Knock-Down of Endogenous Bornavirus-Like Nucleoprotein 1 Inhibits Cell Growth and Induces Apoptosis in Human Oligodendroglia Cells
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Results
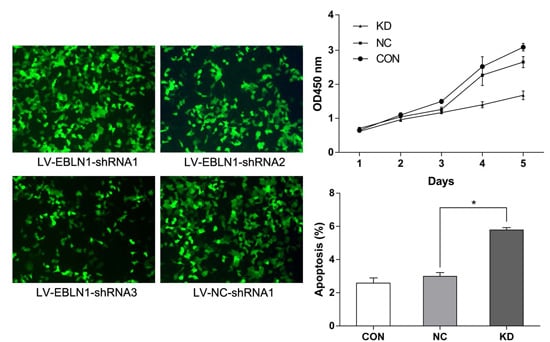
2.1. Effective Reduction of Endogenous Bornavirus-Like Nucleoprotein 1 (EBLN1) mRNA Expression with an shRNA
2.2. EBLN1 Silencing Inhibits Oligodendroglia (OL) Cell Proliferation
2.3. EBLN1 Silencing Induces Apoptosis and Inhibits Colony Formation of OL Cells
2.4. EBLN1 Silencing Induces G2/M Phase Arrest in OL Cells
2.5. EBLN1 Silencing Has No Effect on the Migration of OL Cells
2.6. EBLN1 Silencing Changes Gene Expression Profiles in OL Cells
2.7. Verification of Differential Genes by Quantitative Reverse Transcription Polymerase Chain Reaction (qRT-PCR)
3. Discussion
4. Experimental Section
4.1. Cells and Culture
4.2. Construction of an EBLN1 shRNA-Expressing Lentiviral Vector and Infection
4.3. Detection of EBLN1 mRNA Expression
4.4. Cell Proliferation Analysis
4.5. Analysis of Apoptosis
4.6. Colony-Formation Assay
4.7. Cell Cycle Analysis
4.8. In Vitro Wound-Healing Assay
4.9. Transwell-Migration Assay
4.10. Microarray Analysis
4.11. Verification of Differential Genes by Quantitative Reverse Transcription Polymerase Chain Reaction (qRT-PCR)
4.12. Statistical Analysis
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Acknowledgments
Author Contributions
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Feschotte, C. Virology: Bornavirus enters the genome. Nature 2010, 463, 39–40. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Young, G.R.; Stoye, J.P.; Kassiotis, G. Are human endogenous retroviruses pathogenic? An approach to testing the hypothesis. BioEssays 2013, 35, 794–803. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Suntsova, M.; Garazha, A.; Ivanova, A.; Kaminsky, D.; Zhavoronkov, A.; Buzdin, A. Molecular functions of human endogenous retroviruses in health and disease. Cell. Mol. Life Sci. 2015, 72, 3653–3675. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Huang, W.; Li, S.; Hu, Y.; Yu, H.; Luo, F.; Zhang, Q.; Zhu, F. Implication of the ENV gene of the human endogenous retrovirus W family in the expression of BDNF and DRD3 and development of recent-onset schizophrenia. Schizophr. Bull. 2011, 37, 988–1000. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Balestrieri, E.; Pitzianti, M.; Matteucci, C.; D’Agati, E.; Sorrentino, R.; Baratta, A.; Caterina, R.; Zenobi, R.; Curatolo, P.; Garaci, E.; et al. Human endogenous retroviruses and ADHD. World J. Biol. Psychiatry 2014, 15, 499–504. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Downey, R.F.; Sullivan, F.J.; Wang-Johanning, F.; Ambs, S.; Giles, F.J.; Glynn, S.A. Human endogenous retrovirus K and cancer: Innocent bystander or tumorigenic accomplice? HERV-K activation in cancer and impact on tumor biology. Int. J. Cancer 2015, 137, 1249–1257. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Goering, W.; Schmitt, K.; Dostert, M.; Schaal, H.; Deenen, R.; Mayer, J.; Schulz, W.A. Human endogenous retrovirus HERV-K(HML-2) activity in prostate cancer is dominated by a few loci: HERV-K expression in prostate cancer. Prostate 2015, 75, 1958–1971. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Horie, M.; Honda, T.; Suzuki, Y.; Kobayashi, Y.; Daito, T.; Oshida, T.; Ikuta, K.; Jern, P.; Gojobori, T.; Coffin, J.; et al. Endogenous non-retroviral RNA virus elements in mammalian genomes. Nature 2010, 463, 84–87. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cubitt, B.; Oldstone, C.; de la Torre, J.C. Sequence and genome organization of Borna disease virus. J. Virol. 1994, 68, 1382–1396. