser, E.; Kaatz, G.W. Catechin gallates inhibit multidrug resistance (MDR) in Staphylococcus aureus. Planta Med. 2004, 70, 1240–1242. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Qin, R.; Xiao, K.; Li, B.; Jiang, W.; Peng, W.; Zheng, J.; Zhou, H. The combination of catechin and epicatechin gallate from Fructus crataegi potentiates β-lactam antibiotics against methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus (MRSA) in vitro and in vivo. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2013, 14, 1802–1821. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kateete, D.P.; Kimani, C.N.; Katabazi, F.A.; Okeng, A.; Okee, M.S.; Nanteza, A.; Joloba, M.L.; Najjuka, F.C. Identification of Staphylococcus aureus: DNase and Mannitol salt agar improve the efficiency of the tube coagulase test. Ann. Clin. Microbiol. Antimicrob. 2010, 9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ergene, A.; Guler, P.; Tan, S.; Mirici, S.; Hamzaoglu, E. Antimicrobial and antifungal activity of Heracleum sphondylium subsp. artivinense. Afr. J. Biotechnol. 2006, 5, 1087–1089. [Google Scholar]
- Sakharkar, M.K.; Jayaraman, P.; Soe, W.M.; Chow, V.T.; Sing, L.C.; Sakharkar, K.R. In vitro combinations of antibiotics and phytochemicals against Pseudomonas aeruginosa. J. Microbiol. Immunol. Infect. 2009, 42, 364–370. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Arima, H.; Ashida, H.; Danno, G.I. Rutin-enhanced antibacterial activities of flavonoids against Bacillus cereus and Salmonella enteritidis. Biosci. Biotechnol. Biochem. 2002, 66, 1009–1014. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- European Committee on Antimicrobial Susceptibility Testing. Terminology relating to methods for the determination of susceptibility of bacteria to antimicrobial agents. EUCAST Definitive Document E. Def 1.2. Clin. Microbiol. Infect. 2000, 6, 503–508. [Google Scholar]
- Resende, F.A.; Vilegas, W.; Dos Santos, L.C.; Varanda, E.A. Mutagenicity of flavonoids assayed by bacterial reverse mutation (Ames) test. Molecules 2012, 17, 5255–5268. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]








| Method | MRSA ATCC 43300 Strain MIC (µg/mL) | MRSA Clinical Isolates MIC (µg/mL) |
|---|---|---|
| Serial half dilution | 500 | 500 (n = 39) |
| 1000 (n = 61) | ||
| Incremental increase approach | 500 | 516.83 ± 15.67 a |
| MIC range: 500–540 |
| Method | MRSA ATCC 43300 Strain MIC (µg/mL) | MRSA Clinical Isolates MIC (µg/mL) |
|---|---|---|
| Serial half dilution | 400 + 200 | 400 + 200 (n = 42) |
| 800 + 400 (n = 58) | ||
| Incremental increase approach | 380 + 200 | (394.06 ± 13.75 a) + (215.04 ± 12.72) |
| MIC range: L = 380–420 Q = 200–240 |
| Antibiotics | Q + L with Antibiotic MIC (µg/mL) |
|---|---|
| AMO (amoxicillin) † | 200 + 380 |
| AMO * | 214.06 ± 13.72 a + 394.06 ± 13.75 *** |
| MIC * RANGE | Q = 200–240 |
| L = 380–420 | |
| AMP (ampicillin) † | 120 + 280 |
| AMP * | 134.06 ± 13.85 + 294.06 ± 13.75 *** |
| MIC * RANGE | Q = 120–160 |
| L = 280–320 | |
| CEPH (cephradine) † | 100 + 260 |
| CEPH * | 116.06 ± 15.80 + 278.06 ± 15.61 *** |
| MIC* RANGE | Q = 100–140 |
| L = 260–300 | |
| CET(ceftriaxone) † | 80 + 240 |
| CET * | 94.06 ± 15.43 + 254.06 ± 14.21 *** |