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Tomonaga, K.; Kobayashi, T.; Ikuta, K. Molecular and cellular biology of Borna disease virus infection. Microbes Infect. 2002, 4, 491–500. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bode, L.; Dürrwald, R.; Rantam, F.A.; Ferszt, R.; Ludwig, H. First isolates of infectious human Borna disease virus from patients with mood disorders. Mol. Psychiatry 1996, 1, 200–212. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Li, Q.; Wang, Z.; Zhu, D.; Xu, M.; Chen, X.; Peng, D.; Iwata, Y.; Xie, P. Detection and analysis of Borna disease virus in Chinese patients with neurological disorders. Eur. J. Neurol. 2009, 16, 399–403. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nakamura, Y.; Takahashi, H.; Shoya, Y.; Nakaya, T.; Watanabe, M.; Tomonaga, K.; Iwahashi, K.; Ameno, K.; Momiyama, N.; Taniyama, H.; et al. Isolation of Borna disease virus from human brain tissue. J. Virol. 2000, 74, 4601–4611. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wensman, J.J.; Jäderlund, K.H.; Holst, B.S.; Berg, M. Borna disease virus infection in cats. Vet. J. 2014, 201, 142–149. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, L.; Xu, M.M.; Zeng, L.; Liu, S.; Liu, X.; Wang, X.; Li, D.; Huang, R.Z.; Zhao, L.B.; Zhan, Q.L.; et al. Evidence for Borna disease virus infection in neuropsychiatric patients in three western China provinces. Eur. J. Clin. Microbiol. Infect. Dis. 2014, 33, 621–627. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nobach, D.; Bourg, M.; Herzog, S.; Lange-Herbst, H.; Encarnação, J.A.; Eickmann, M.; Herden, C. Shedding of infectious borna disease virus-1 in living bicolored white-toothed shrews. PLoS ONE 2015, 10, e0137018. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, S.; Bode, L.; Zhang, L.; He, P.; Huang, R.; Sun, L.; Chen, S.; Zhang, H.; Guo, Y.; Zhou, J.; et al. GC–MS-based metabonomic profiling displayed differing effects of borna disease virus natural strain Hu-H1 and laboratory strain V infection in rat cortical neurons. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2015, 16, 19347–19368. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bonnaud, E.M.; Szelechowski, M.; Bétourné, A.; Foret, C.; Thouard, A.; Gonzalez-Dunia, D.; Malnou, C.E. Borna disease virus phosphoprotein modulates epigenetic signaling in neurons to control viral replication. J. Virol. 2015, 89, 5996–6008. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rudolph, M.G.; Kraus, I.; Dickmanns, A.; Eickmann, M.; Garten, W.; Ficner, R. Crystal structure of the Borna disease virus nucleoprotein. Structure 2003, 11, 1219–1226. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Planz, O.; Pleschka, S.; Oesterle, K.; Berberich-Siebelt, F.; Ehrhardt, C.; Stitz, L.; Ludwig, S. Borna disease virus nucleoprotein interacts with the Cdc2-cyclin B1 complex. J. Virol. 2003, 77, 11186–11192. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Song, W.; Kao, W.; Zhai, A.; Qian, J.; Li, Y.; Zhang, Q.; Zhao, H.; Hu, Y.; Li, H.; Zhang, F. Borna disease virus nucleoprotein inhibits type I interferon induction through the interferon regulatory factor 7 pathway. Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 2013, 438, 619–623. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Belyi, V.A.; Levine, A.J.; Skalka, A.M. Unexpected Inheritance: Multiple integrations of ancient bornavirus and ebolavirus/marburgvirus sequences in vertebrate genomes. PLoS Pathog. 2010, 6, e1001030. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fujino, K.; Horie, M.; Honda, T.; Merriman, D.K.; Tomonaga, K. Inhibition of Borna disease virus replication by an endogenous bornavirus-like element in the ground squirrel genome. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2014, 111, 13175–13180. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Parrish, N.F.; Fujino, K.; Shiromoto, Y.; Iwasaki, Y.W.; Ha, H.; Xing, J.; Makino, A.; Kuramochi-Miyagawa, S.; Nakano, T.; Siomi, H.; et al. piRNAs derived from ancient viral processed pseudogenes as transgenerational sequence-specific immune memory in mammals. RNA 2015, 21, 1691–1703. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sofuku, K.; Parrish, N.F.; Honda, T.; Tomonaga, K. Transcription profiling demonstrates epigenetic control of non-retroviral RNA virus-derived elements in the human genome. Cell Rep. 2015, 12, 1548–1554. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bautista, J.R.; Schwartz, G.J.; De La Torre, J.C.; Moran, T.H.; Carbone, K.M. Early and persistent abnormalities in rats with neonatally acquired Borna disease virus infection. Brain Res. Bull. 1994, 34, 31–40. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lancaster, K.; Dietz, D.; Moran, T.; Pletnikov, M. Abnormal social behaviors in young and adult rats neonatally infected with Borna disease virus. Behav. Brain Res. 2007, 176, 141–148. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Solbrig, M.V. Animal models of CNS viral disease: Examples from Borna disease virus models. Interdiscip. Perspect. Infect. Dis. 2010, 2010, 1–6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Haga, S.; Yoshimura, M.; Motoi, Y.; Arima, K.; Aizawa, T.; Ikuta, K.; Tashiro, M.; Ikeda, K. Detection of Borna disease virus genome in normal human brain tissue. Brain Res. 1997, 770, 307–309. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mazaheri-Tehrani, E.; Maghsoudi, N.; Shams, J.; Soori, H.; Atashi, H.; Motamedi, F.; Bode, L.; Ludwig, H. Borna disease virus (BDV) infection in psychiatric patients and healthy controls in Iran. Virol. J. 2014, 11, 161. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, X.; Bode, L.; Zhang, L.; Wang, X.; Liu, S.; Zhang, L.; Huang, R.; Wang, M.; Yang, L.; Chen, S.; et al. Health care professionals at risk of infection with Borna disease virus—Evidence from a large hospital in China (Chongqing). Virol. J. 2015, 12, 39. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Stacey, K.J.; Sagulenko, V. A clear link between endogenous retroviral LTR activity and Hodgkin’s lymphoma. Cell Res. 2010, 20, 869–871. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Schmidt, K.L.M.; Vangsted, A.J.; Hansen, B.; Vogel, U.B.; Hermansen, N.E.U.; Jensen, S.B.; Laska, M.J.; Nexø, B.A. Synergy of two human endogenous retroviruses in multiple myeloma. Leuk. Res. 2015, 39, 1125–1128. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Williams, B.L.; Hornig, M.; Yaddanapudi, K.; Lipkin, W.I. Hippocampal poly(ADP-ribose) polymerase 1 and caspase 3 activation in neonatal bornavirus infection. J. Virol. 2008, 82, 1748–1758. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Poenisch, M.; Burger, N.; Staeheli, P.; Bauer, G.; Schneider, U. Protein X of borna disease virus inhibits apoptosis and promotes viral persistence in the central nervous systems of newborn-infected rats. J. Virol. 2009, 83, 4297–4307. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, D.; Lei, Y.; Deng, J.; Zhou, C.; Zhang, Y.; Li, W.; Huang, H.; Cheng, S.; Zhang, H.; Zhang, L.; et al. Human but not laboratory borna disease virus inhibits proliferation and induces apoptosis in human oligodendrocytes in vitro. PLoS ONE 2013, 8, e66623. [Google Scholar]