| MIC * RANGE | Q = 80−120 |
| L = 240−300 | |
| IMP (imipenem) † | 80 + 260 |
| IMP * | 97.40 ± 14.49 + 274.06 ± 14.02 *** |
| MIC * RANGE | Q = 80−120 |
| L = 260−300 | |
| ME(methicillin) † | 120 + 300 |
| ME * | 134.12 ± 14.95 + 314.06 ± 14.21 *** |
| MIC * RANGE | Q = 120−160 |
| L = 300−340 |
| Flavonoids + Antibiotics | FICI | ||
|---|---|---|---|
| MRSA ATCC 43300 | MRSA Clinical Isolates (n = 100) | Inference | |
| L + AMP (ampicillin) | 0.9 | 1 | Additive |
| L + CEPH (cephradine) | 0.8 | 1 | Additive |
| L + CET (ceftriaxone) | 0.85 | 1 | Additive |
| L + IMP (imipenem) | 0.82 | 0.9 | Additive |
| L + ME (methicillin) | 0.9 | 1 | Additive |
| Q + L + AMP | 0.65 | 0.68 | Additive |
| Q + L + CEPH | 0.60 | 0.65 | Additive |
| Q + L + CET | 0.45 | 0.50 | Synergistic |
| Q + L + IMP | 0.45 | 0.49 | Synergistic |
| Q + L + ME | 0.65 | 0.69 | Additive |
| Flavonoids | Concentrations Used (µg) |
|---|---|
| Quercetin | 100, 200, 300 |
| Luteolin | 100, 200, 300, 400, 500 |
| Flavonoids | Concentration Ranges Used for MIC Assays (µg/mL) | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Broth Half Dilution Assay | Incremental Assay (Exact MIC) † | |||
| Maximum | Minimum | Maximum | Minimum | |
| Luteolin | 1000 | 125 | 600 | 460 |
| Quercetin + Luteolin | 400 + 800 | 100 + 200 | 320 + 500 | 180 + 360 |
© 2016 by the authors; licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC-BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Usman Amin, M.; Khurram, M.; Khan, T.A.; Faidah, H.S.; Ullah Shah, Z.; Ur Rahman, S.; Haseeb, A.; Ilyas, M.; Ullah, N.; Umar Khayam, S.M.; et al. Effects of Luteolin and Quercetin in Combination with Some Conventional Antibiotics against Methicillin-Resistant Staphylococcus aureus. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2016, 17, 1947. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms17111947
Usman Amin M, Khurram M, Khan TA, Faidah HS, Ullah Shah Z, Ur Rahman S, Haseeb A, Ilyas M, Ullah N, Umar Khayam SM, et al. Effects of Luteolin and Quercetin in Combination with Some Conventional Antibiotics against Methicillin-Resistant Staphylococcus aureus. International Journal of Molecular Sciences. 2016; 17(11):1947. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms17111947
Chicago/Turabian StyleUsman Amin, Muhammad, Muhammad Khurram, Taj Ali Khan, Hani S. Faidah, Zia Ullah Shah, Shafiq Ur Rahman, Abdul Haseeb, Muhammad Ilyas, Naseem Ullah, Sahibzada Muhammad Umar Khayam, and et al. 2016. "Effects of Luteolin and Quercetin in Combination with Some Conventional Antibiotics against Methicillin-Resistant Staphylococcus aureus" International Journal of Molecular Sciences 17, no. 11: 1947. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms17111947
APA StyleUsman Amin, M., Khurram, M., Khan, T. A., Faidah, H. S., Ullah Shah, Z., Ur Rahman, S., Haseeb, A., Ilyas, M., Ullah, N., Umar Khayam, S. M., & Iriti, M. (2016). Effects of Luteolin and Quercetin in Combination with Some Conventional Antibiotics against Methicillin-Resistant Staphylococcus aureus. International Journal of Molecular Sciences, 17(11), 1947. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms17111947