- Ma, W.; Wong, C.C.L.; Tung, E.K.K.; Wong, C.M.; Ng, I.O.L. RhoE is frequently down-regulated in hepatocellular carcinoma (HCC) and suppresses HCC invasion through antagonizing the Rho/Rho-Kinase/Myosin phosphatase target pathway. Hepatology 2013, 57, 152–161. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tang, Y.; Hu, C.; Yang, H.; Cao, L.; Li, Y.; Deng, P.; Huang, L. Rnd3 regulates lung cancer cell proliferation through notch signaling. PLoS ONE 2014, 9, e111897. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hernández-Sánchez, M.; Poch, E.; Guasch, R.M.; Ortega, J.; López-Almela, I.; Palmero, I.; Pérez-Roger, I. RhoE is required for contact inhibition and negatively regulates tumor initiation and progression. Oncotarget 2015, 6, 17479–17490. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, B.; Lin, X.; Yang, X.; Dong, H.; Yue, X.; Andrade, K.C.; Guo, Z.; Yang, J.; Wu, L.; Zhu, X.; et al. Downregulation of RND3/RhoE in glioblastoma patients promotes tumorigenesis through augmentation of notch transcriptional complex activity. Cancer Med. 2015, 4, 1404–1416. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- David, E.; Tirode, F.; Baud’huin, M.; Guihard, P.; Laud, K.; Delattre, O.; Heymann, M.F.; Heymann, D.; Redini, F.; Blanchard, F. Oncostatin M is a growth factor for ewing sarcoma. Am. J. Pathol. 2012, 181, 1782–1795. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Natesh, K.; Bhosale, D.; Desai, A.; Chandrika, G.; Pujari, R.; Jagtap, J.; Chugh, A.; Ranade, D.; Shastry, P. Oncostatin-M differentially regulates mesenchymal and proneural signature genes in gliomas via STAT3 Signaling. Neoplasia 2015, 17, 225–237. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Izumi, S.; Saito, A.; Kanemoto, S.; Kawasaki, N.; Asada, R.; Iwamoto, H.; Oki, M.; Miyagi, H.; Ochi, M.; Imaizumi, K. The endoplasmic reticulum stress transducer BBF2H7 suppresses apoptosis by activating the ATF5-MCL1 pathway in growth plate cartilage. J. Biol. Chem. 2012, 287, 36190–36200. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sheng, Z.; Li, L.; Zhu, L.J.; Smith, T.W.; Demers, A.; Ross, A.H.; Moser, R.P.; Green, M.R. A genome-wide RNA interference screen reveals an essential CREB3L2-ATF5-MCL1 survival pathway in malignant glioma with therapeutic implications. Nat. Med. 2010, 16, 671–677. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]







© 2016 by the authors; licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons by Attribution (CC-BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
He, P.; Sun, L.; Zhu, D.; Zhang, H.; Zhang, L.; Guo, Y.; Liu, S.; Zhou, J.; Xu, X.; Xie, P. Knock-Down of Endogenous Bornavirus-Like Nucleoprotein 1 Inhibits Cell Growth and Induces Apoptosis in Human Oligodendroglia Cells. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2016, 17, 435. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms17040435
He P, Sun L, Zhu D, Zhang H, Zhang L, Guo Y, Liu S, Zhou J, Xu X, Xie P. Knock-Down of Endogenous Bornavirus-Like Nucleoprotein 1 Inhibits Cell Growth and Induces Apoptosis in Human Oligodendroglia Cells. International Journal of Molecular Sciences. 2016; 17(4):435. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms17040435
Chicago/Turabian StyleHe, Peng, Lin Sun, Dan Zhu, Hong Zhang, Liang Zhang, Yujie Guo, Siwen Liu, Jingjing Zhou, Xiaoyan Xu, and Peng Xie. 2016. "Knock-Down of Endogenous Bornavirus-Like Nucleoprotein 1 Inhibits Cell Growth and Induces Apoptosis in Human Oligodendroglia Cells" International Journal of Molecular Sciences 17, no. 4: 435. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms17040435
APA StyleHe, P., Sun, L., Zhu, D., Zhang, H., Zhang, L., Guo, Y., Liu, S., Zhou, J., Xu, X., & Xie, P. (2016). Knock-Down of Endogenous Bornavirus-Like Nucleoprotein 1 Inhibits Cell Growth and Induces Apoptosis in Human Oligodendroglia Cells. International Journal of Molecular Sciences, 17(4), 435. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms17040435